Wheatley Trichrome Staining – Principle, Procedure, Uses
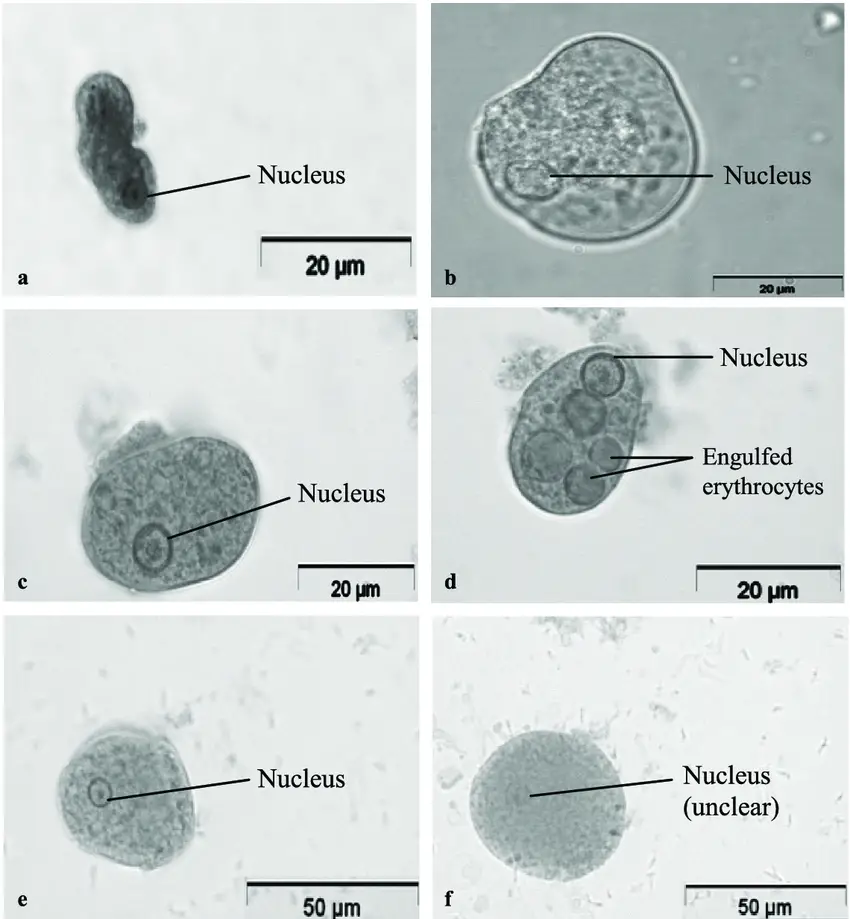
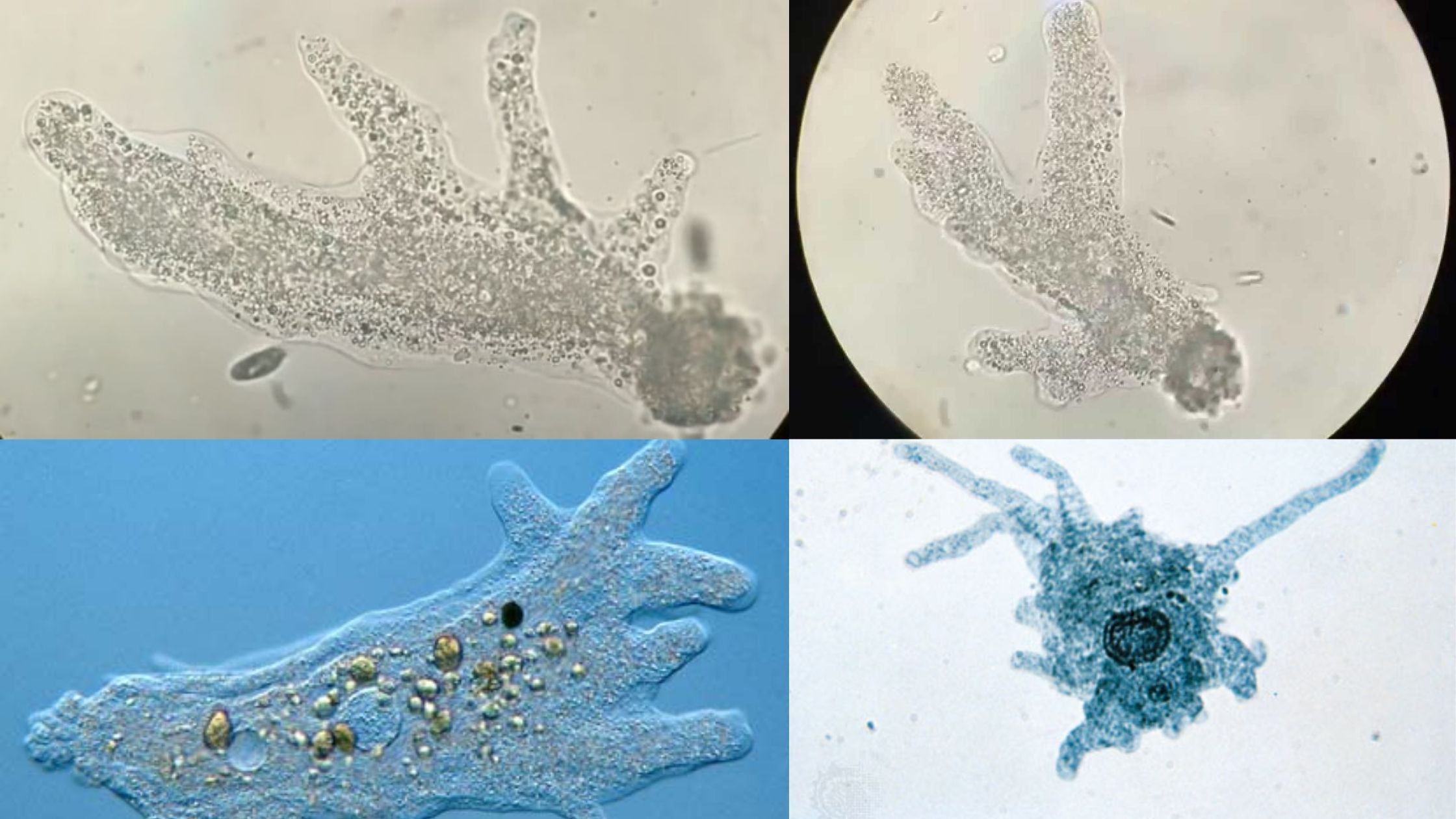
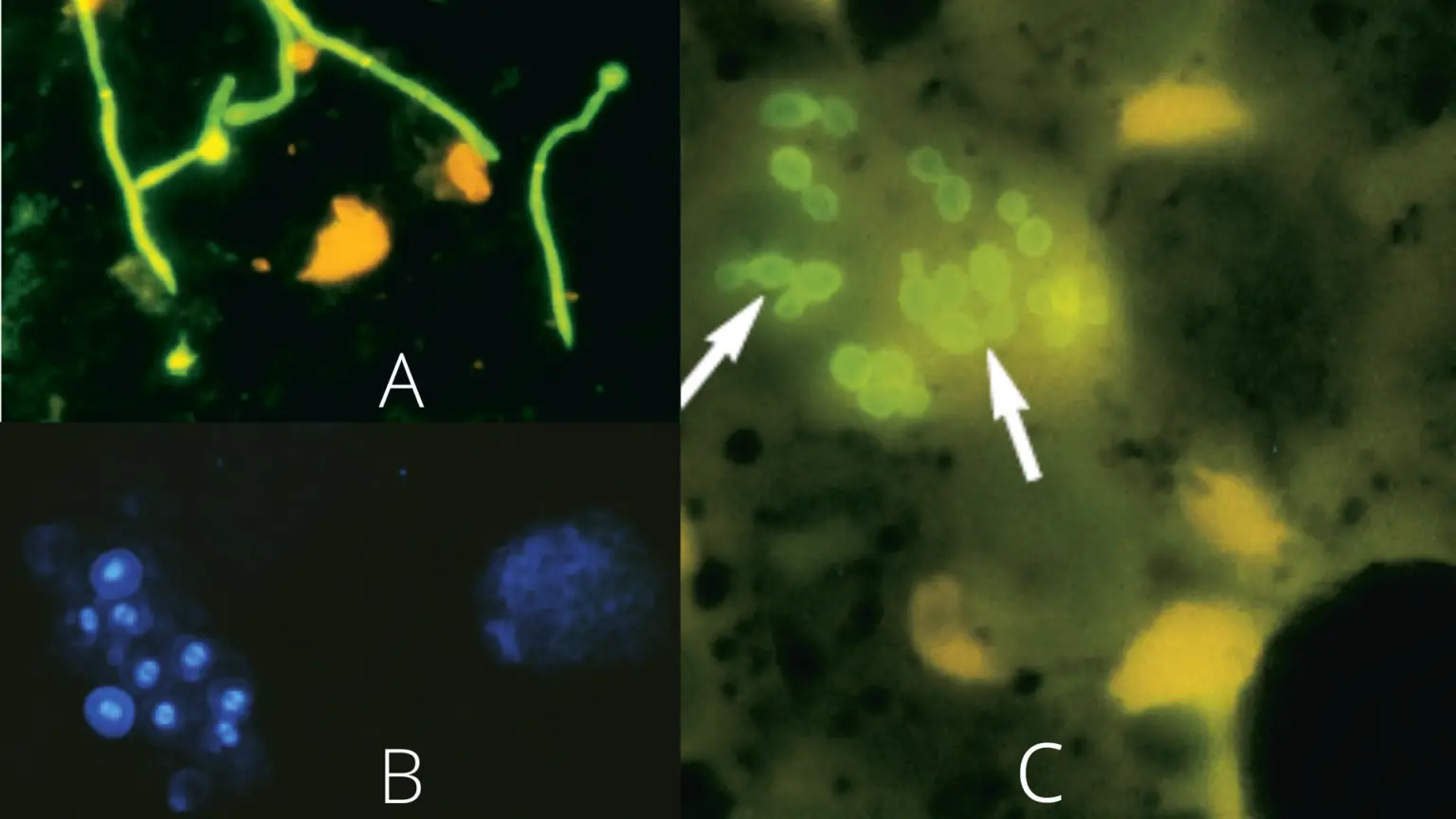
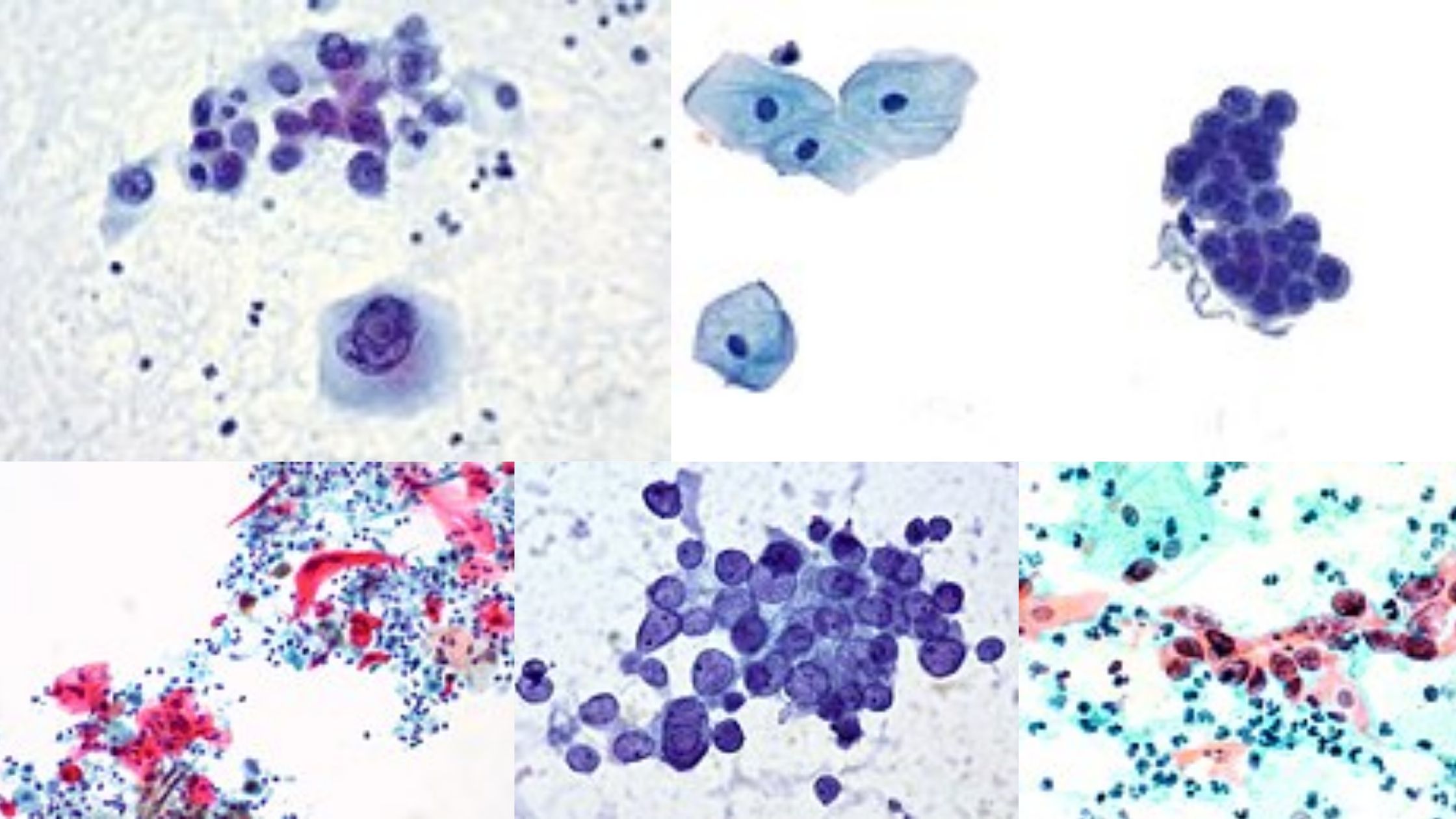
Wheatley Trichrome Staining is the permanent staining method used in parasitology for detecting intestinal protozoans from stool samples, and it is mainly applied when cysts and trophozoites is to be identified in a fixed smear. It is the process in which three dyes are used so that the parasite structures get a clear differential colour … Read more