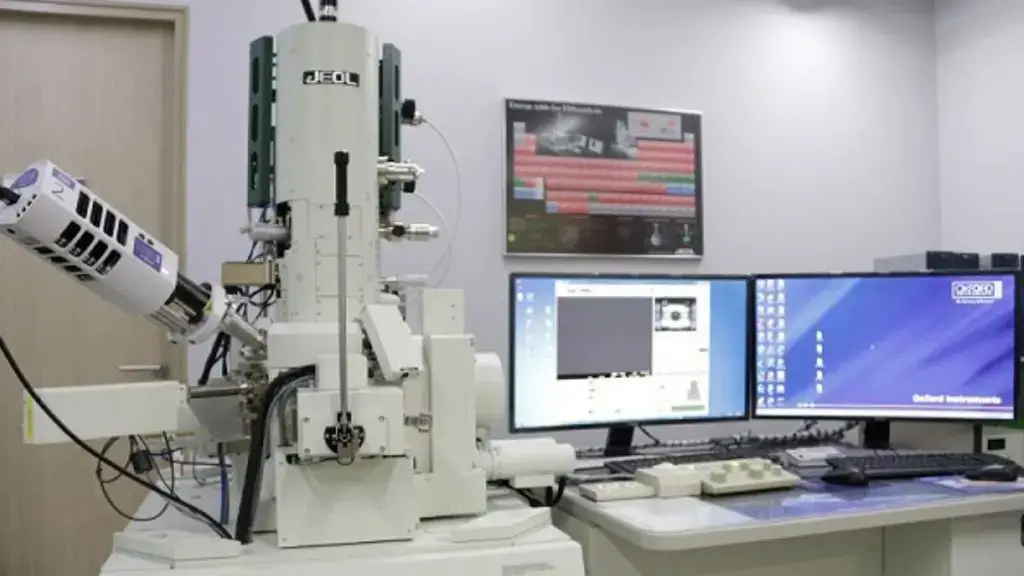
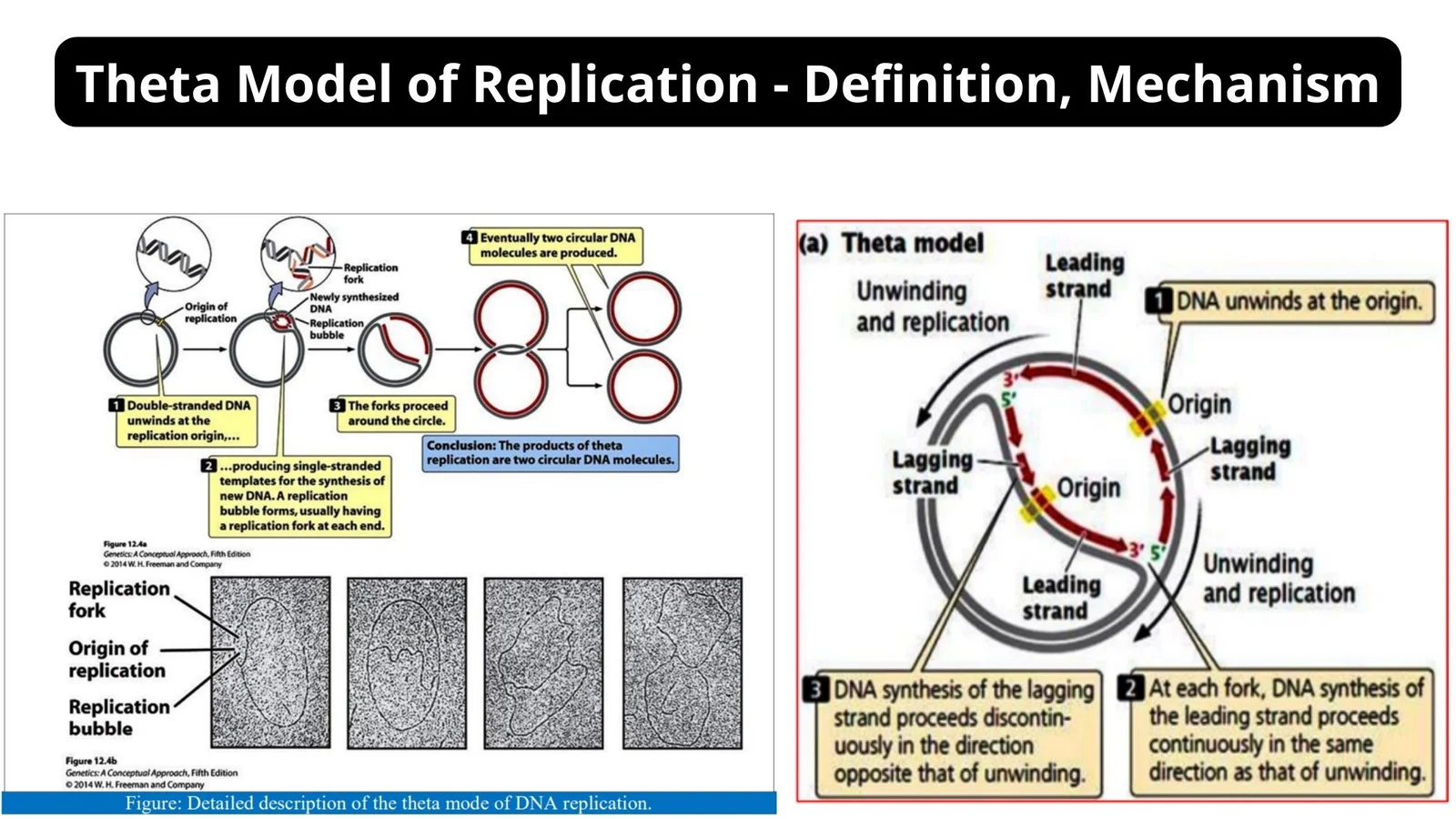
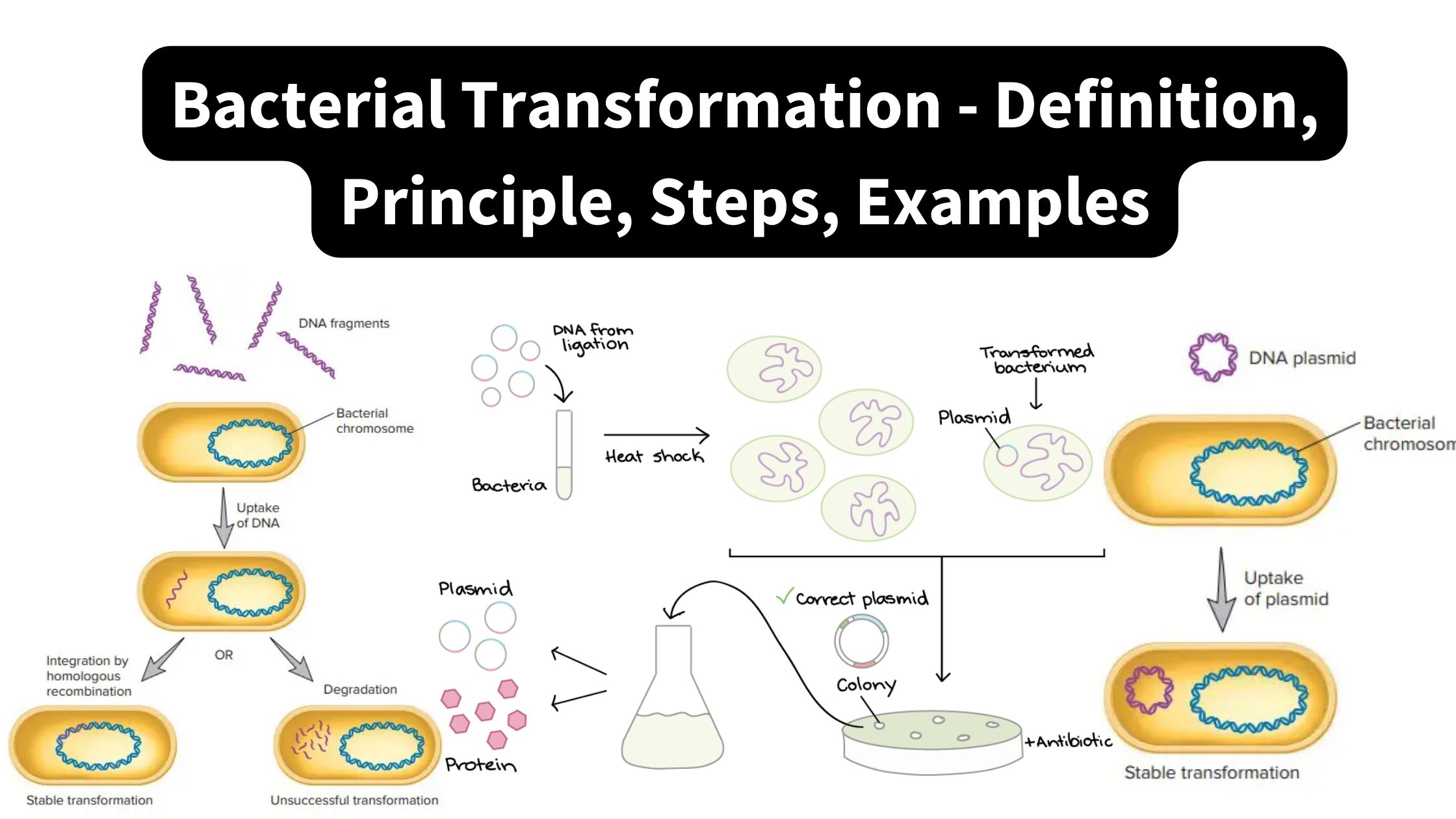
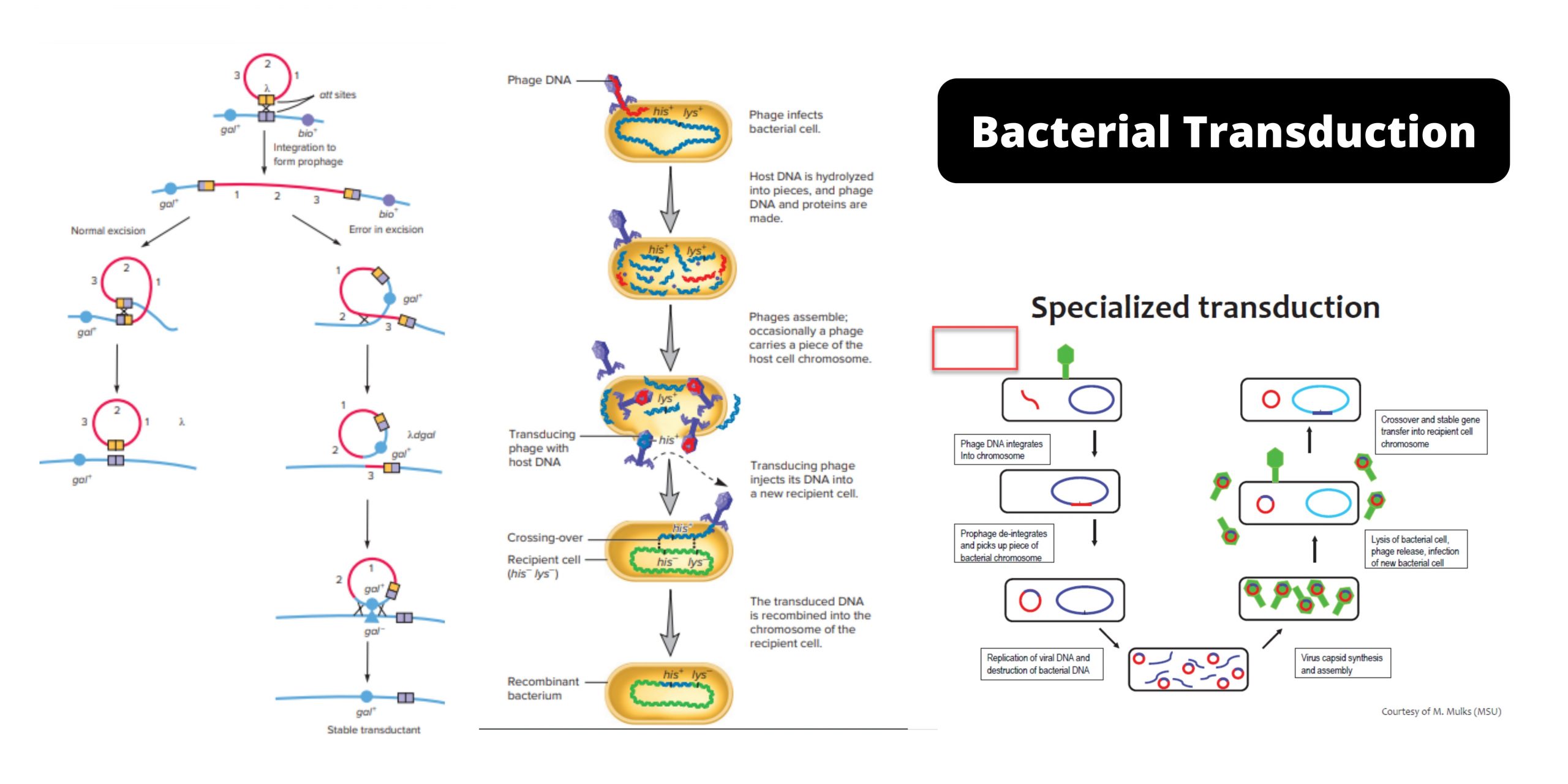
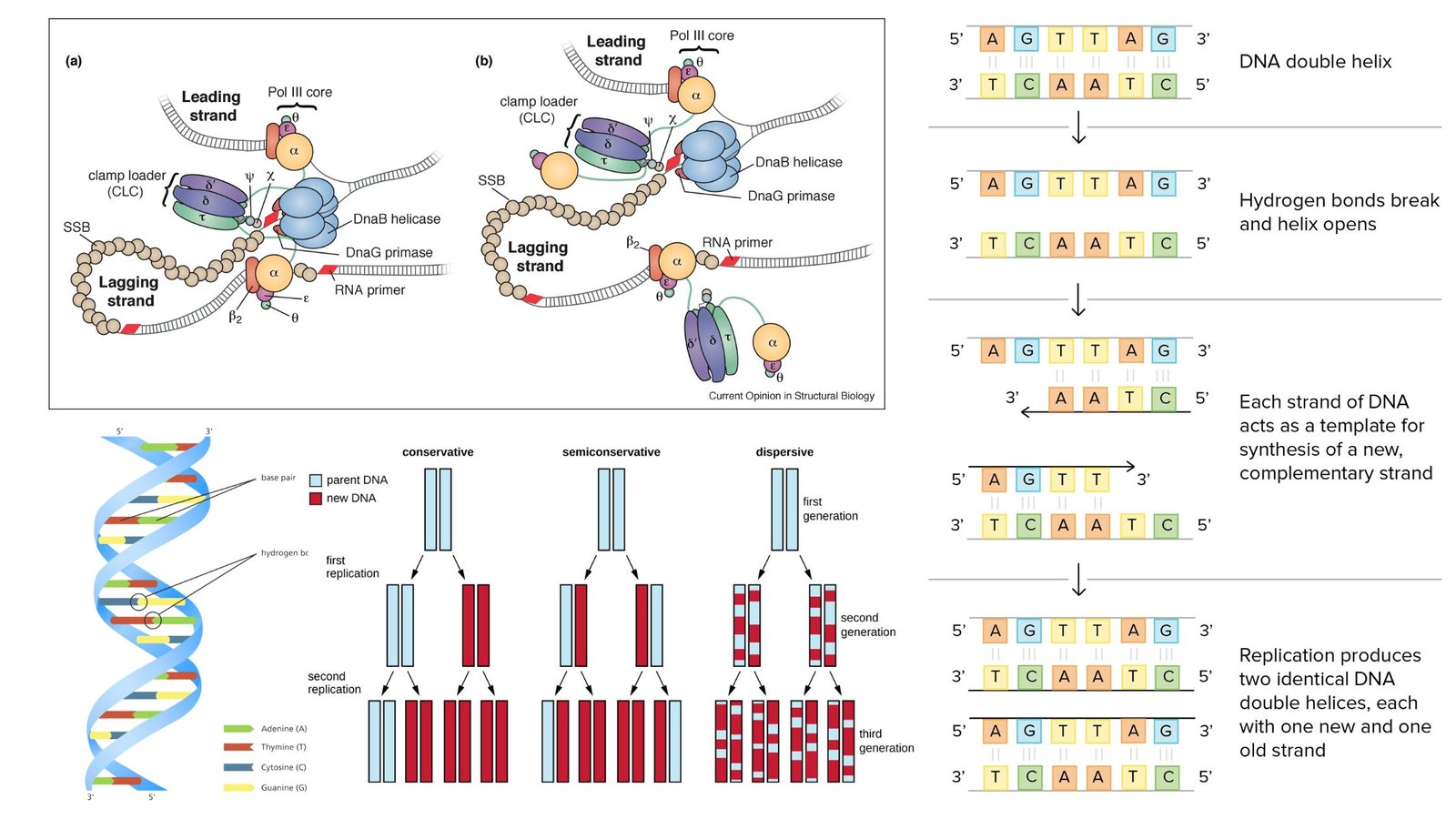
Electron Microscope – Principle, Types, Parts, Application, Diagram
An electron microscope is an instrument which produces an image of a sample by means of a beam of electrons. Optical microscopes use light to form an image, electron microscopes have greater resolution, and can be used to observe objects that are too small to be seen with an optical microscope. In a large variety … Read more