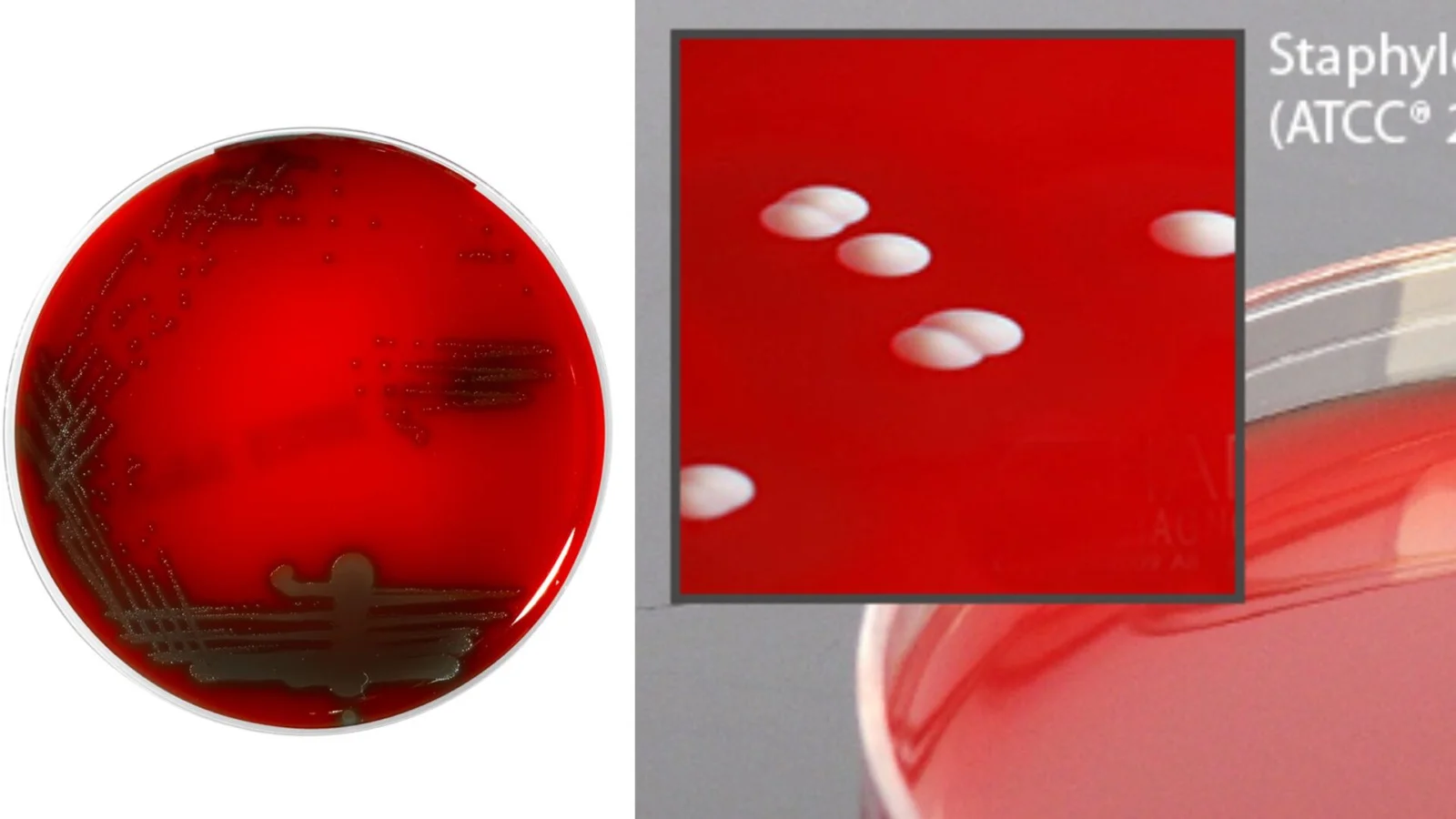
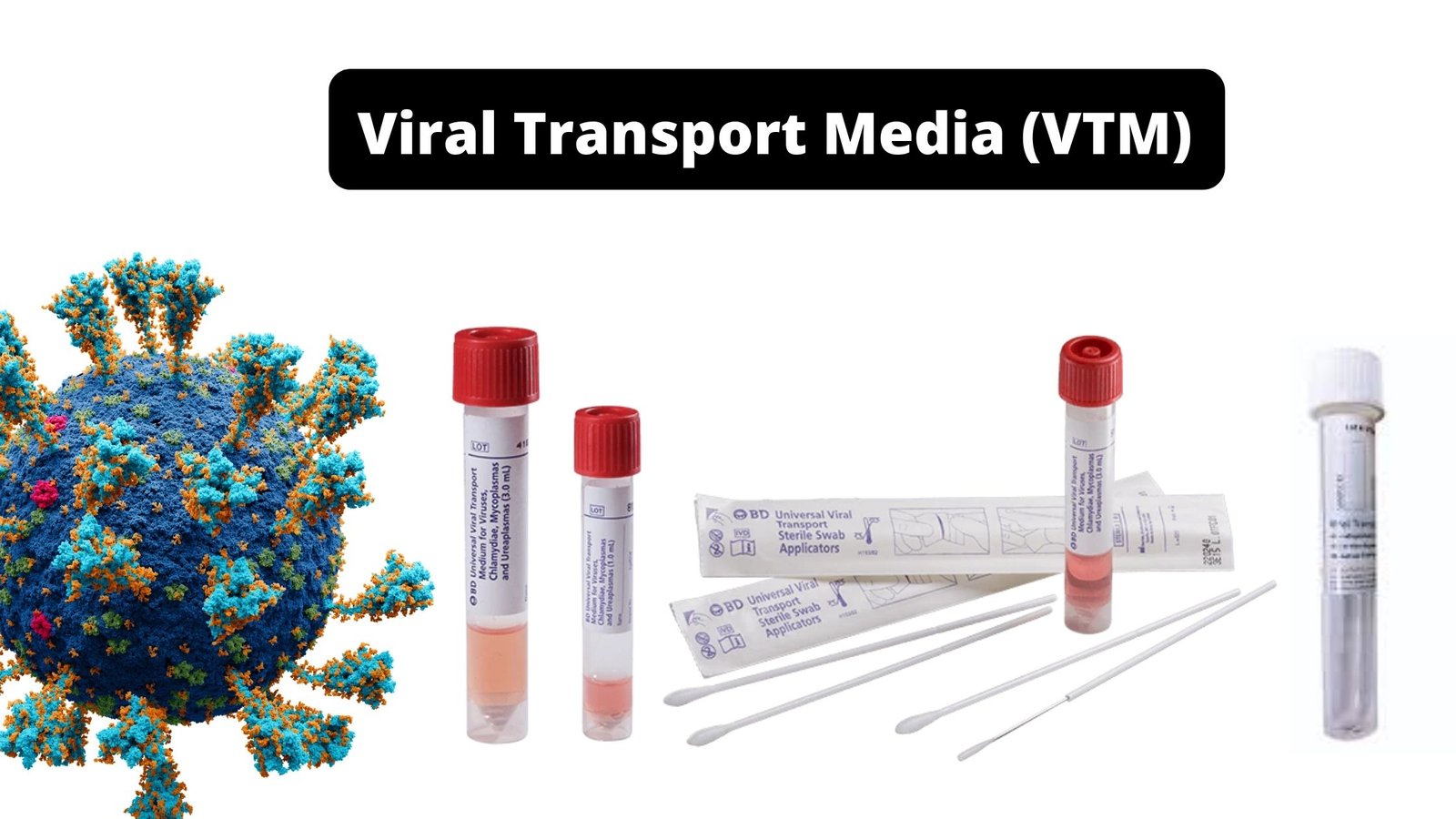
Viral Transport Media (VTM) – Definition, Principle, Preparation, Application
A viral transport medium (VTM) is an essential nutrient that is used to transport and sustain the viability of samples (viruses) to an laboratory for analysis and identification of the specimen.