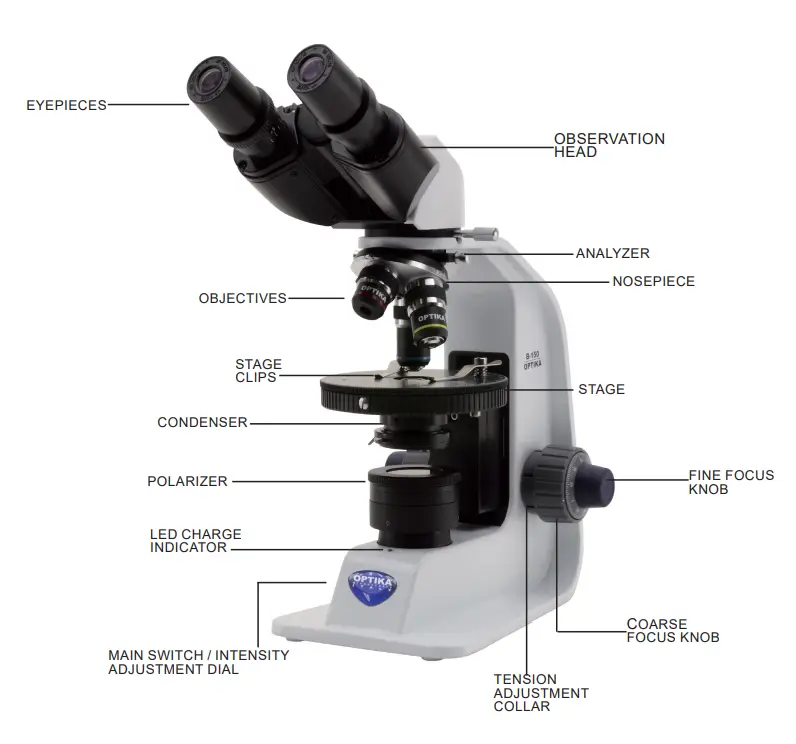
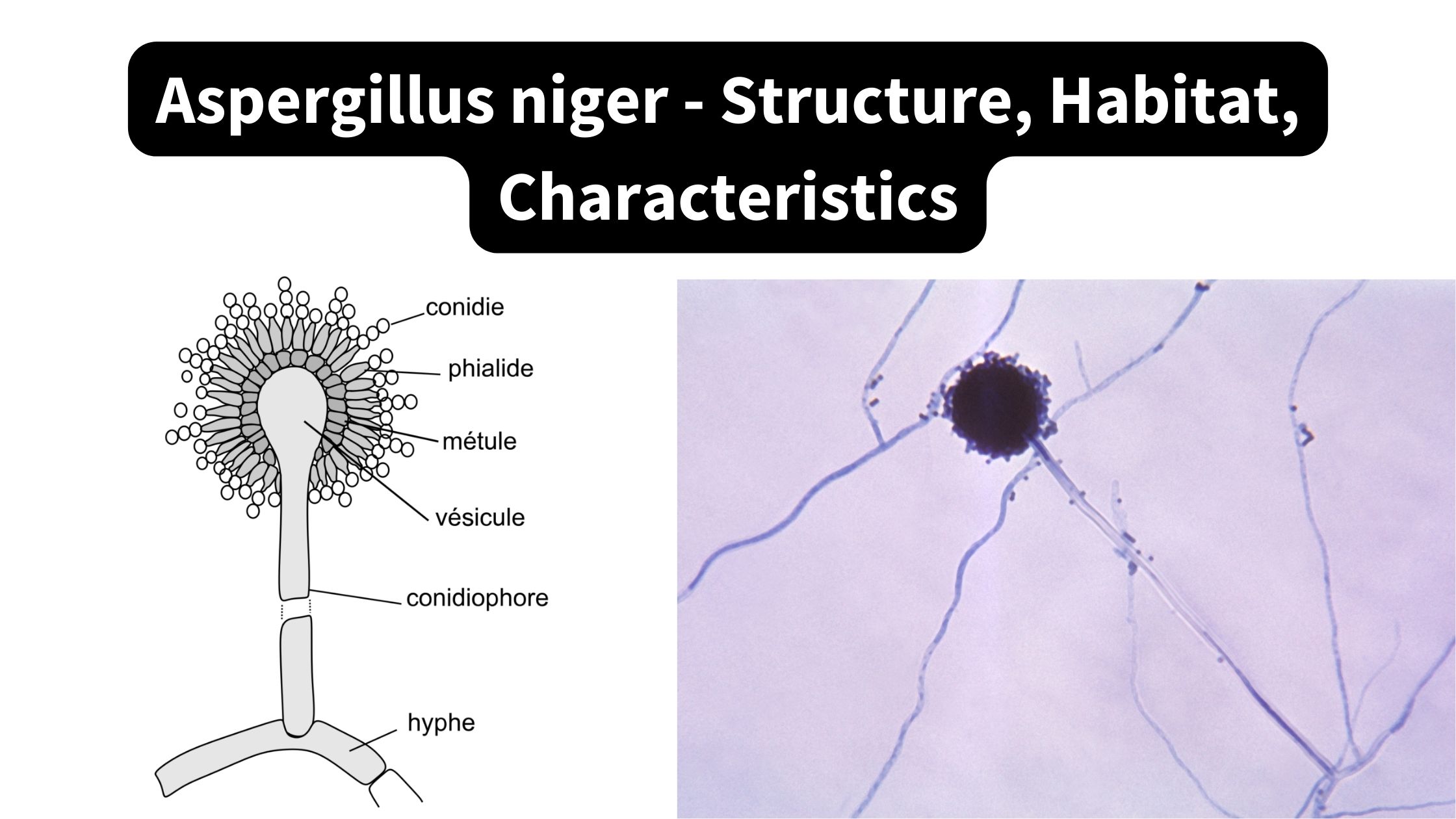
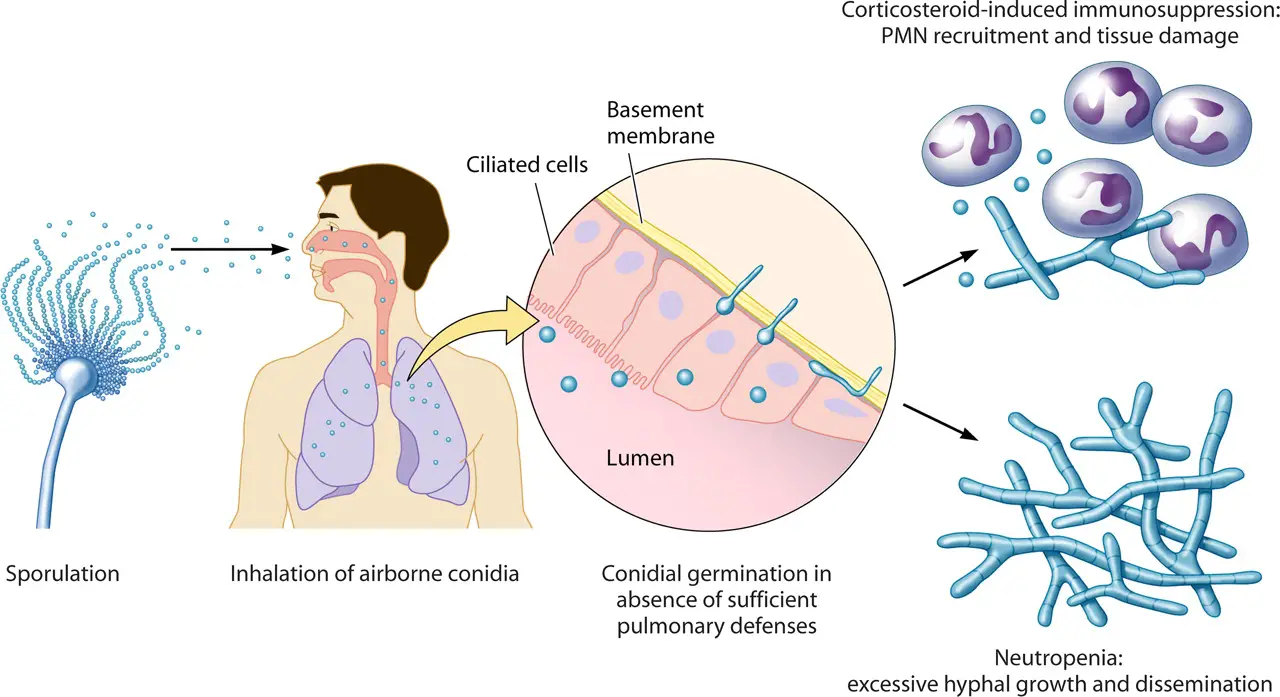
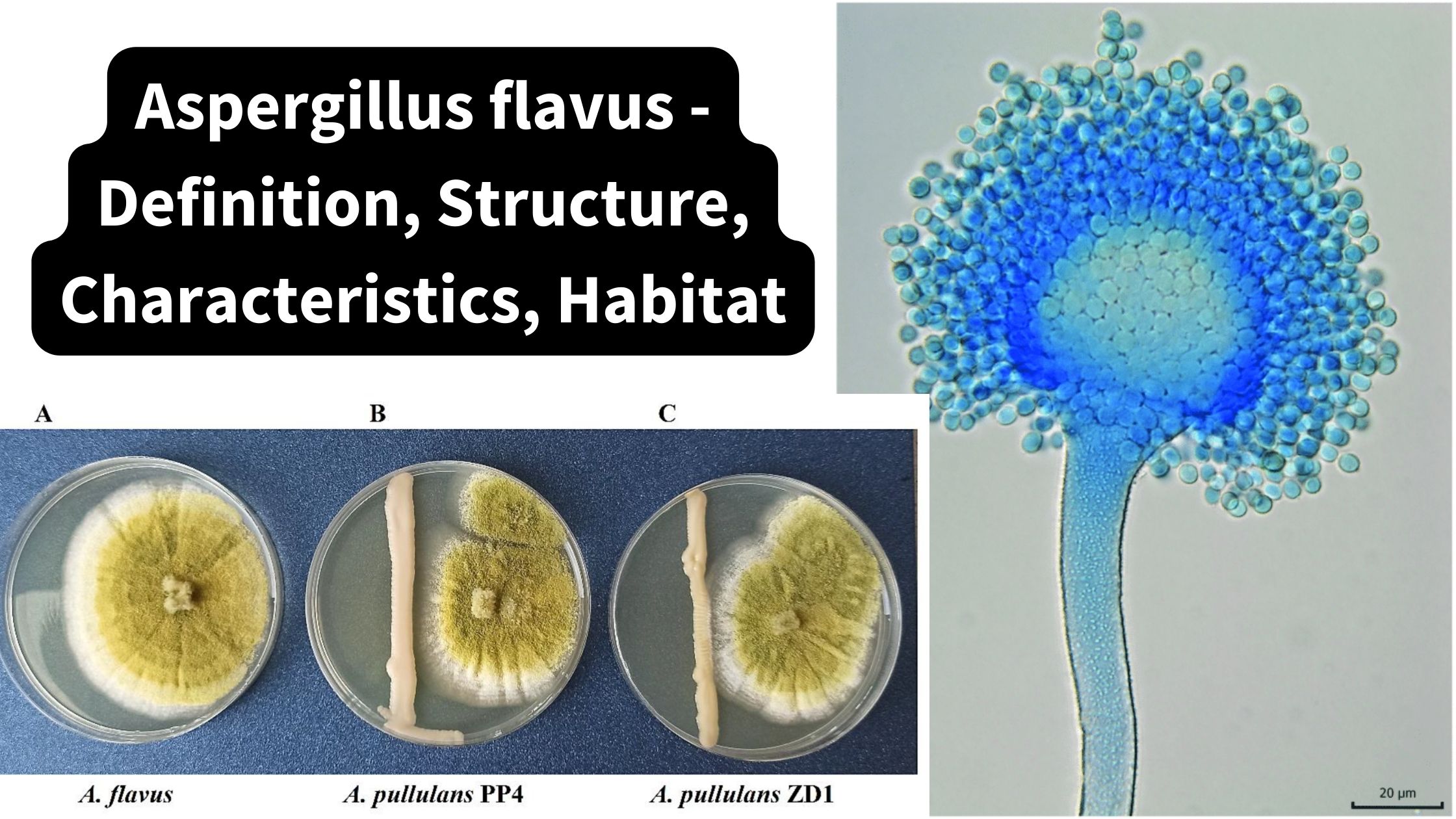
Microorganisms are everywhere in their the distribution. In any given environment, many microorganisms are present at any given time. It is difficult to identify a specific kind of microbe until we understand their ecological needs. For instance, anaerobic microbes do not require oxygen those that are aerobic require oxygen micro-aerophiles to have oxygen however, in a small amount. So, we require cotton plugs to provide an conditions that are aerobic and keep the growing culture uninvolved with unwanted microbes. Cotton plugs are made of cotton along with air pours. Air can flow through air pours, but not the bacteria that cause microbial contamination. They are fixed to the surface of cotton fibres , and prevent them from being able from getting into flasks, tubes, etc. Air aids in for the development of microorganisms within glass equipment.