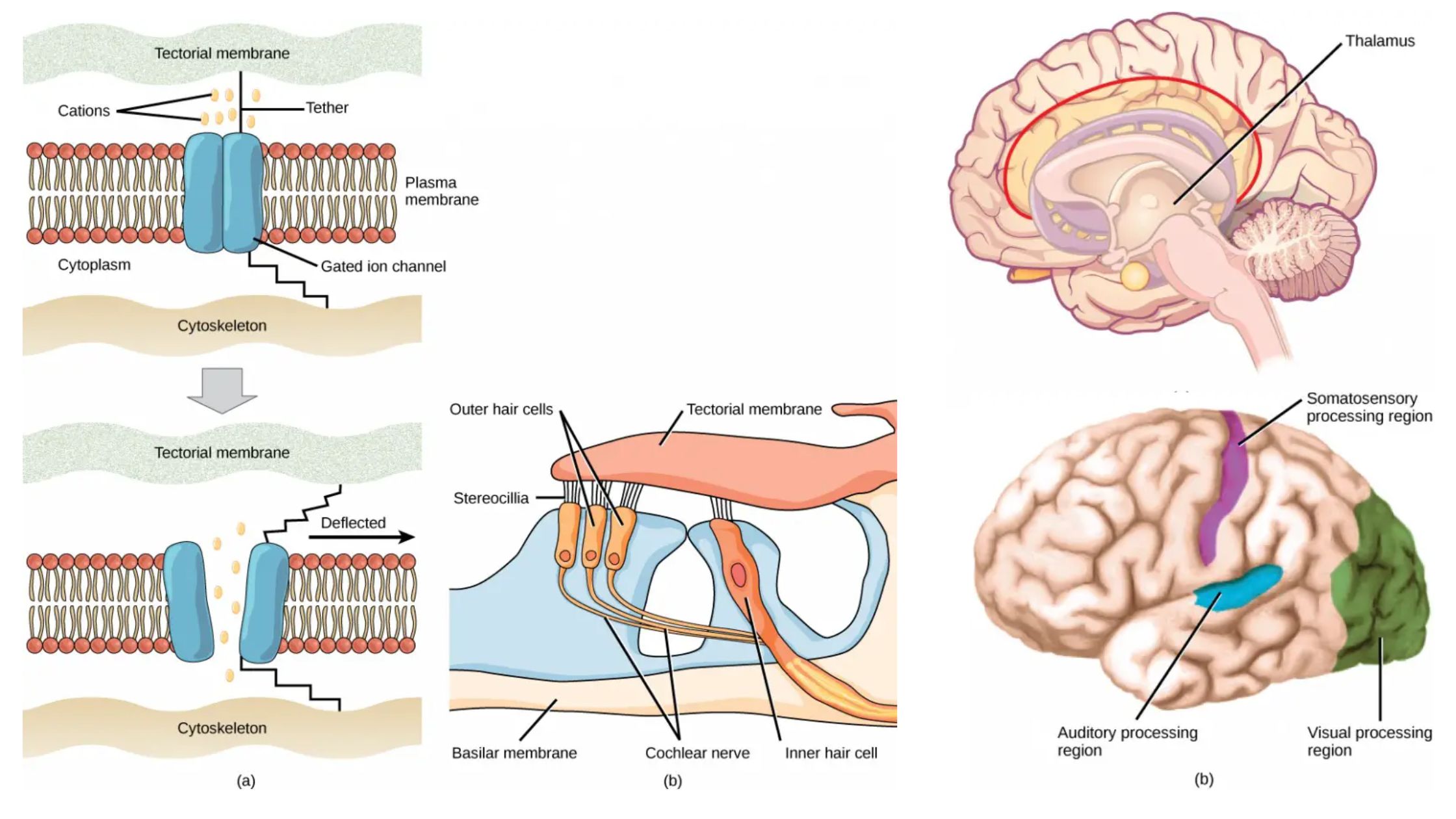
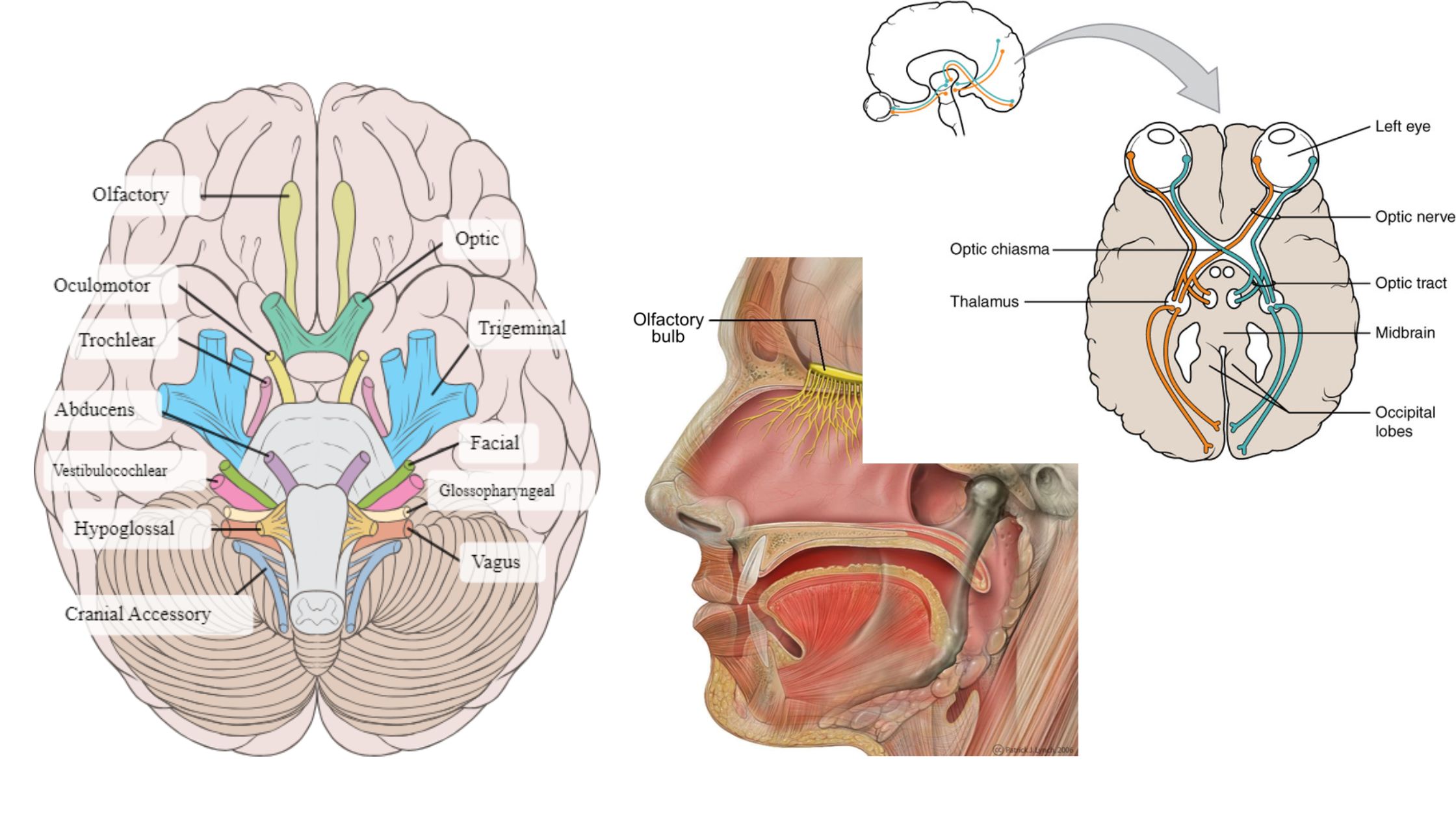
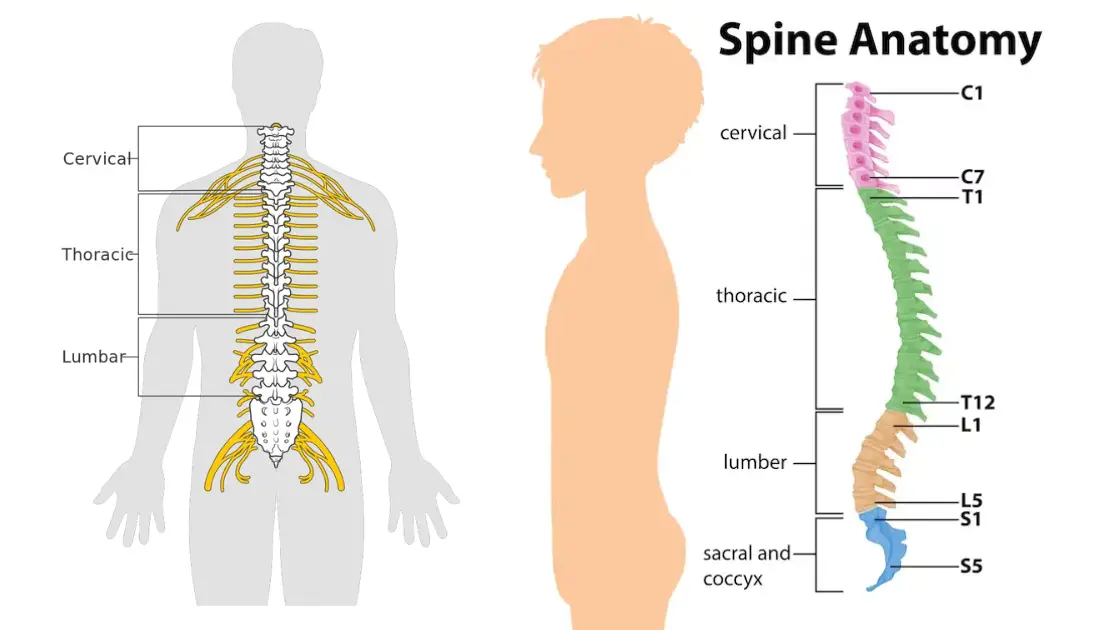
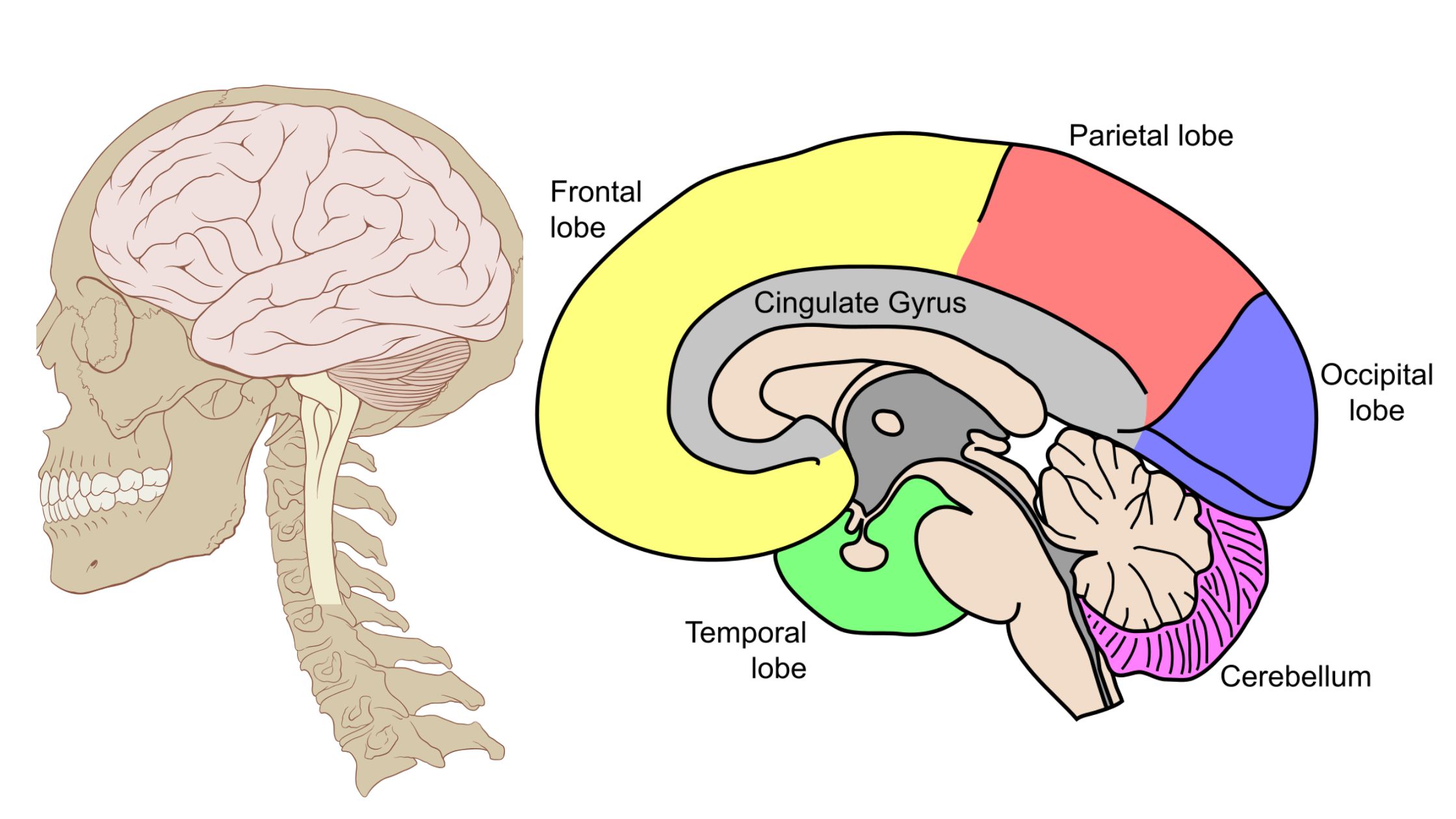
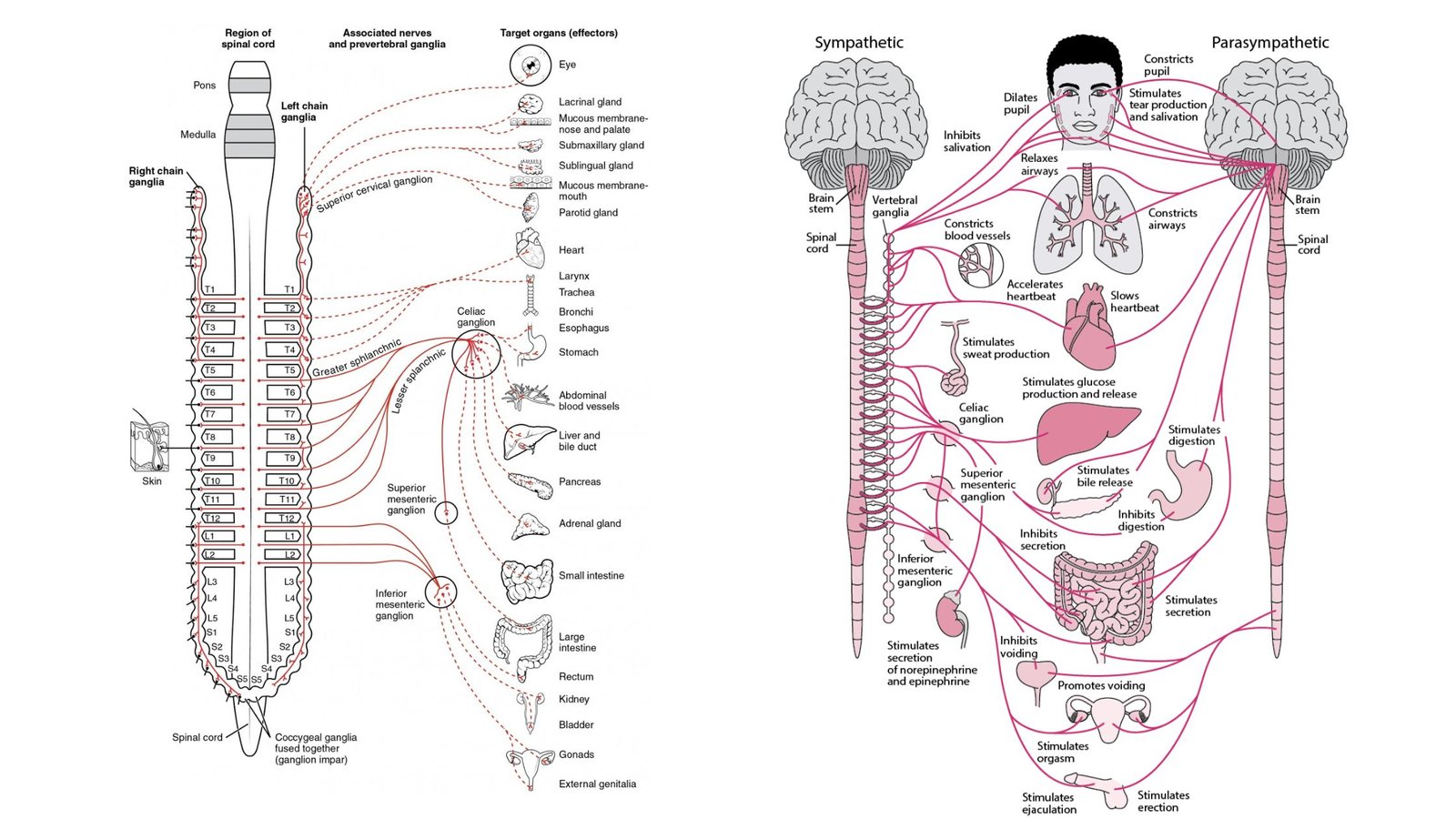
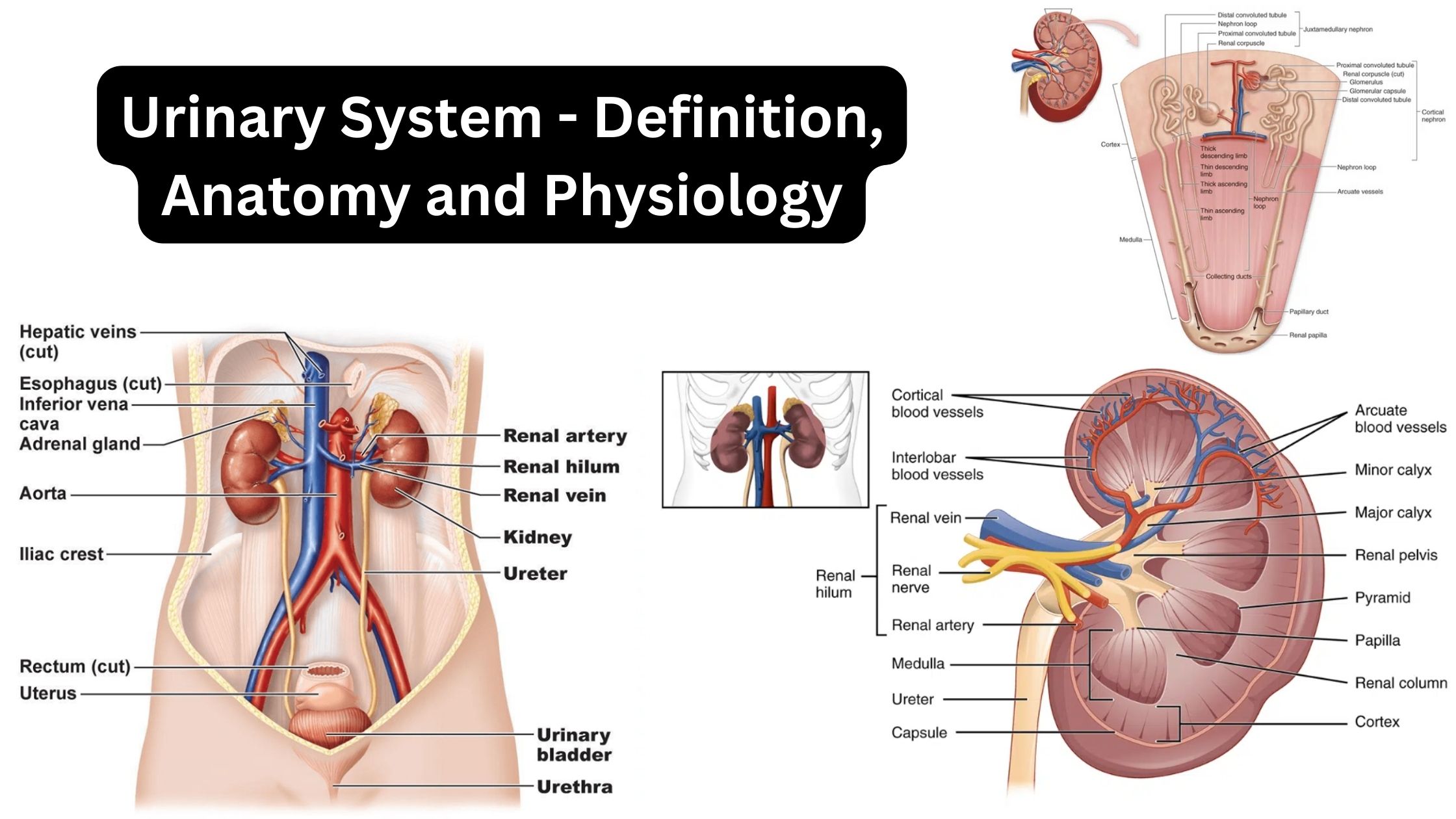
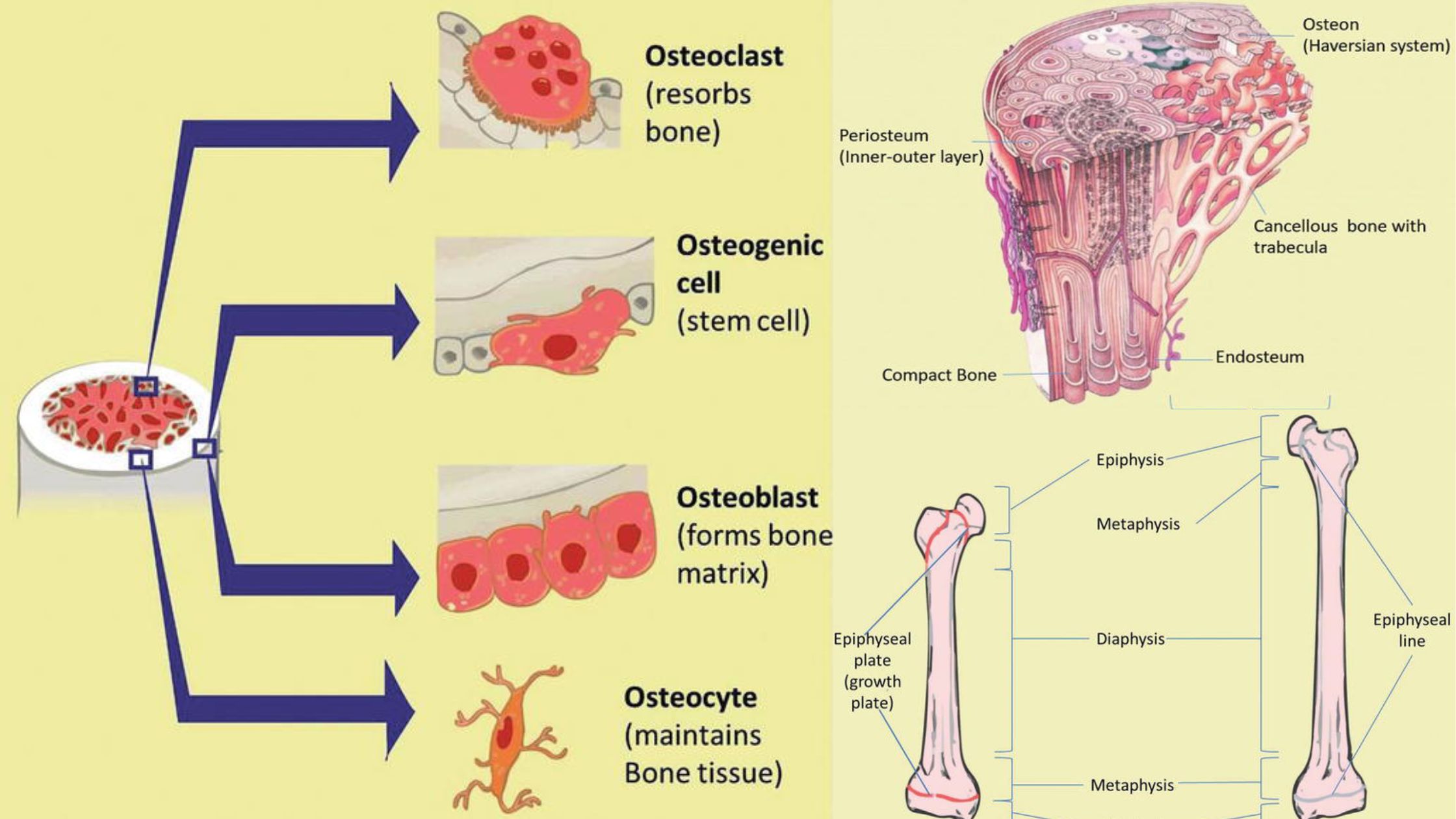
Sensory Receptors – Definition, Types, Mechanism, Functions
What is Sensory Receptor? Definition of Sensory Receptor A sensory receptor is a structure or specialized cell that detects and responds to physical stimuli in the environment, both internally and externally. It converts these stimuli into electrical signals that are transmitted to the central nervous system for processing and perception. How Sensory Systems Work? Classification … Read more