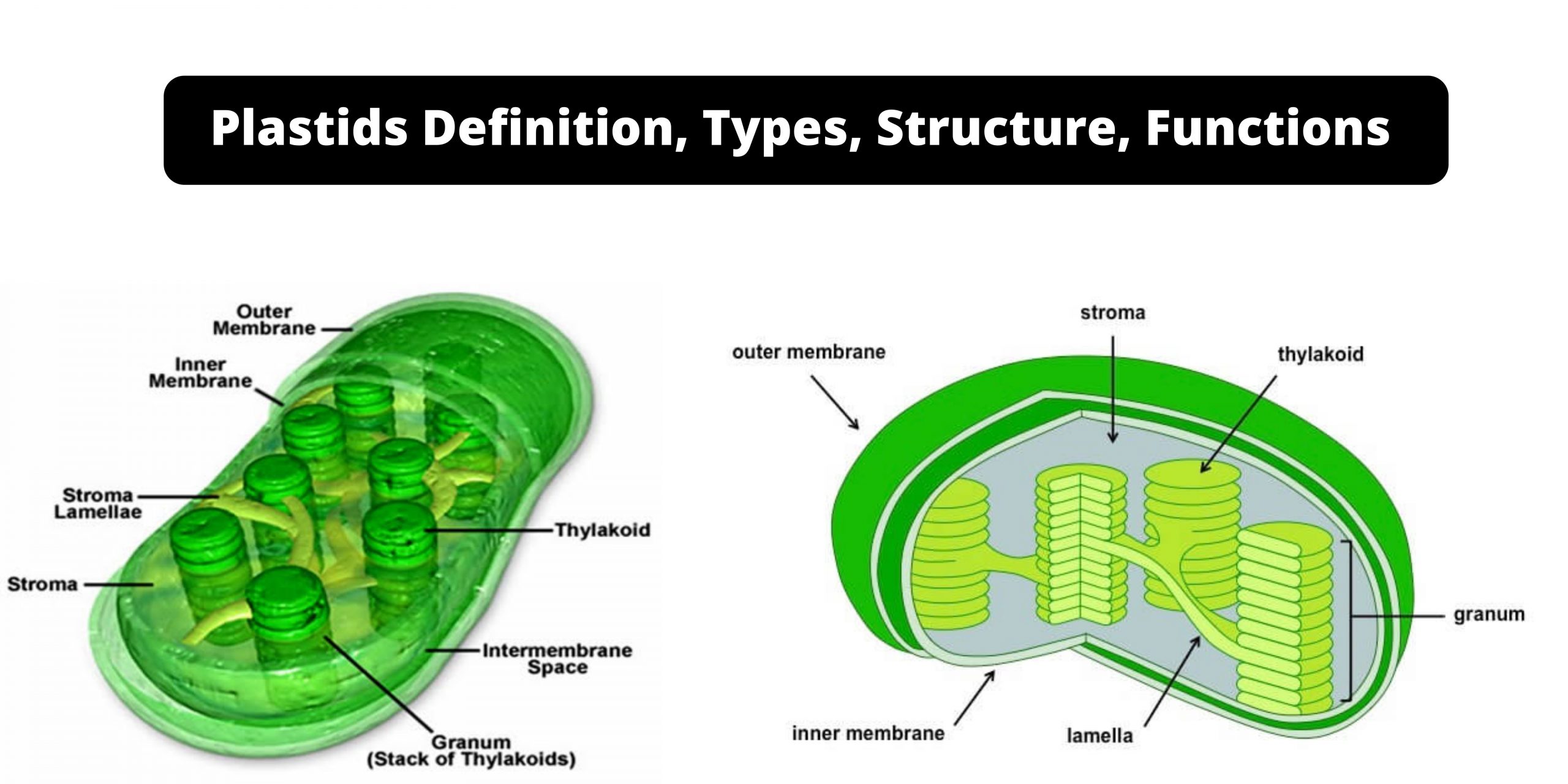
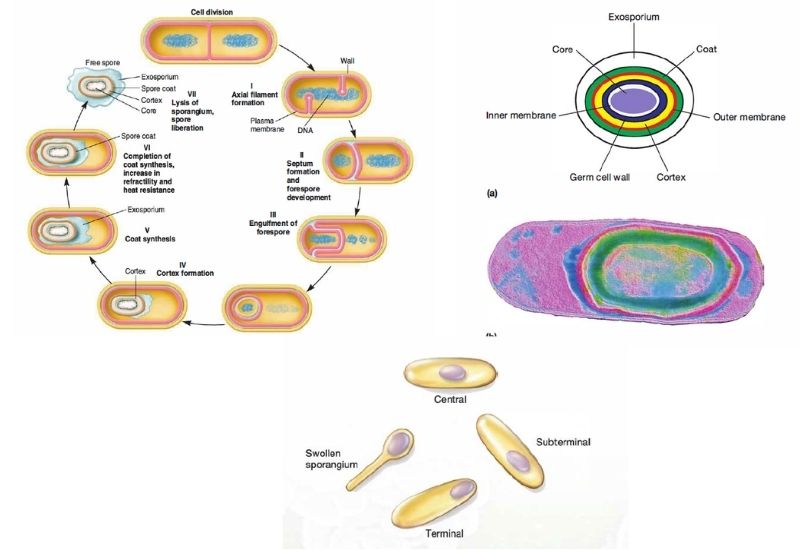
Protozoa – Definition, Classification, Characteristics, Structure, Locomotion, Examples
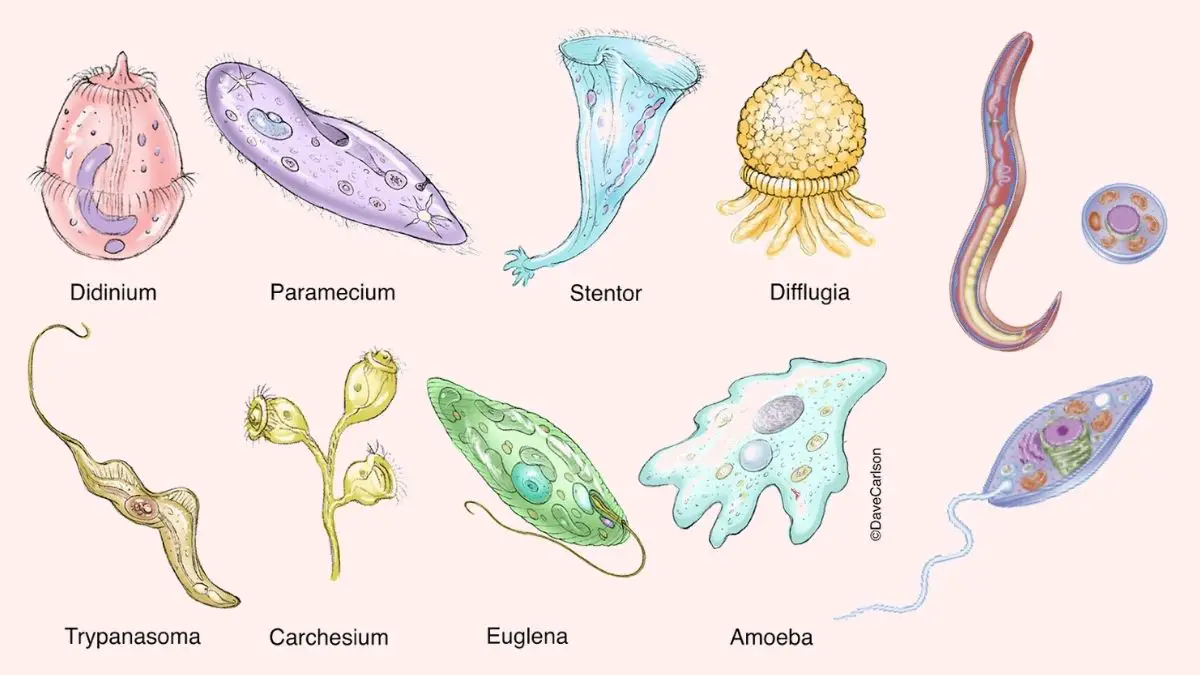
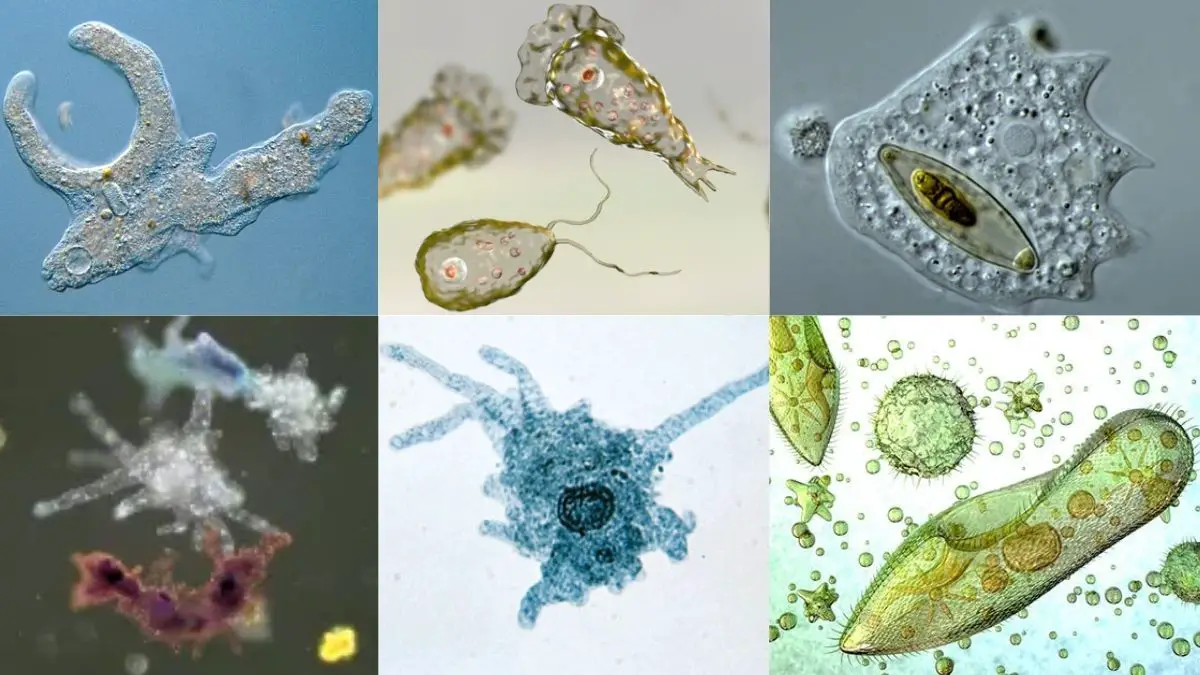
What is Protozoa? Protozoa Definition Protozoa are a diverse group of single-celled eukaryotic organisms that can be either free-living or parasitic. They primarily feed on organic matter, including microorganisms and organic debris. Protozoa are characterized by their lack of a rigid cell wall, motility, and heterotrophic feeding habits. Examples include Amoeba, Paramecium, Euglena, and Trypanosoma. … Read more