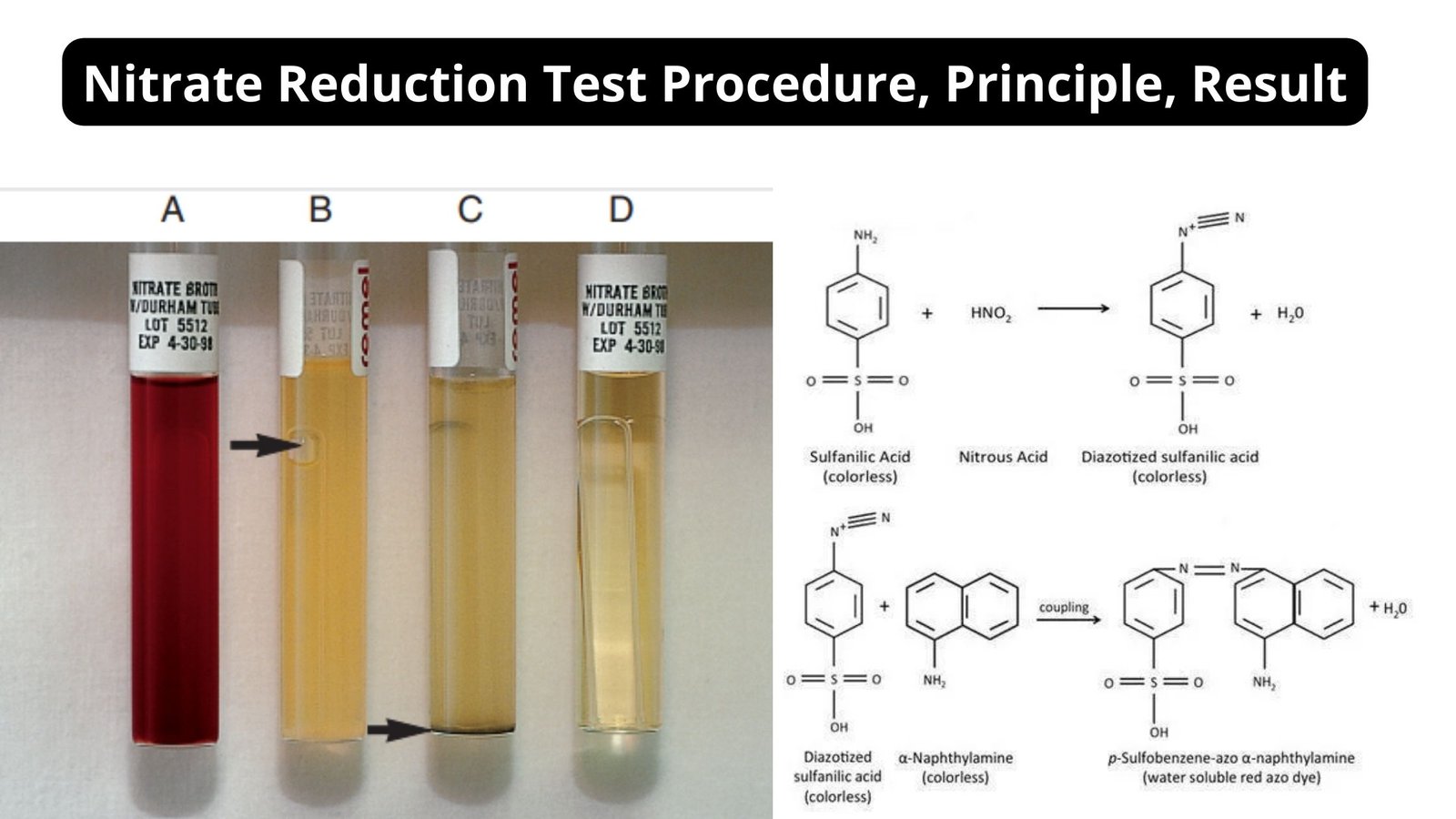
Nitrate Reduction Test – Procedure, Principle, Result
What is Nitrate Reduction Test? Purpose of Nitrate Reduction Test Principle of Nitrate Reduction Test Reactions of Nitrate Reduction Test Use of Zinc powder Use of A Durham tube Requirements Composition of Nitrate broth (medium) Ingredients Gms / Litre Peptic digest of animal tissue 5.000 Meat extract 3.000 Potassium nitrate 1.000 Sodium chloride 30.000 Final … Read more