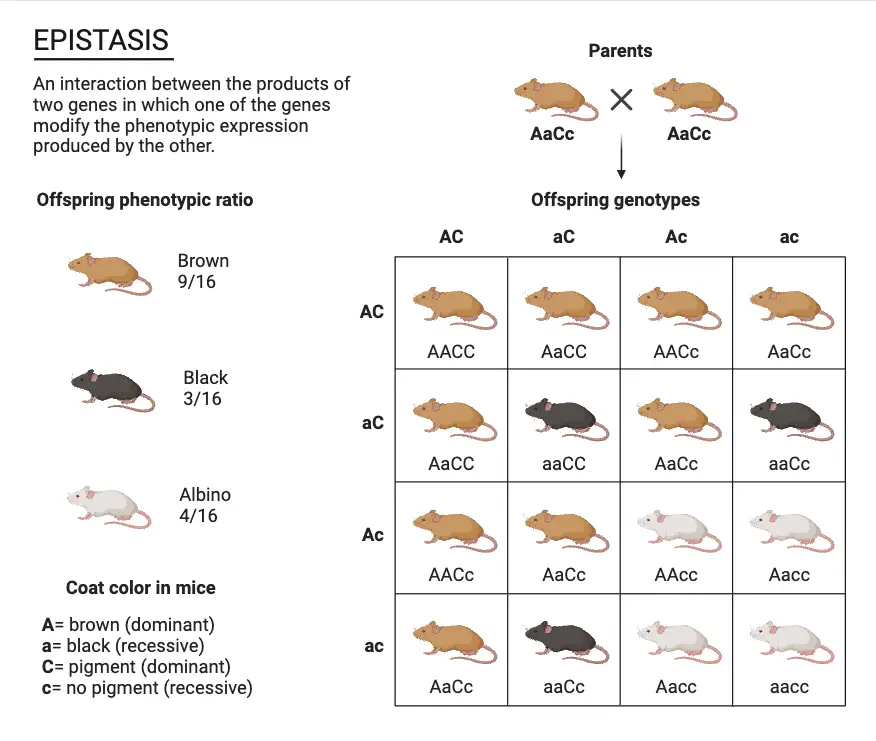
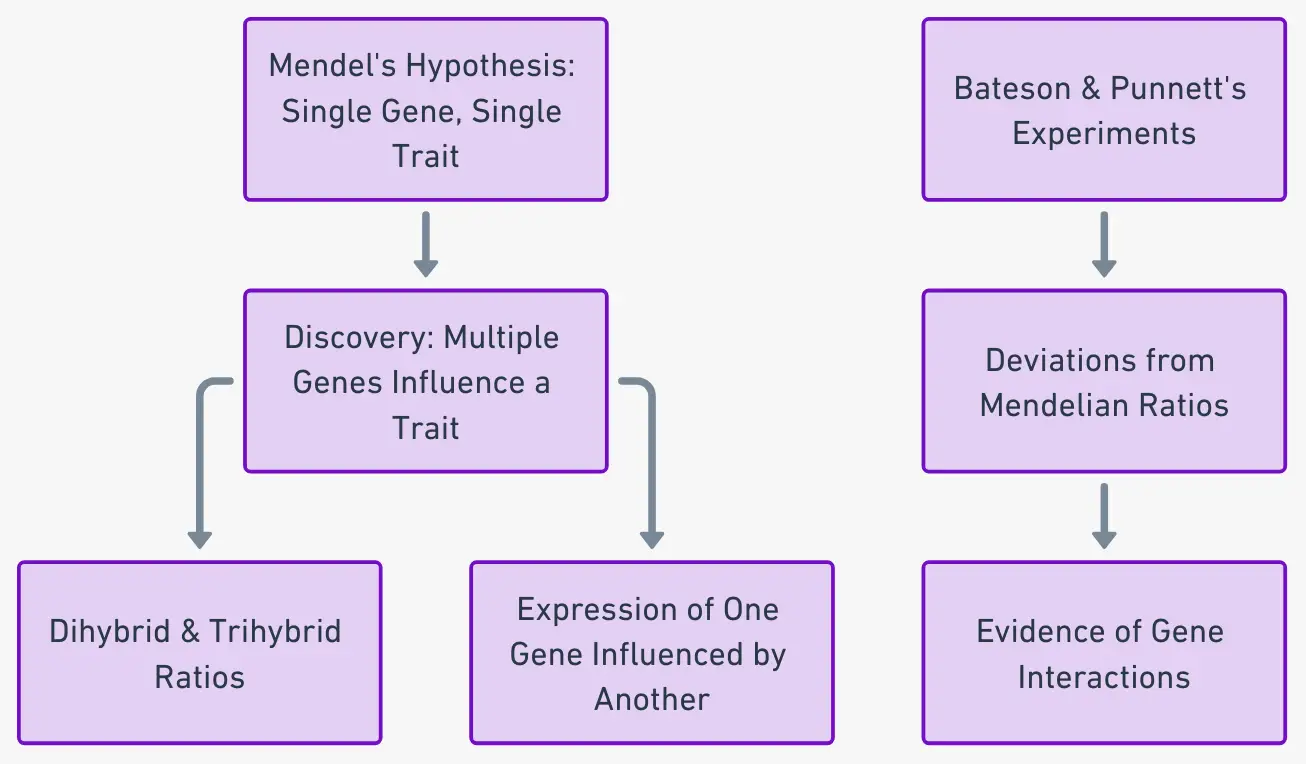
Pedigree Analysis – Types, Chart, Symbols, Methods, Examples
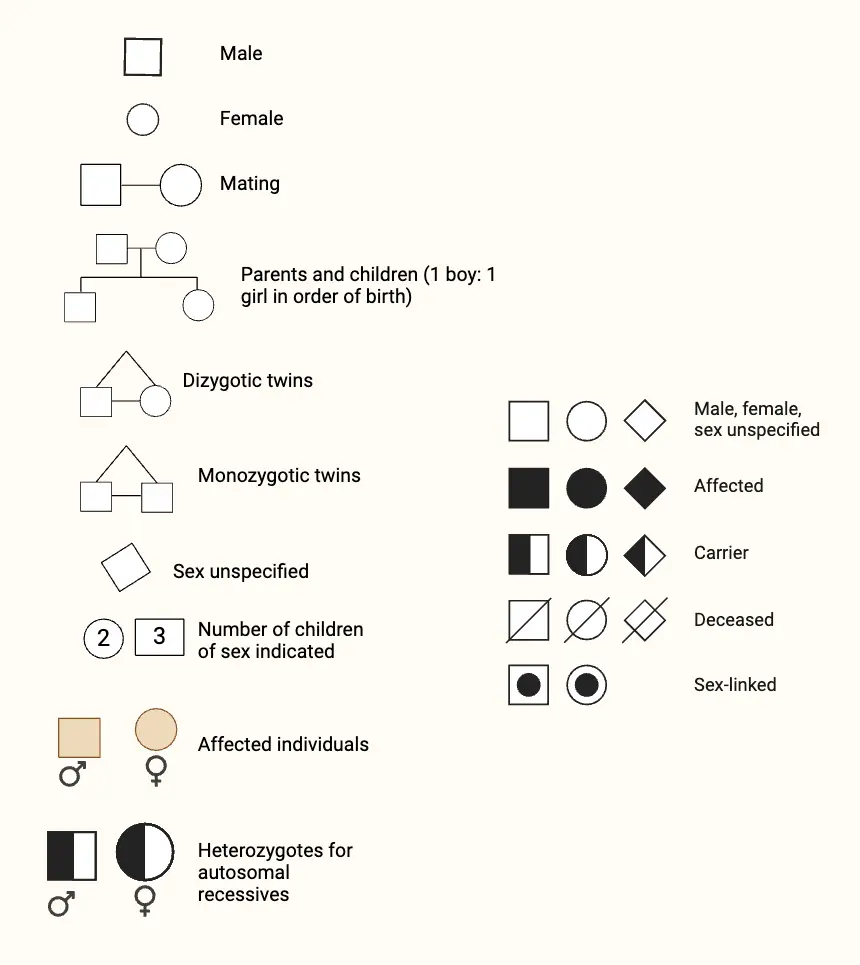
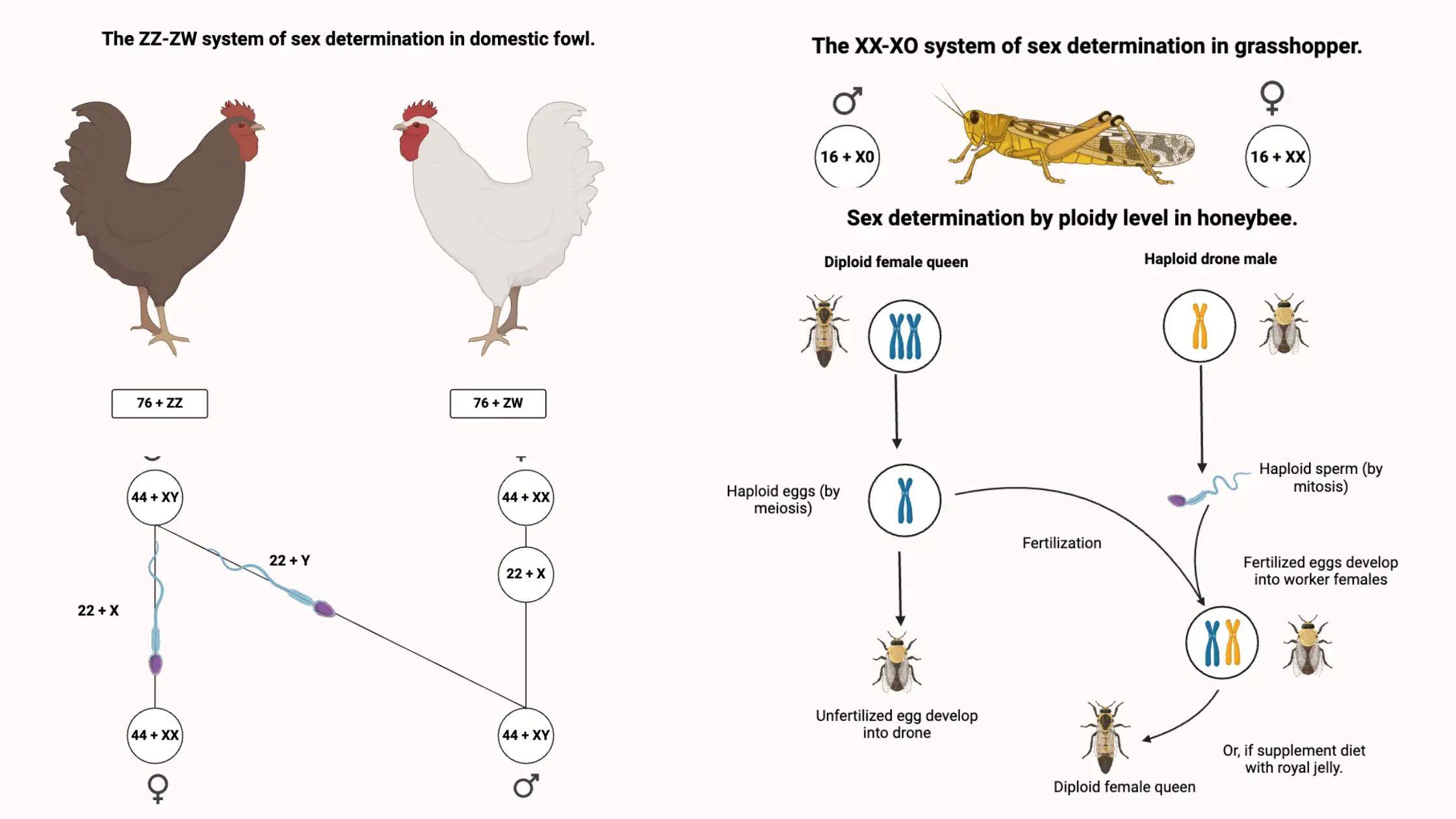
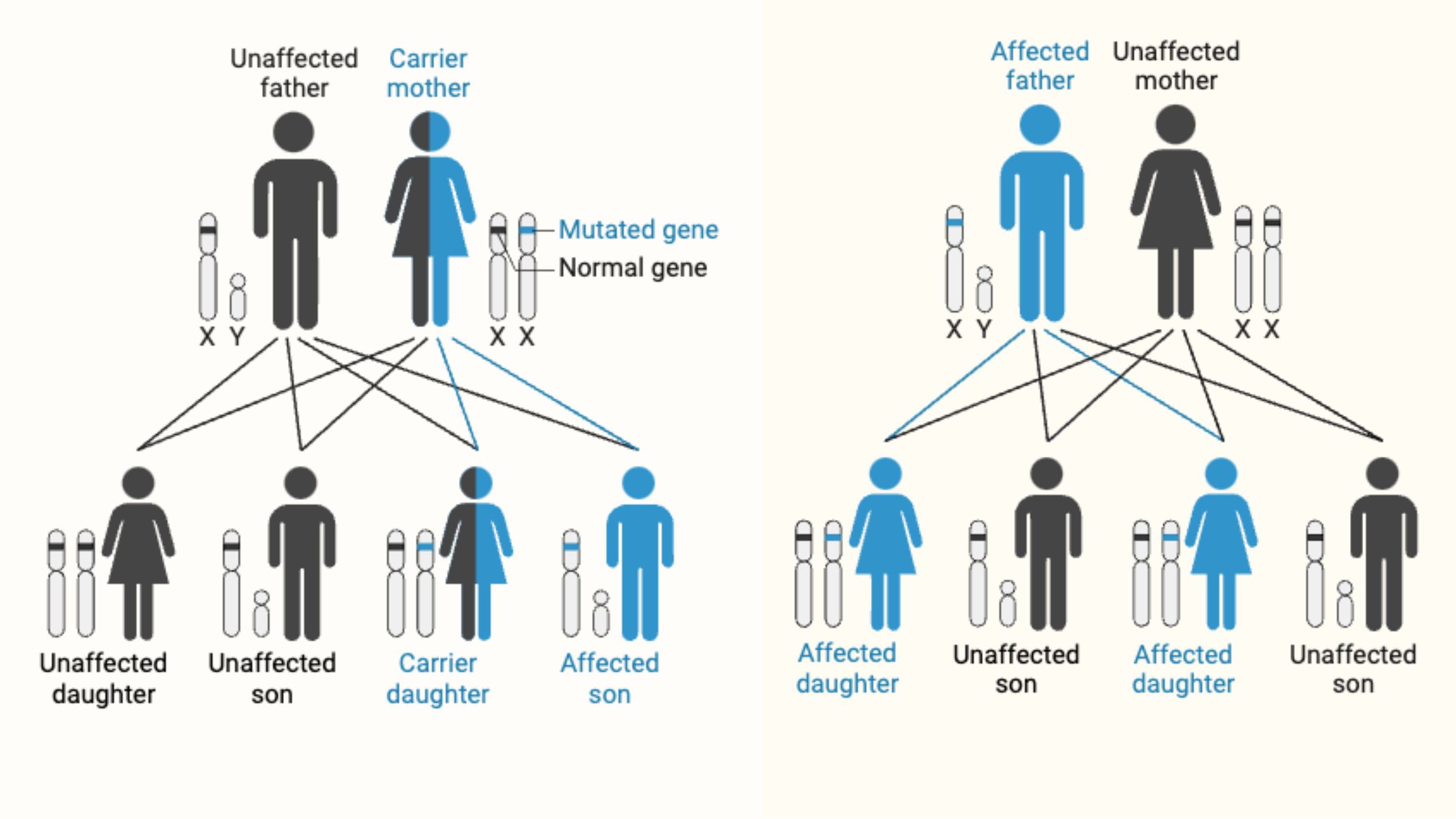
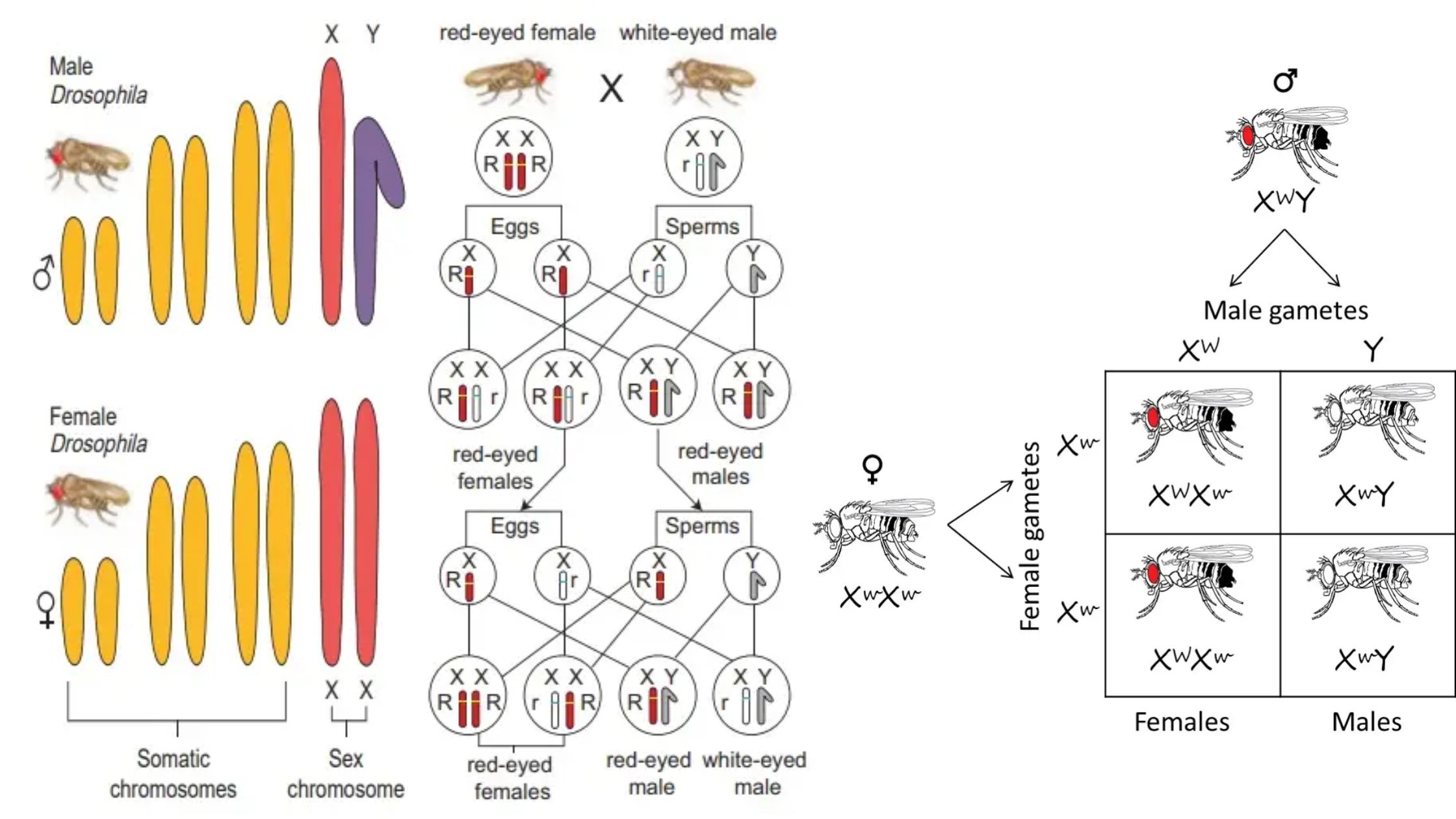
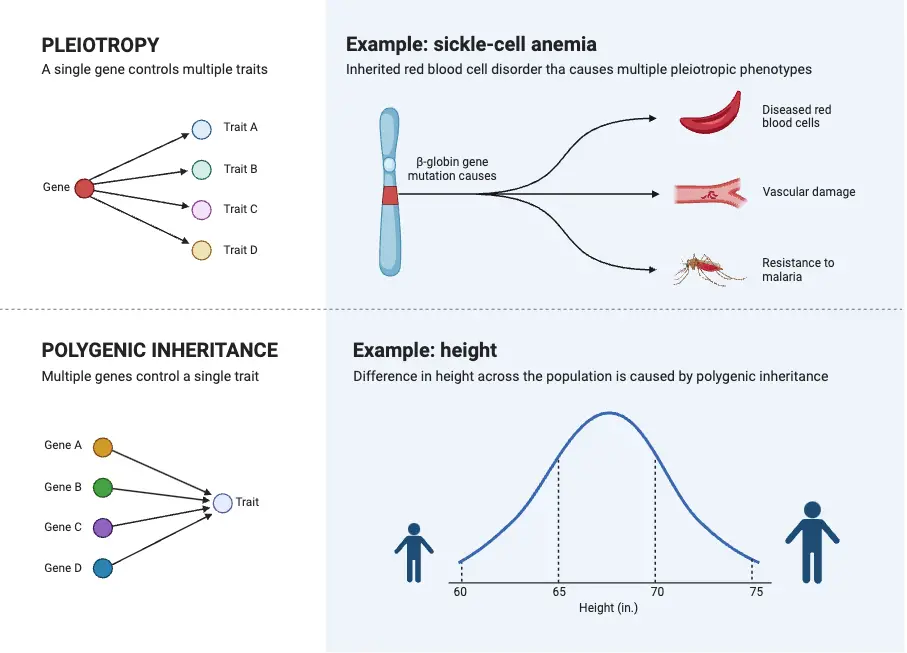
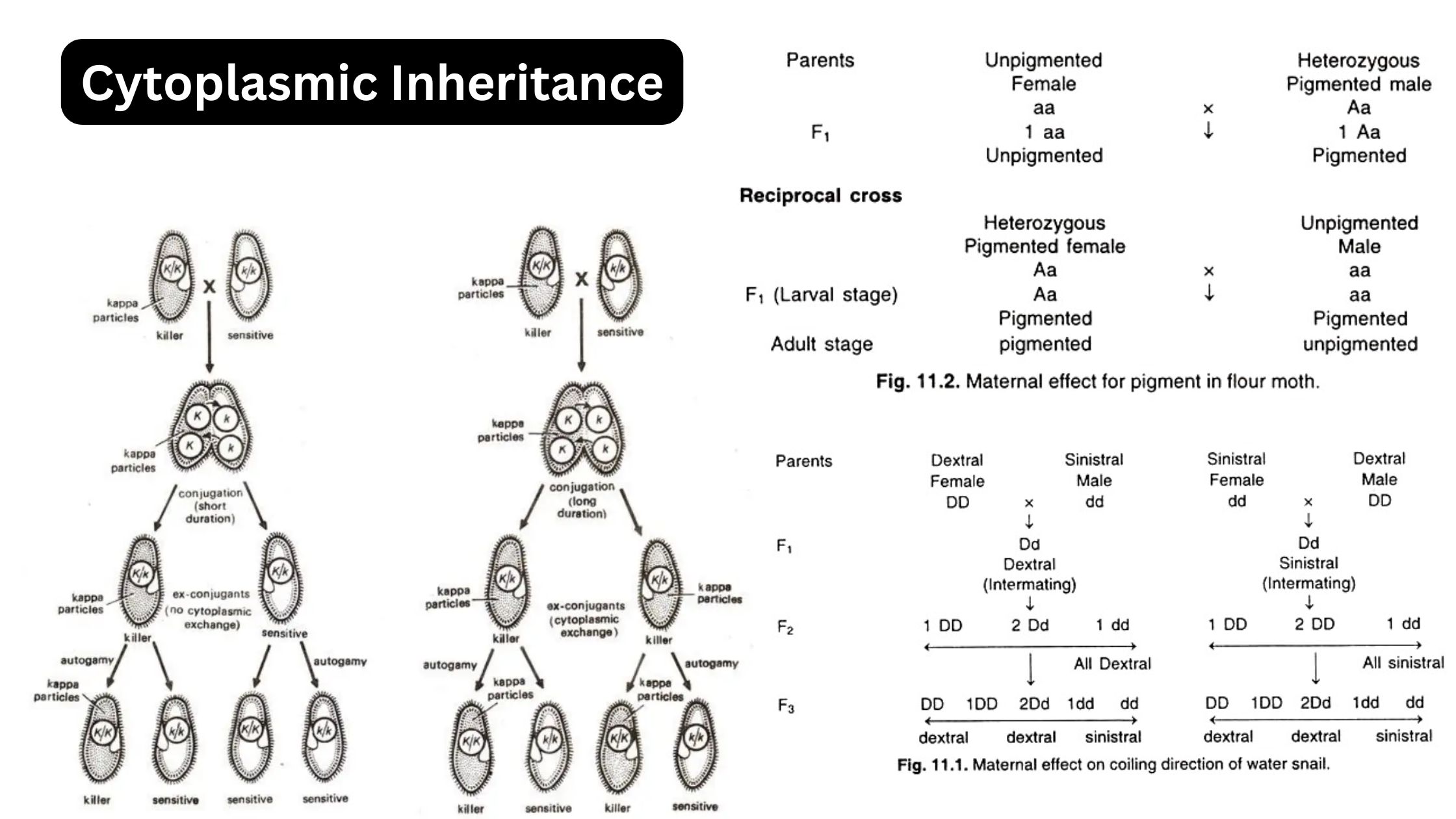
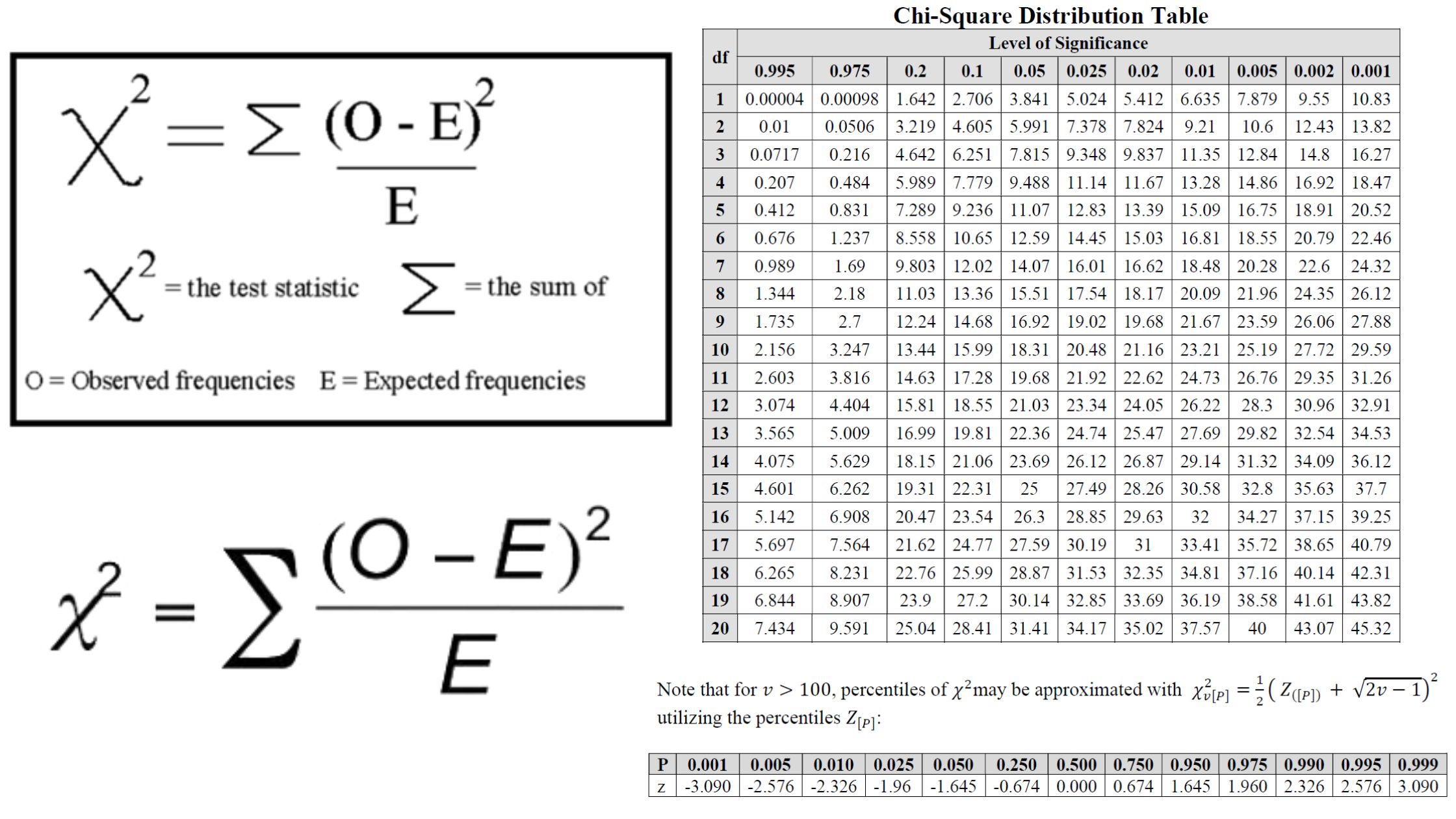
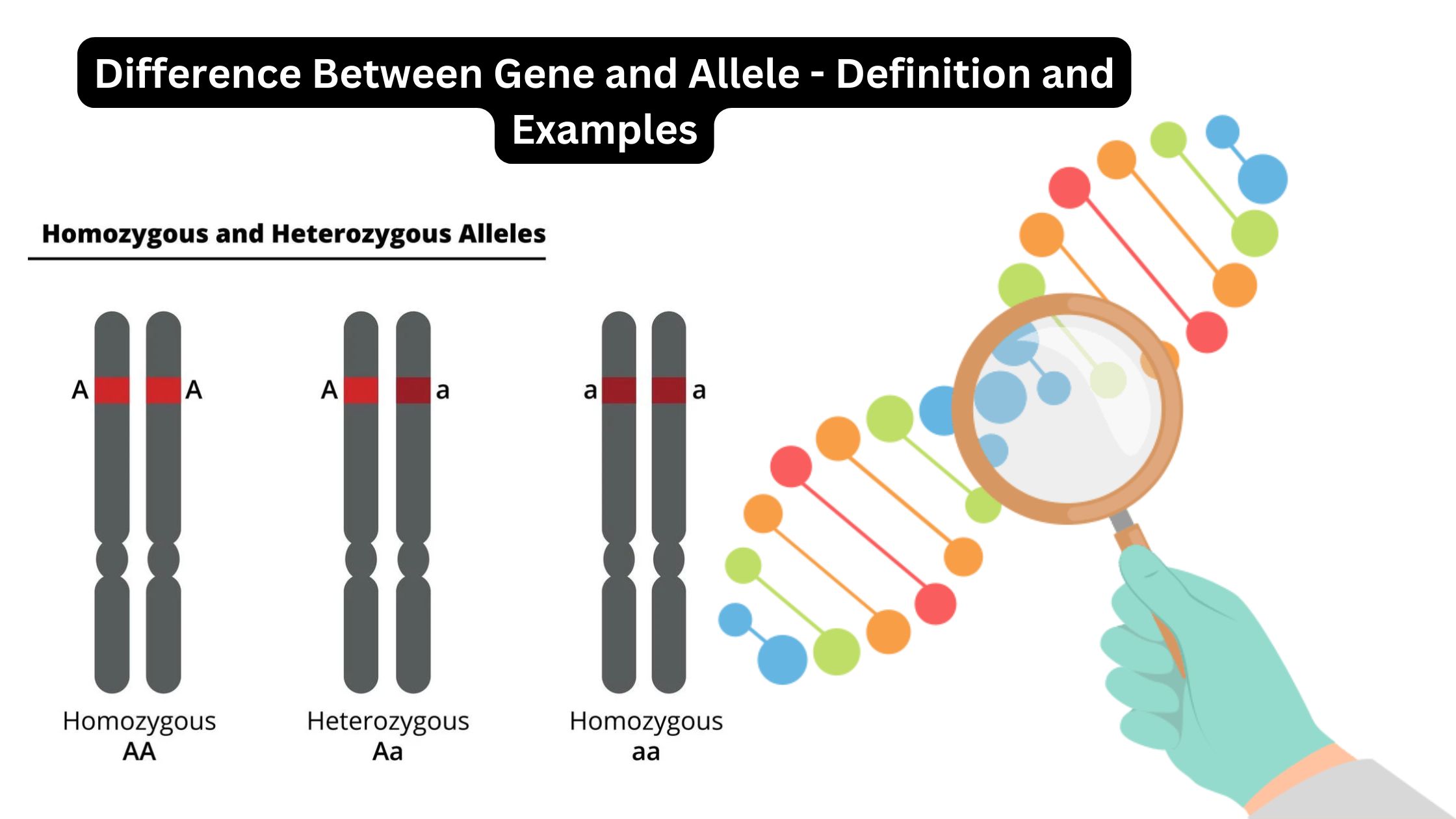
What is Pedigree? What is Pedigree Analysis? Pedigree Analysis Definition Pedigree analysis is a genetic tool used to trace the inheritance patterns of traits or disorders through generations of a family, helping to predict the likelihood of their occurrence in offspring based on familial history. Basic Steps of Pedigree Analysis Pedigree analysis involves several systematic … Read more