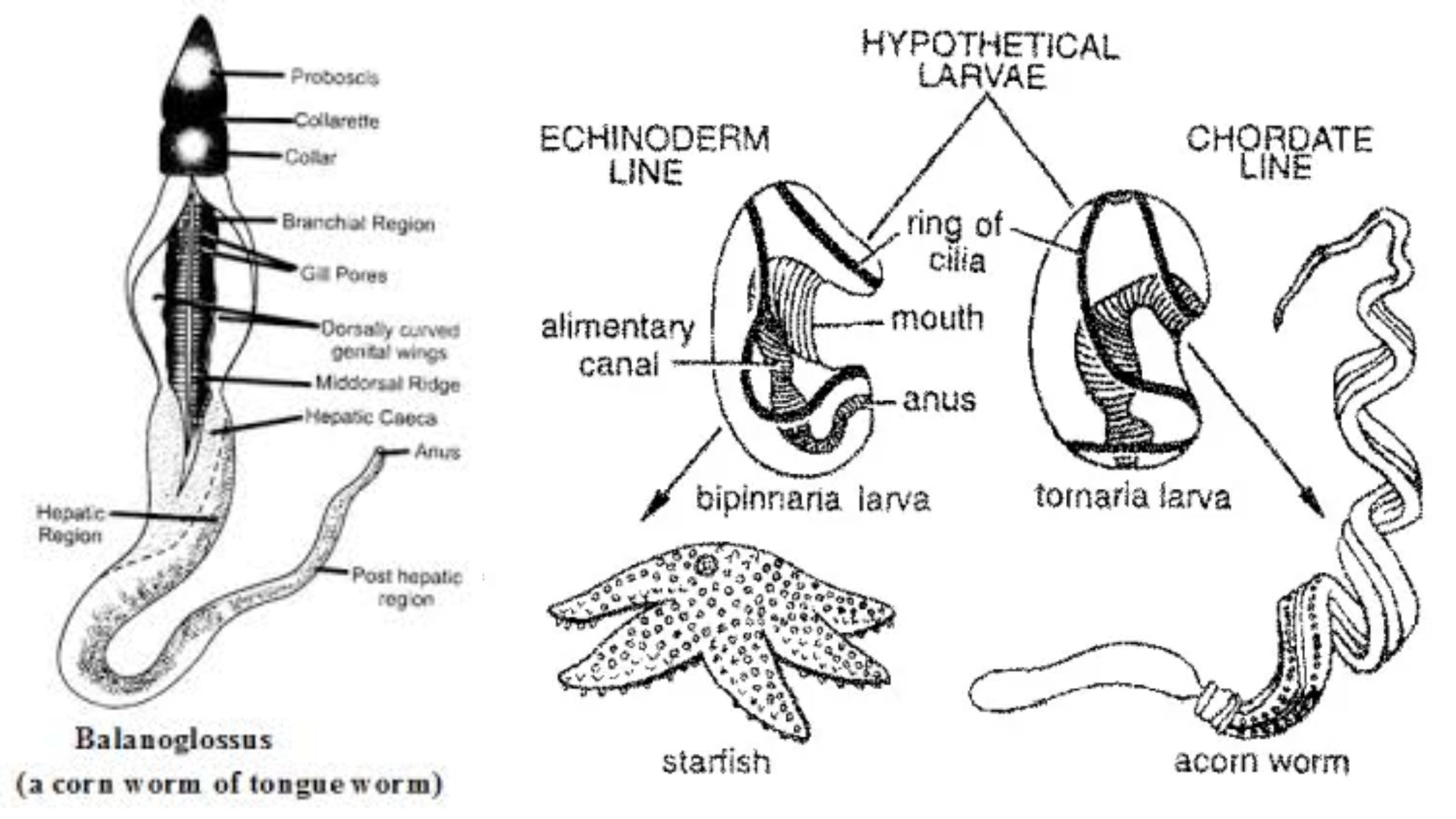
Protochordata – Characteristics and Classification
What is Protochordata? Characteristics of Protochordata Protochordata, often referred to as primitive chordates, exhibit several defining features that differentiate them from more advanced vertebrates. These organisms are primarily marine and show a blend of both invertebrate and vertebrate characteristics. Below is a detailed overview of the key characteristics of protochordates: Classification of Protochordata Protochordate is … Read more