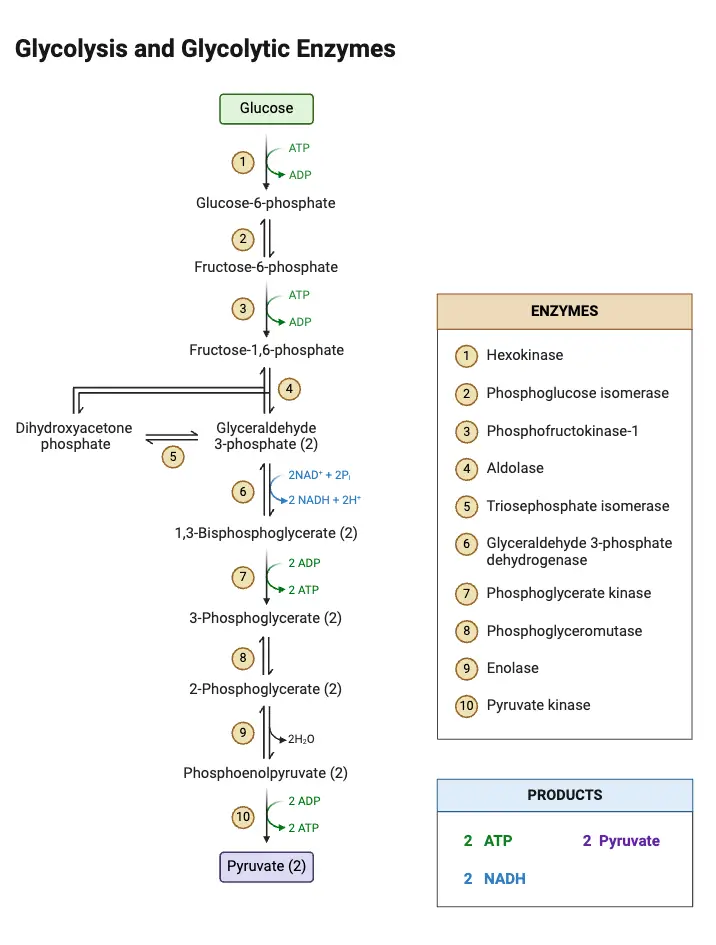
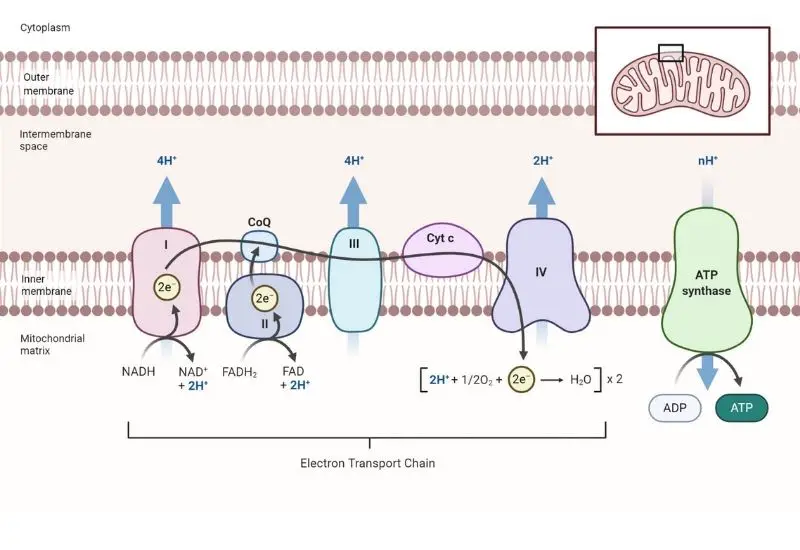
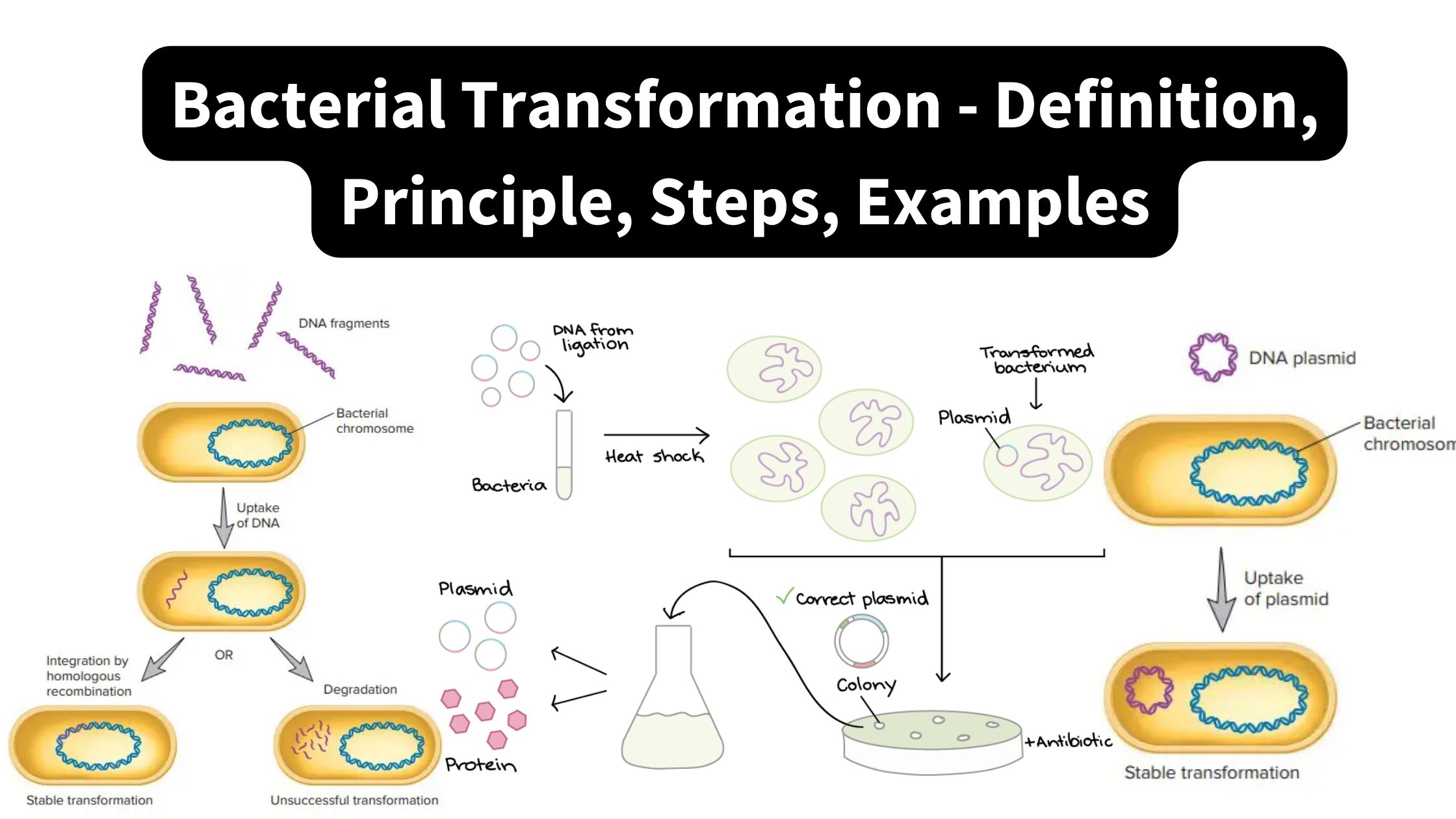
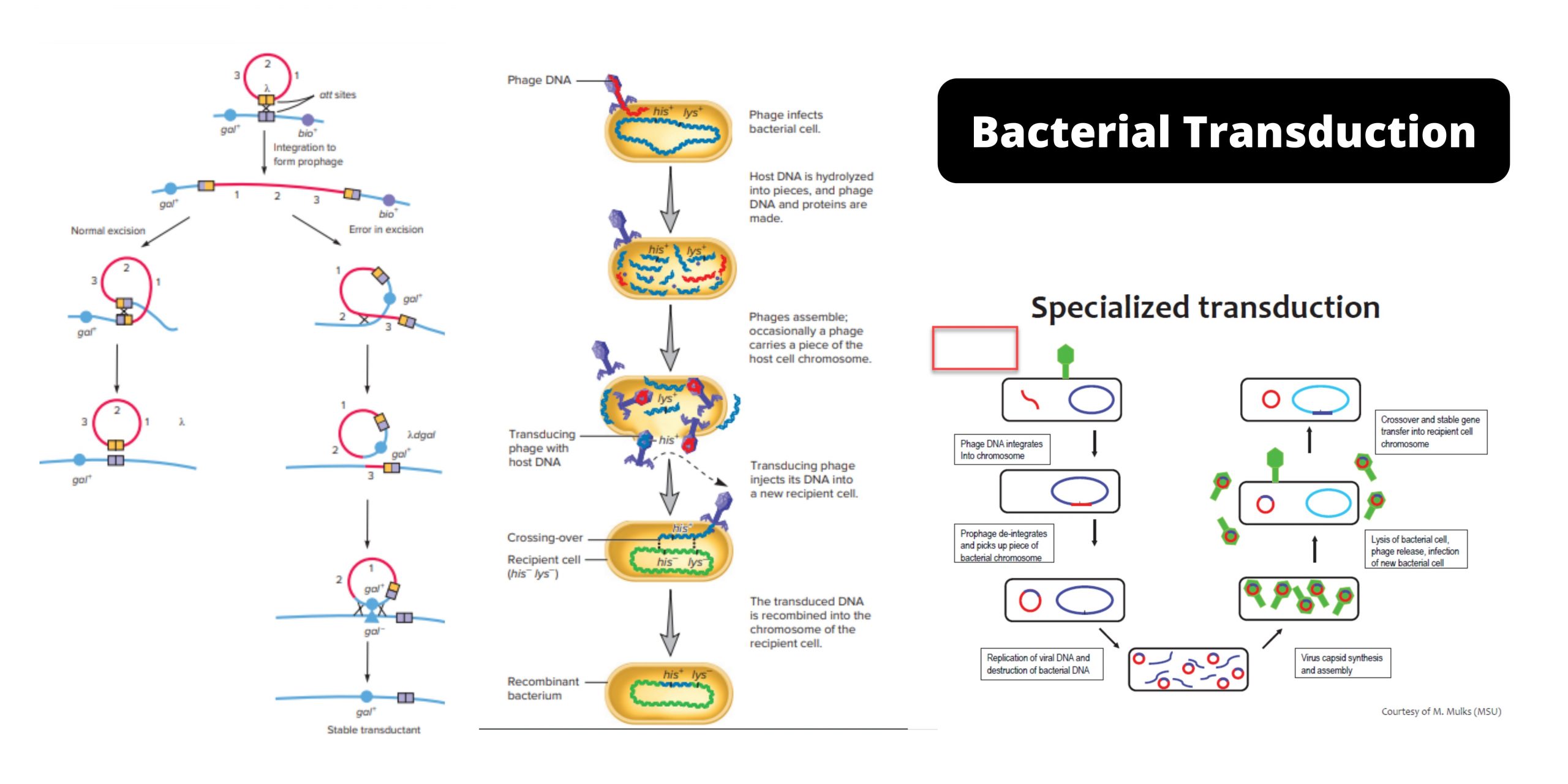
Galactose Metabolism – Steps, Importance, Leloir Pathway
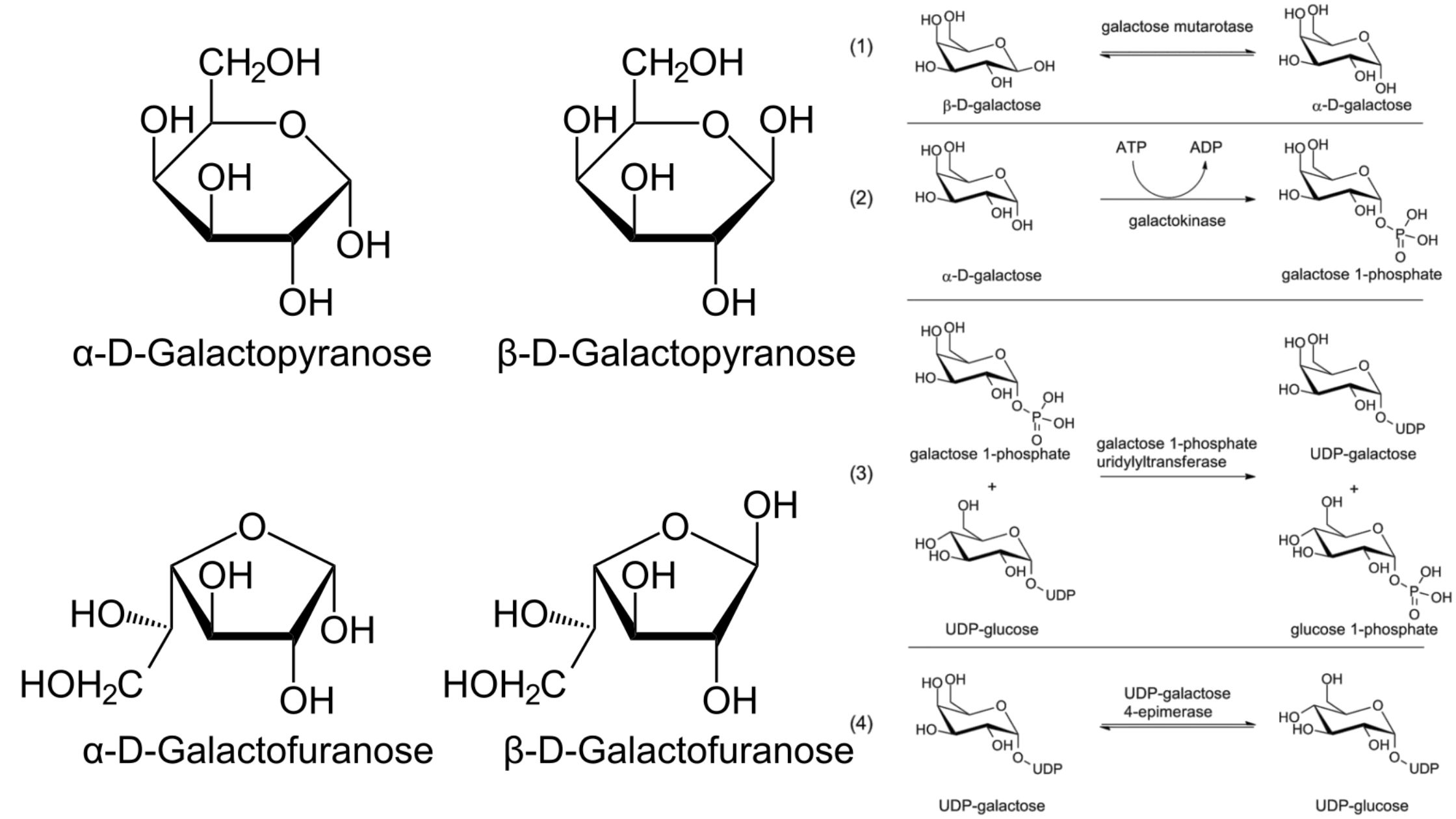
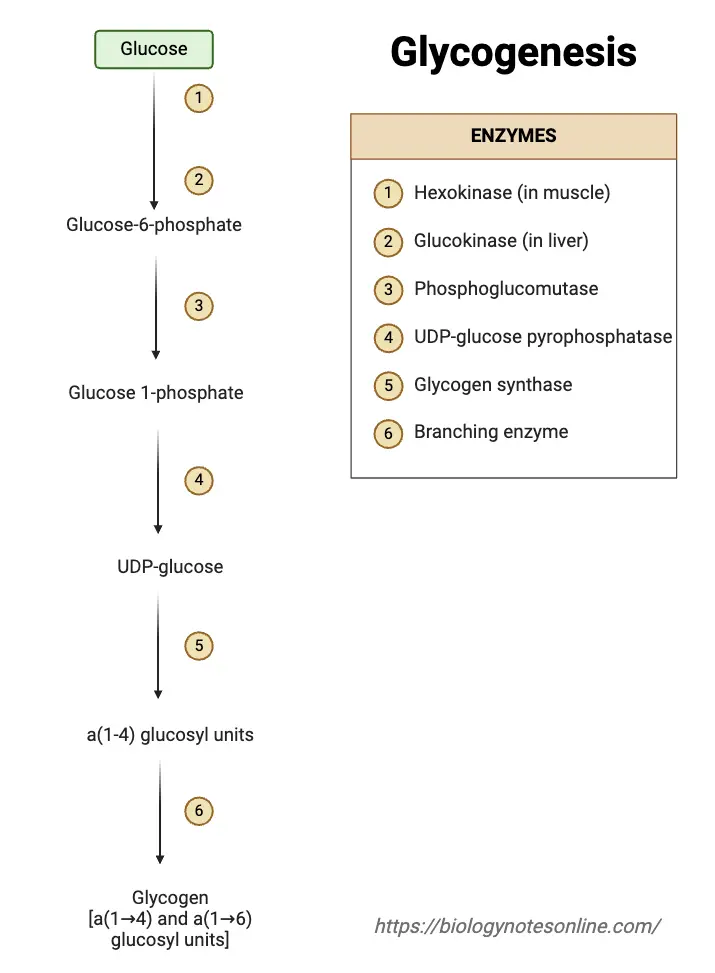
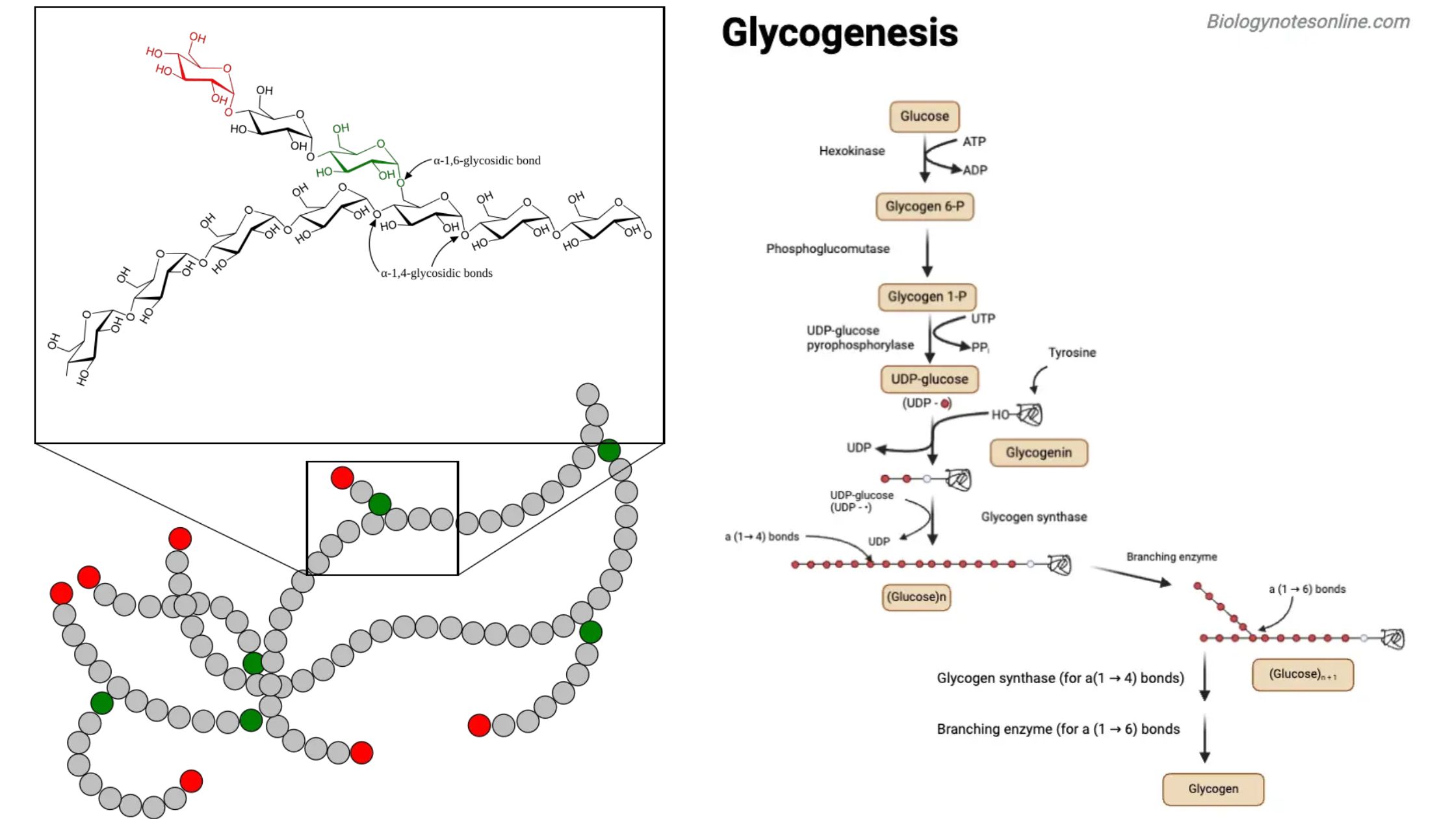
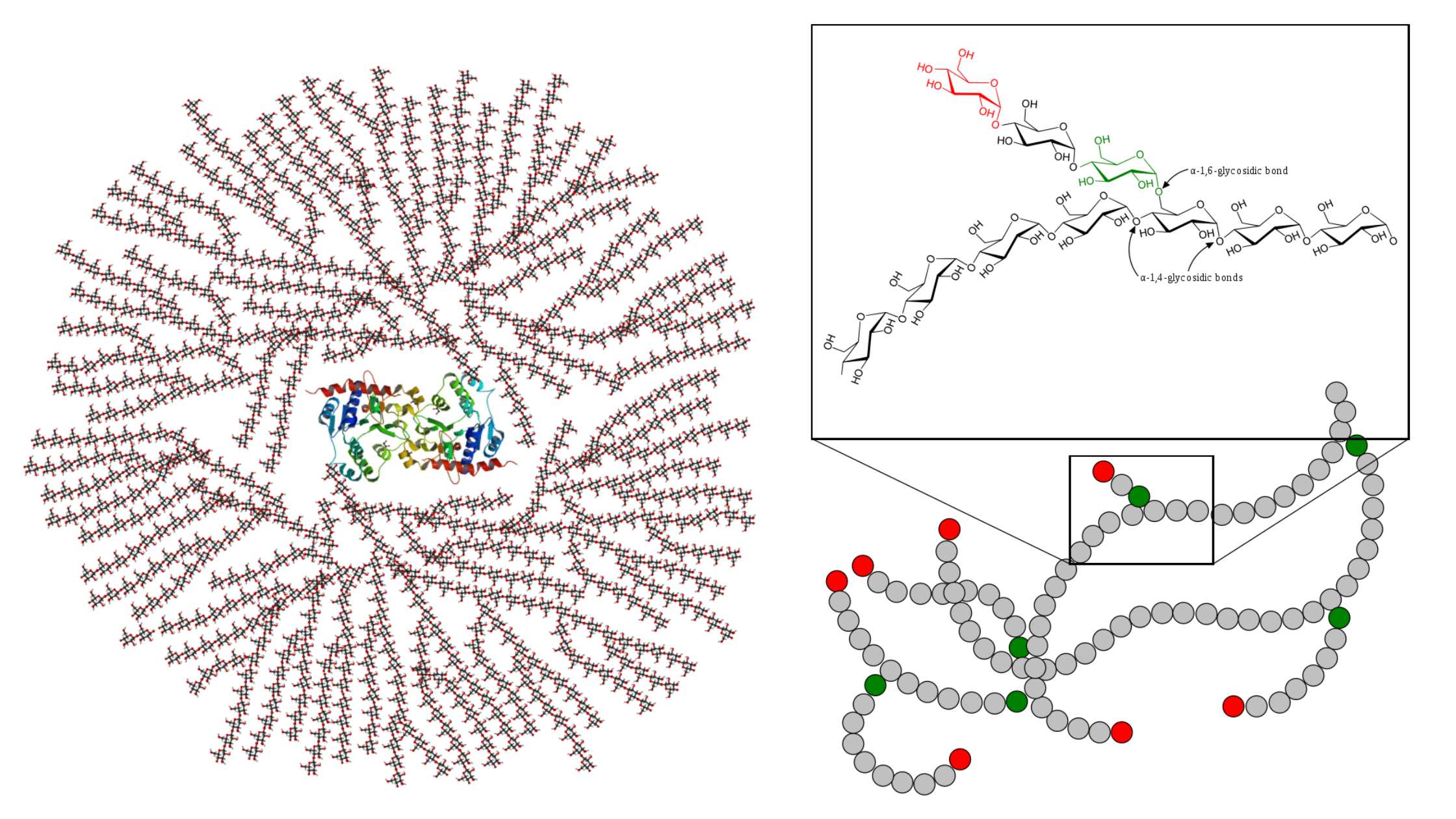
What is Galactose? Galactose is a monosaccharide sugar that is an aldohexose. It is a C-4 epimer of glucose having the same structure as glucose, except that the atoms around carbon no. 4 are arranged differently. This sugar is around 65% of the sweetness of sucrose and is less sweet. It is paired with glucose … Read more