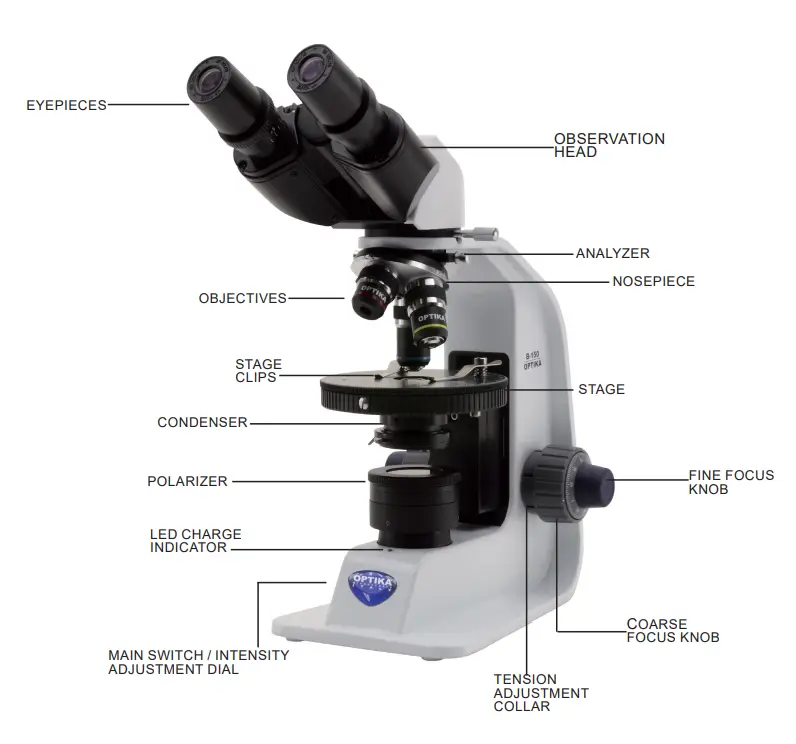
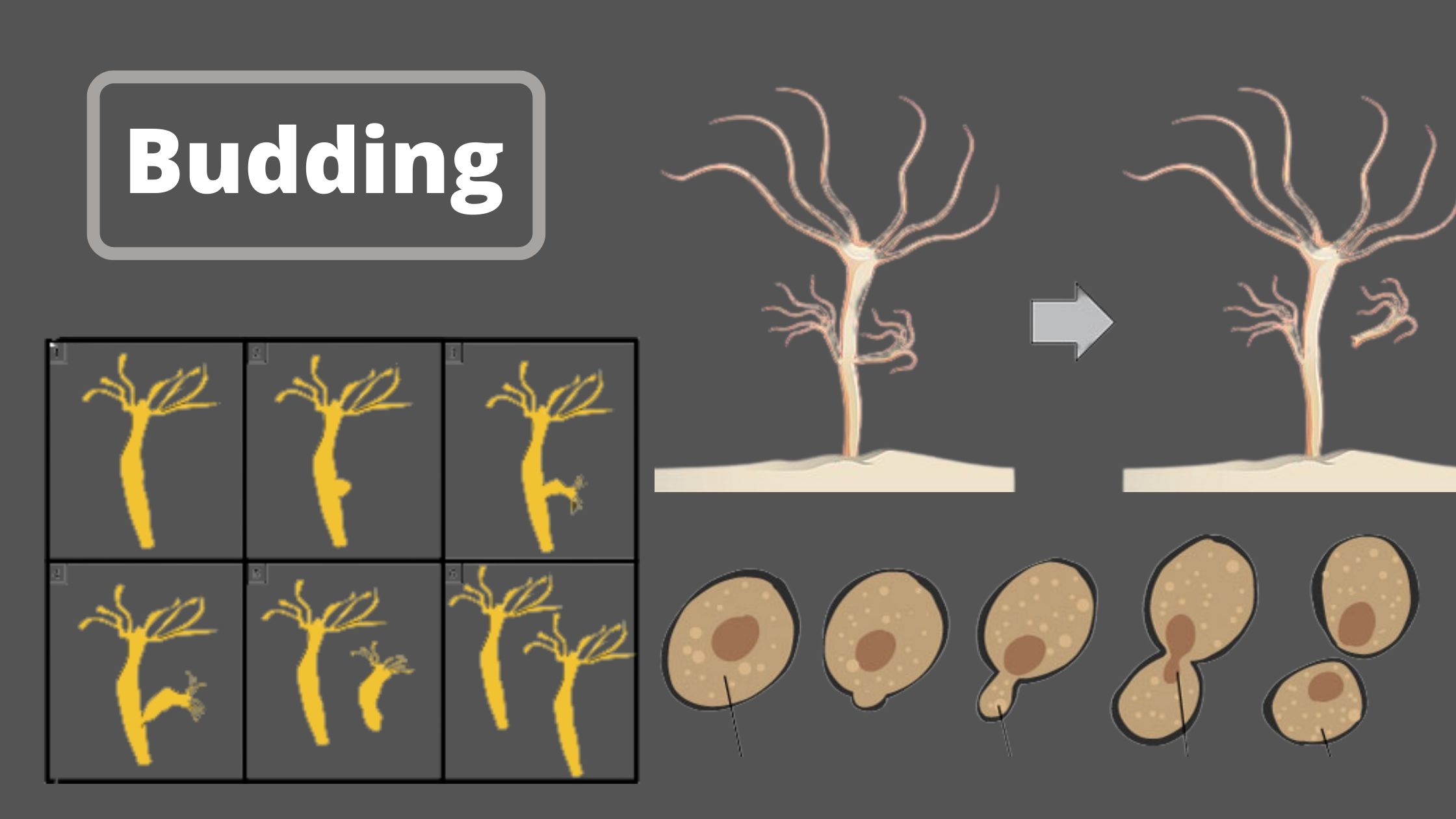
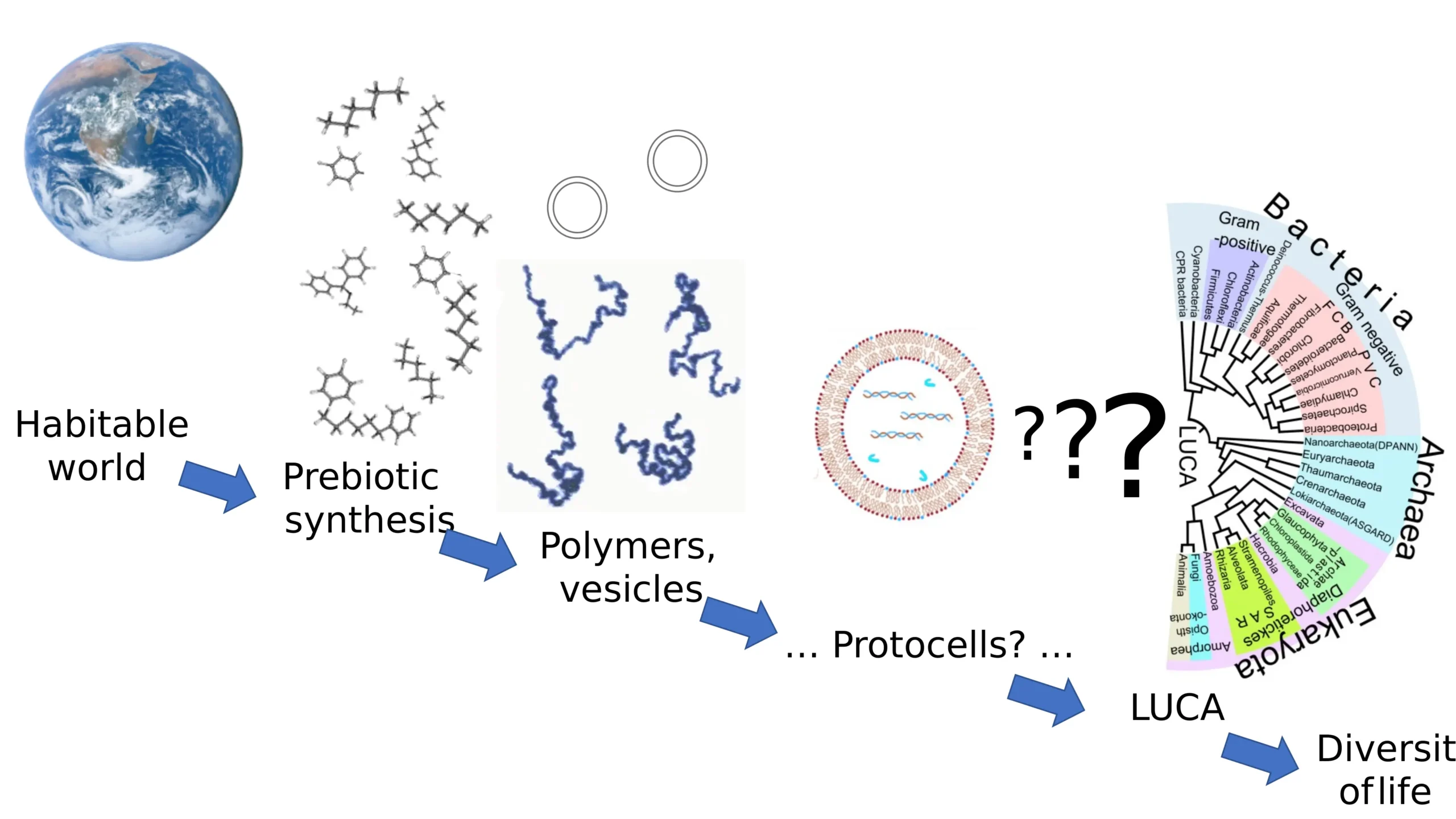
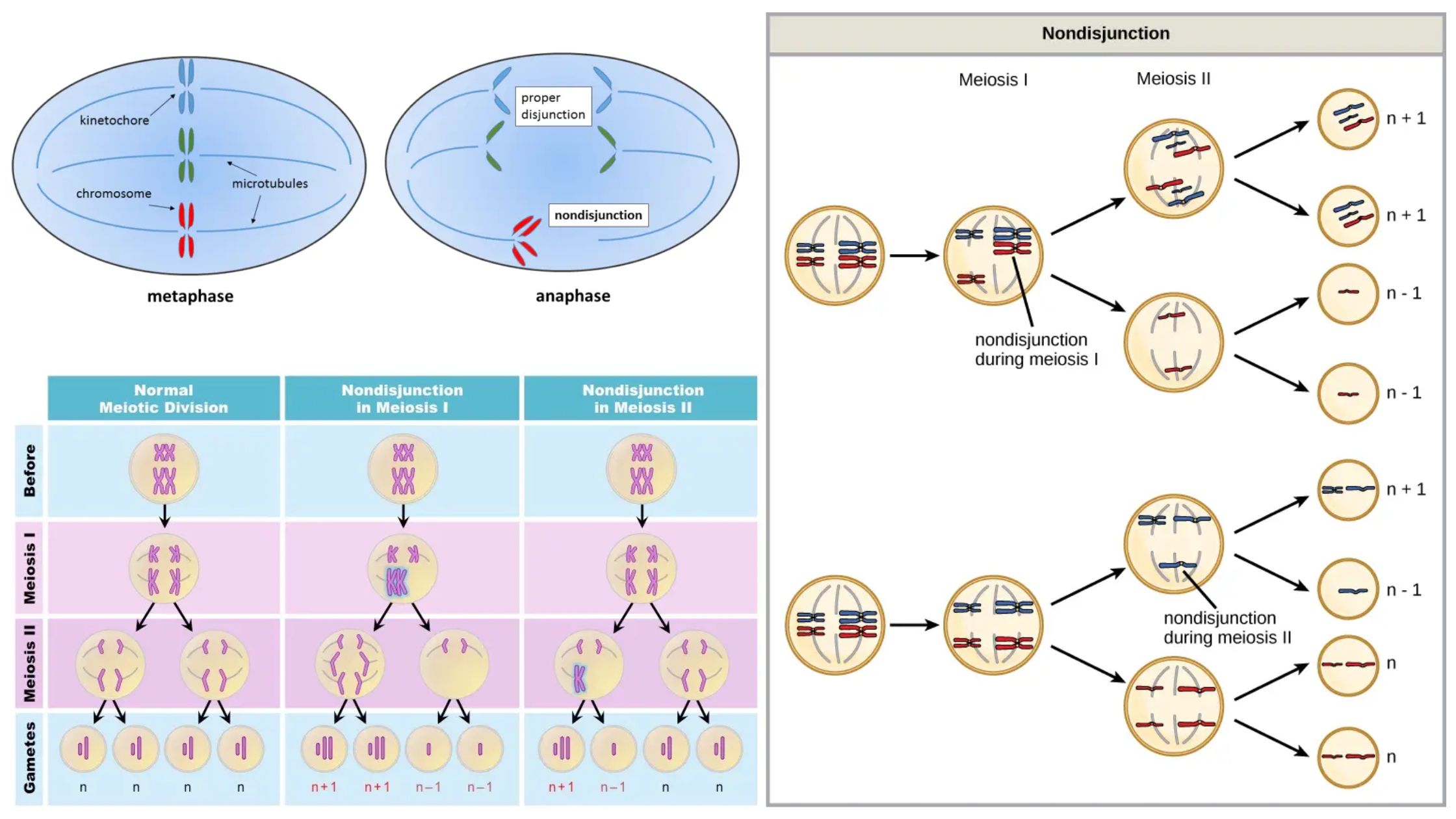
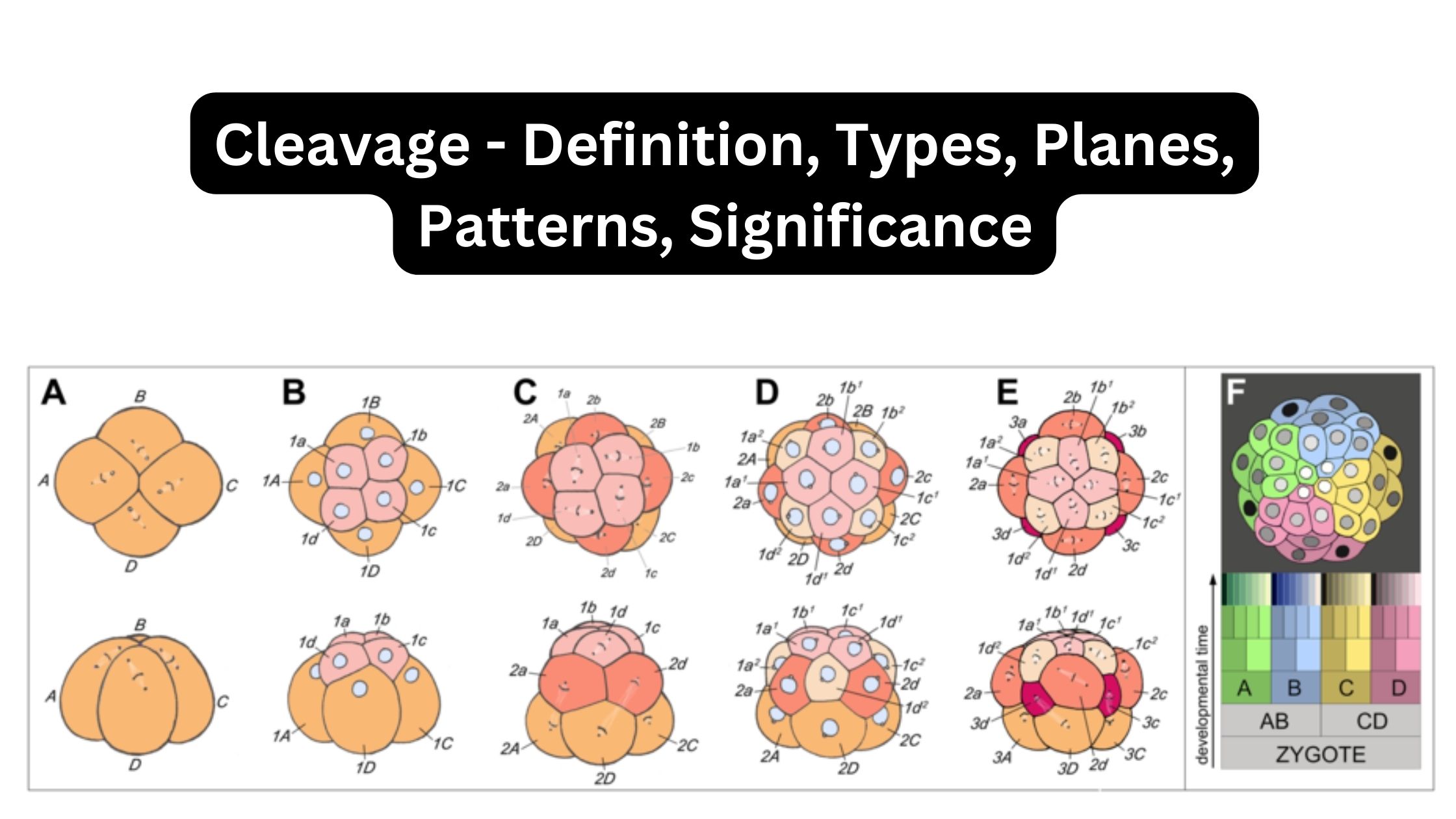
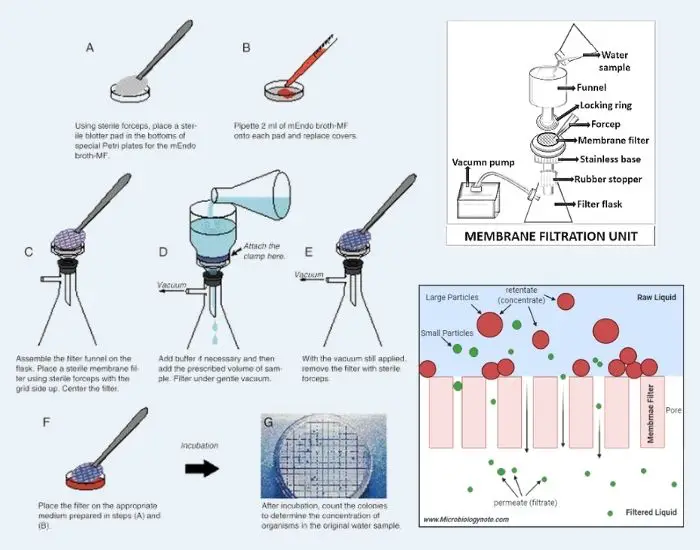
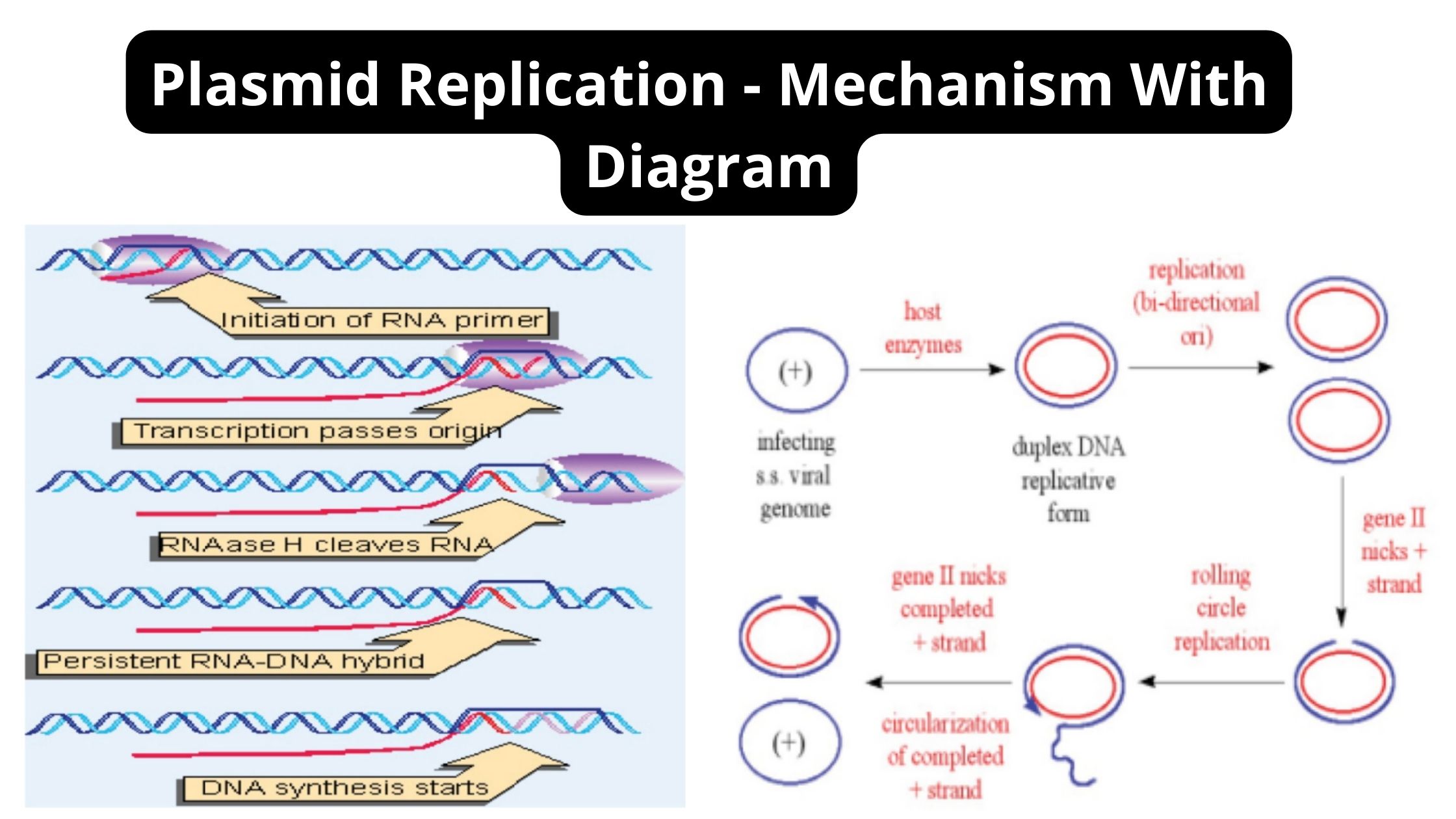
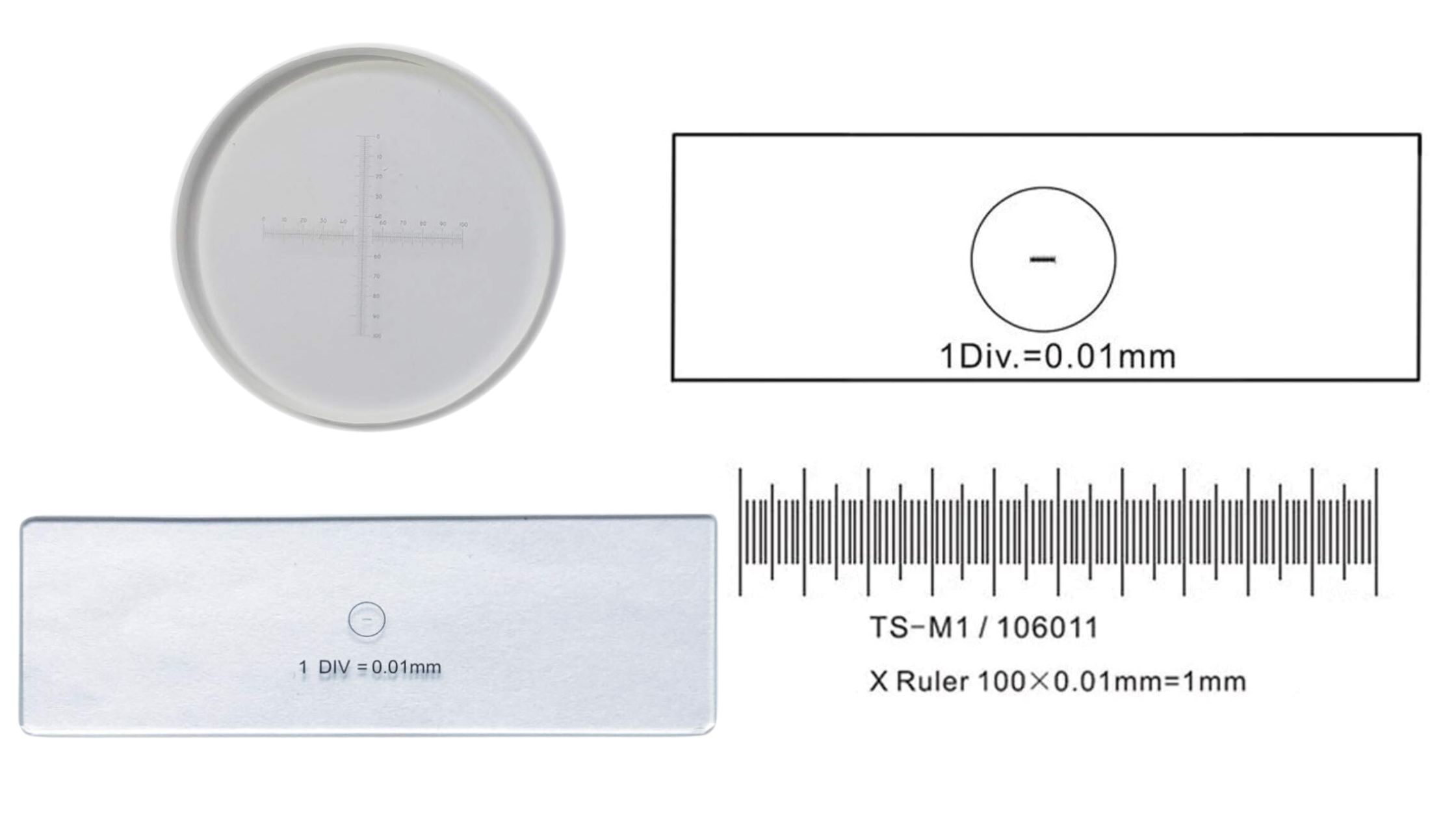
Difference Between Analytical Balance and Triple Beam Balance
What is Analytical balance? What is Triple beam balance? Difference Between Analytical Balance Vs Triple Beam Balance 1. Precision – Analytical balance gives very high precision (up to 0.0001 g) while triple beam balance only measure till 0.01 g, so less sensitive comparatively. 2. Power Source – Analytical balance mostly works on electric / electronic … Read more