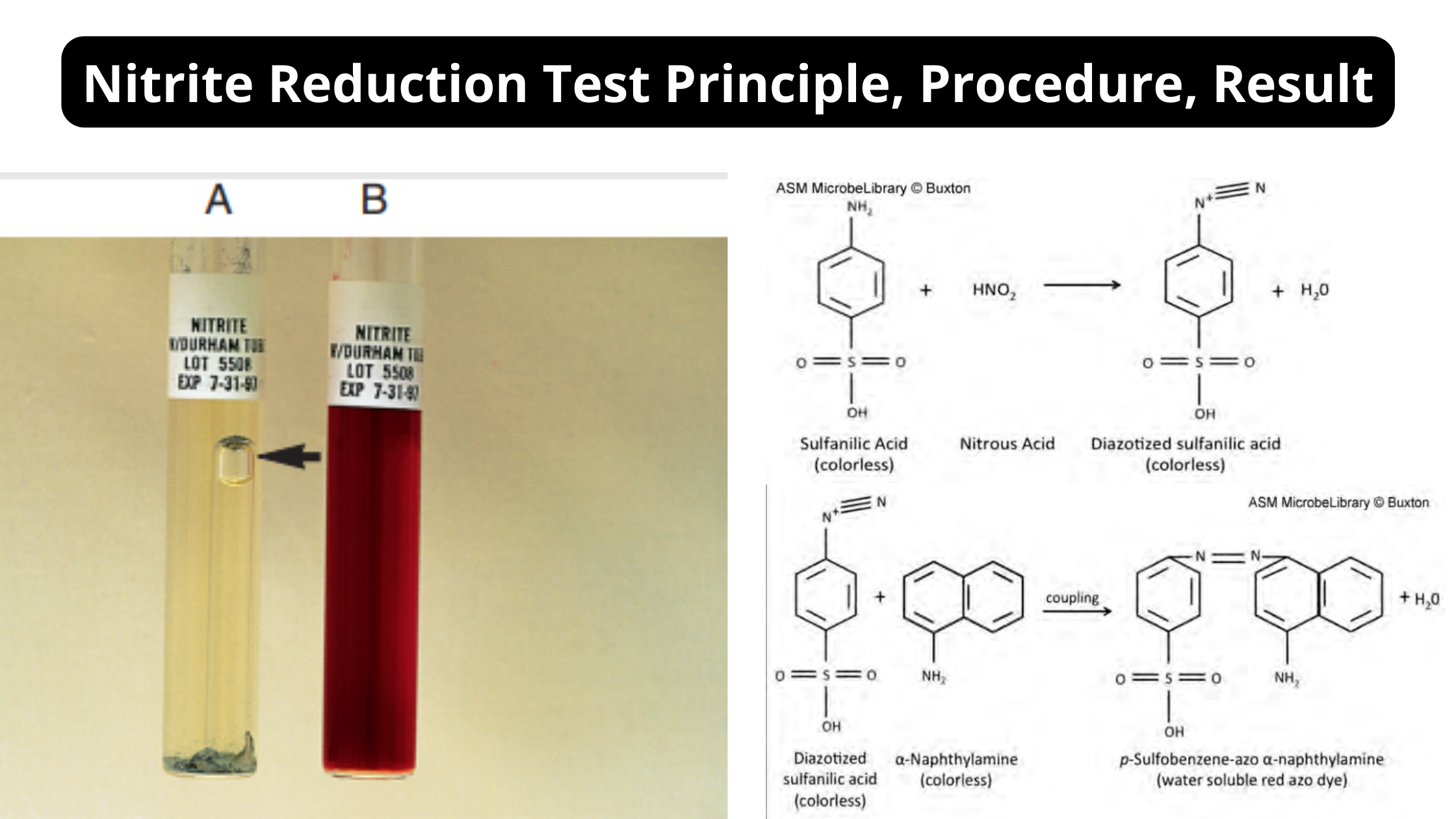
Glucose Tolerance Test – Principle, Procedure, Types, Applications
What is a Glucose Tolerance Test? A glucose tolerance test is a test that is used to diagnose diabetes or prediabetes. It involves measuring the body’s ability to process glucose, a type of sugar that is the main source of energy for the body. During the test, a person will drink a solution containing a … Read more