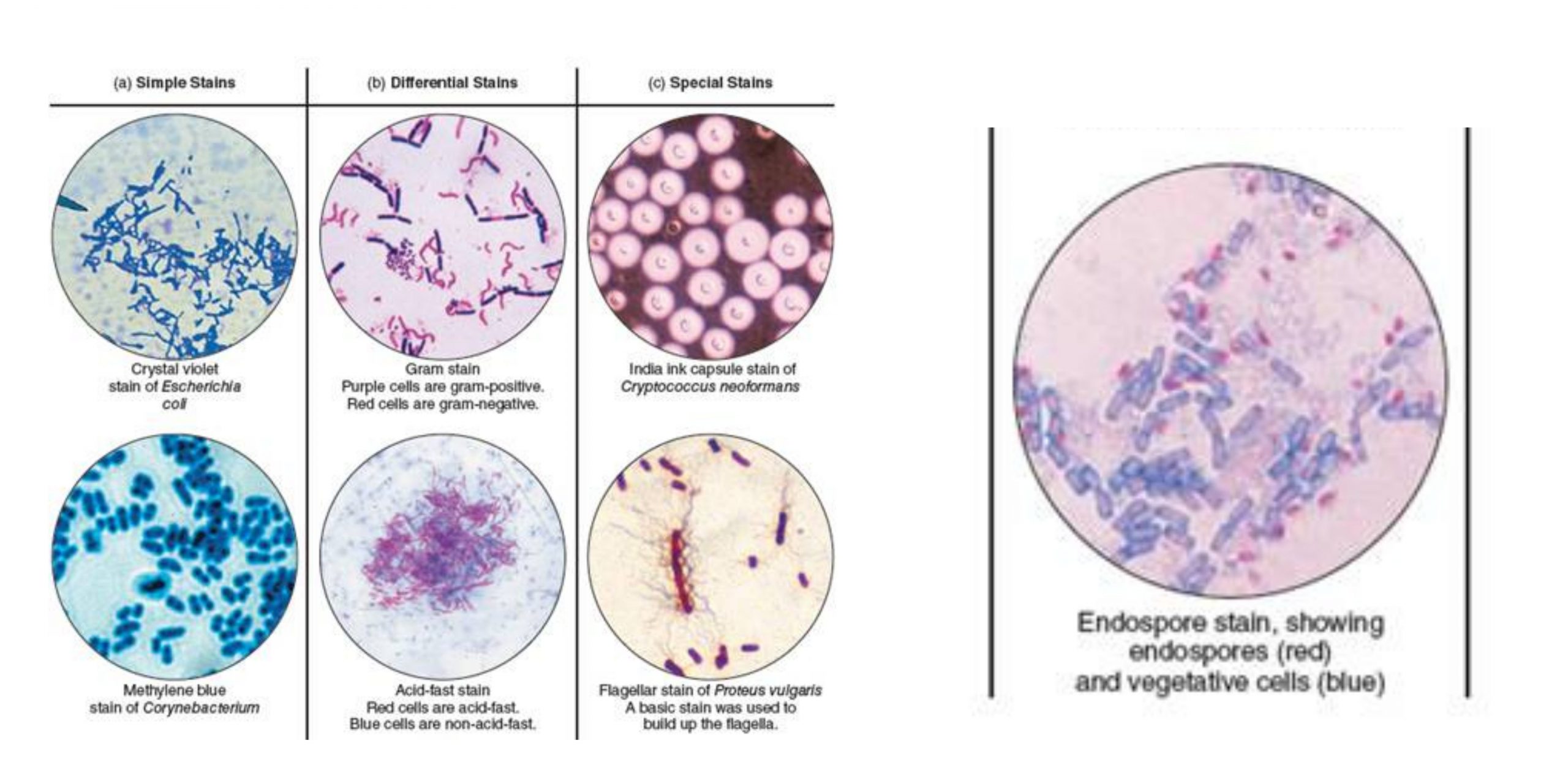
Positive staining of Viruses – Principle, Procedure, Result
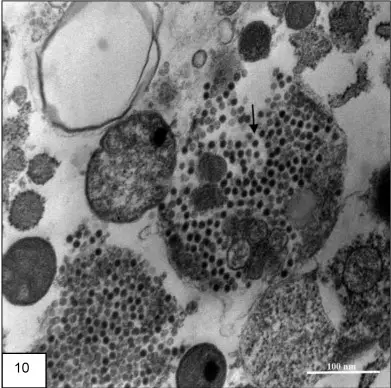
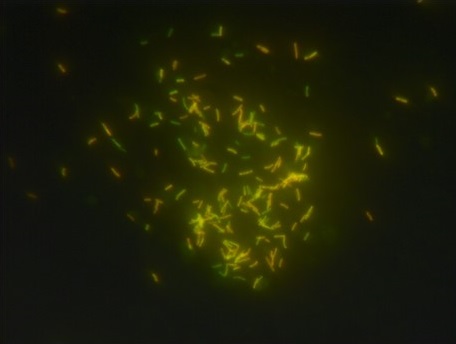
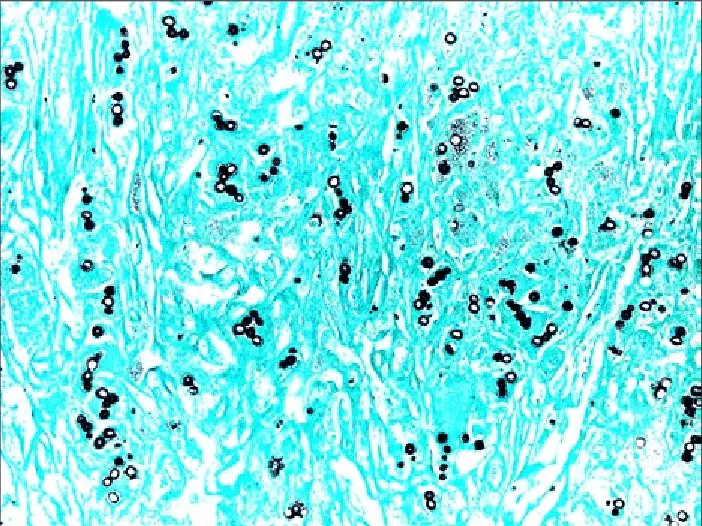
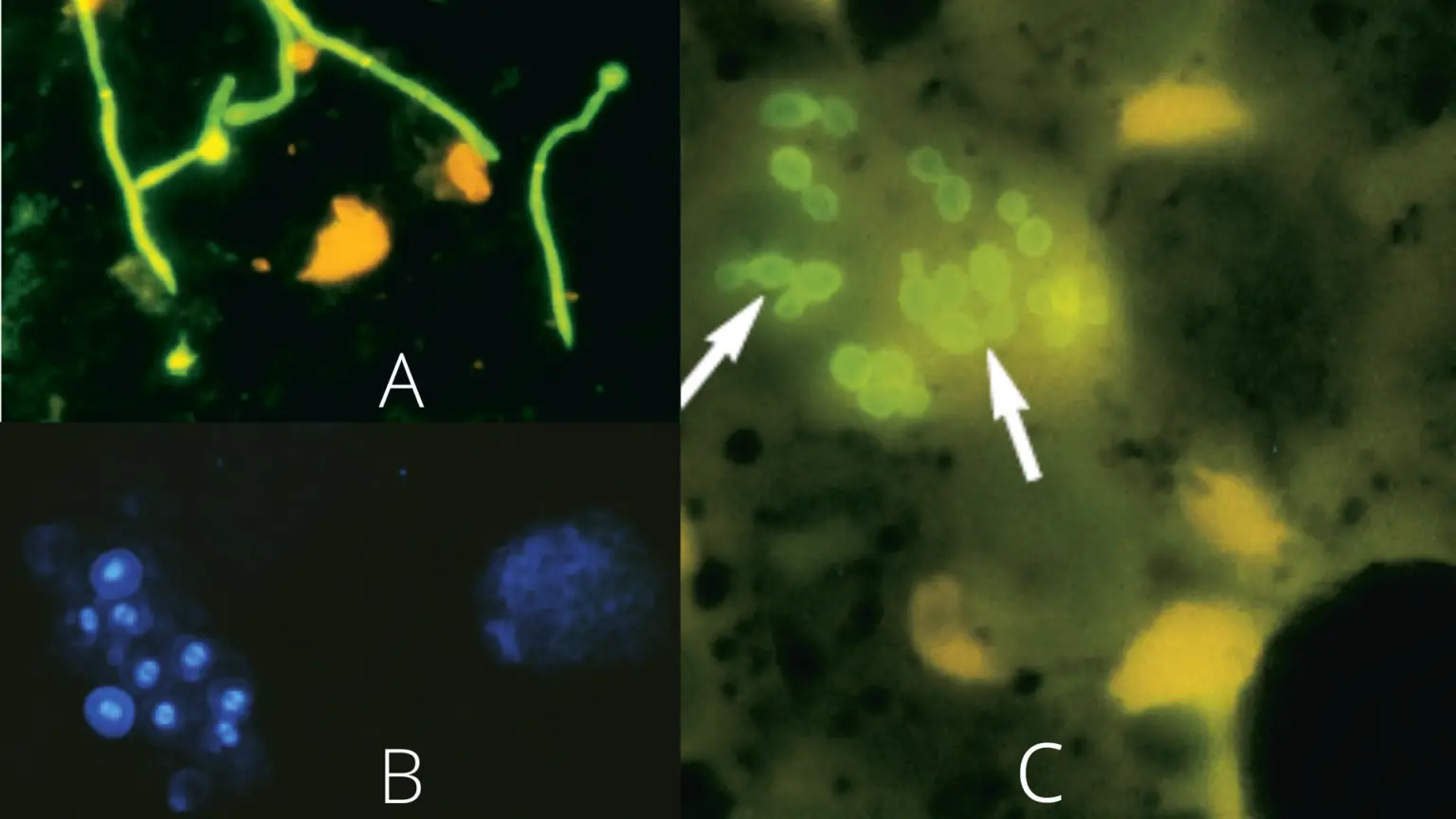
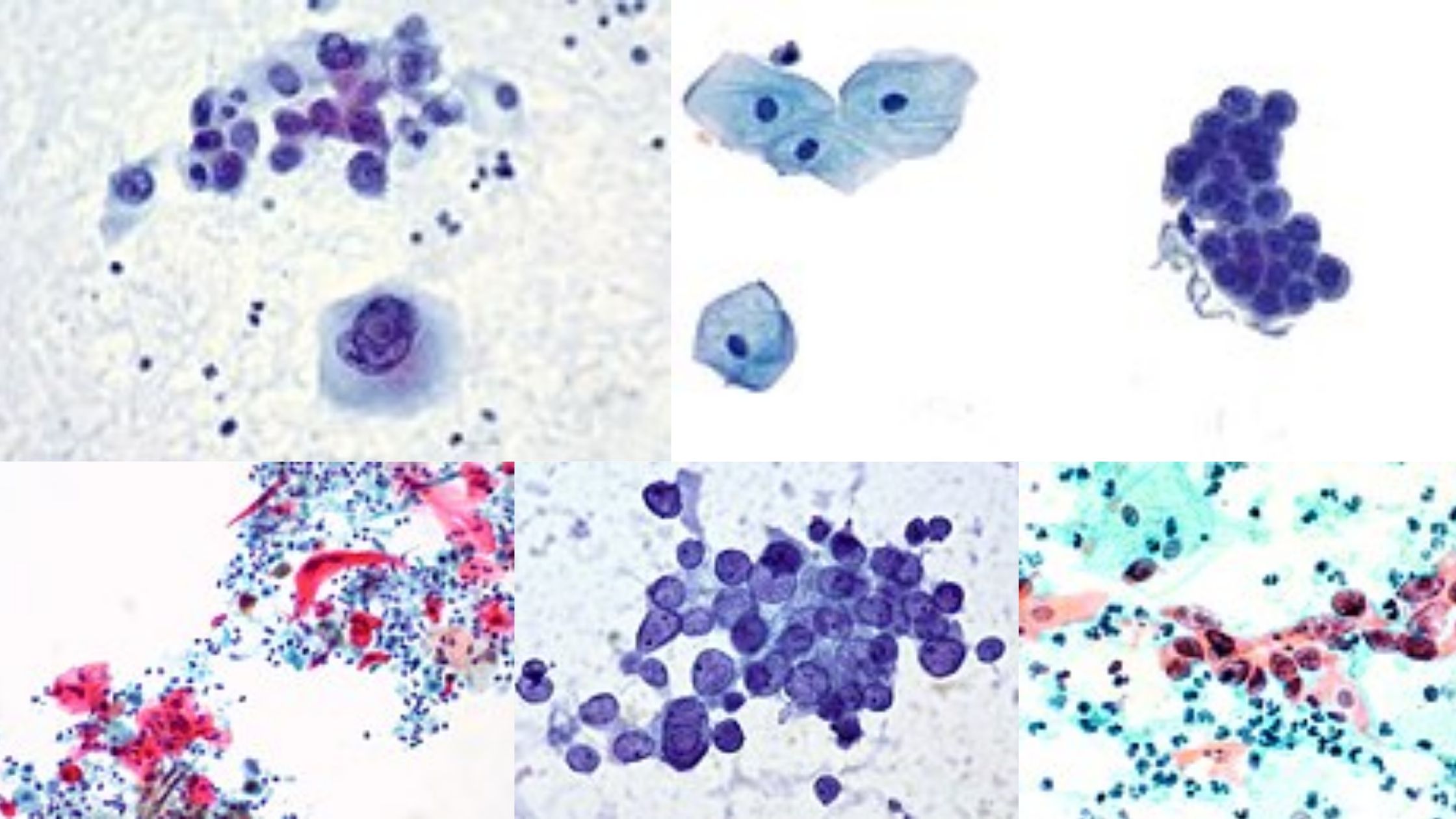
What is positive staining of Virus? Positive staining of viruses is the process in which the viral particle is made dark on a light background. It is the opposite of negative staining where the virus image is light and the background becomes dark. It is used widely to study the diverse morphology of viruses especially … Read more