What is Centrifugal force?
- Centrifugal force refers as an apparent force which acts outward on a body that moves around in a circular path.
- It is considered as a fictitious or pseudo-force, because it doesn’t arise from any physical interaction but rather from the inertia of motion.
- When a body rotates or moves in circular motion, it tends to move away from the center / axis of rotation due to inertia, this effect is called centrifugal force.
- In real sense, the centripetal force acts toward the center to keep the body in the circular path, while centrifugal force is felt in the opposite direction.
- For example, when a vehicle takes a sharp turn, passengers feel pushed outward — that outward push is felt due to centrifugal effect.
- It is measured as F=mω2r where, m is mass of object, ω angular velocity, and r is radius of circular path.
- This force is used in devices like centrifuge, washing machine drum, and rotating separators etc., for separating mixtures by density difference.
- Inside rotating reference frame, this force is considered acting on the object to balance centripetal one, so that system appear steady to observer.
- Sometimes the concept confused with centripetal, but both are opposite in direction though equal in magnitude.
- In simple words – centrifugal force is “outward pull” experienced by a body in rotation, which actually results by body’s tendency to move in straight line (inertia).
Definition of Centrifugal force
Centrifugal force is an outward fictitious force experienced by objects moving in a circular path, directed away from the center of rotation.
Centrifugal force formula
Centrifugal Force Formula refers as the mathematical relation which express the outward acting force on rotating body.
It is generally written as F = m ω² r, where –
- F = centrifugal force (in newton, N)
- m = mass of body (in kg)
- ω = angular velocity (in rad/s)
- r = radius of circular path (in meters).
Sometimes it also written in linear velocity form as F = m v² / r, both gives same result because ω = v / r.
The formula derived from Newton’s Second Law of motion, which tells that force proportional to mass and acceleration.
Here the acceleration is centripetal acceleration which act toward the center, while centrifugal is its equal opposite in direction.
During calculation, care must be taken for proper unit conversion (like r in m, v in m/s etc.) otherwise the value come wrong.
Example – if a body of 2 kg rotating with angular velocity 10 rad/s in a circle of radius 0.5 m,
then F = m ω² r = 2 × (10)² × 0.5 = 100 N.
The result means that an outward acting force of 100 newton experienced by object during rotation.
Sometimes the value increase drastically if angular velocity doubled, since it depends on square of ω, so even small rise produce large force.
In practical use like centrifuges, this calculation help to determine rotation speed (rpm) needed to separate components efficiently.
Hence centrifugal force calculation important in many rotating systems / mechanical designs / biological devices etc., where motion occur in circular path.
Principle of Centrifugal force
- Principle of Centrifugal Force refers as the basic concept that when a body moves in a circular path, it experiences an apparent force directed outward from center of rotation.
- The principle based on Newton’s First Law of motion – a body tends to remain in its state of rest or uniform motion unless acted by external force.
- When object is forced to move in circle, its inertia try to move it straight, but because of rotation, an outward force seems to act on it, called centrifugal force.
- In other words, centrifugal force arise as a reaction of centripetal force, which acts toward the center and keep the body on circular track.
- Within rotating reference frame, the outward force appear real to observer, though in inertial frame it considered pseudo or fictitious.
- The magnitude of this force depend on mass of body (m), its angular velocity (ω) and radius (r) of path – as expressed by formula F = m ω² r.
- So, as speed of rotation increases, centrifugal force increase rapidly since it proportional to square of ω.
- The same principle utilized in centrifugation / rotating separators / cream separator etc., where denser particles move outward due to higher centrifugal effect.
- It can define as “The tendency of a rotating body to move away from the center of its circular path due to inertia”.
- Hence, the principle of centrifugal force explain how balance between centripetal and outward inertial effect maintain circular motion of bodies.
How to Calculate centrifugal force? – a step by step guide
Centrifugal force calculated by using the basic rotational motion formula which relate mass, angular speed and radius of rotation.
The standard equation used as F = m ω² r, where –
- F is centrifugal force (in newtons, N)
- m is mass of rotating object (in kilograms)
- ω is angular velocity (in radians per second)
- r is radius of the circular path (in meters).
The formula derived from the relation of centripetal acceleration, since both forces are equal in magnitude but opposite in direction.
In linear form, the same equation written as F = m v² / r, by replacing ω = v / r, where v is linear velocity.
For practical calculations, units must be kept consistent – radius in m, angular speed in rad/s etc., otherwise the output come incorrect.
The calculation performed by multiplying the mass with square of angular velocity and then with radius value.
Example – if a body has m = 3 kg, ω = 4 rad/s and r = 0.8 m, then F = 3 × (4)² × 0.8 = 38.4 N.
So, the object experience outward force of 38.4 newton while rotating, which act opposite to centripetal direction.
The same method applied in centrifugation devices / mechanical rotors / vehicle turning analysis etc.
In short, centrifugal force calculated based on inertia of body moving in circular motion, its magnitude increasing rapidly with higher angular velocity.
Applications of Centrifugal force
- Centrifugal force used in centrifugation process for separating substances of different densities (like blood components, plasma, serum, etc.).
- In washing machines, centrifugal force applied for removing water from clothes during spin-drying, where water thrown outward through perforated drum.
- It used in industrial separators, for example in dairy industry to separate cream from milk by spinning action.
- In space crafts or artificial satellites, centrifugal force simulated to create artificial gravity for astronauts during long missions, though it’s difficult to maintain exact uniform gravity.
- It also utilized by centrifugal pumps and fans, where fluid thrown outward by impeller blades and converted kinetic energy to pressure energy.
- In vehicle dynamics, centrifugal force helps in design of roads/railway curves (banking of roads) to reduce risk of skidding when vehicles move at high speed.
- Used in centrifugal casting, where molten metal distributed uniformly by rotation of mold, producing dense and strong metal parts.
- In centrifugal clutch of automobiles, the working depends upon centrifugal force that engage/disengage automatically with change in speed of rotation.
- In centrifugal governors, force acts on rotating masses to control fuel supply and maintain constant engine speed (like in steam engine).
- In laboratory work, centrifugal force used for separating cellular organelles, macromolecules, or precipitates from solutions using high-speed centrifuges.
- Used in centrifugal compressors for compressing gases by converting rotational kinetic energy to pressure, widely used in jet engines and turbines.
- In blood bank, plasma and RBCs separated by centrifuge which works on centrifugal principle, it’s essential in clinical diagnosis.
- In paint industry, centrifugal mixers use high-speed spinning for uniform mixing of paints and pigment dispersion.
- It applied in uranium enrichment, where isotopes like U-235 separated from U-238 using gas centrifugation process (based on slight mass difference).
- In agriculture sprayers, centrifugal force used for atomizing the liquid pesticide/fertilizer into fine droplets for uniform distribution.
- Amusement rides like “rotor” or spinning rides rely on centrifugal force to press riders against wall when platform spins at high speed.
- In sugar industries, it used for separating molasses from sugar crystals by rotating basket (centrifugal machine).
- In cement industry, centrifugal separators used for separating fine particles from coarse powder.
- In oil refining, centrifugal clarifiers applied to remove water and impurities from crude oil or lubricating oil efficiently.
- In biotechnology, centrifugal force helps in pelleting of cells, viruses, organelles etc. during purification or isolation steps.
- In hydraulic systems, centrifugal filters used for cleaning of lubricants or fuel by continuous rotation which drive impurities outward.
- In jet aircrafts, pilots experience centrifugal force during turning, which considered for training and design of suits to resist blackout.
- It also applied by centrifugal driers for drying granules, pellets and small parts without direct heating, mainly in chemical industries.
- In centrifugal compressors/turbines, the energy transformation highly depend on rotational speed and resulting centrifugal effect.
- Many centrifugal toys or amusement devices work on same principle for fun demonstration of force acting outward.
- Even in meteorology, air movement around cyclone or anticyclone affected by centrifugal force along with coriolis and pressure gradient forces.
- Centrifugal separators used in pharmaceutical production, to purify and clarify liquids or suspensions etc., ensuring product quality.
- In aeronautics, centrifugal force calculations required for balancing and stability analysis of rotating parts (like propeller, rotor blades).
- Centrifugal force used by engineers for testing material strength under rotating load conditions (centrifugal testing machines).
- It also find use in food industries, like for separation of fruit pulp from juice or removing excess oil from fried items.
Examples of Centrifugal force

1. Centrifuge – centrifugal force is used to separate blood components, plasma and RBCs are separated by spinning, this step is common in clinical labs.
2.Washing machine– Water is expelled from clothes when drum spins (spin-drying / spin drying), the water is forced outward through drum holes and removed.
3. Cream separator – In dairy industry cream is separated from milk by rotation, cream and skim milk are split by density differences.
4. Amusement ride – Riders are pressed against wall in “rotor” or spinning rides when platform rotates fast, many feel an outward push and it’s demonstrated vividly.
5. Centrifugal pump – Fluid is flung outward by impeller blades and pressure is produced, pumps are widely used in water supply and industry.
6.Centrifugal clutch – Engagement is caused by weights moving outward with speed, the clutch engages automatically when rpm rises.
7.Gas centrifuge (uranium enrichment) – Slight mass difference between U-235 and U-238 is exploited, isotopes are separated by high-speed spinning and the lighter ones are collected, process is sensitive and sometimes prevail issues occur.
8.Spin coater – Thin films are produced by depositing solution on a substrate that is spun, solution is spread outward and solvent is removed quickly (used in microfabrication).
9.Centrifugal casting – Molten metal is thrown to mold walls by rotation and dense, defect-free parts are formed.
10. Carousel / merry-go-round – Objects and people are forced outward when ride spins, simple demonstration of centrifugal effect is provided.
11. Aircraft turn (banked) – Passengers are subjected to outward force during turning, pilots are trained for g-forces and anti-G measures are considered for high-performance flying.
12.Microcentrifuge (lab) – Small tubes are pelleted and cells, organelles or precipitates are separated at high g, many protocols rely on this rapid separation step.
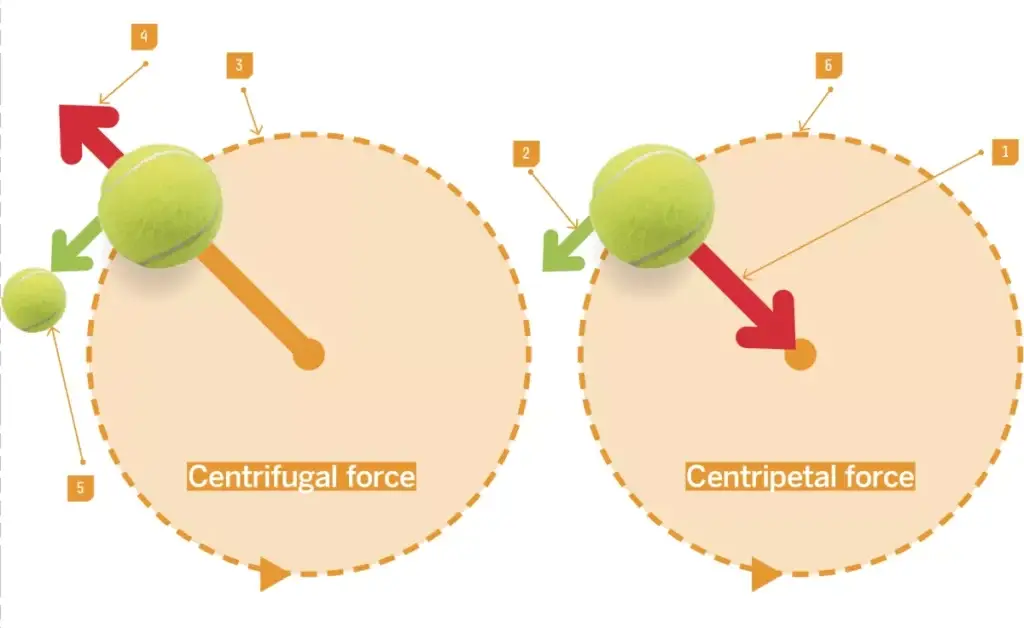
Centrifugal force vs Centripetal force
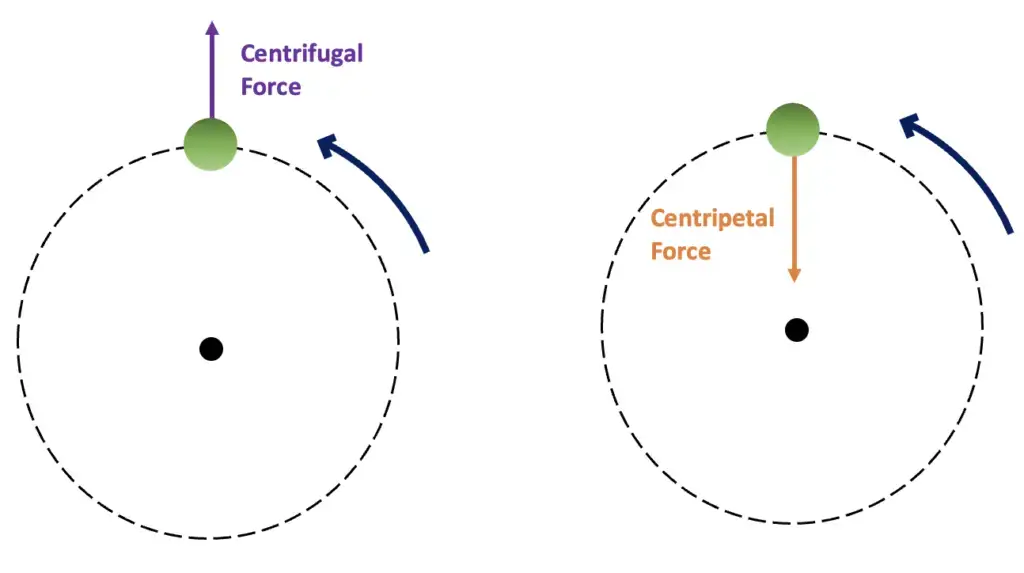
- Centripetal force termed as the real force which act towards center of circular path or axis of rotation.
- Centrifugal force refers as the apparent or pseudo force that seems acting away from the center.
- In circular motion, centripetal force required for keeping object in its path, otherwise object will fly off tangentially.
- Centrifugal force is felt when observer is inside rotating frame (like in merry-go-round or centrifuge machine).
- The direction of centripetal force always toward center, but centrifugal acts in exactly opposite direction.
- Centripetal force caused by various agencies like tension / gravity / friction / electrostatic etc.
- Centrifugal is not caused by any physical interaction, it appear due to inertia of moving body, that resist change in direction.
- Without centripetal component, circular motion can’t be maintained, so it’s necessary for curved motion of object.
- Example– a stone tied in string and whirled in circle: tension act as centripetal, while stone seems pulling hand outward by centrifugal.
- Centripetal is active, centrifugal is reactive, though some books mislead by calling both equal and opposite.
- In inertial frame only centripetal exist, centrifugal exist only in non-inertial rotating frame.
- Centrifugal force magnitude equals to centripetal (mv²/r), but direction opposite, hence they cancel only in rotating frame perception.
- Many physical devices like washing machine, cream separator use effect of centrifugal for separation, though actual cause is inertia.
- Centripetal force maintain stability of orbital motion (like planet around Sun), centrifugal just appear by observer moving with planet.
- Both terms often confused, but one (centripetal) real, other (centrifugal) imaginary yet practically important for explaining rotating system behavior etc.
| Aspects | Centripetal force | Centrifugal force |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The force acting on a body moving in a circular path along the radius, directed towards the center of the circle. | An outward fictitious force experienced by an object moving in a circular path, directed away from the center of rotation. |
| Nature | Real force with real effects. | Considered a fictitious or pseudo force but has real effects. |
| Direction | Directed towards the center of the circle of rotation. | Directed away from the center of the circle of rotation. |
| Role | Essential for circular motion. | Does not have an independent existence. |
| Origin | Arises from the interaction between the object and the source of the force. | Originates from the inertia of the object. |
| Formula | Dependent on the specific scenario and type of force involved. | Often expressed as the negative of the centripetal force formula. |
| Action | Acts in both inertial and non-inertial frames of reference. | Acts only in the rotating frame (non-inertial frames). |
FAQ
What is centrifugal force?
Centrifugal force is an outward fictitious force experienced by an object moving in a circular path, directed away from the center of rotation. It is a result of the object’s inertia and appears when there is a centripetal force acting on the object.
How is centrifugal force different from centripetal force?
Centripetal force is directed towards the center of the circular path and is responsible for keeping an object in its curved trajectory. In contrast, centrifugal force is directed away from the center and appears as a reaction to the centripetal force.
Is centrifugal force a real force?
Centrifugal force is considered a fictitious or pseudo force. While it has real effects, it does not arise from a fundamental interaction like gravitational or electromagnetic forces.
Can centrifugal force exist without centripetal force?
No, centrifugal force is a reactive force that arises as a response to the centripetal force. Without a centripetal force acting on an object in circular motion, there would be no centrifugal force.
Is centrifugal force present in inertial frames of reference?
Centrifugal force is only observed in non-inertial frames of reference, particularly in rotating frames. In inertial frames, the concept of centrifugal force is not necessary to explain the motion of objects.
What are some applications of centrifugal force?
Centrifugal force finds applications in various fields. It is used in centrifuges for particle separation, centrifugal pumps for fluid transportation, centrifugal governors for maintaining constant speeds, and in rotating space stations to simulate gravity.
Can centrifugal force be calculated?
Centrifugal force can be calculated using formulas that involve parameters like mass, velocity, and distance from the center of rotation. The specific formula used depends on the scenario and the type of circular motion involved.
Does centrifugal force depend on the mass of the object?
Yes, centrifugal force is directly proportional to the mass of the object. A higher mass will result in a greater centrifugal force for a given velocity and distance from the center.
Is centrifugal force the same as inertia?
Centrifugal force is related to inertia, but they are not the same. Inertia is an object’s tendency to resist changes in its state of motion, while centrifugal force is the apparent outward force experienced due to the object’s inertia in a circular path.
Can centrifugal force be observed in everyday life?
Yes, centrifugal force can be observed in various situations. Examples include the sensation of being pushed outward when taking a sharp turn in a car, the water sticking to the inside of a spinning bucket, and the mud being thrown off the rotating wheels of a vehicle.
- Khatry MK et al. Principles of Physics. Aayam Publications.
- https://thefactfactor.com/facts/pure_science/physics/centripetal-force/6311/
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Centrifugal_force_(rotating_reference_frame)
- https://www.sarthaks.com/204136/stone-tied-string-length-whirled-vertical-circle-with-the-other-end-the-string-the-centre
- https://www.livescience.com/52488-centrifugal-centripetal-forces.html
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/earth-and-planetary-sciences/centrifugal-force
- https://www.britannica.com/science/centrifugal-force
- https://www.studysmarter.us/explanations/physics/physics-of-motion/centrifugal-force/
- https://driversed.com/driving-information/driving-conditions/understanding-centrifugal-and-centripetal-forces/
- https://www.diffen.com/difference/Centrifugal_Force_vs_Centripetal_Force