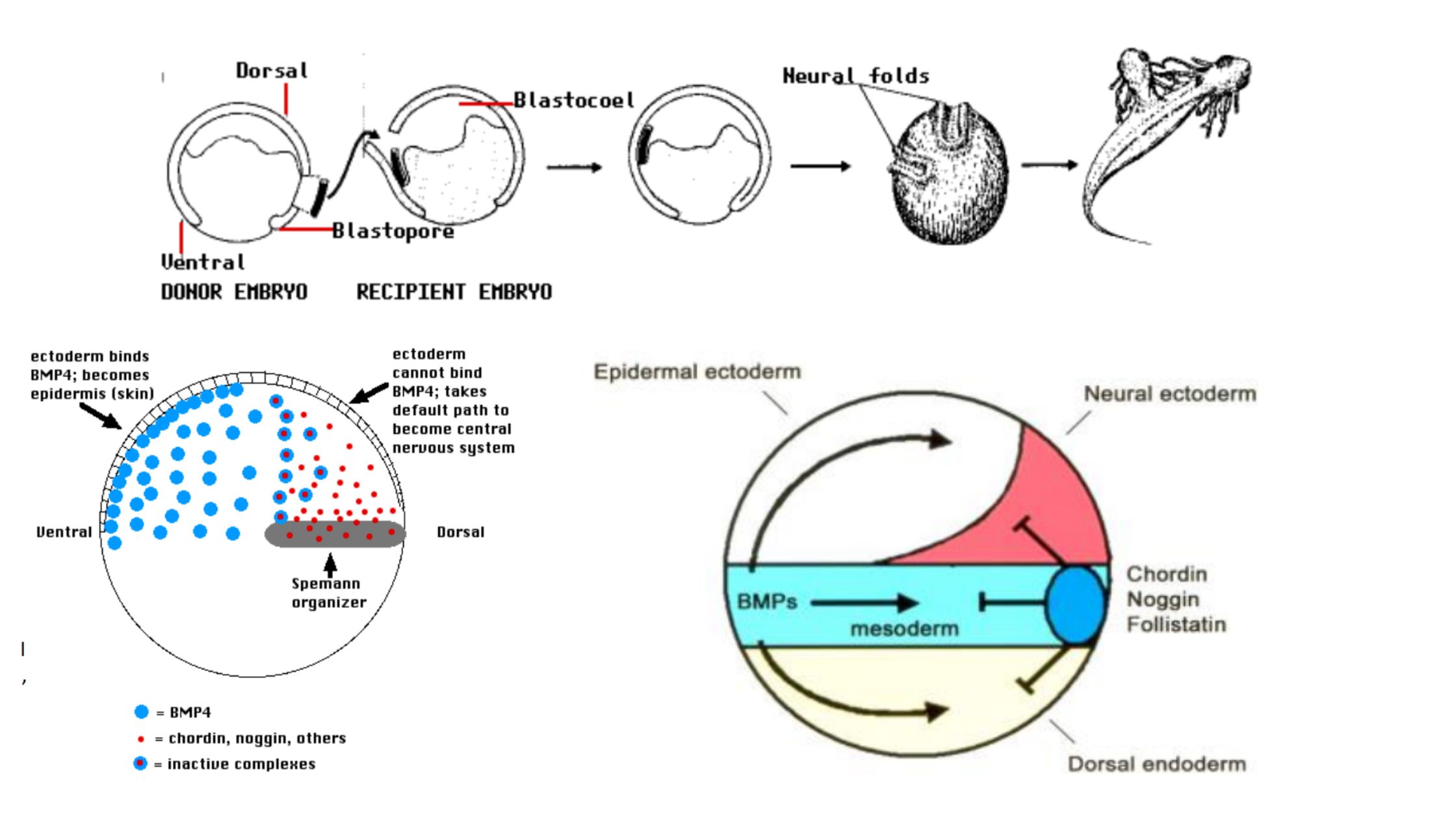
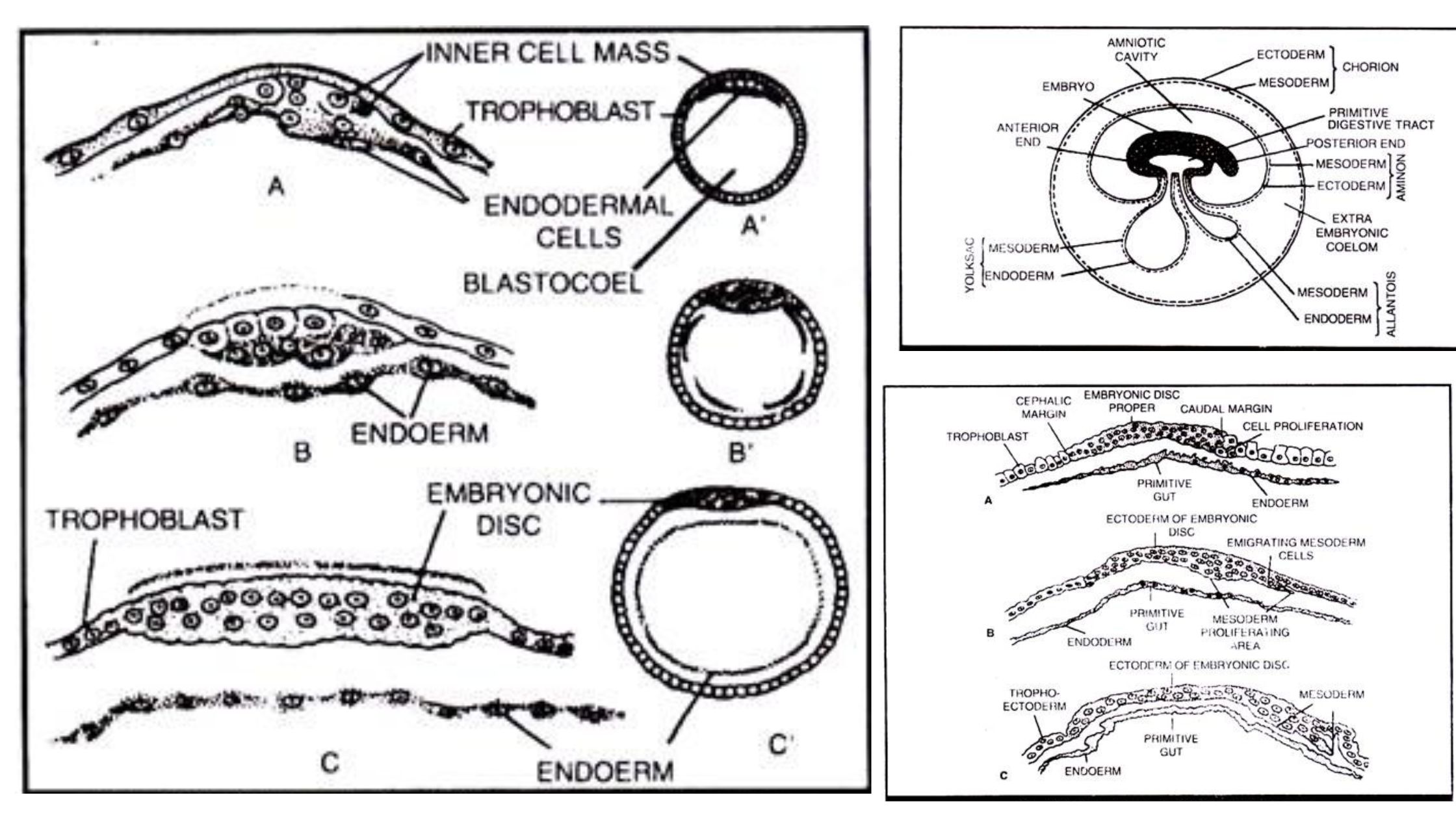
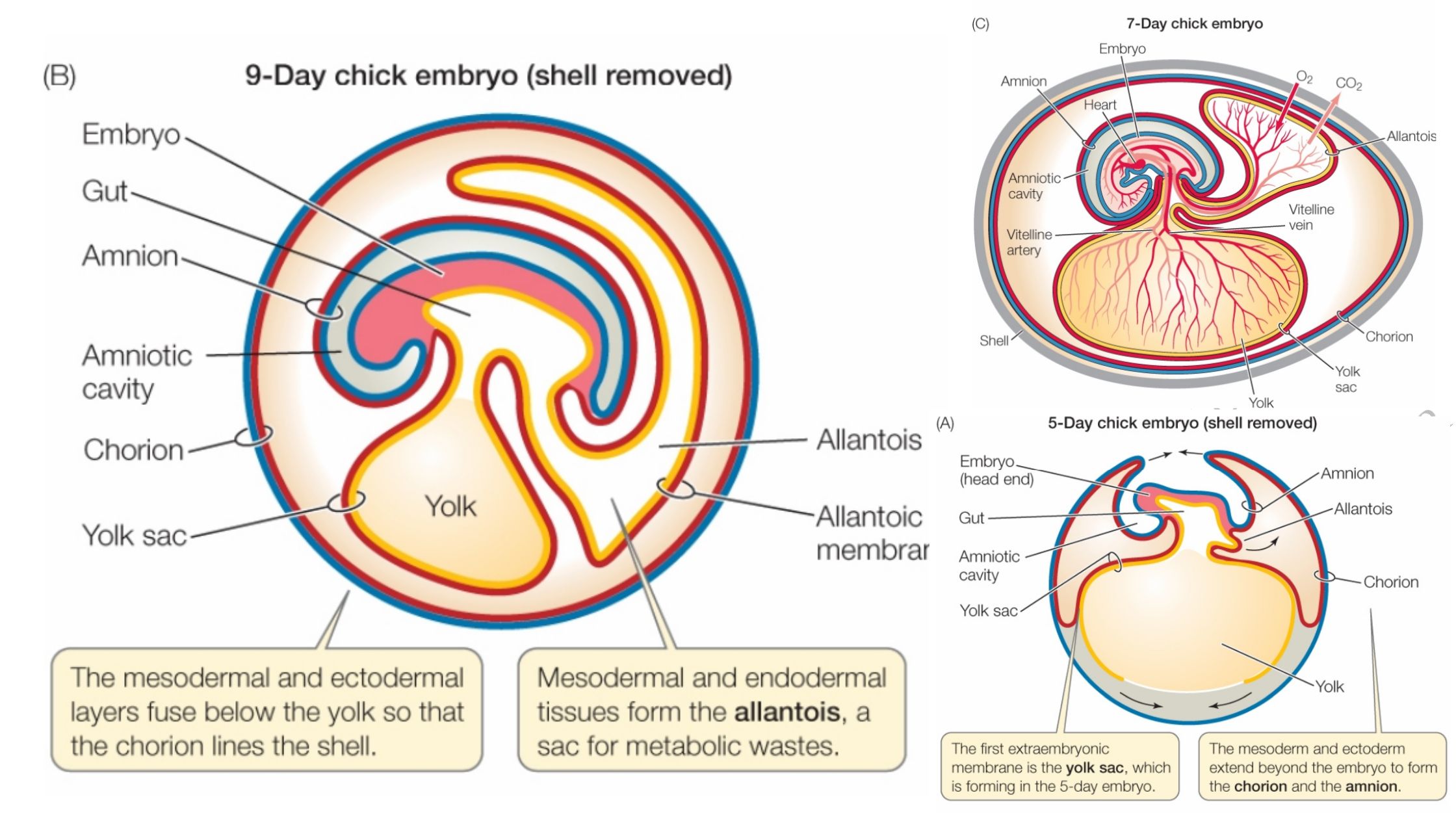
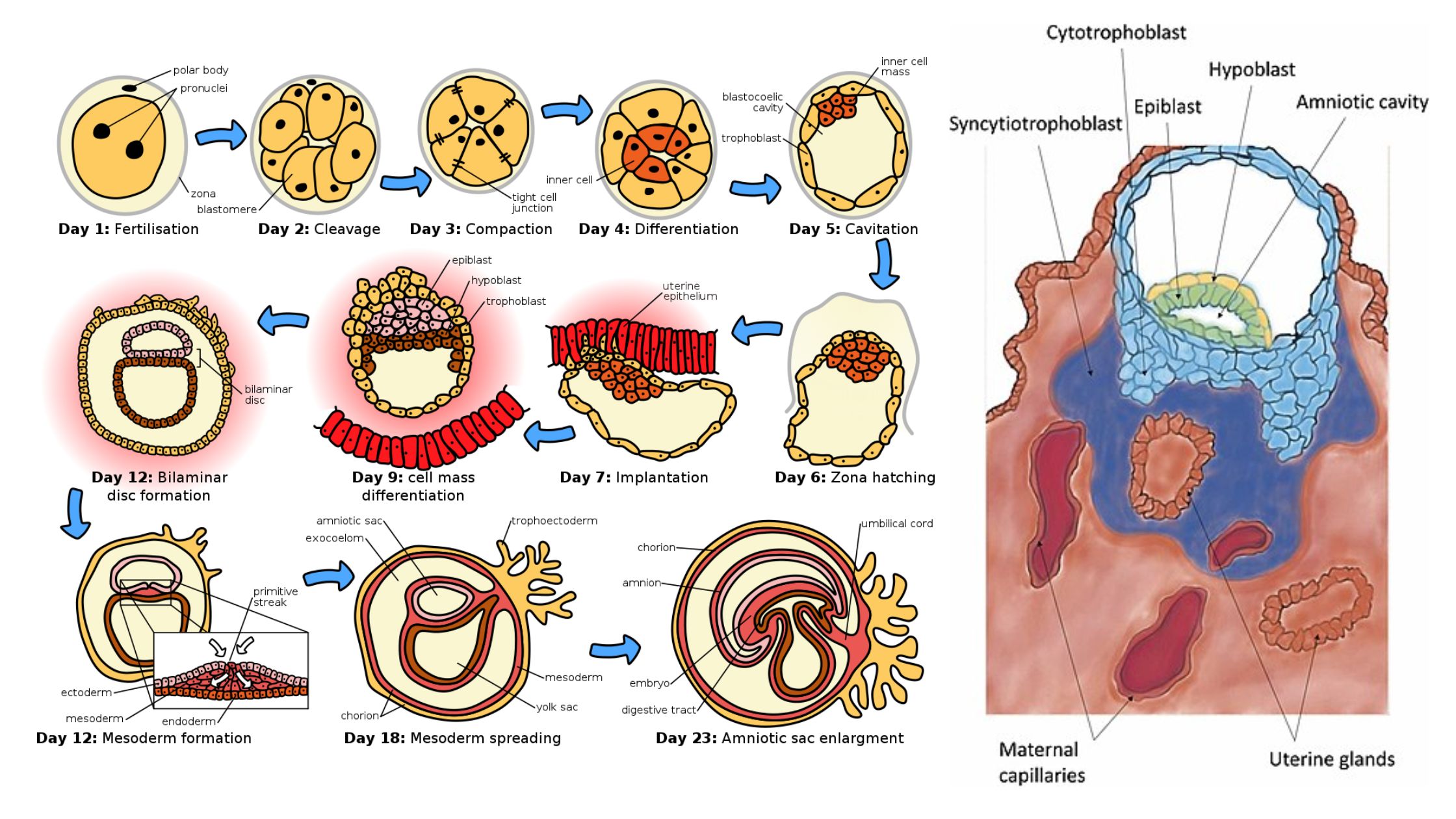
Developmental Biology Introduction, Hisotry and Basic concepts
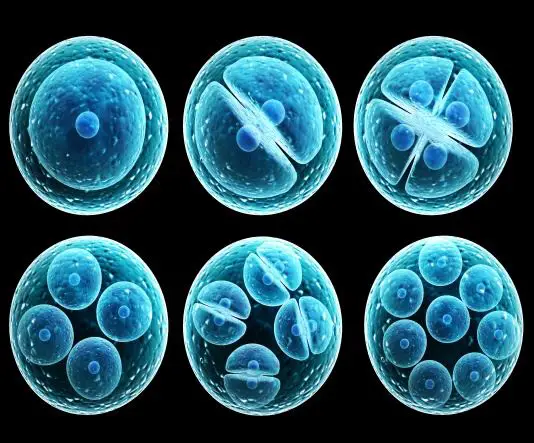
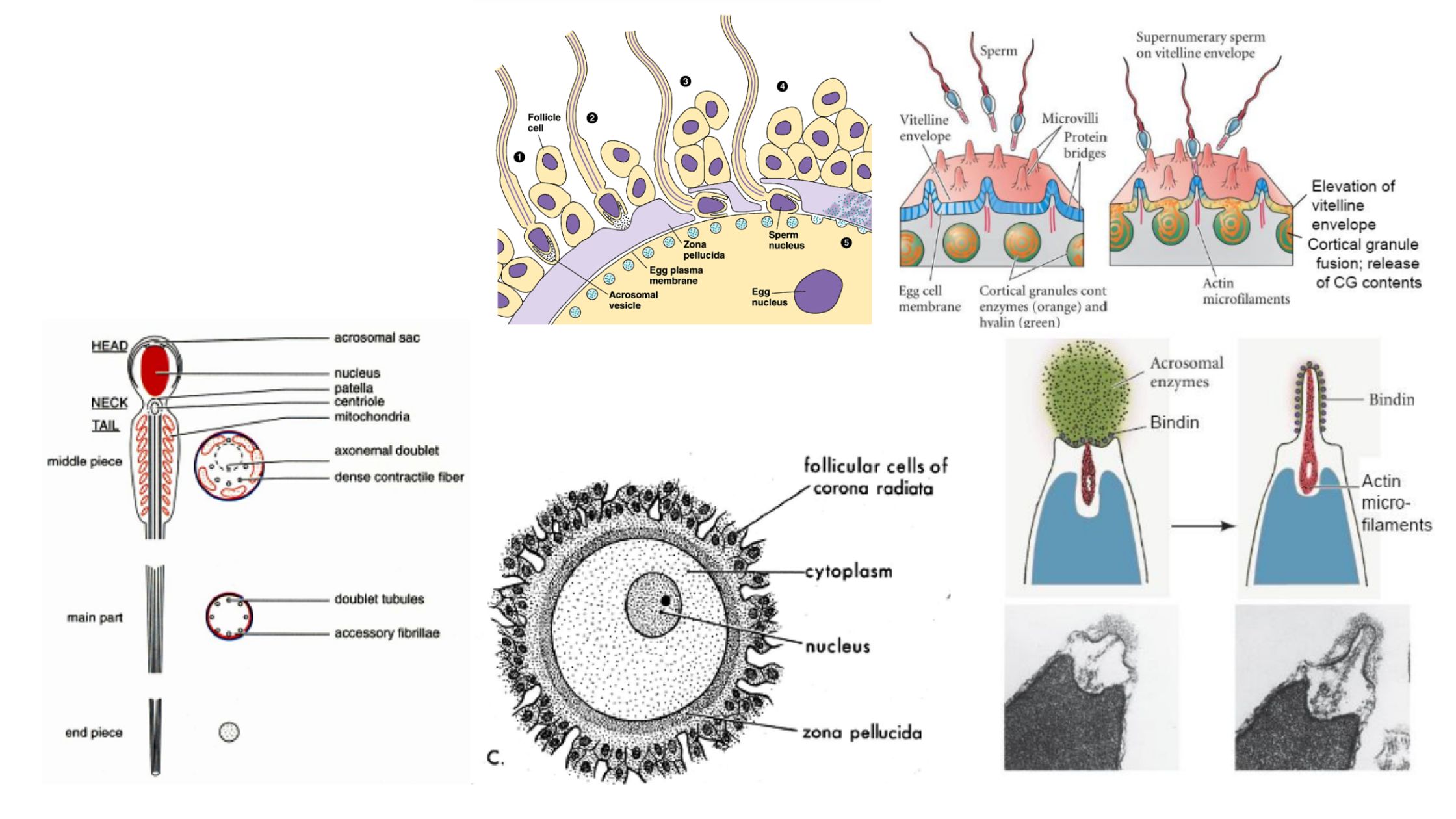
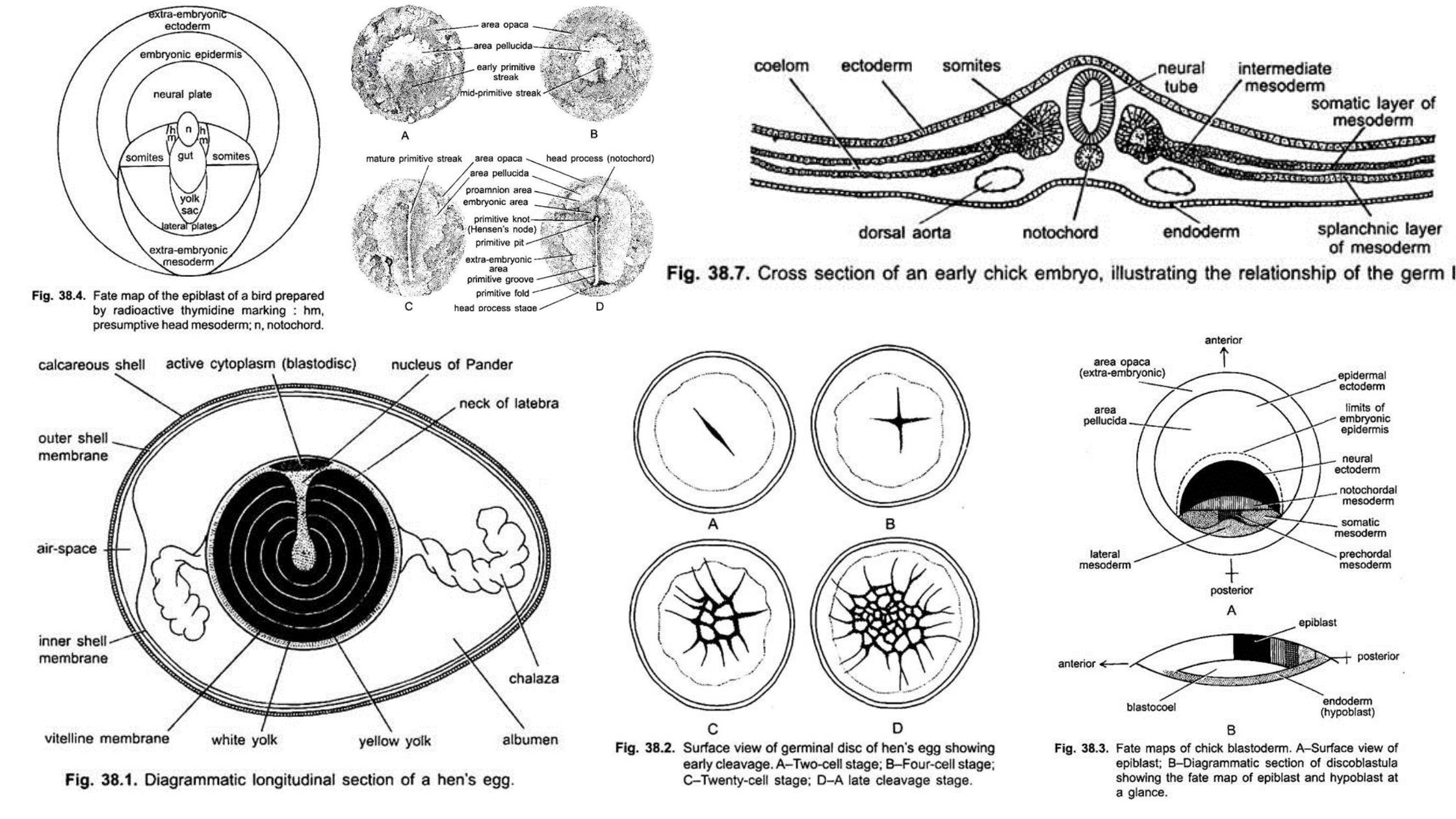
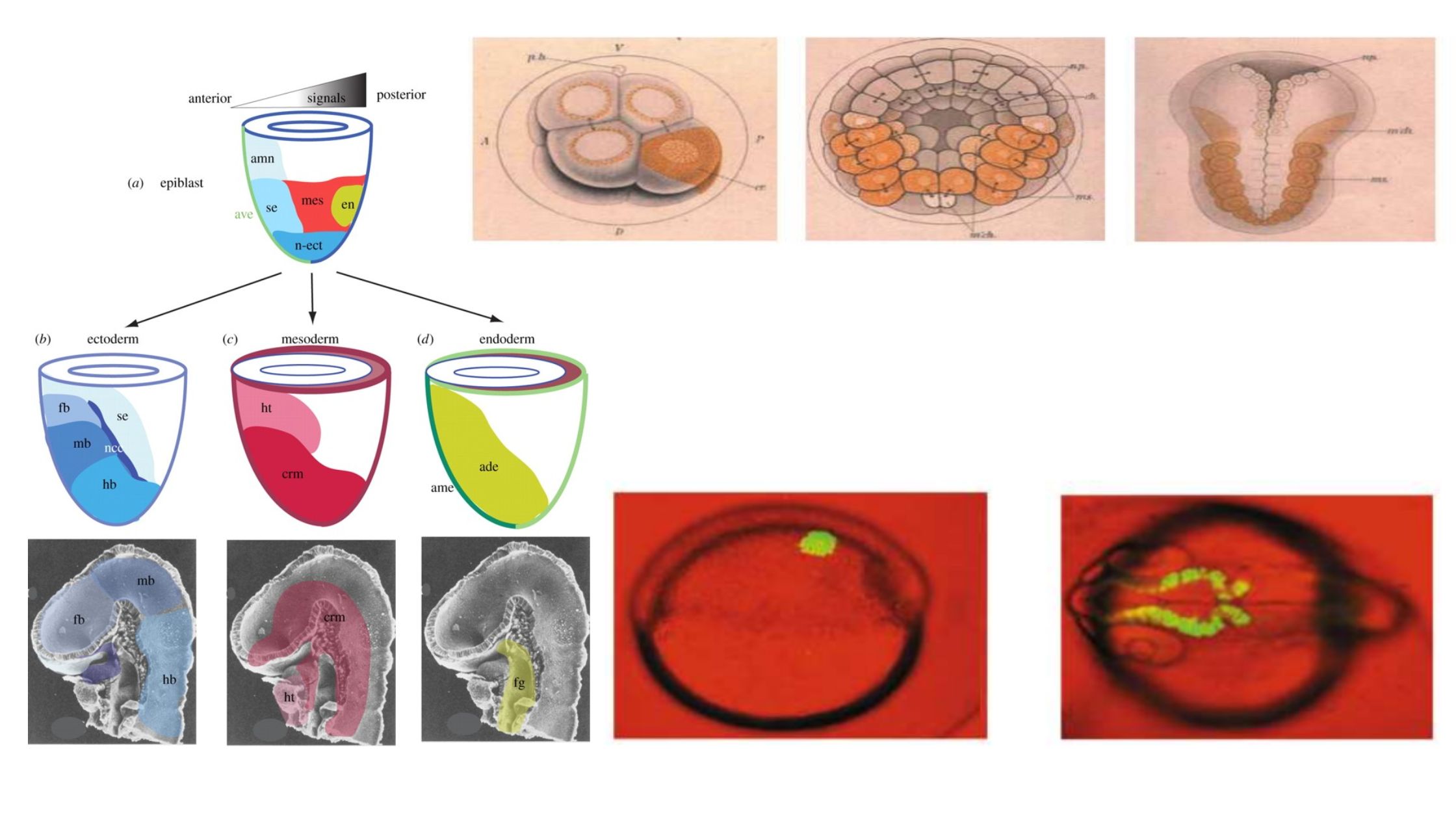
What is Developmental Biology? Developmental biology is a scientific discipline that focuses on understanding how organisms grow, develop, and mature from a fertilized egg into a complex multicellular organism. It explores the processes, mechanisms, and patterns that shape the formation of tissues, organs, and the overall body plan throughout an organism’s life cycle. Developmental biologists … Read more