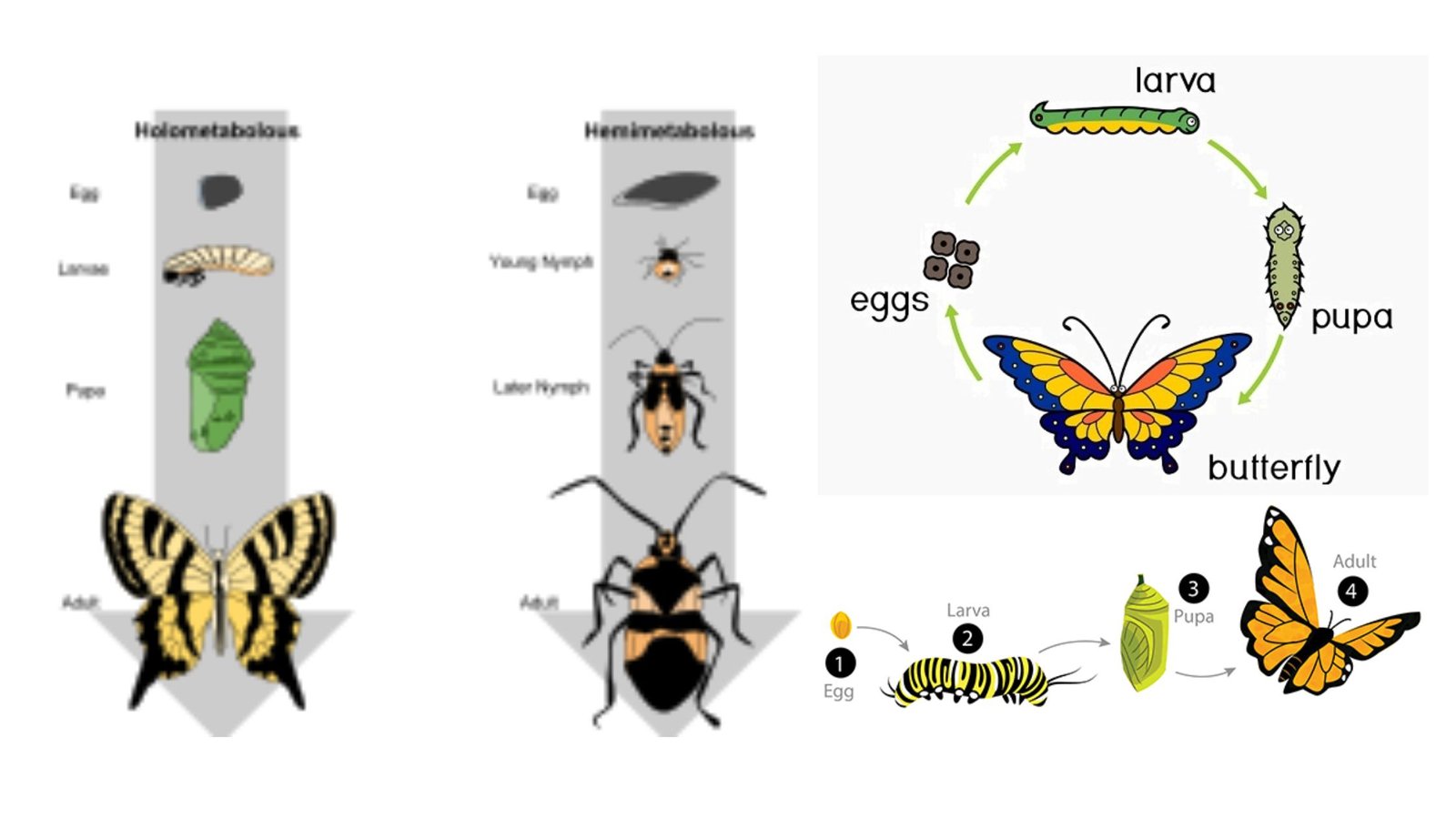
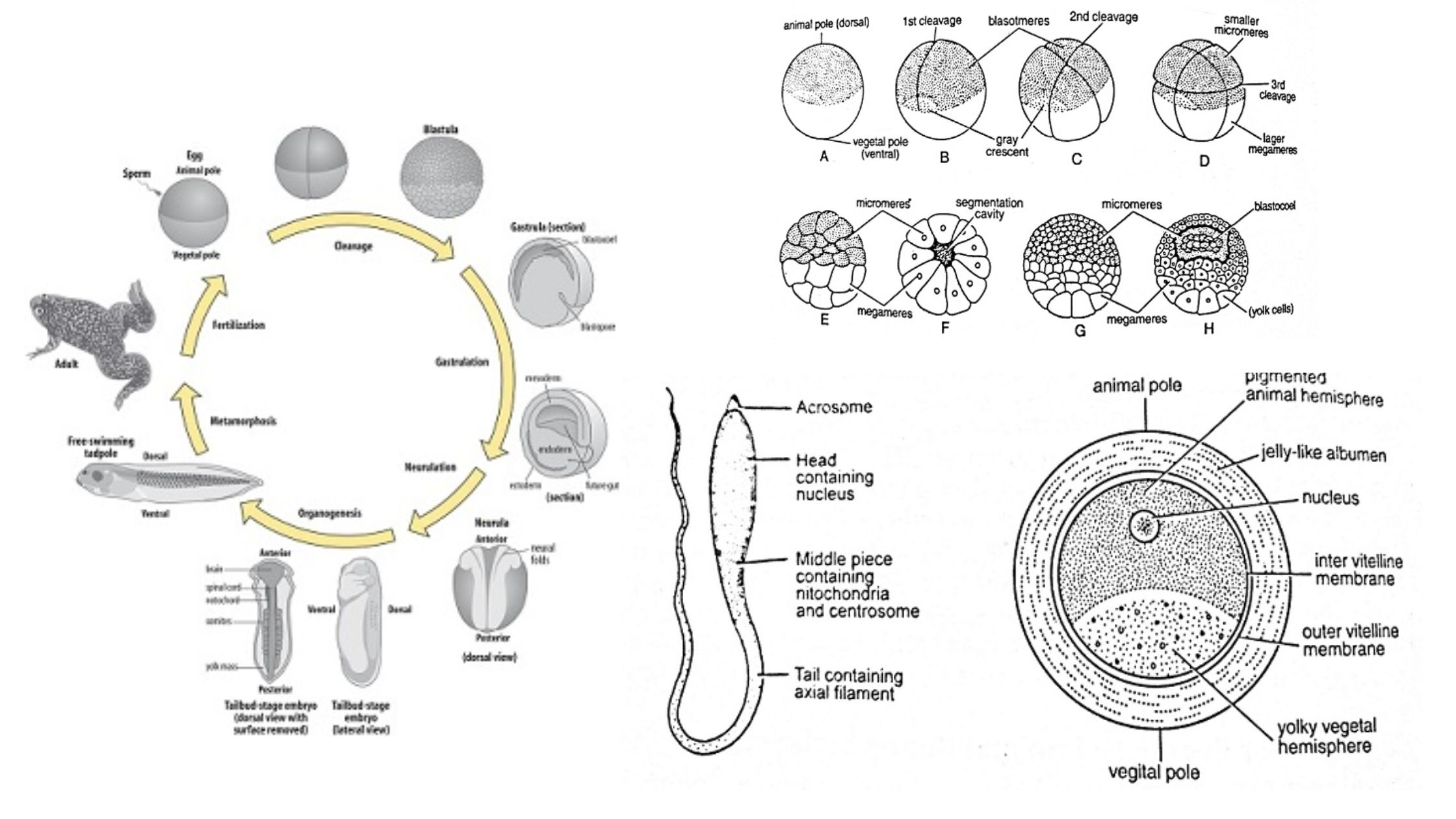
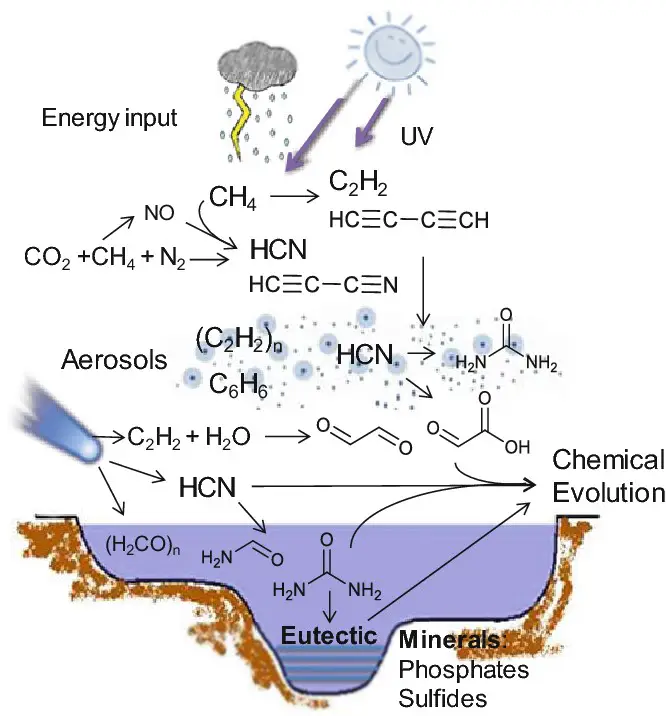
Eggs – Types, Structure, Egg Membranes, Examples
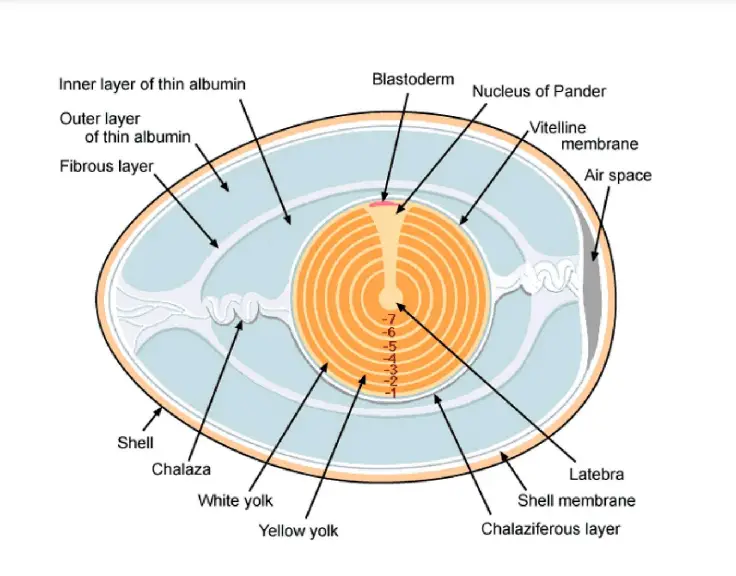
An egg is a biological structure which contains the female gamete and after fertilization it carries the developing embryo. It is an organic vessel that provides protection and nourishment to the embryo till hatching or birth. The major internal component of egg is yolk (vitellin) which acts as reserve food material and supplying energy for … Read more