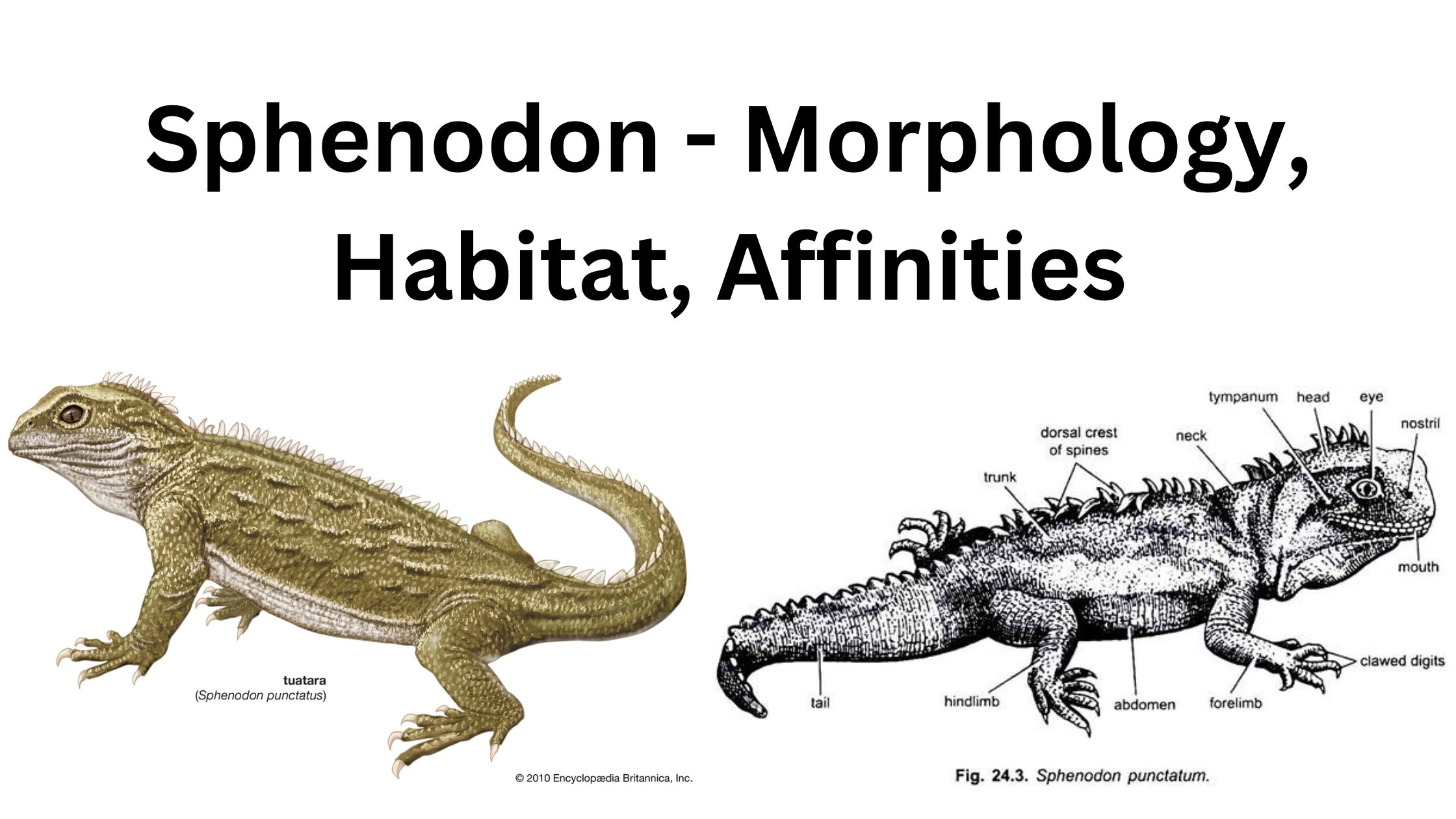
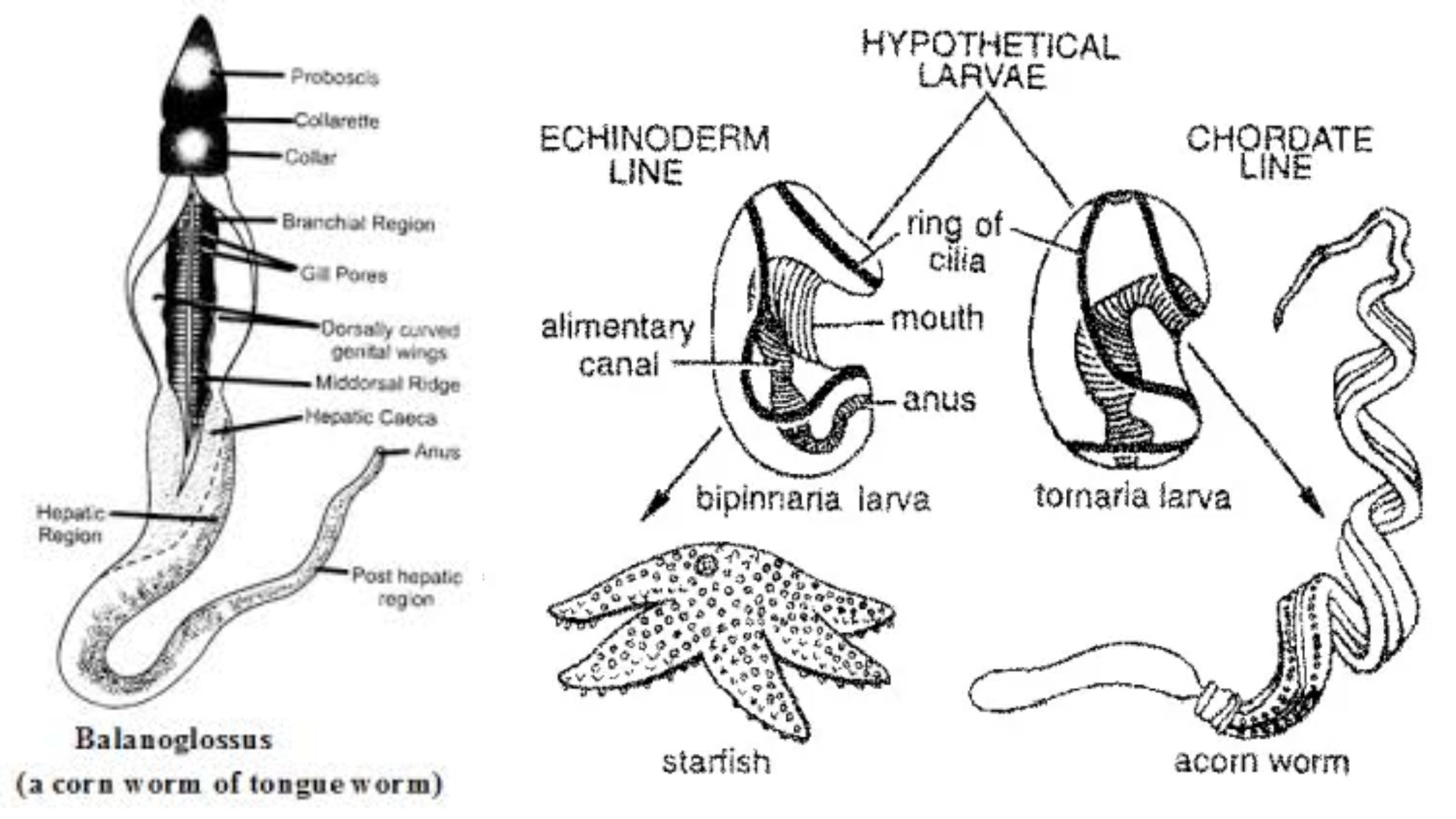
Study of larval forms In Protochordates
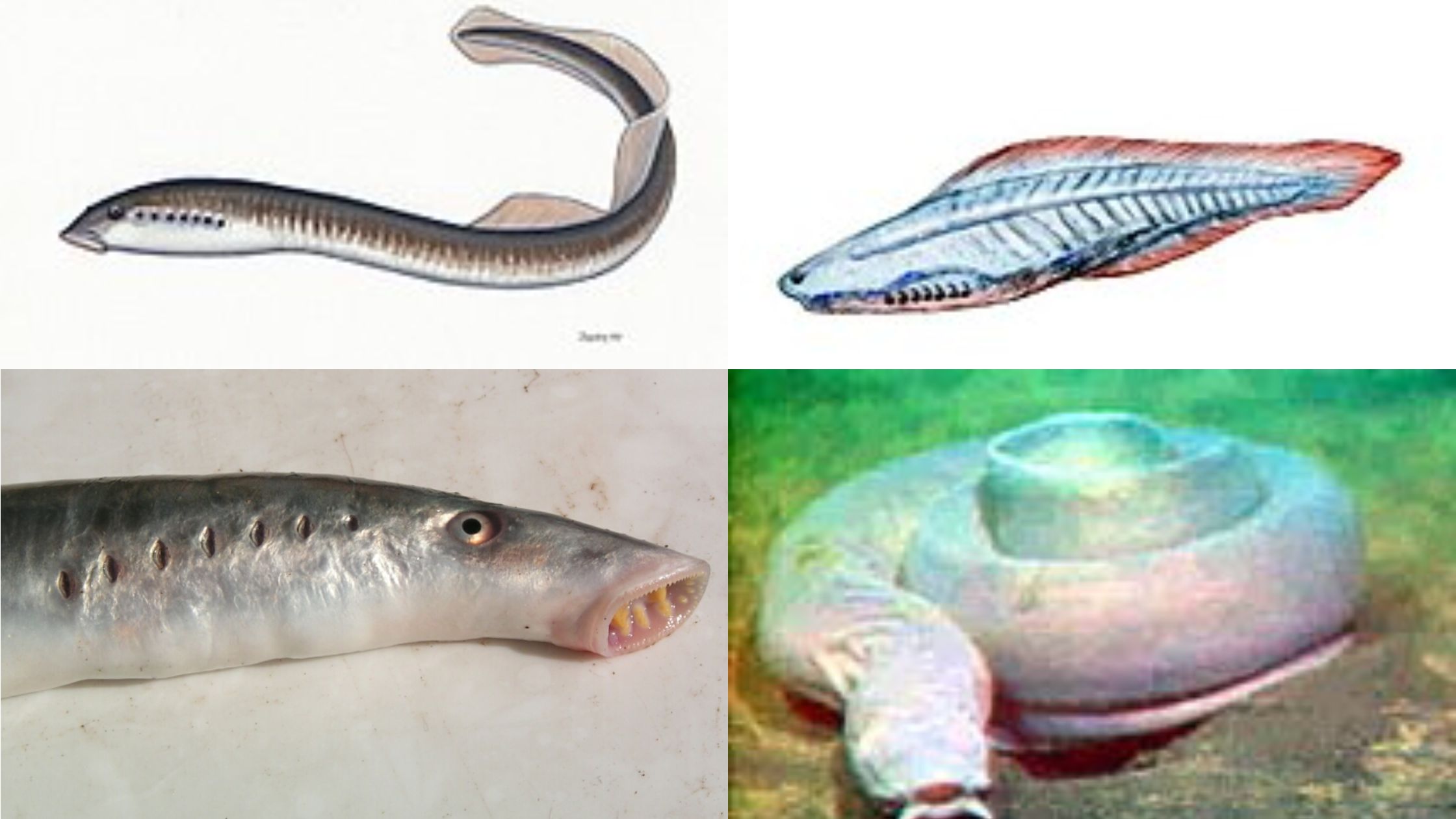
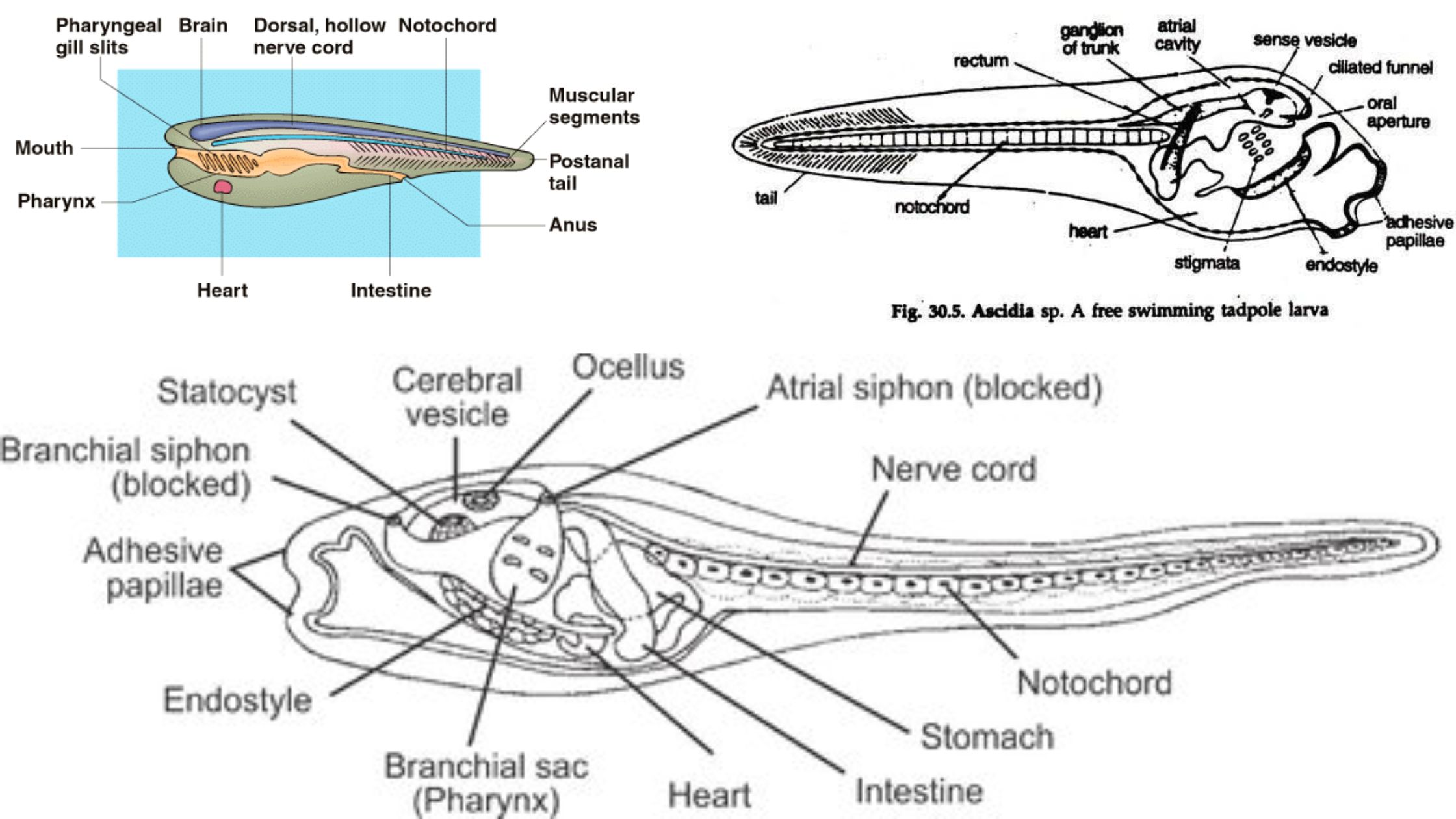
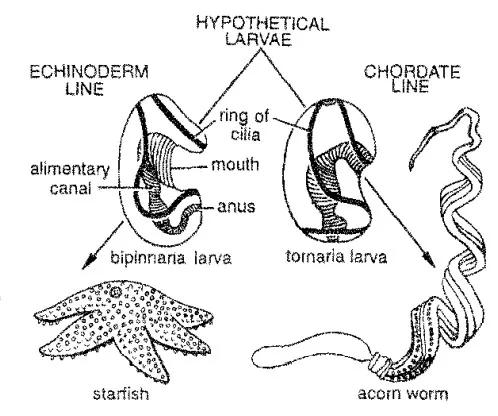
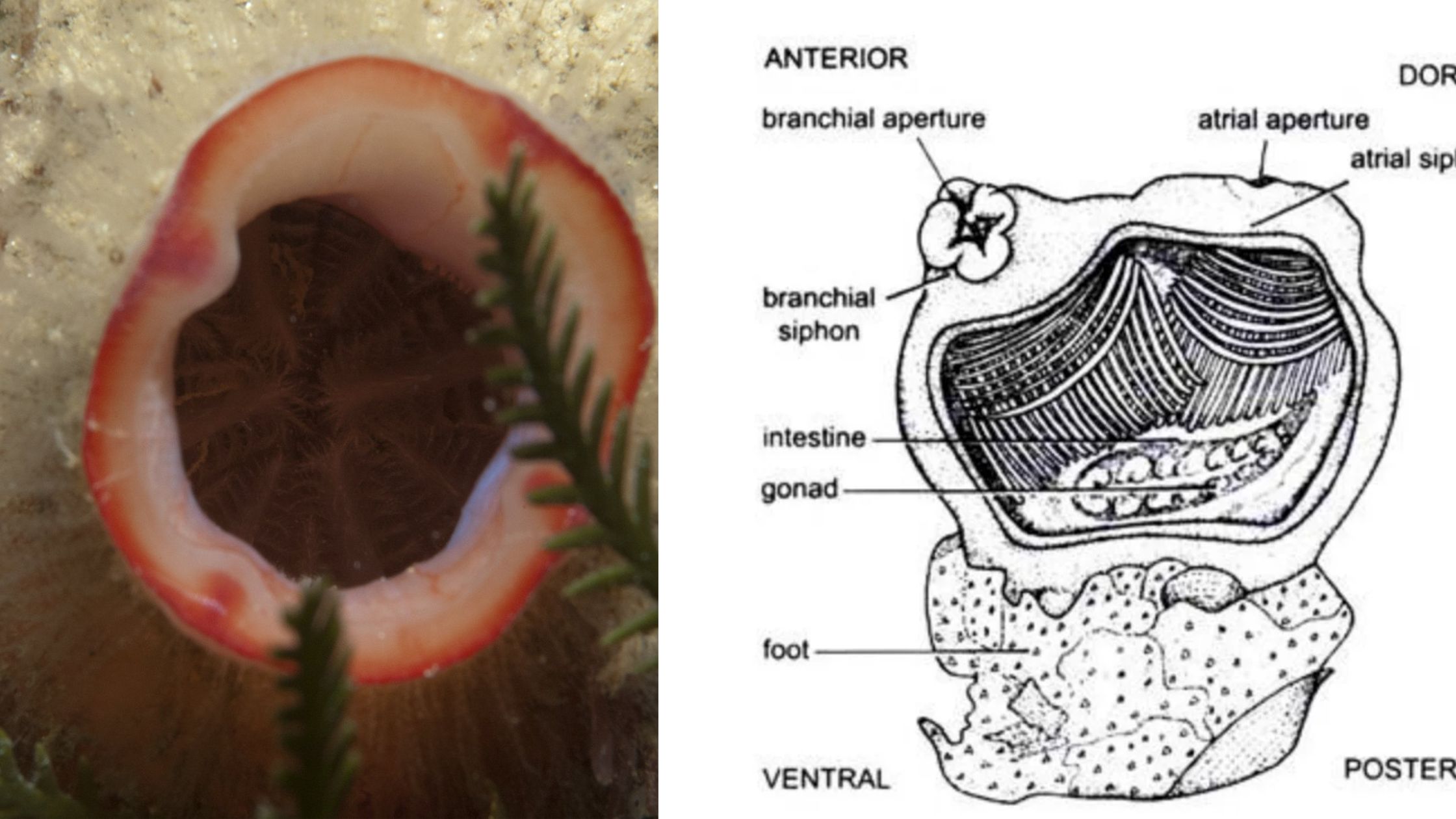
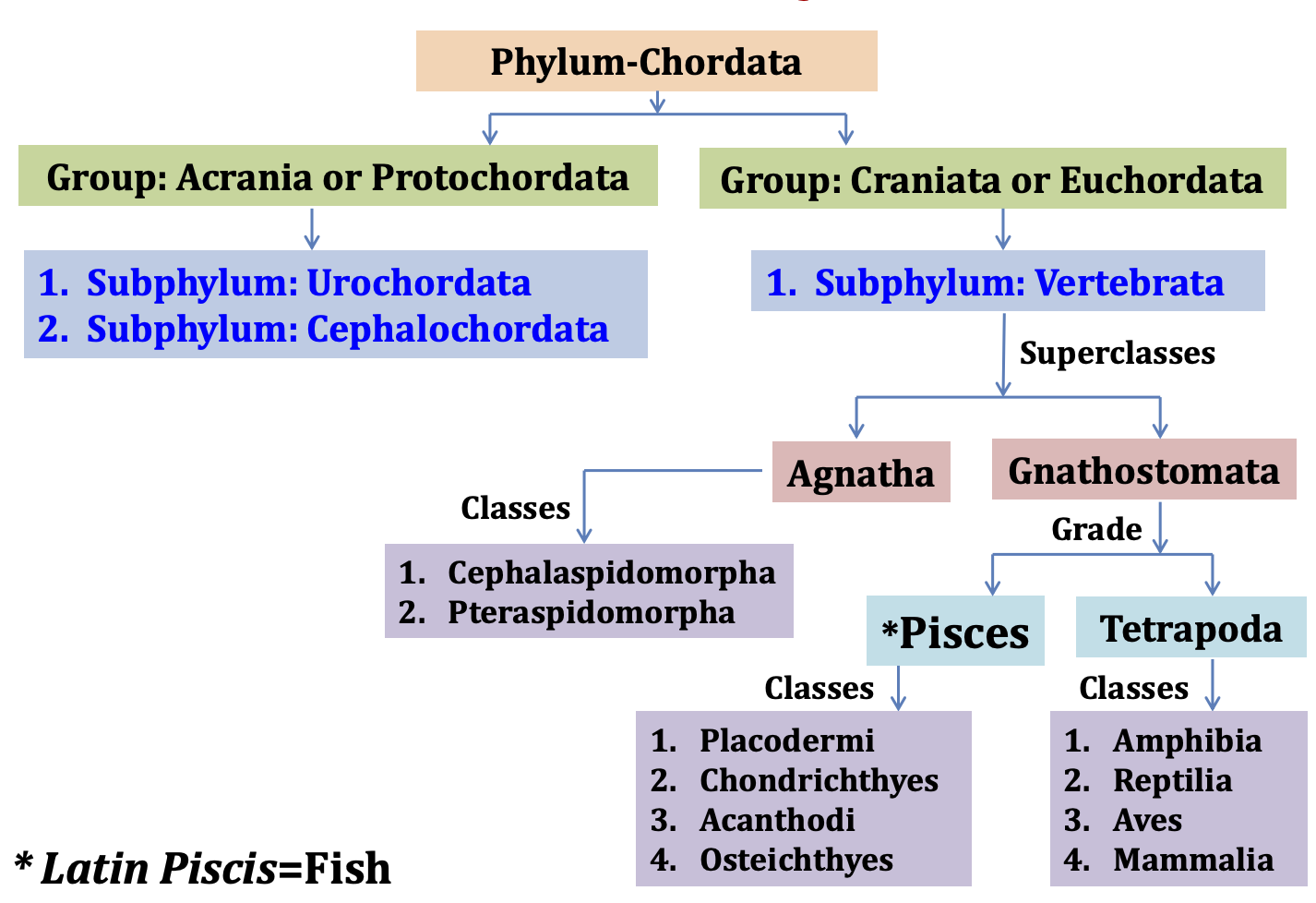
Protochordate larvae is the juvenile stage found in lower chordates, and it is seen in members of Urochordata and Cephalochordata. It is the stage where the animal shows the typical chordate features very clearly. It is the notochord, dorsal hollow nerve cord, pharyngeal slits, and the post-anal tail that appear in this larval period. It … Read more