Lipase Test – Principle, Procedure, Results, Uses
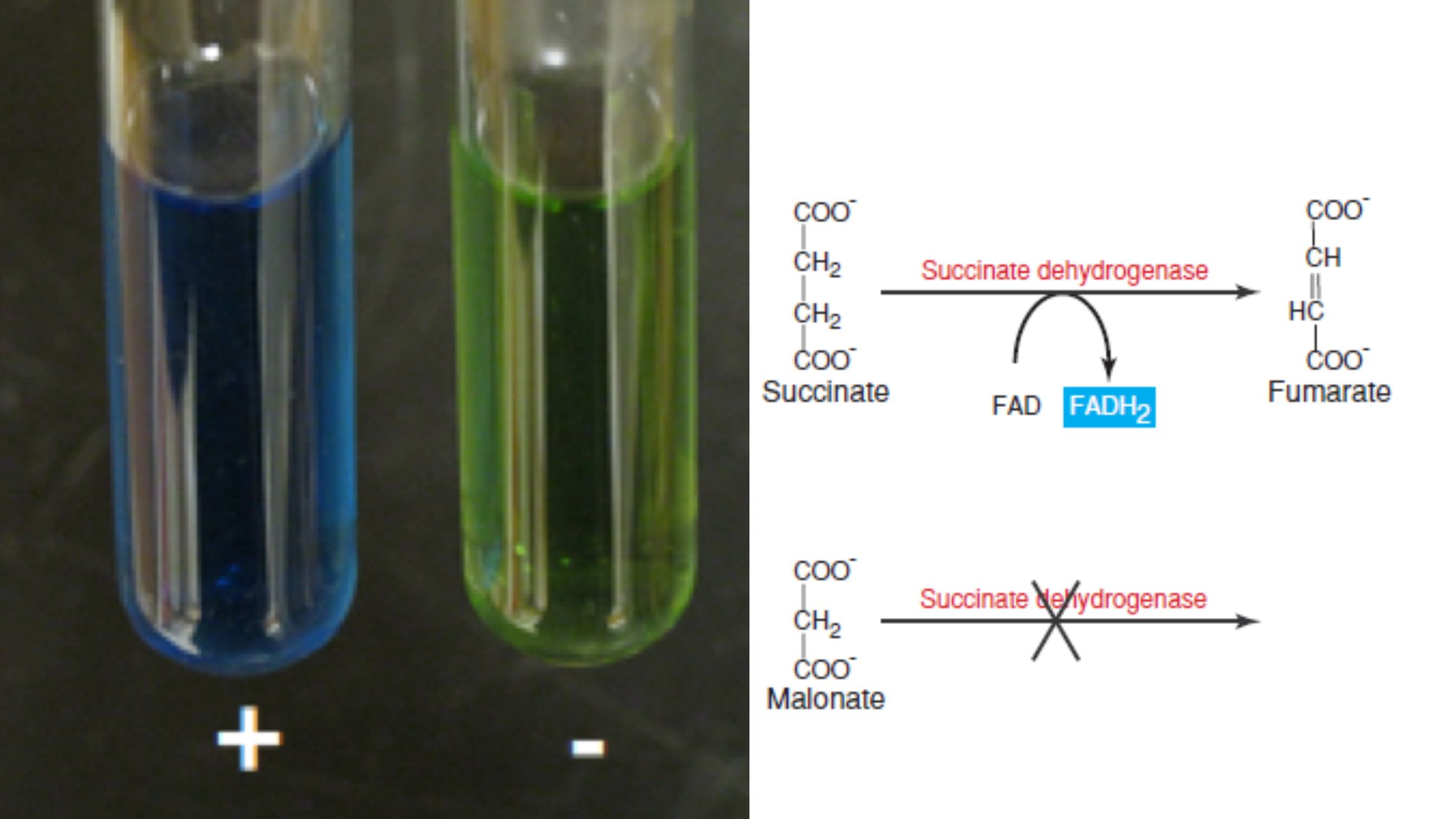
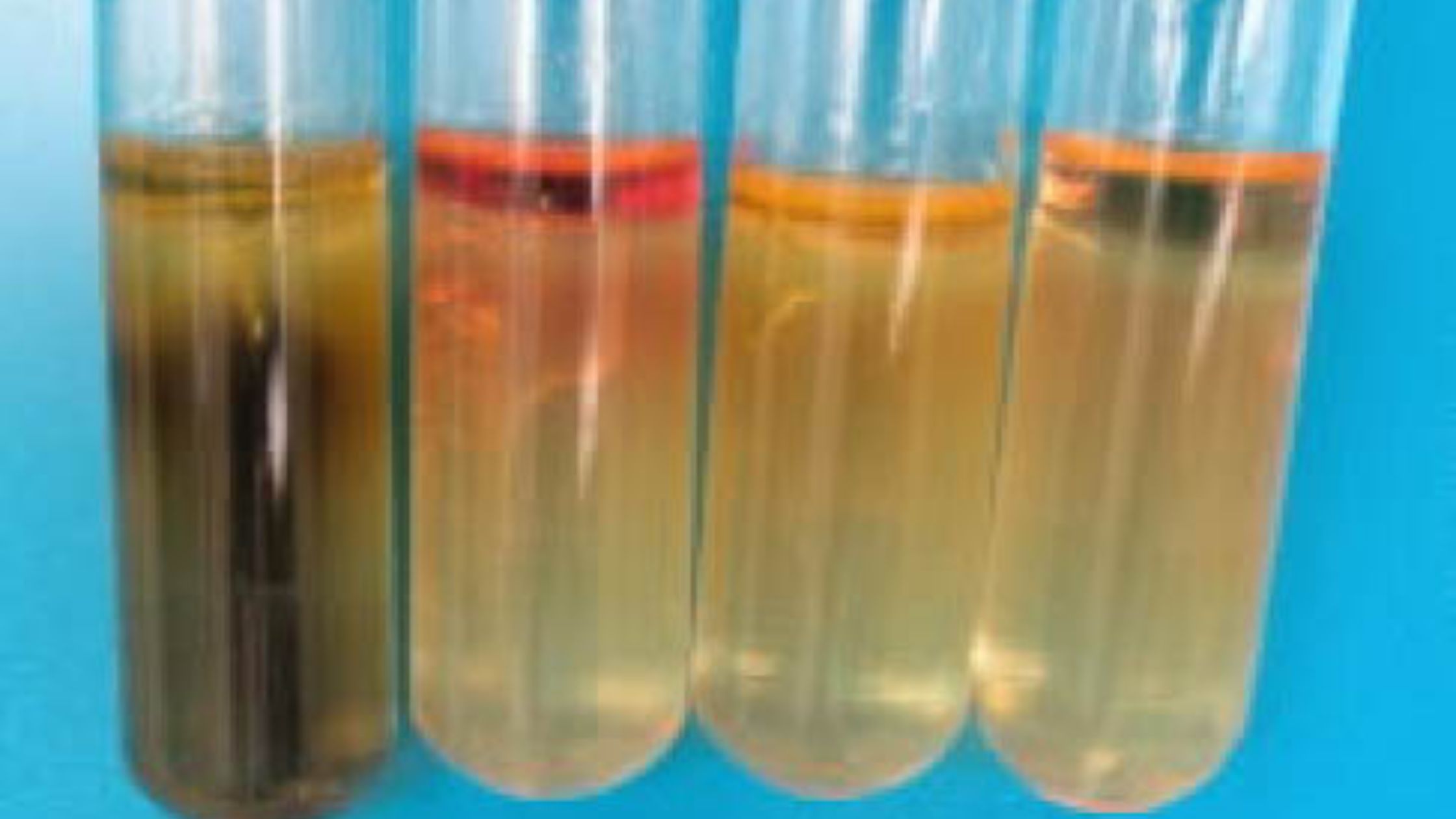
A lipase test is a laboratory diagnostic test which is done to measure the level of lipase enzyme in the blood. Lipase is a digestive enzyme which is mainly produced by pancreas and it helps in digestion of fats. It is the process in which dietary triglycerides are broken down into fatty acids and glycerol … Read more