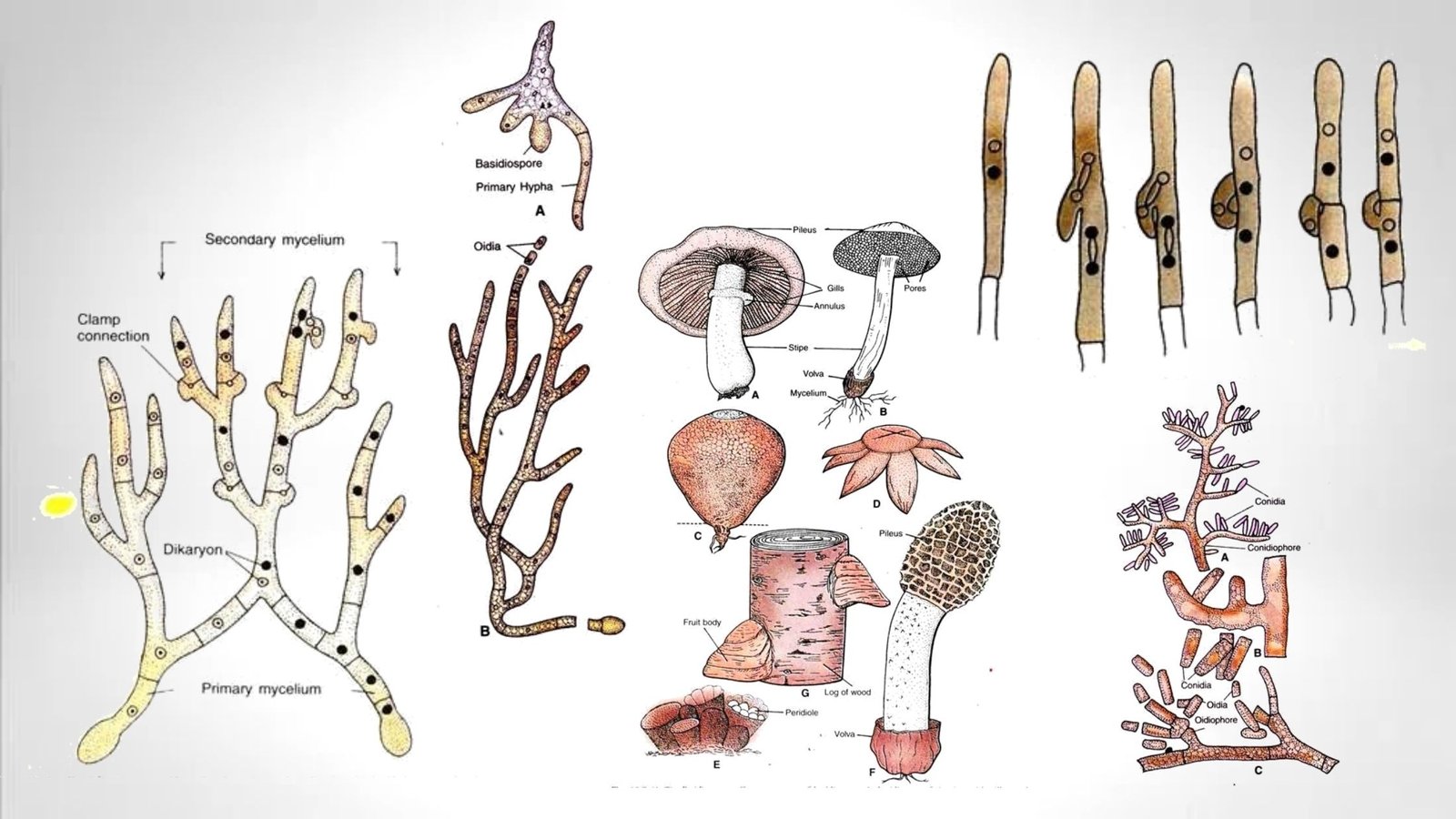
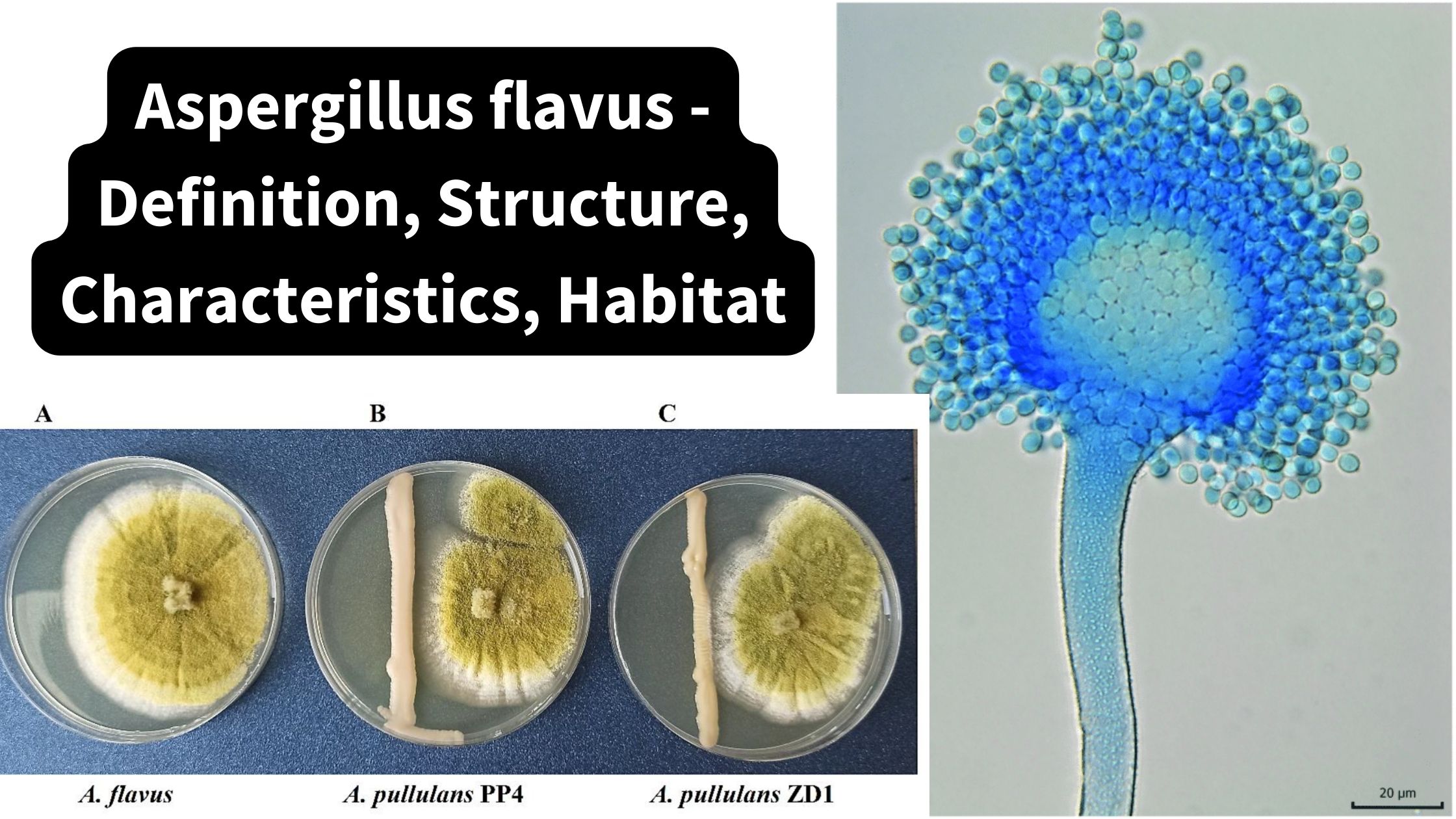
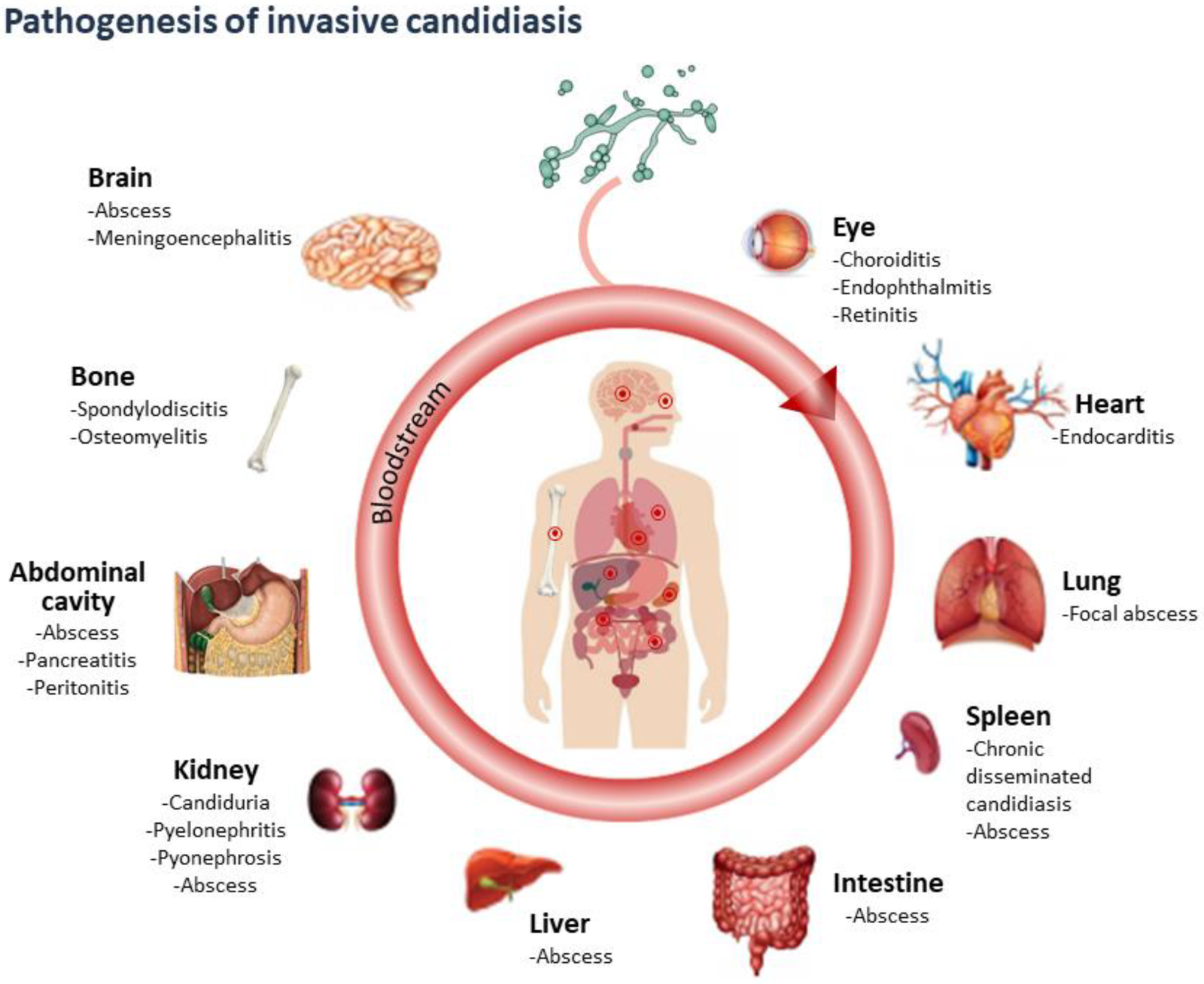
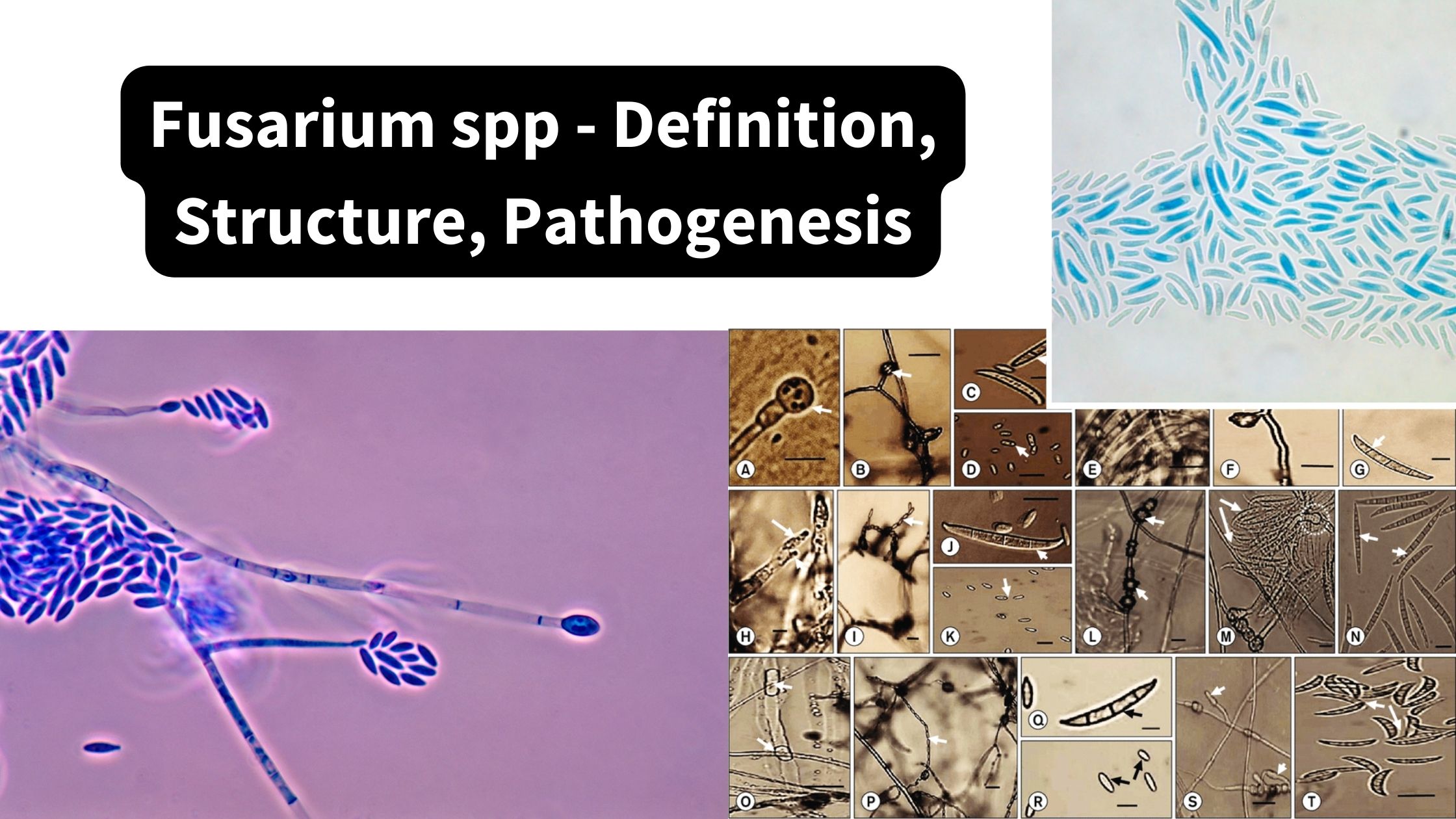
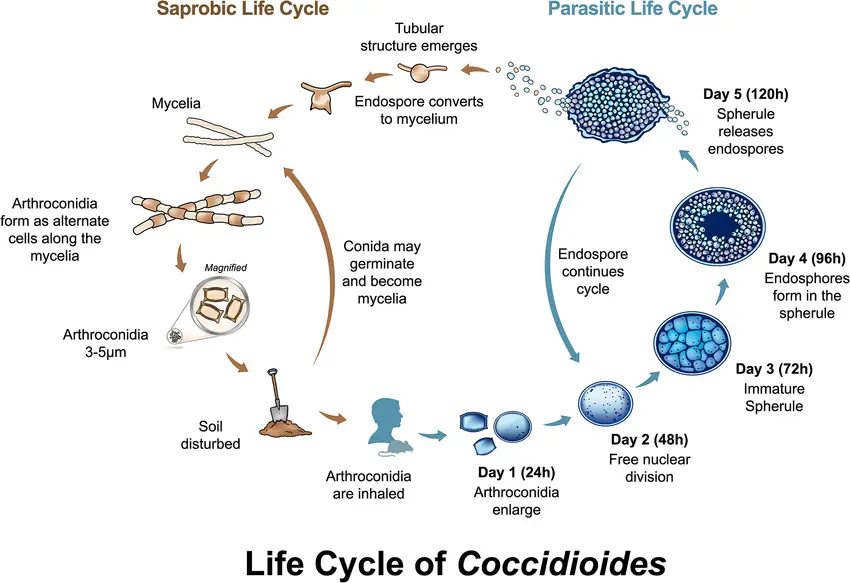
Basidiomycetes – Life cycle, Characteristics, Significance, Mycelium and Examples
Basidiomycetes are harmful as well as useful. Their attack foods and ornamental plants, cause many different diseases including seedling diseases, wood rots, root and stem rots, seed diseases (smuts), and rusts, on the other hand, it used as humans foods.