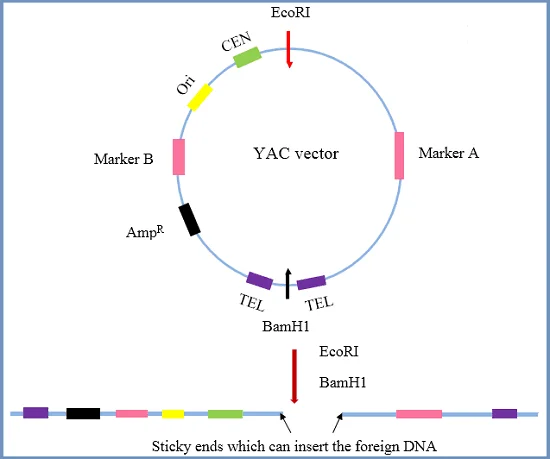
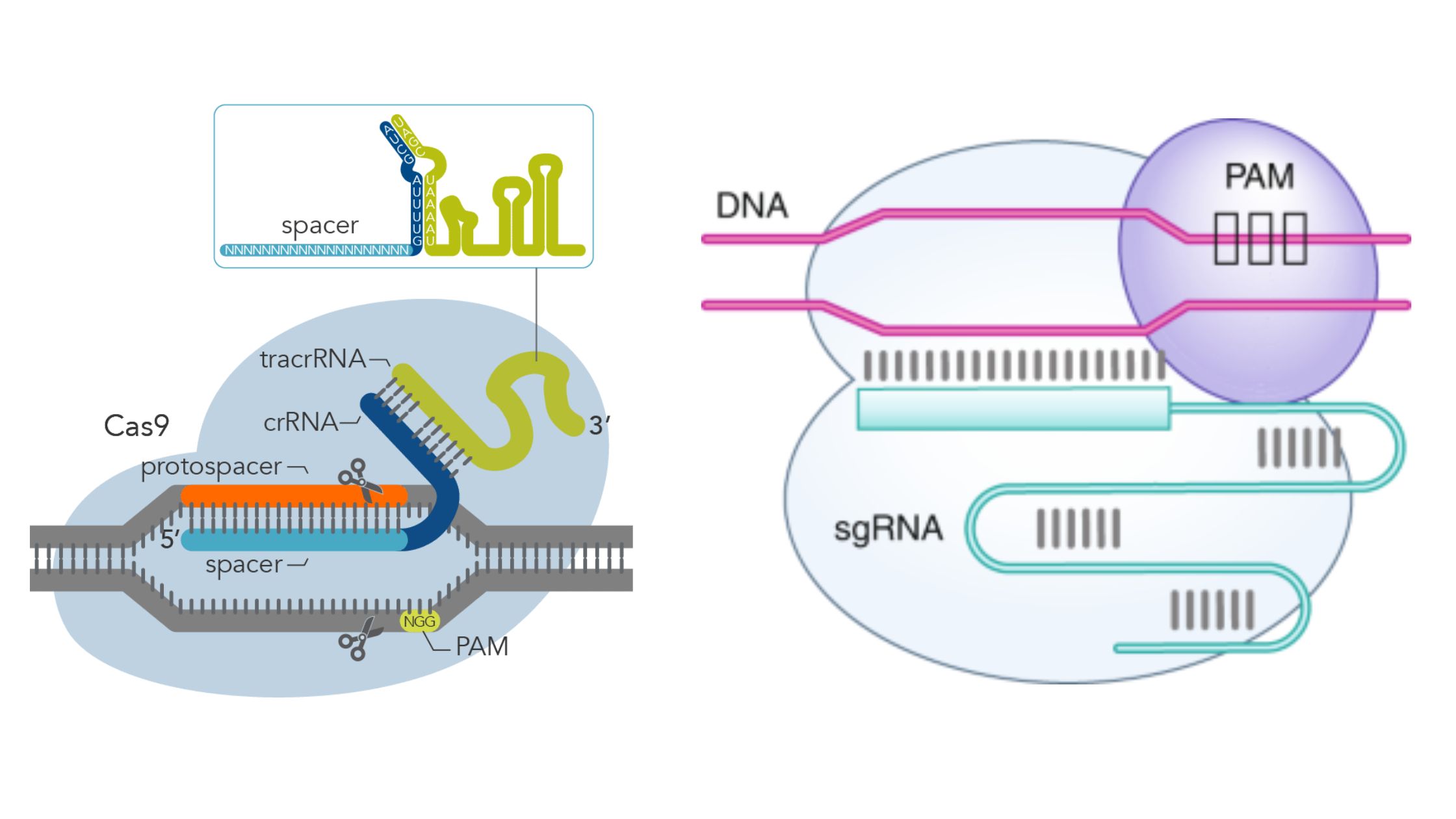
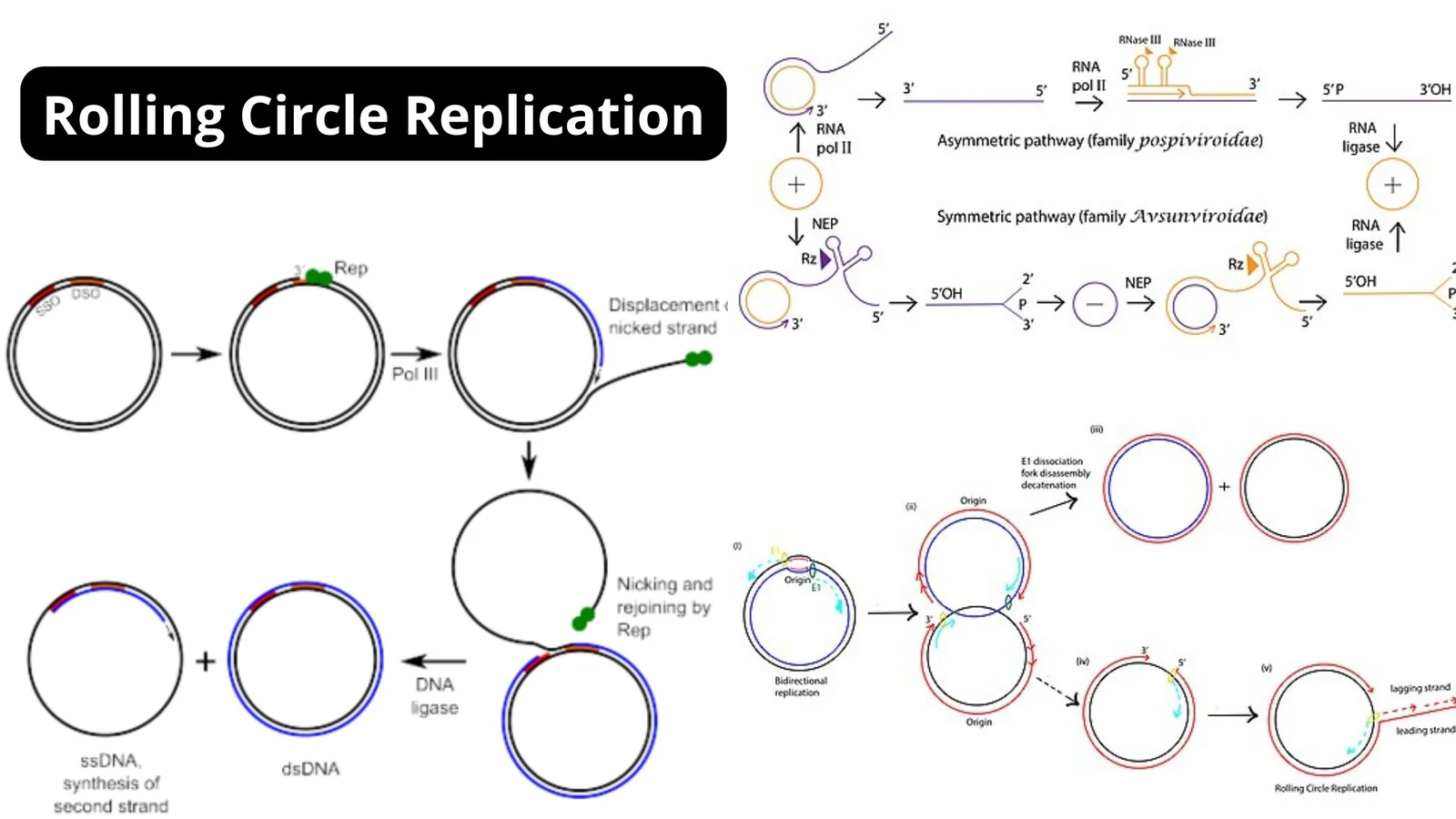
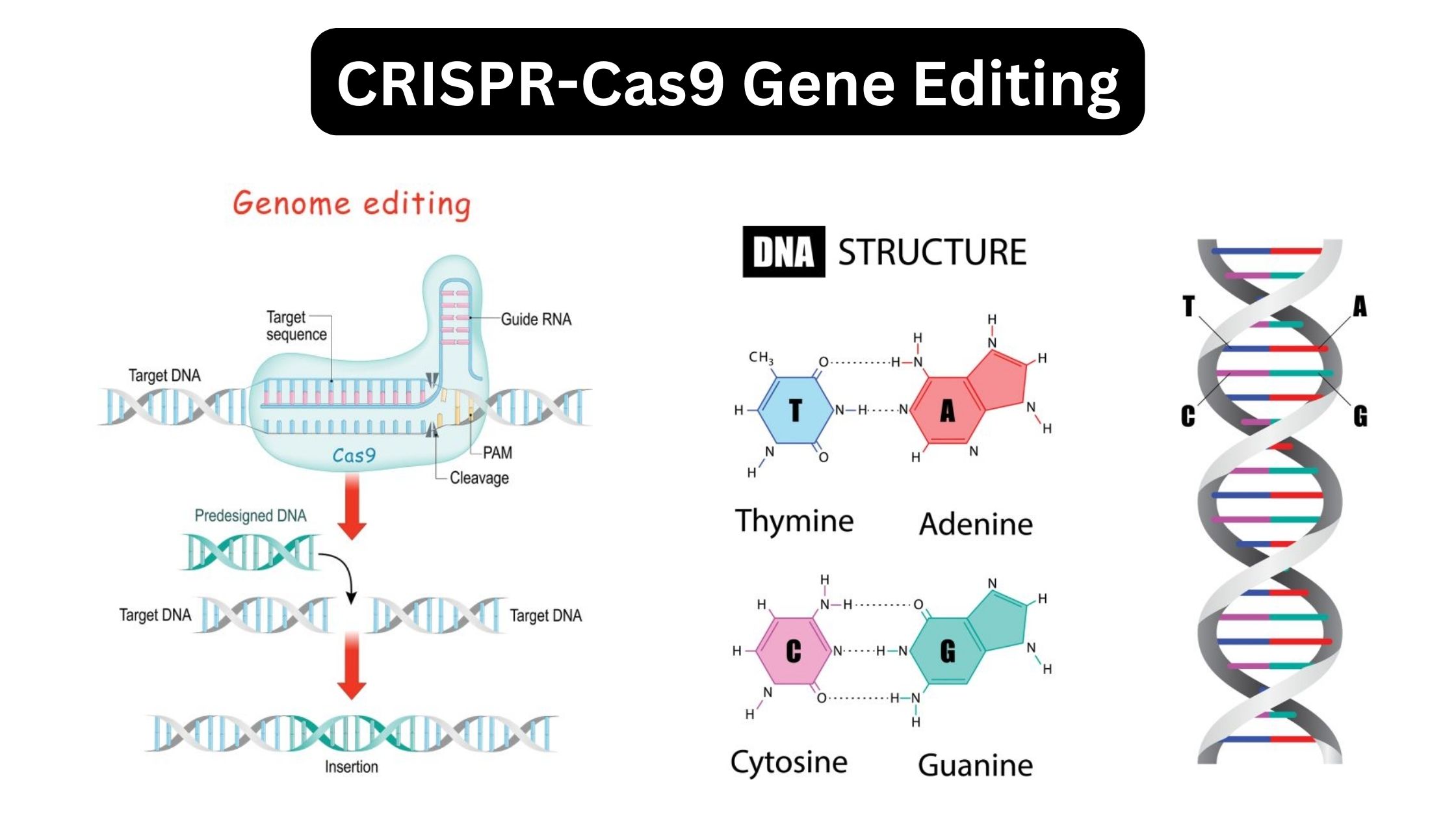
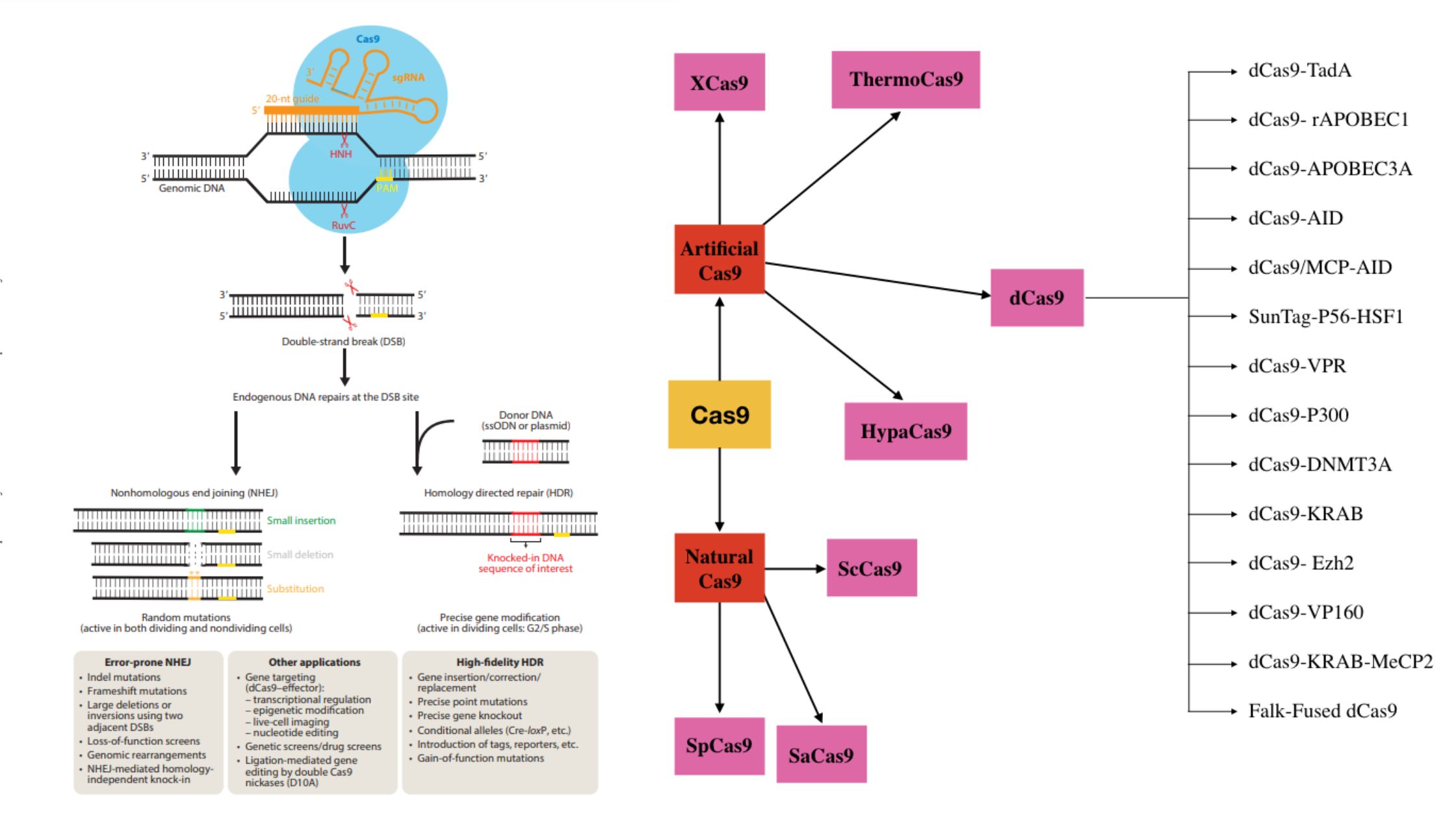
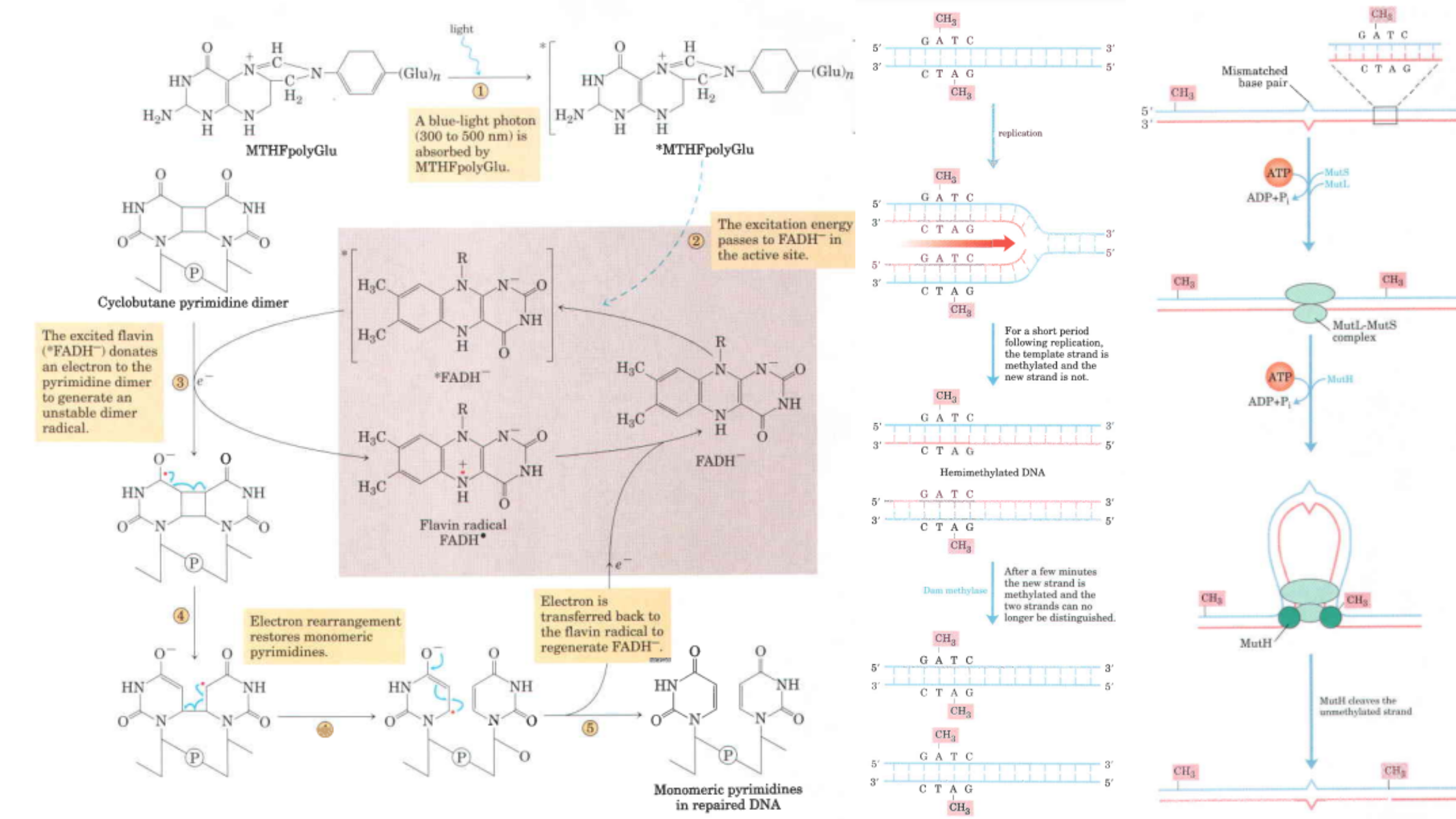
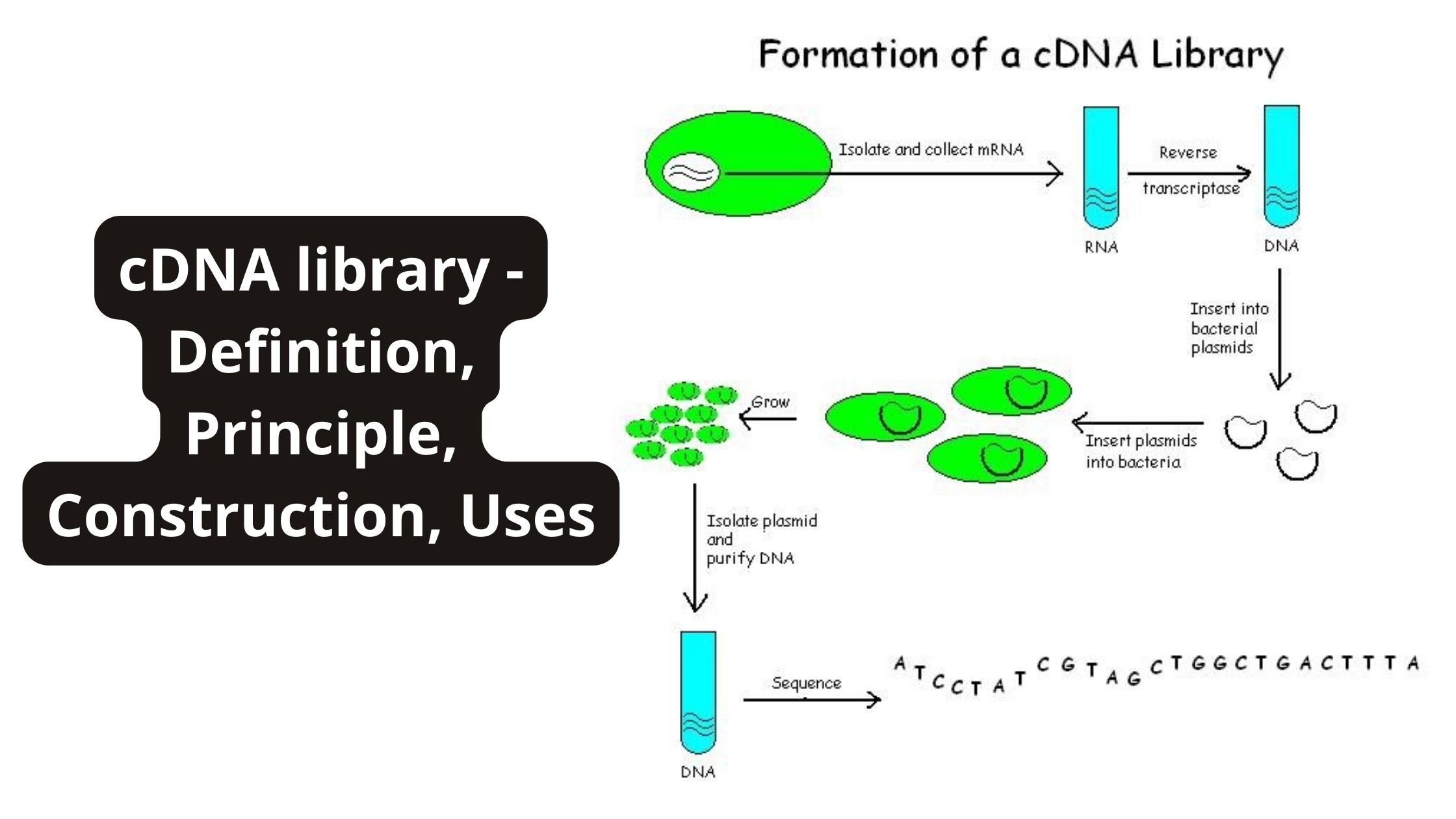
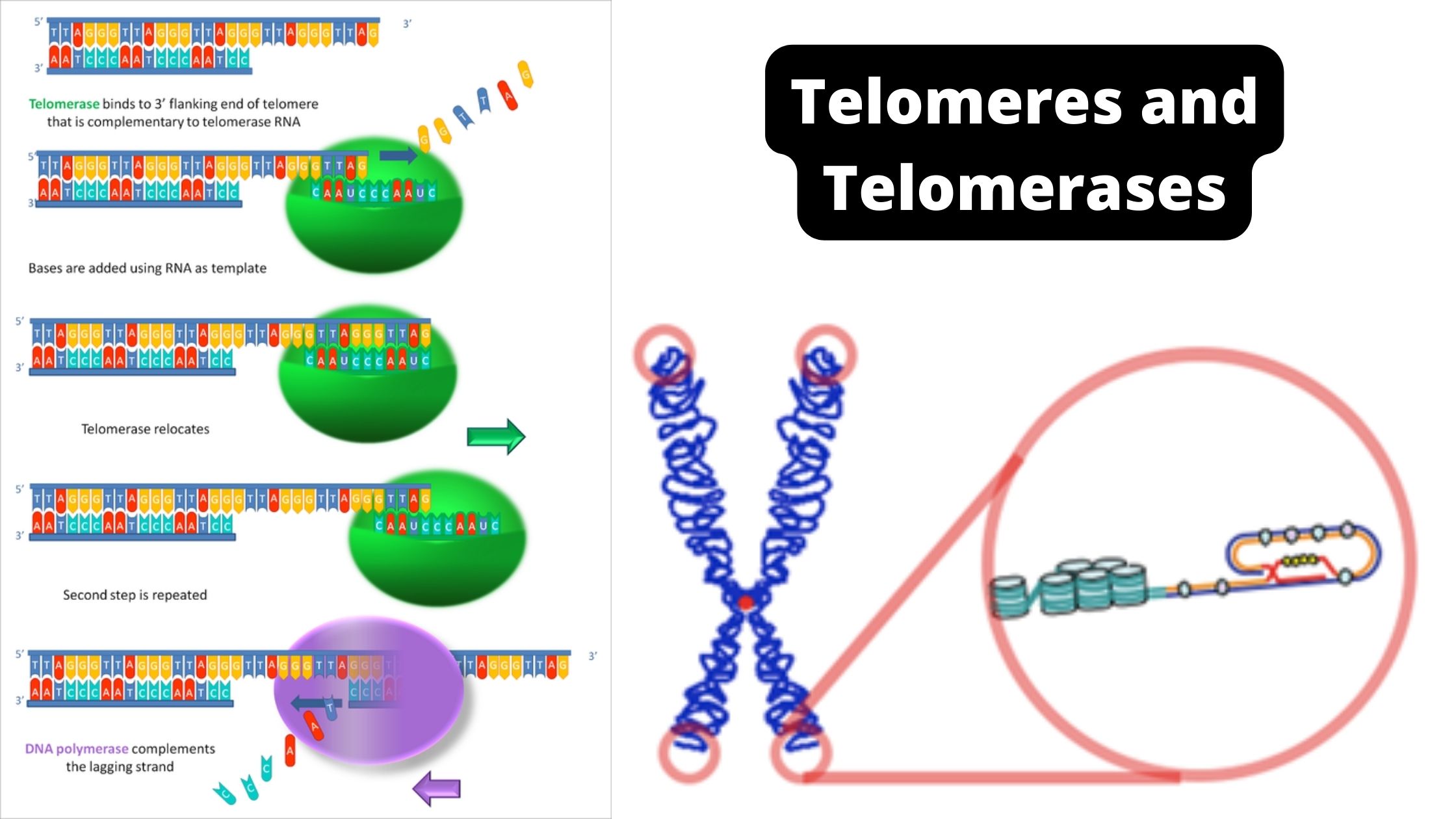
Yeast Artificial Chromosomes (YACs) – Definition, Structure, Construction, Uses
What is Yeast Artificial Chromosomes (YACs)? Yeast artificial chromosomes (YACs) are the result of a recombinant DNA cloning technique used to isolate and propagate extremely large DNA segments in a yeast host. The YAC cloning system enables the replication of exogenous DNA segments as linear molecules on a significantly larger scale than is possible with … Read more