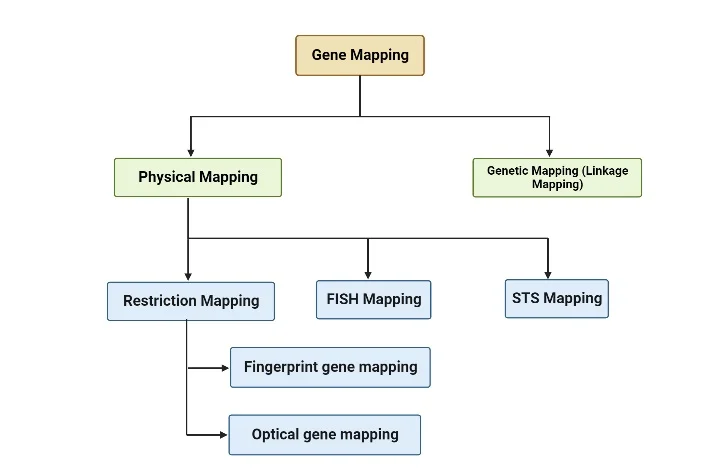
Chromosome Mapping – Definition, Types, Steps, Unit, Importance
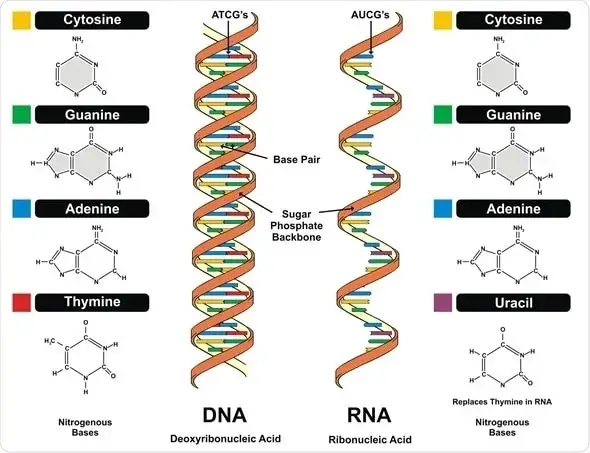
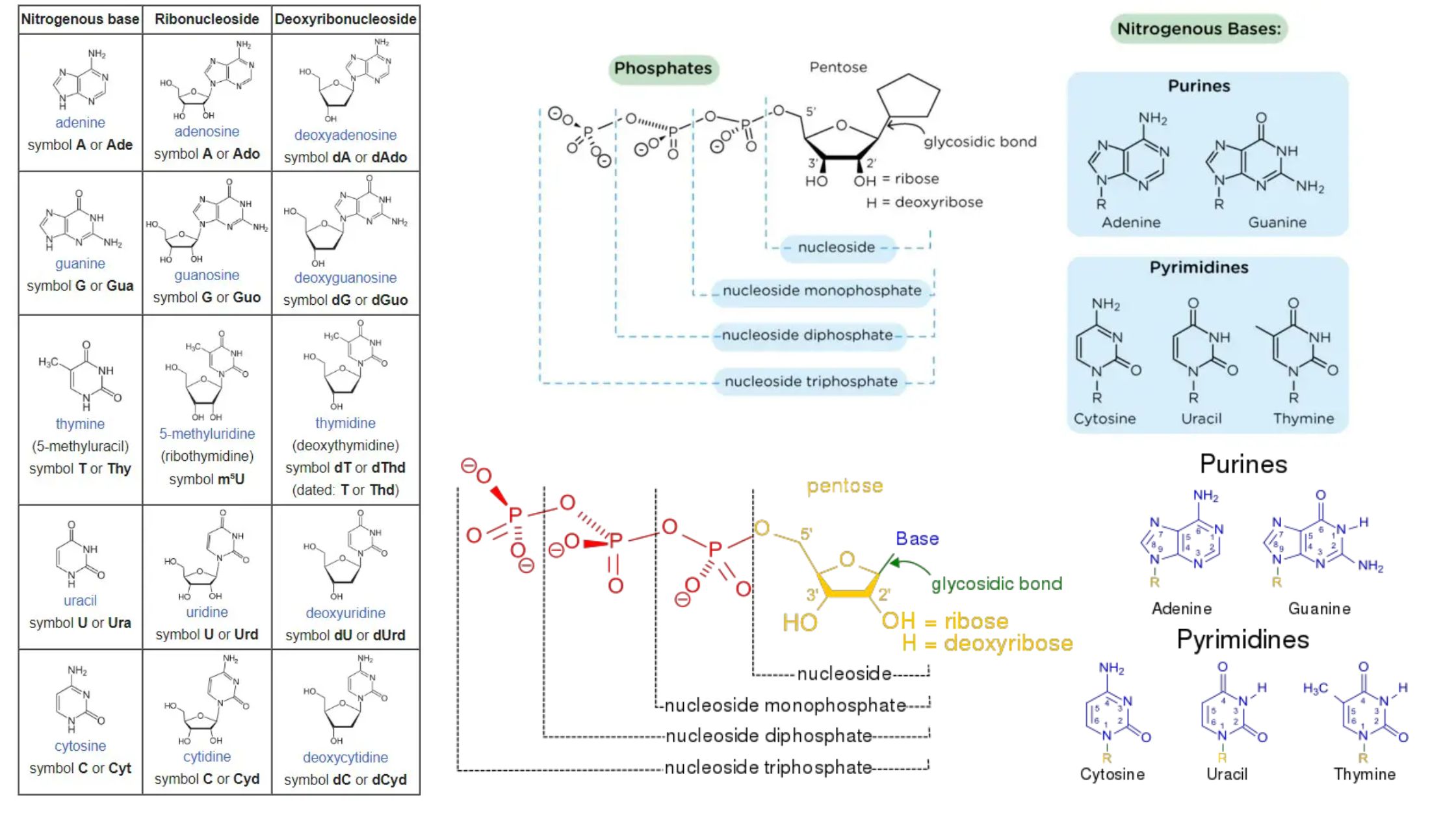
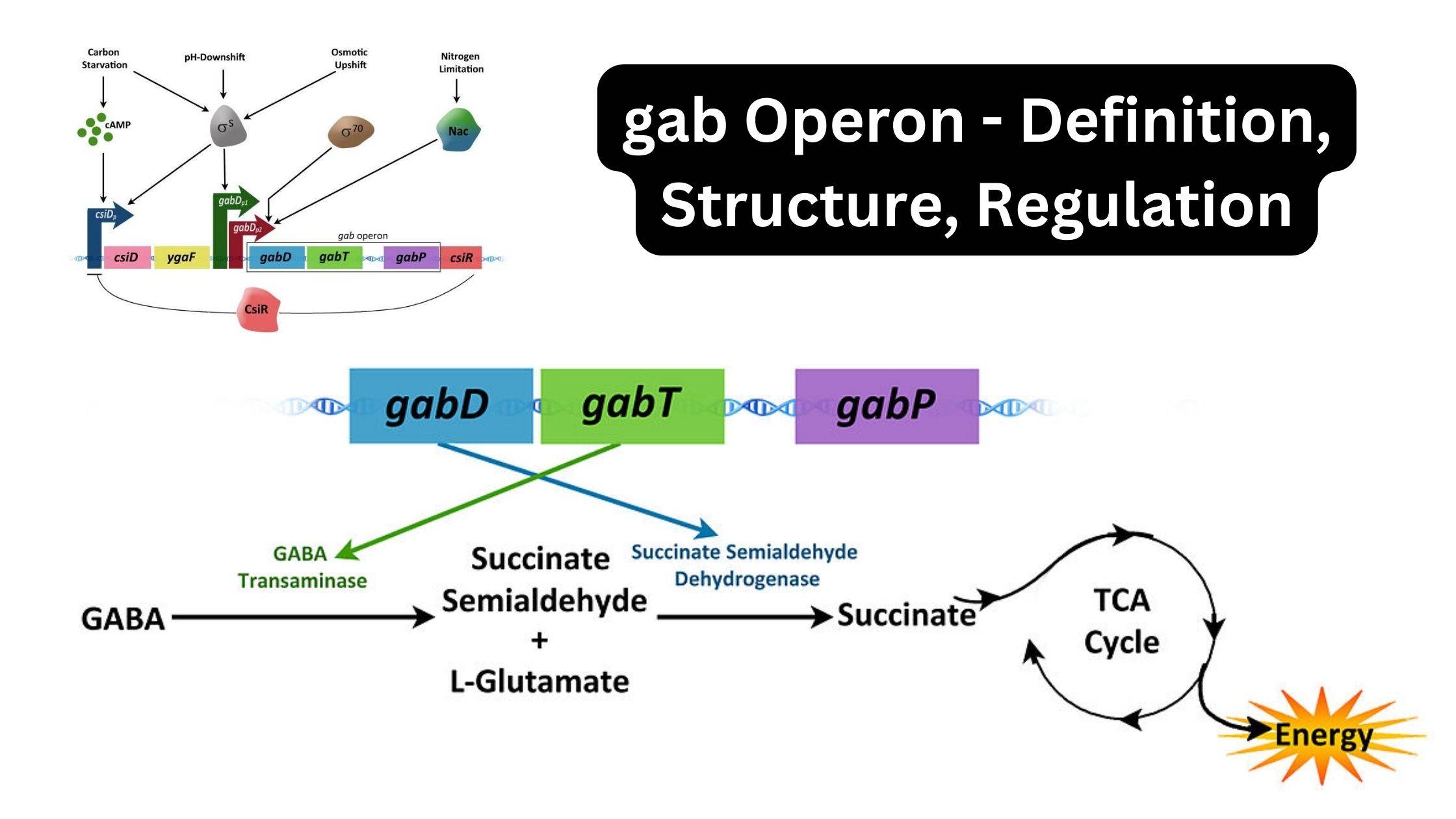
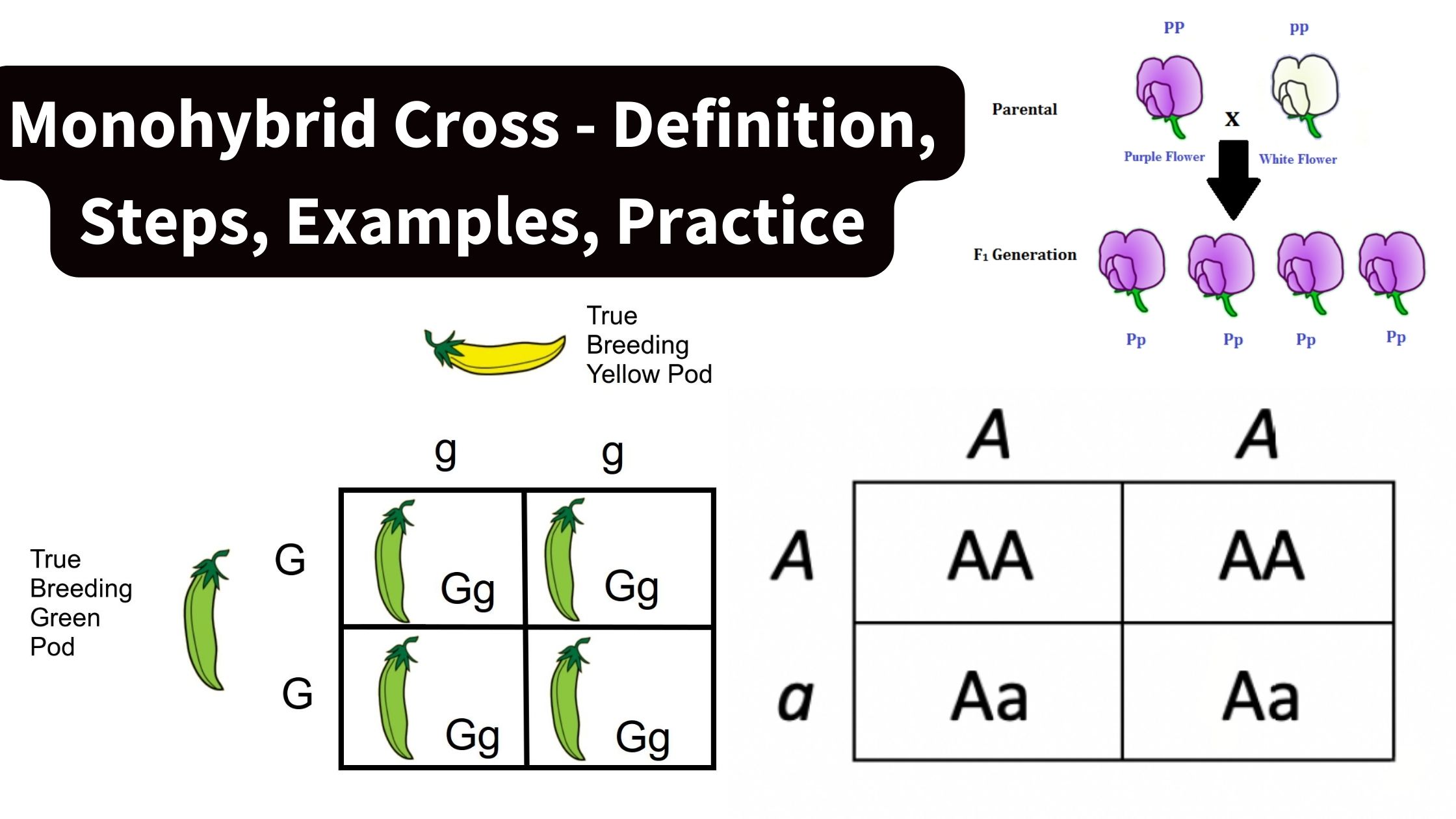
What is Chromosome Mapping? Chromosome mapping is a pivotal technique in genetics that determines the relative positions of genes on a chromosome. This process involves creating maps that systematically organize and elucidate genetic information on chromosomes. These maps not only depict the positions of genes but also the distances between them, scaled to a specific … Read more