Pleiotropism – Definition, Types, Examples
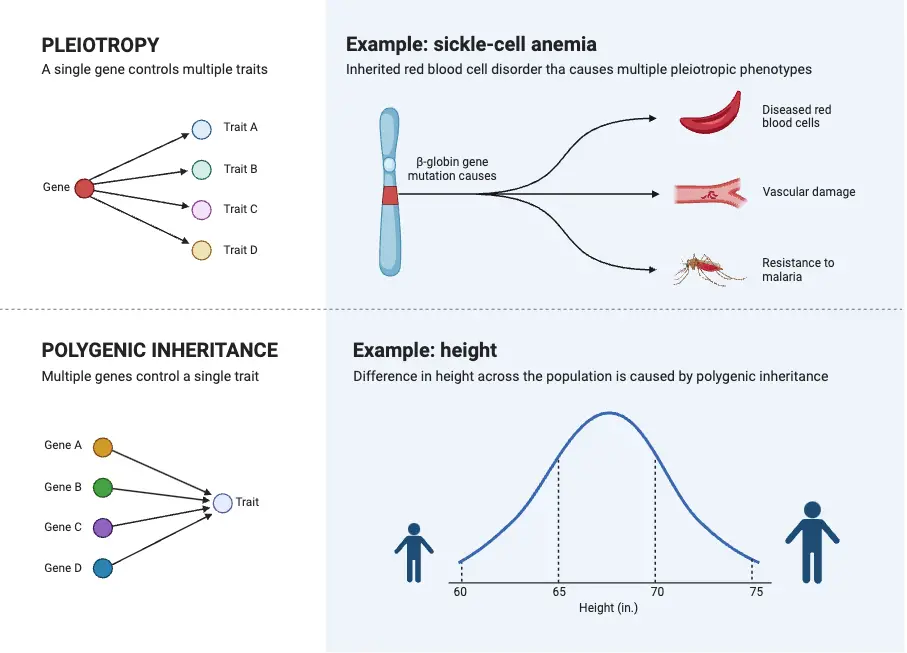
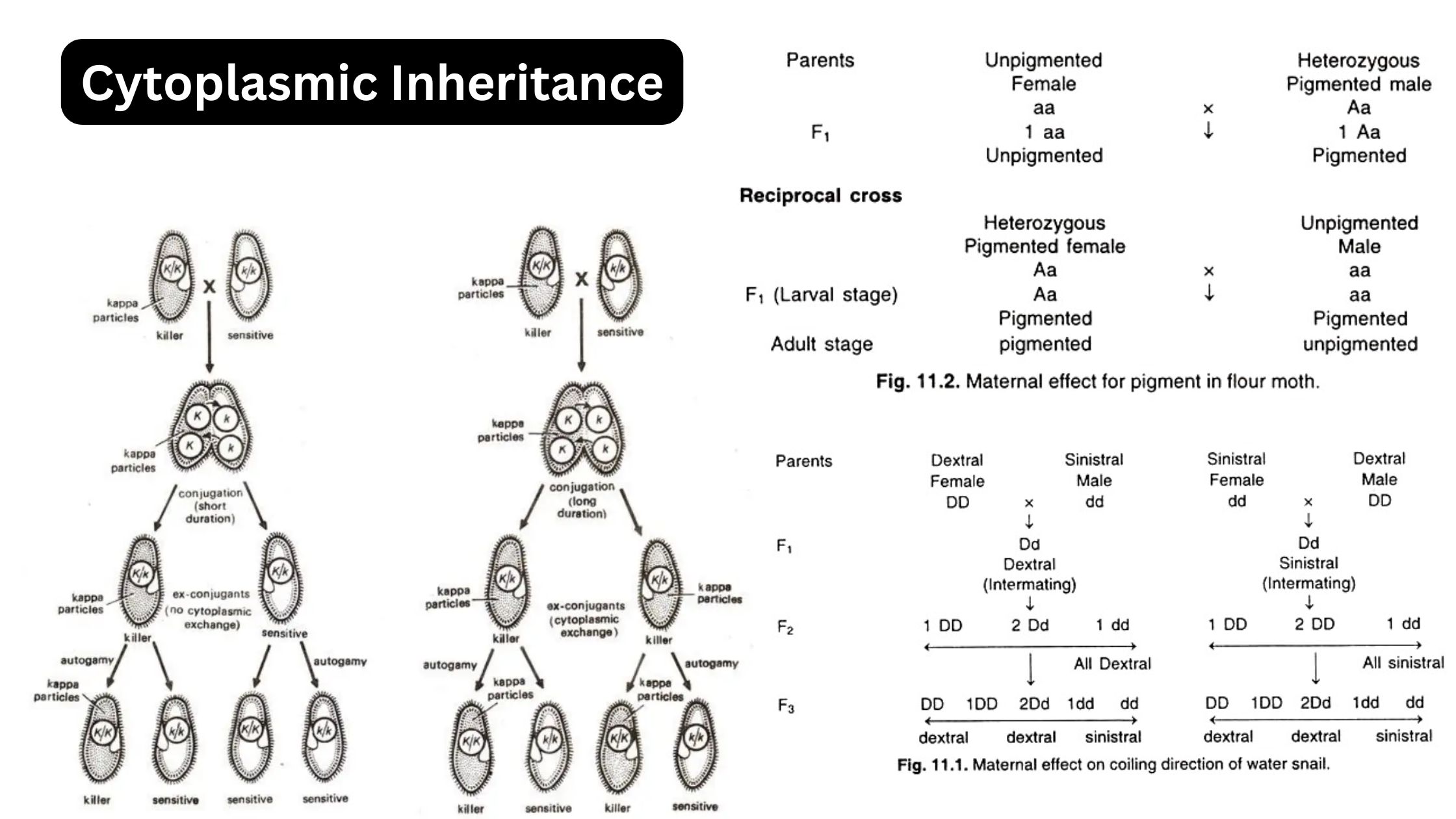
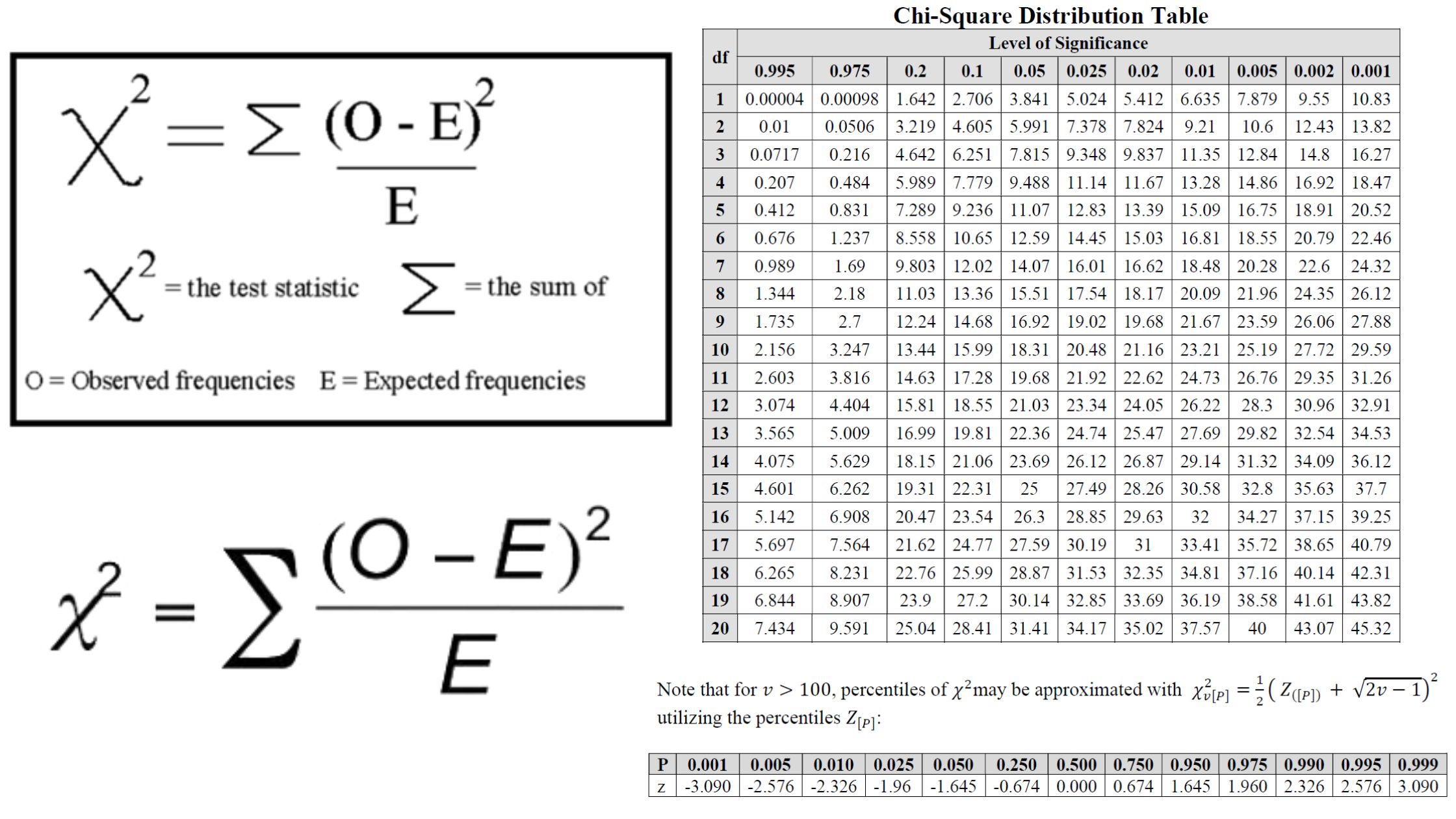
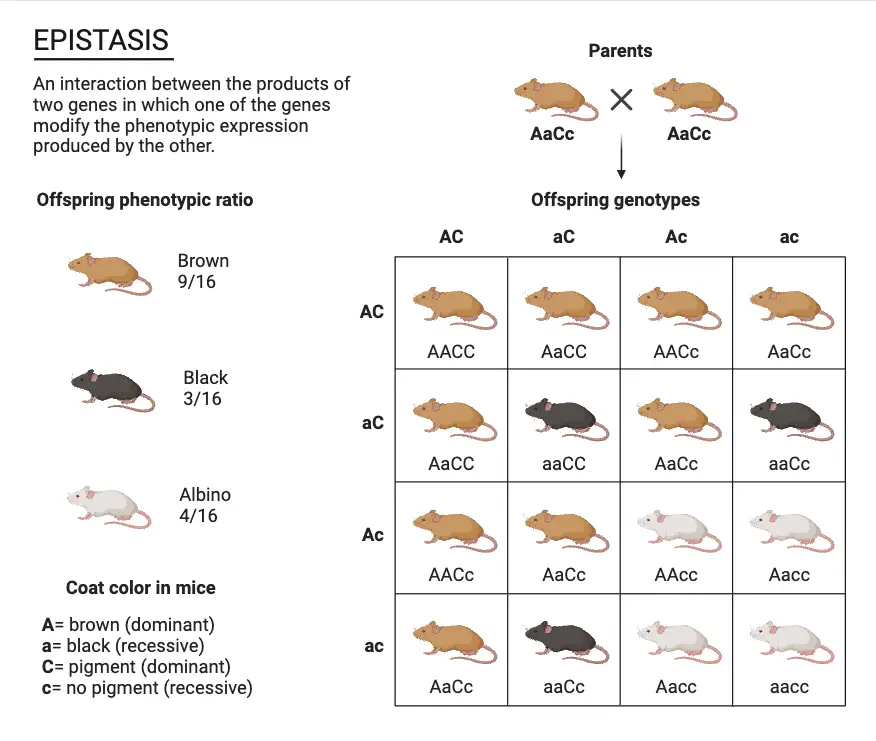
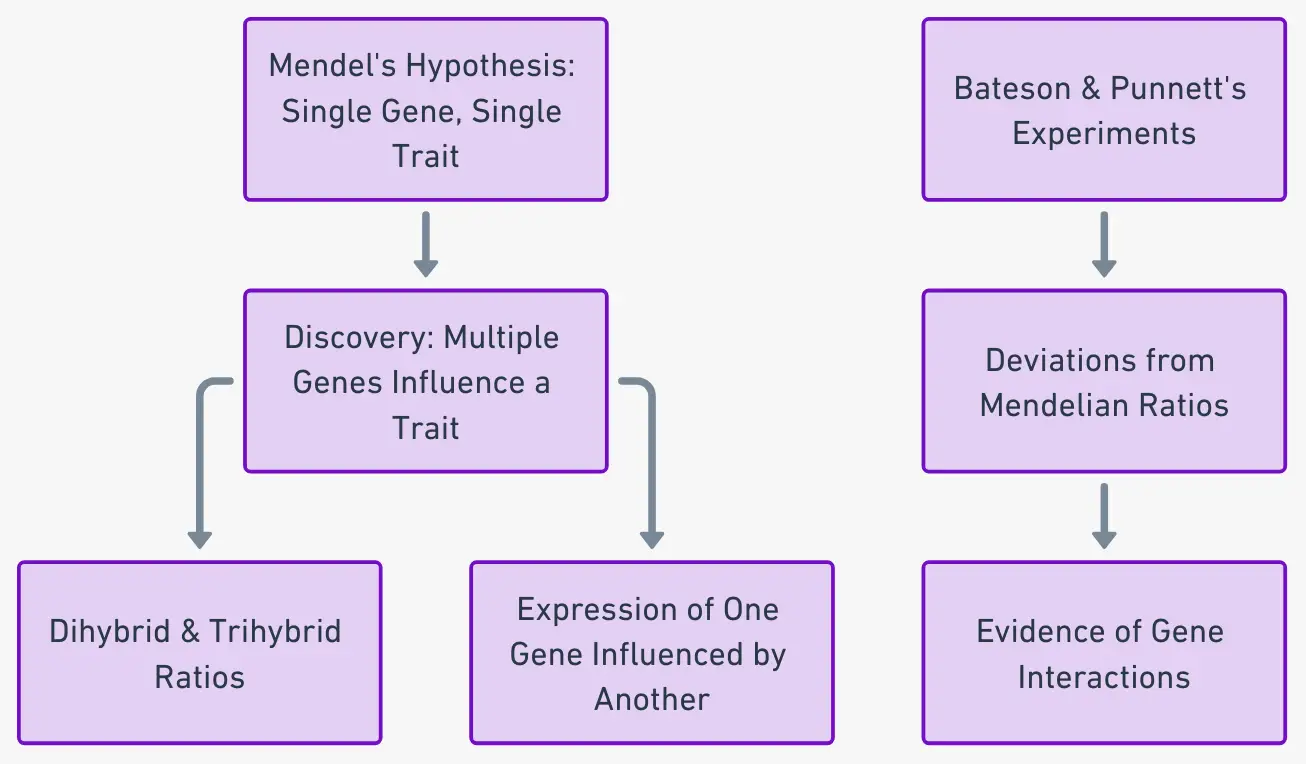
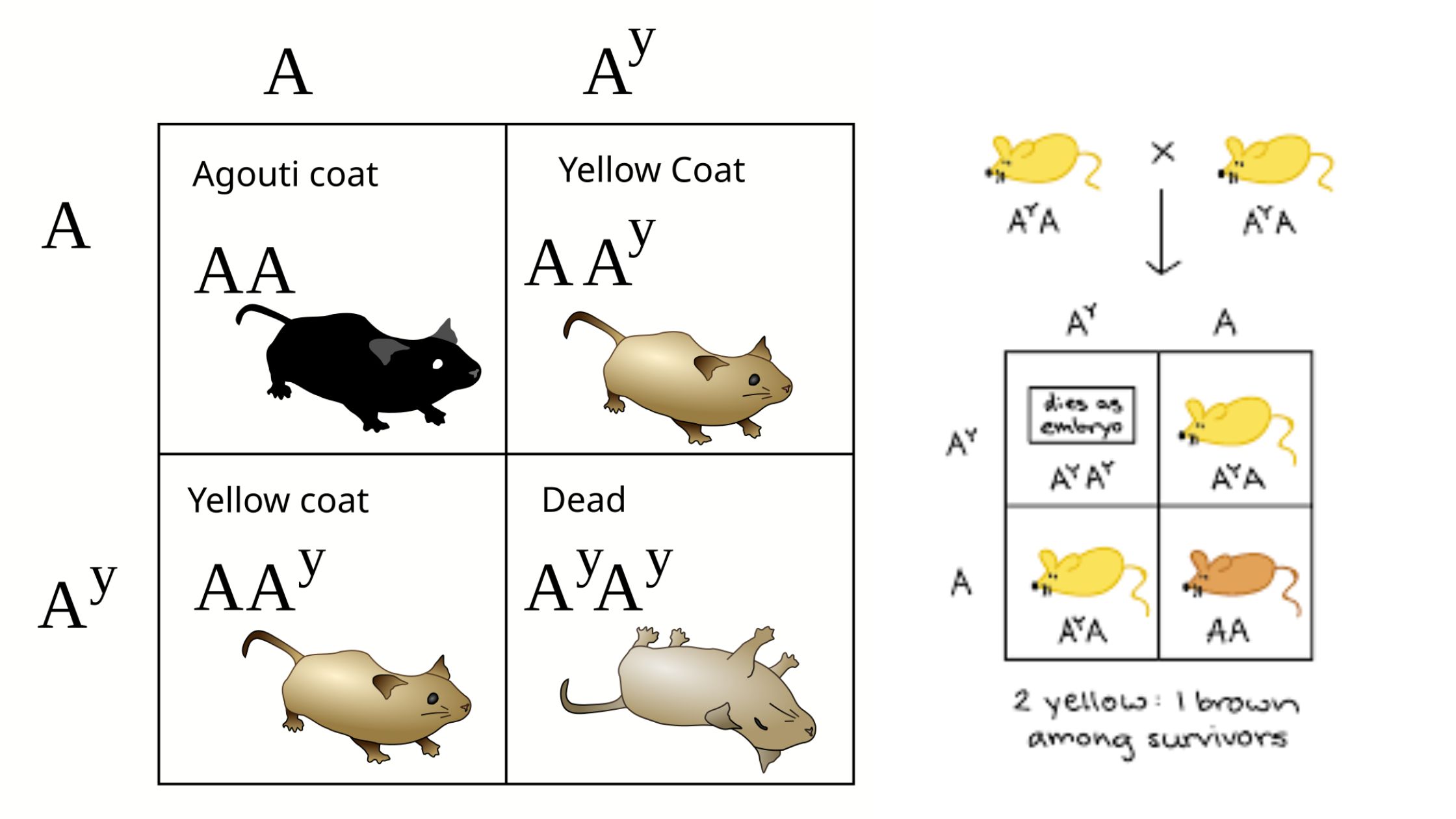
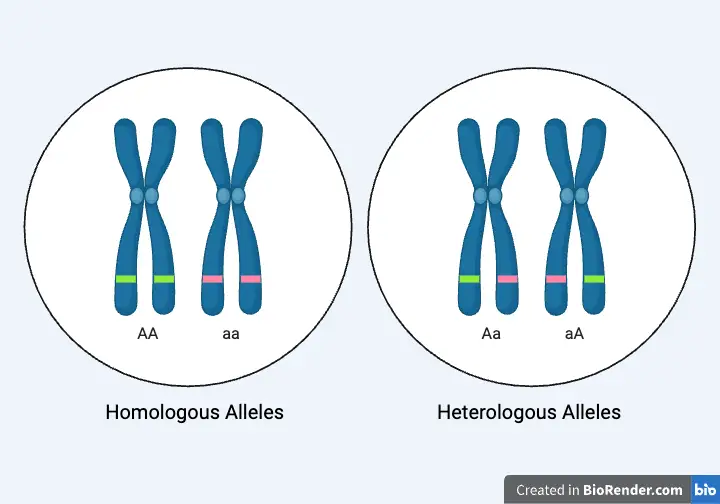
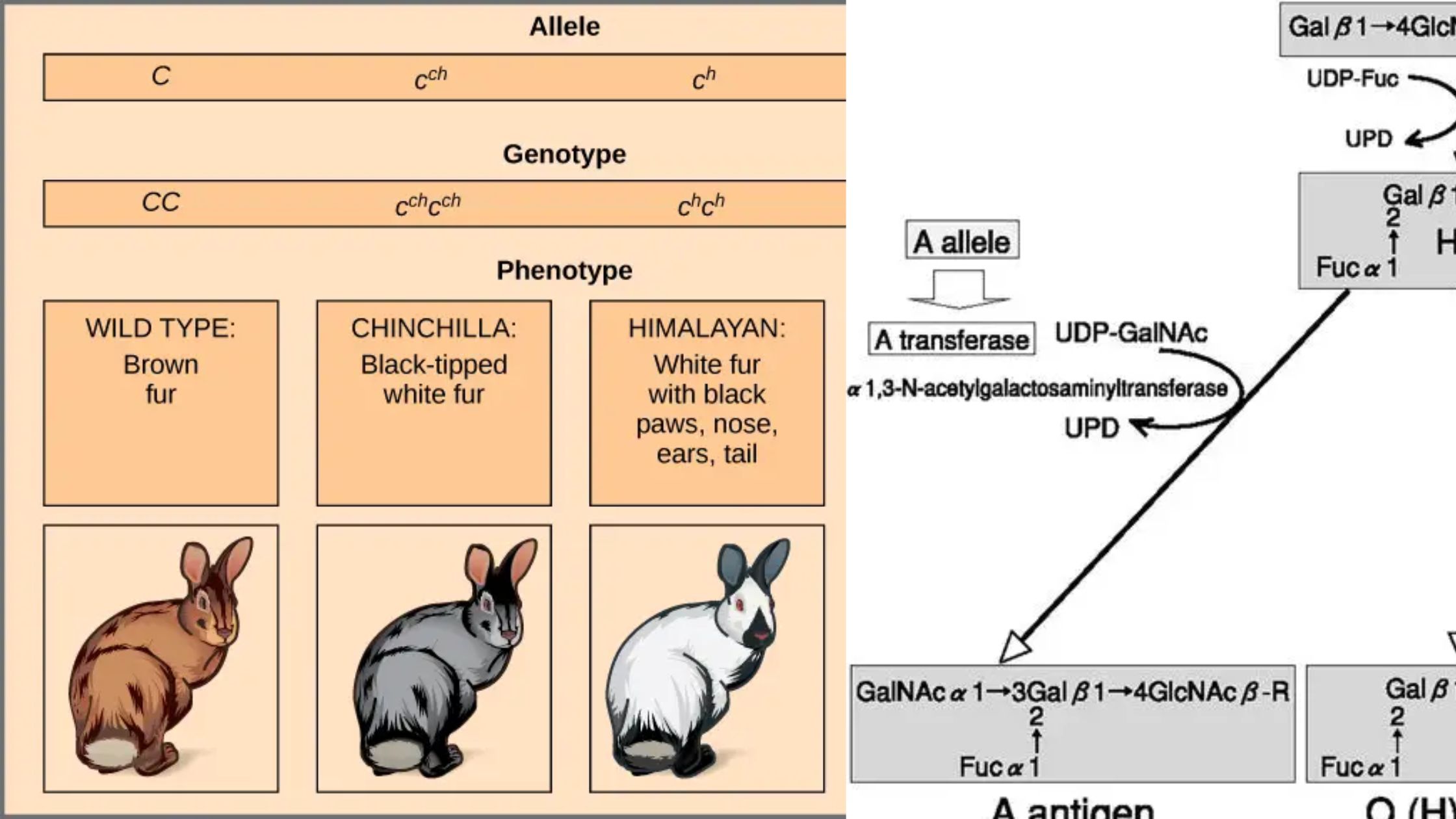
What is Pleiotropism? Short Definition of Pleiotropism Pleiotropism refers to the phenomenon where a single gene or mutation affects multiple, seemingly unrelated traits or physiological processes. This occurs when one genetic change leads to a range of different effects across various aspects of an organism’s phenotype. Types of pleiotropy Examples of Pleiotropism Significance of Pleiotropism