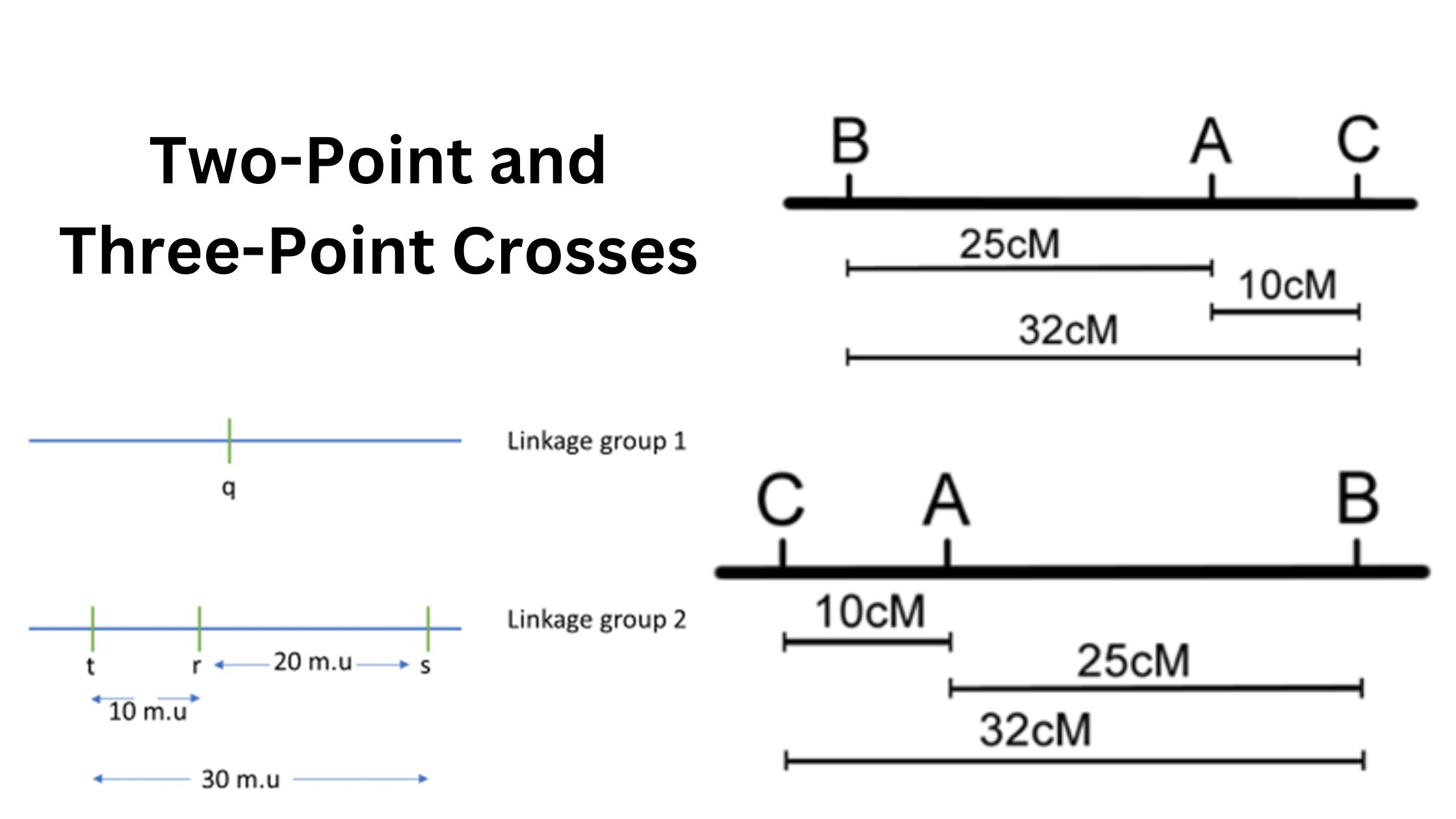
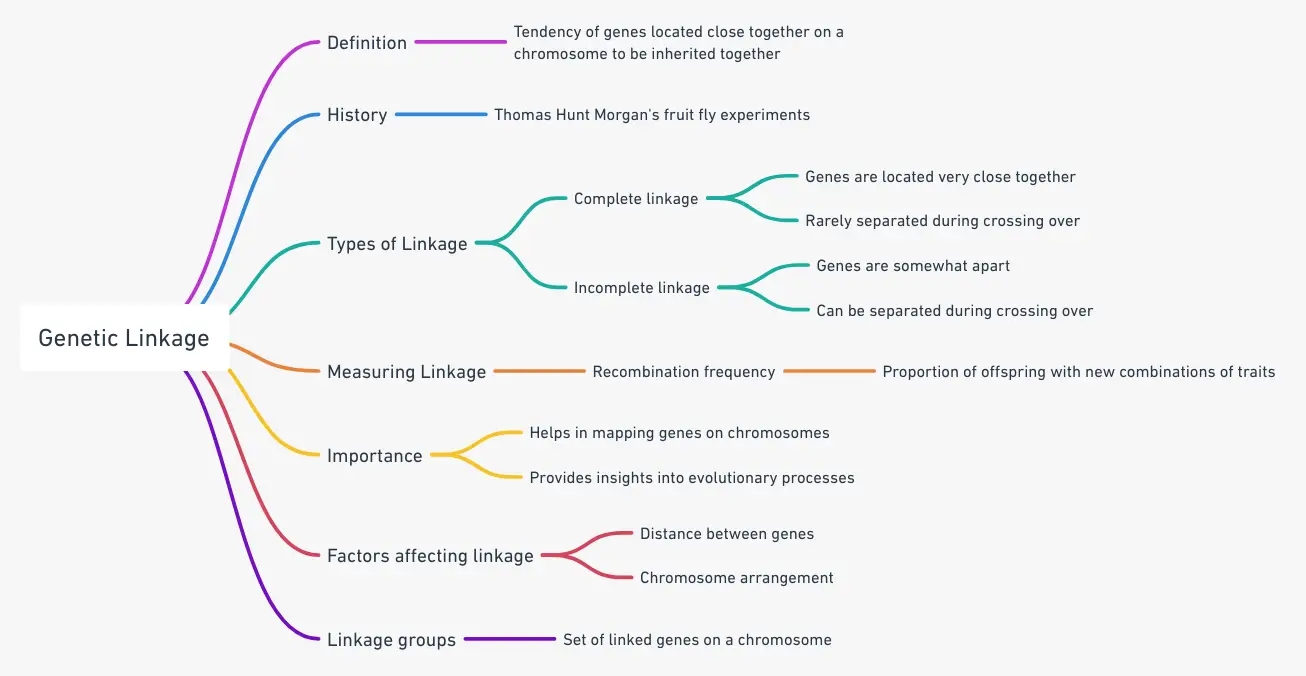
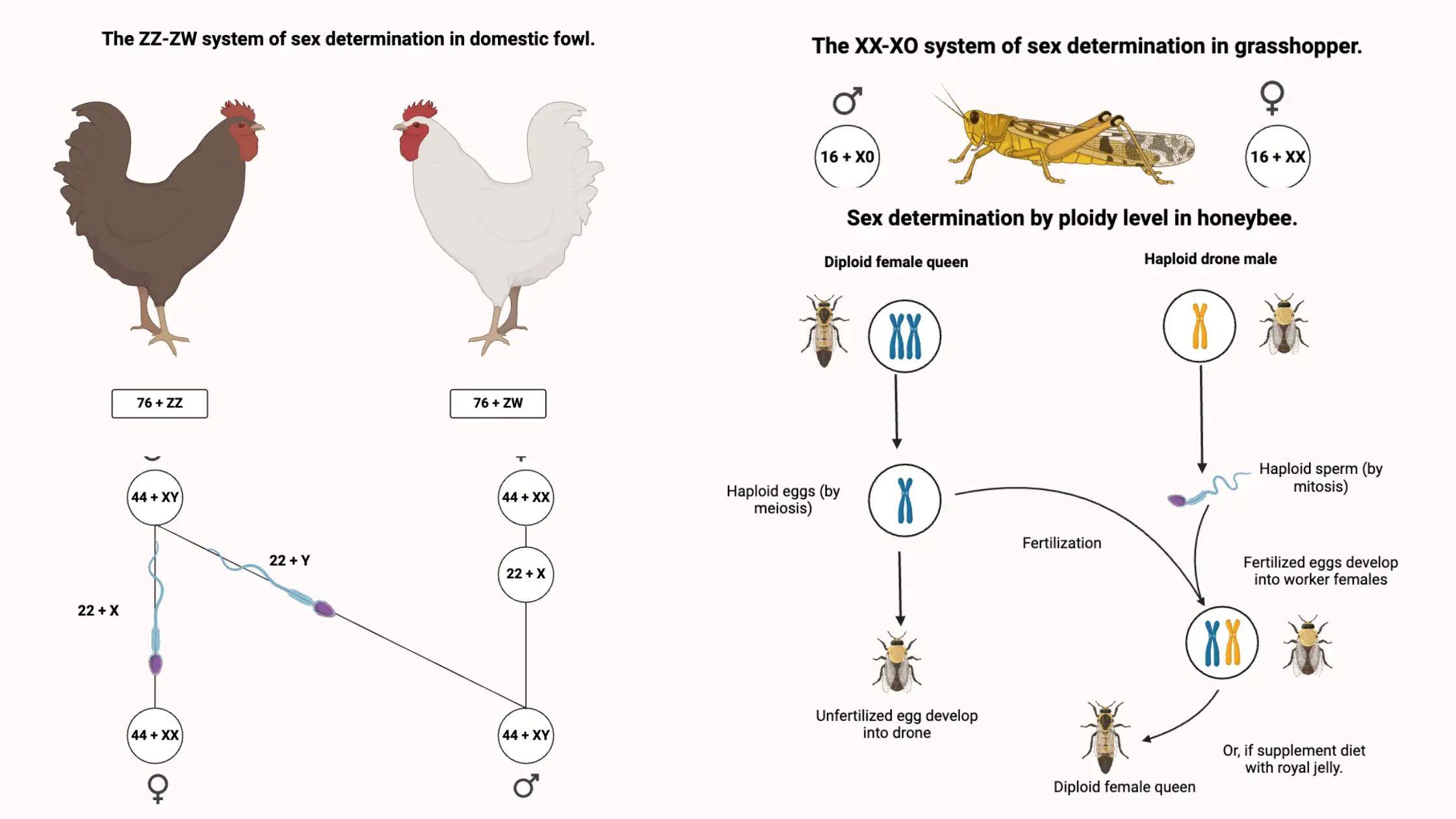
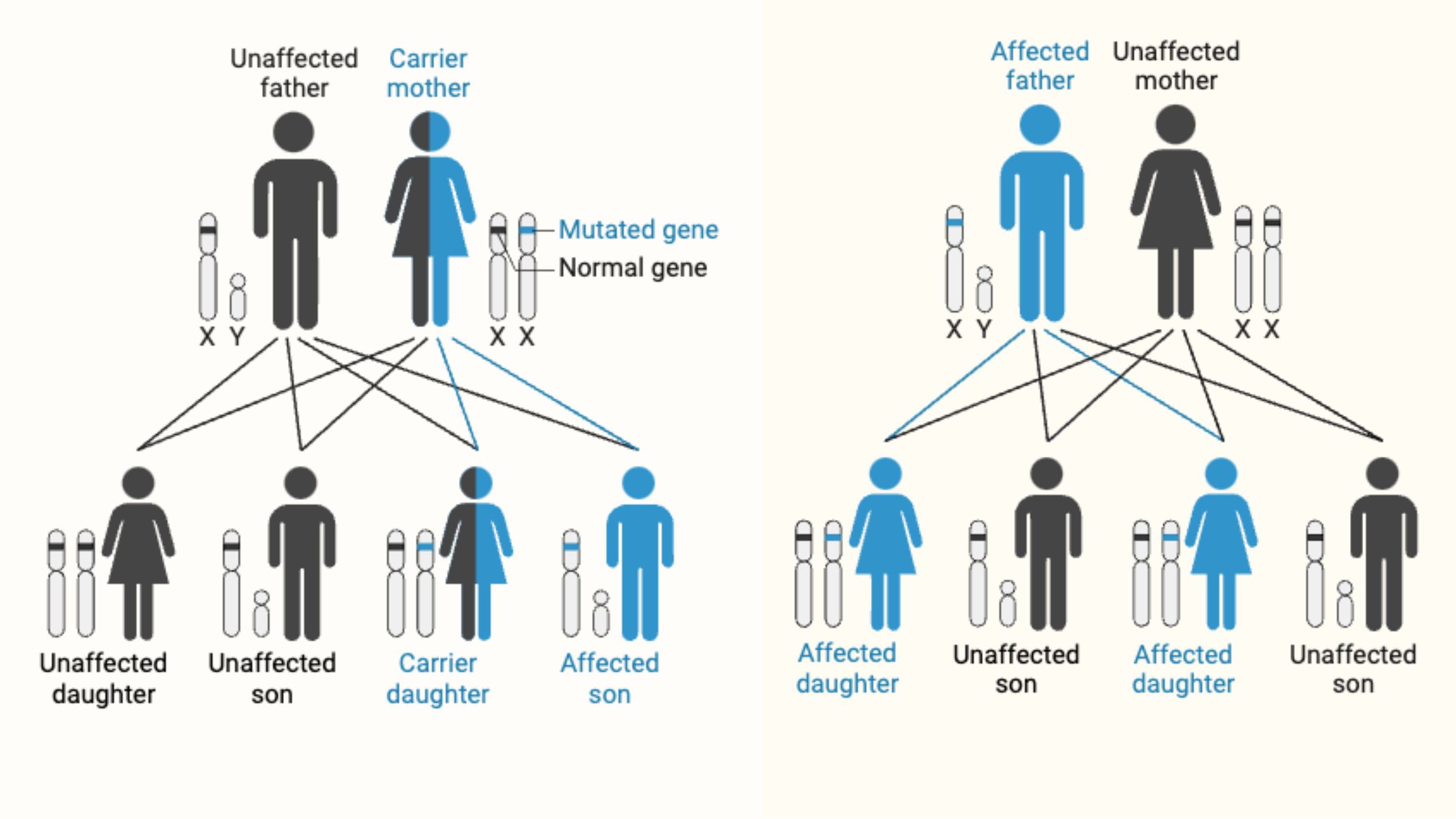
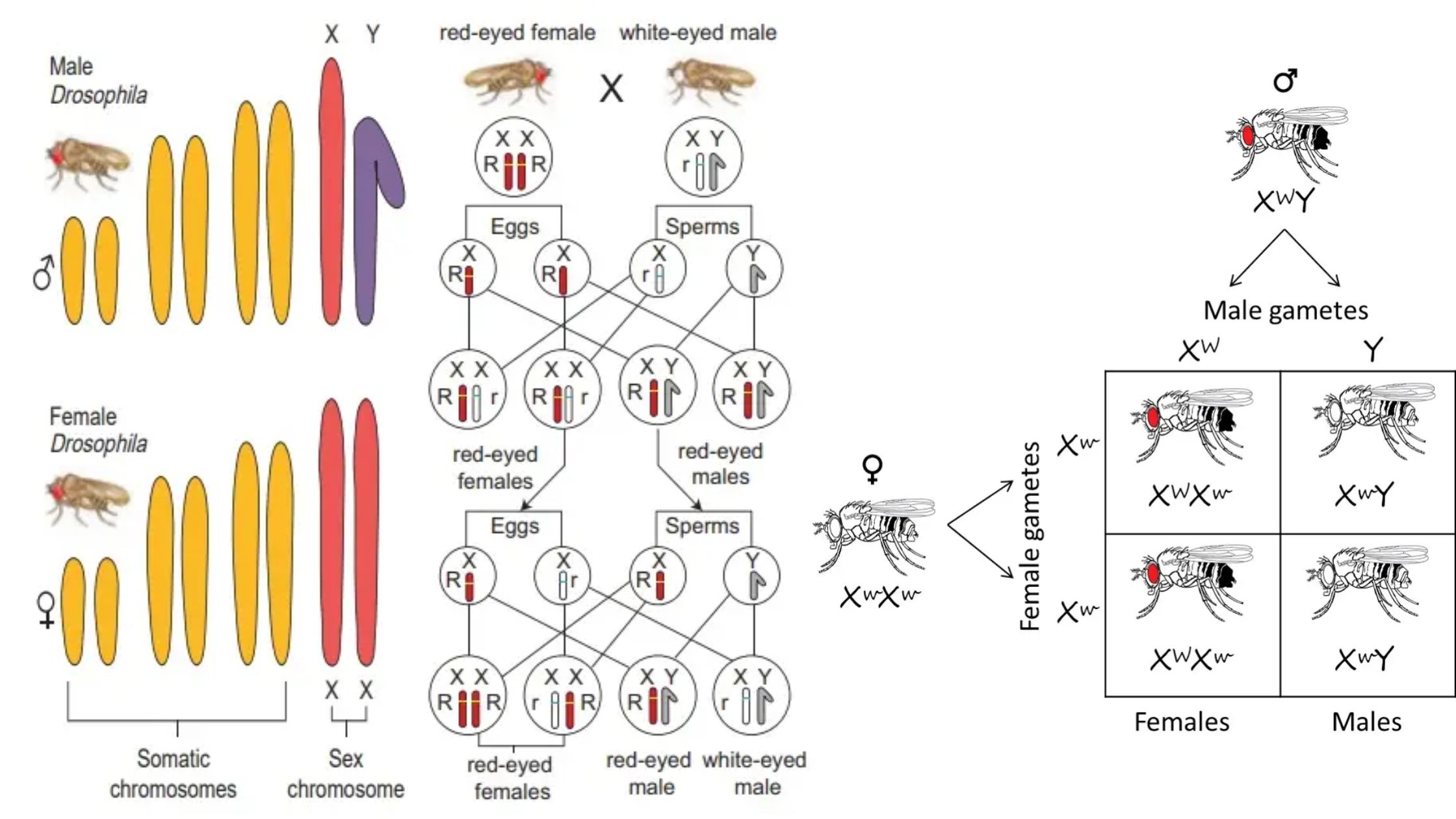
Induced Mutation – Definition, Mechanism, Examples
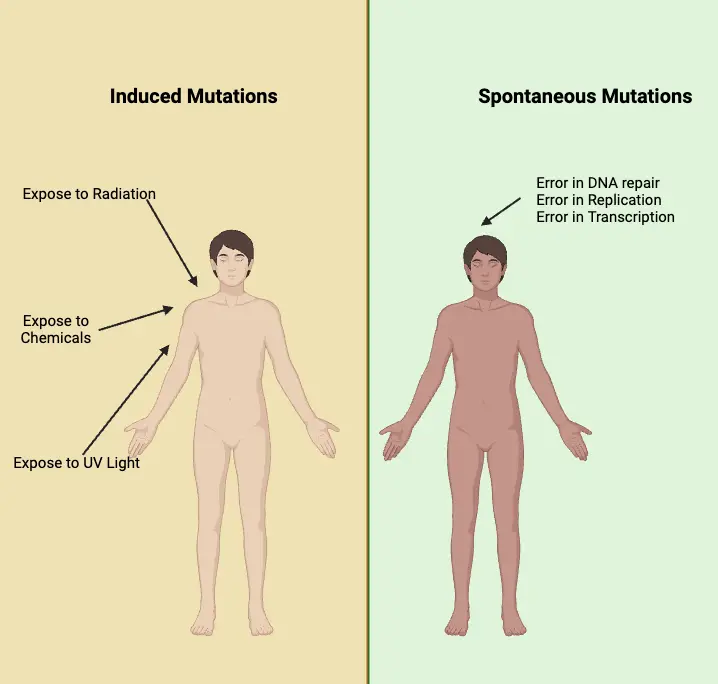
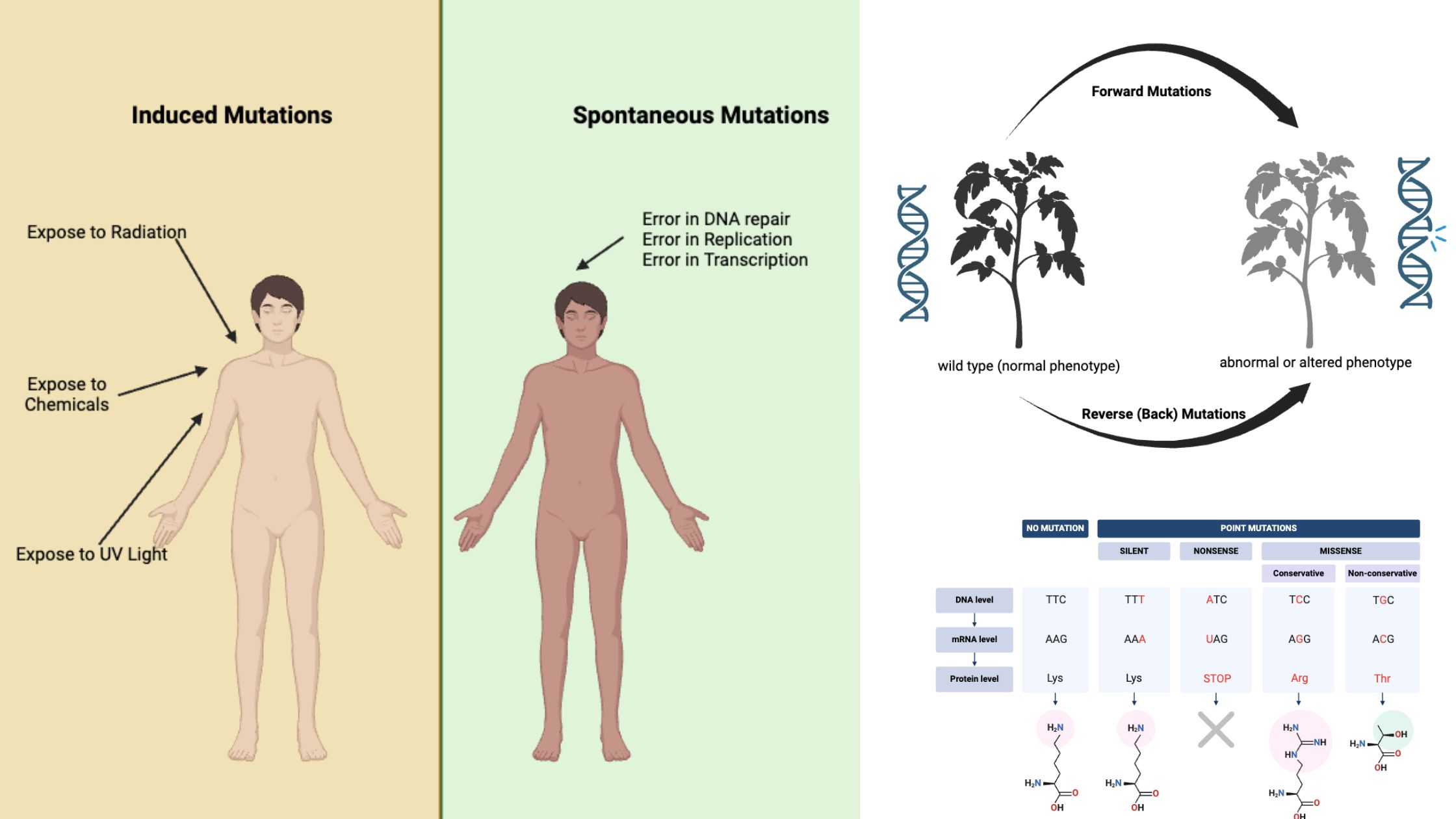
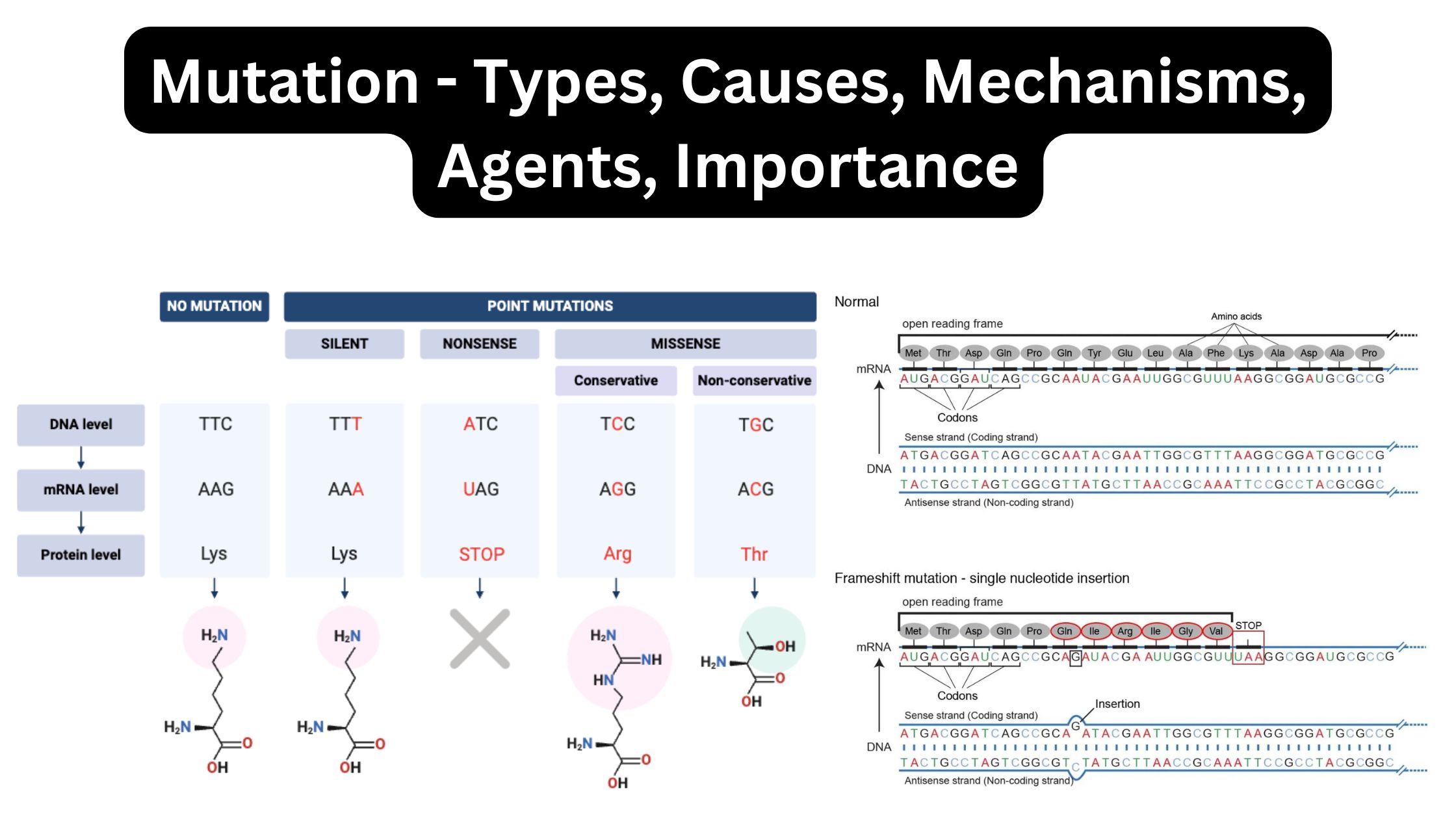
What is Induced Mutation? Mechanism of induced mutation Induced mutations occur when external agents, known as mutagens, alter the structure or sequence of DNA. These mutations can arise through several mechanisms that affect how DNA bases interact or replicate. Let’s explore the primary mechanisms responsible for induced mutations. Base Replacement by Base Analogs Base analogs … Read more