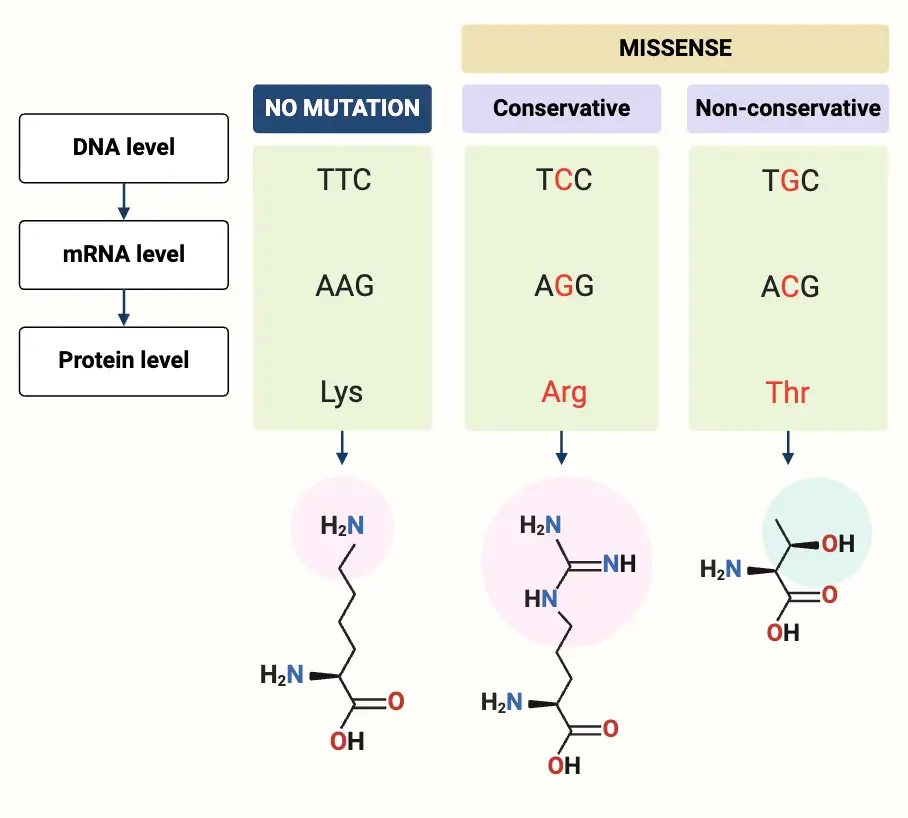
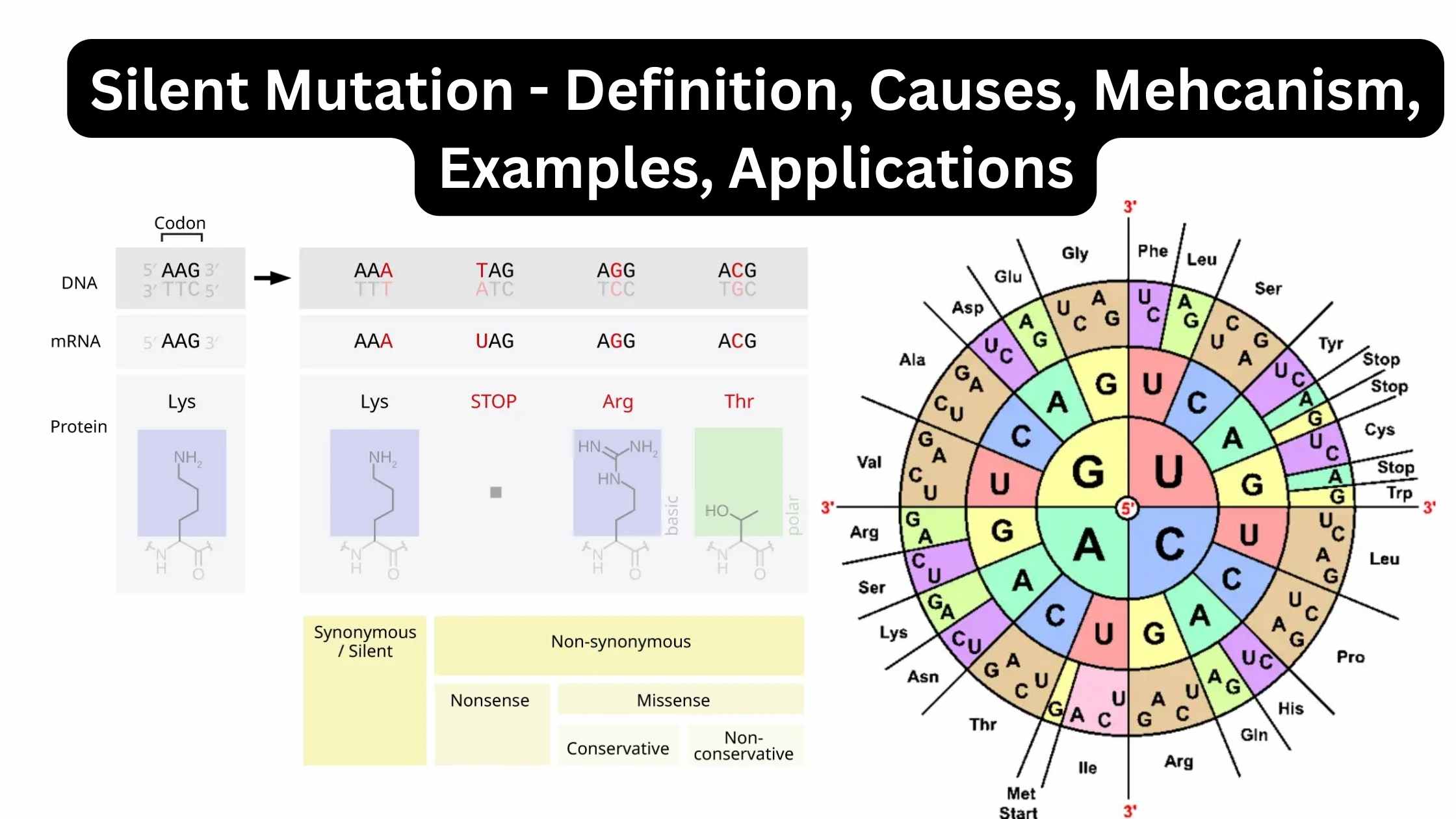
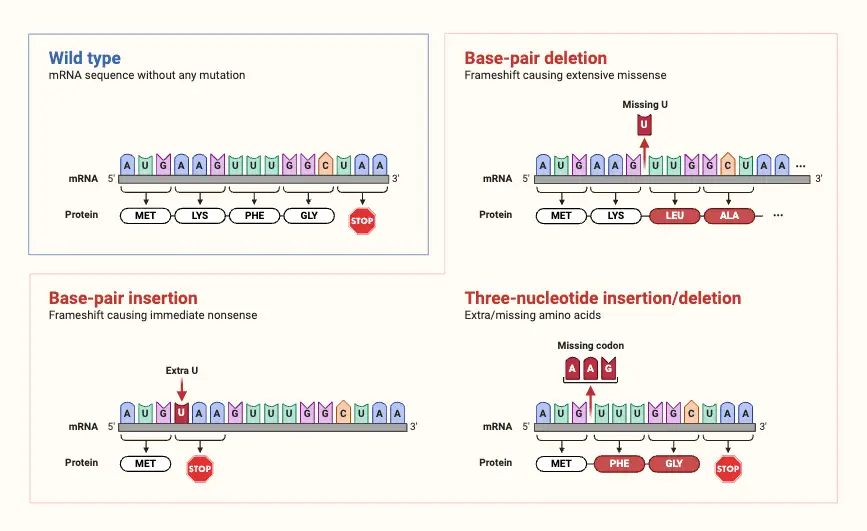
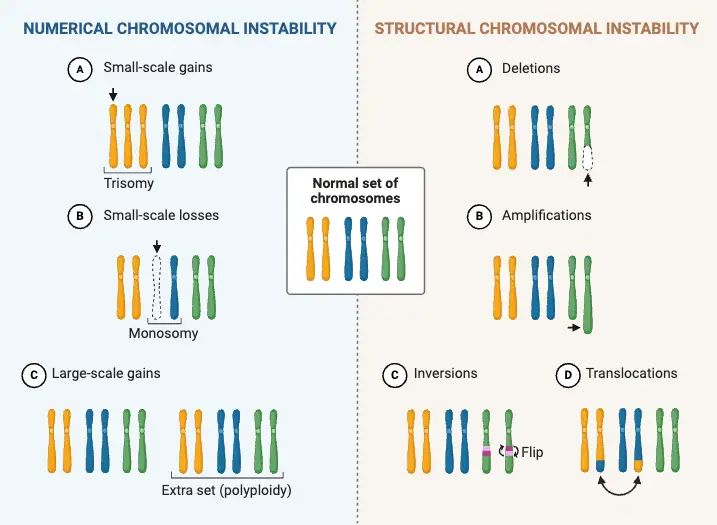
Gene Expression and Cell Specialization – AP Biology Notes
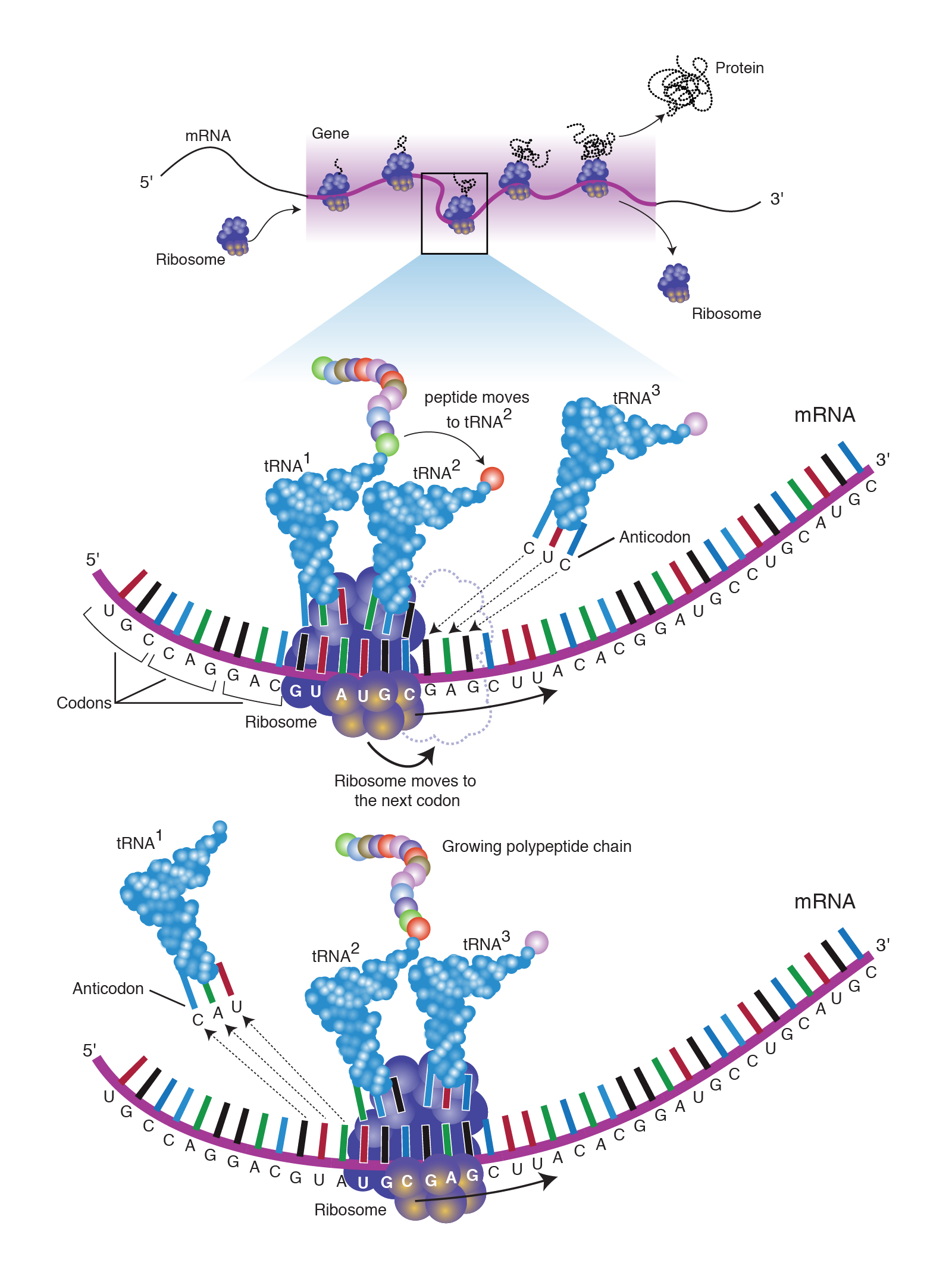
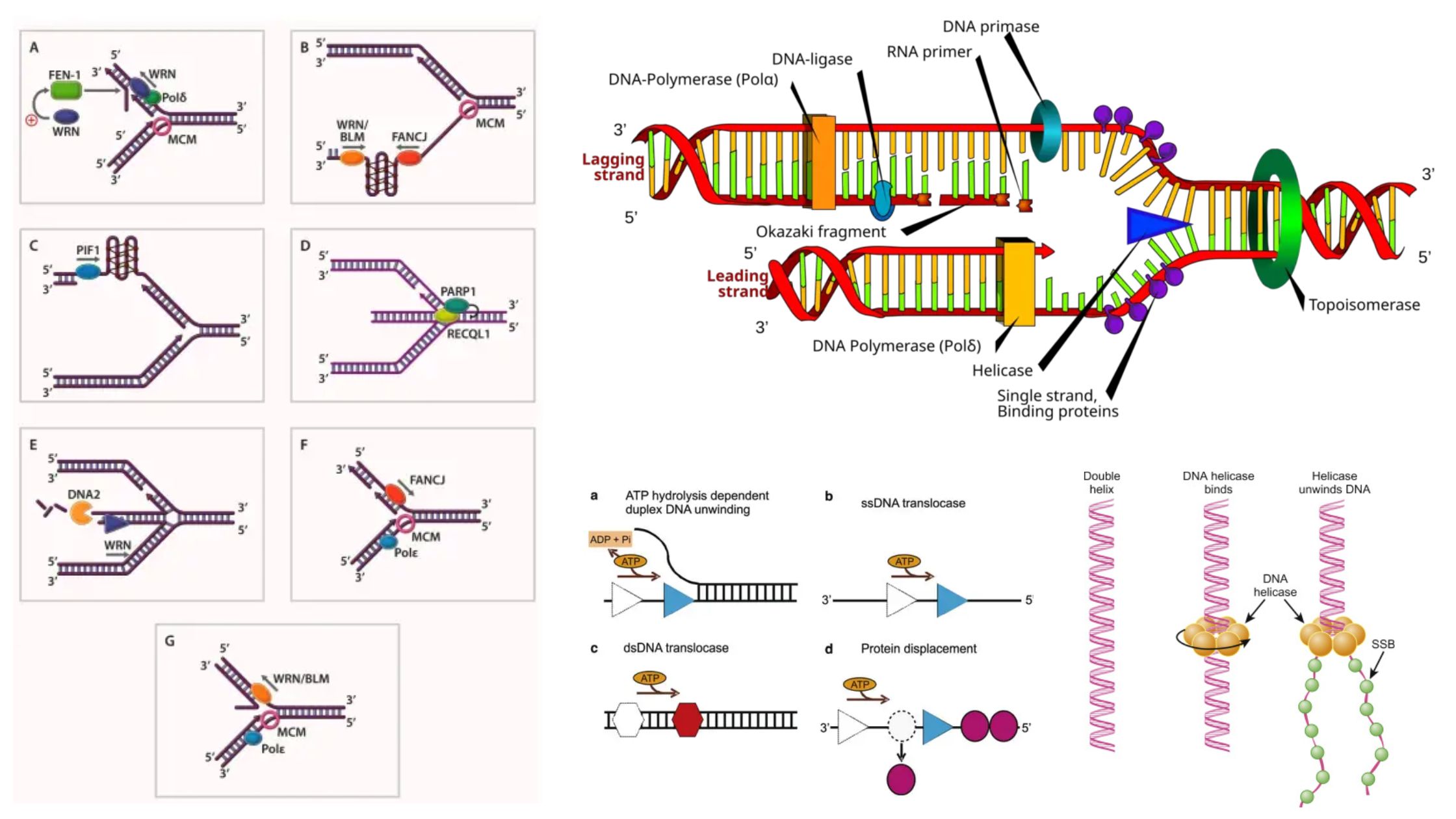
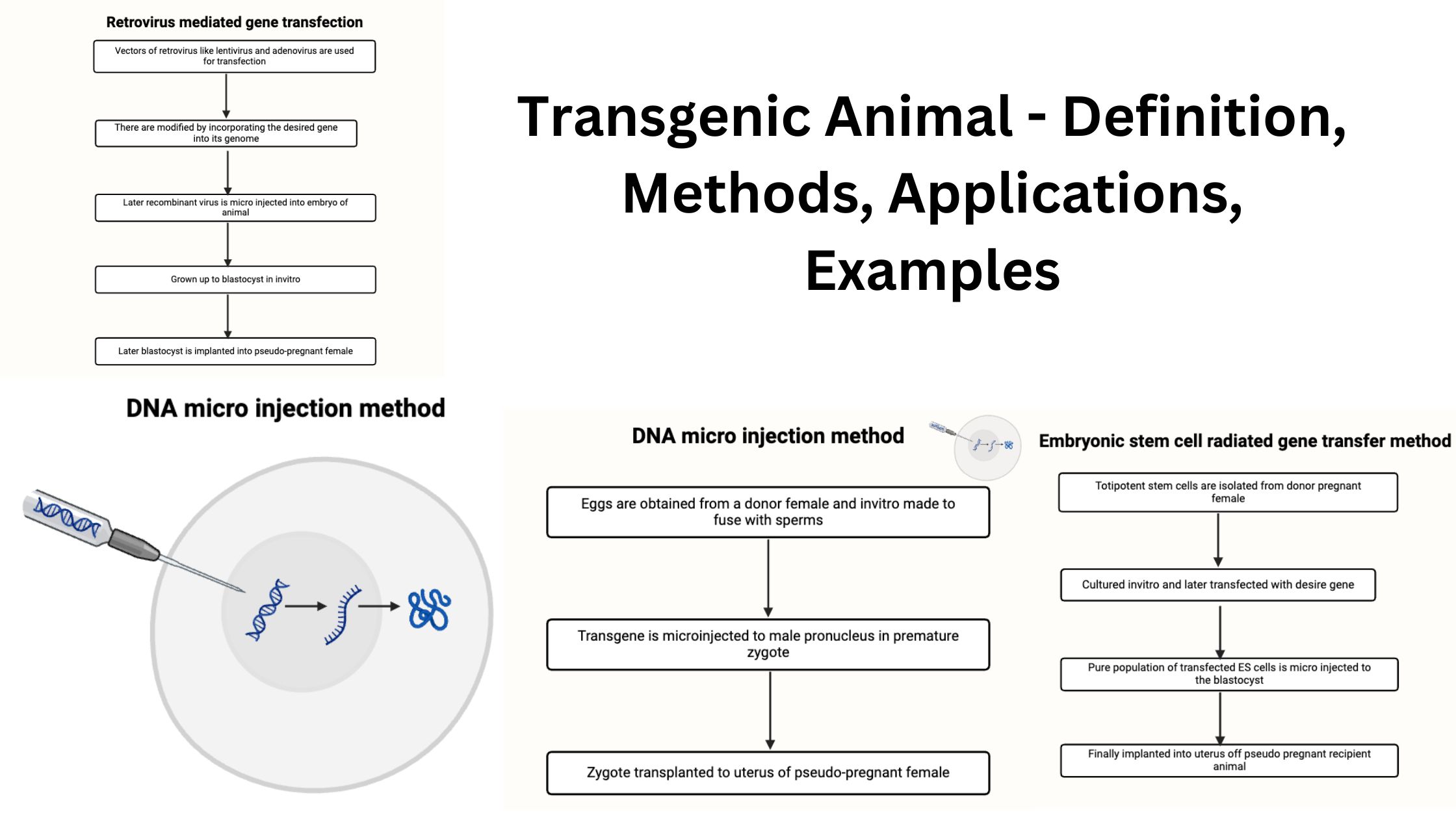
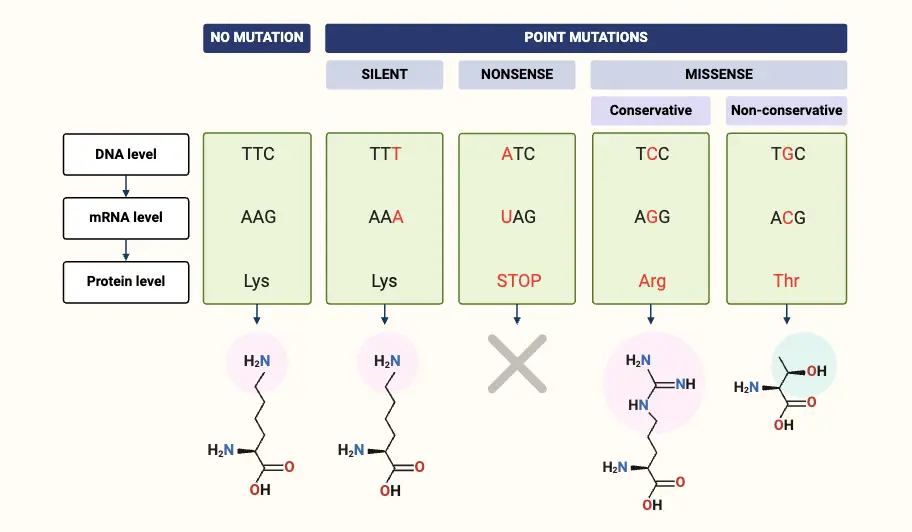
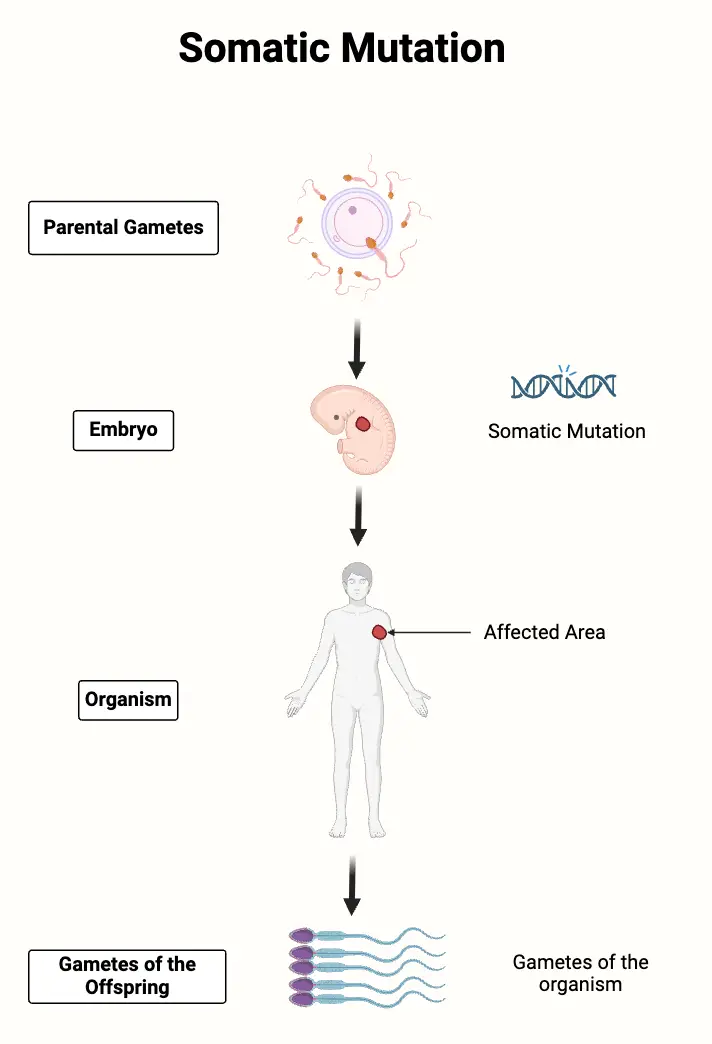
What is gene expression, and how does it relate to cell specialization? Gene expression is a fundamental biological process through which the information encoded in a gene is utilized to produce functional products, primarily proteins. This mechanism plays a crucial role in cell specialization, often referred to as cell differentiation, wherein generic cells evolve into … Read more