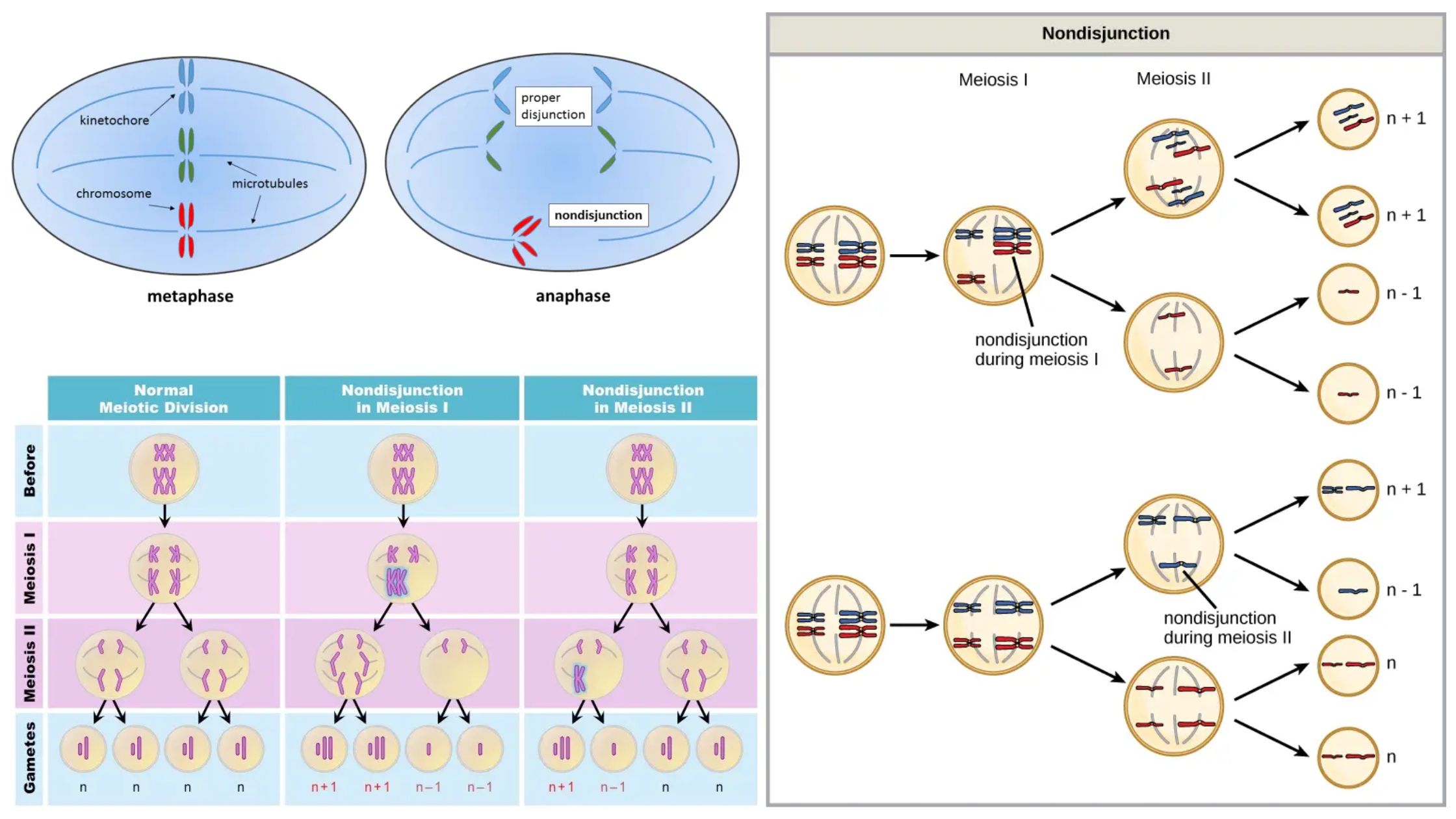
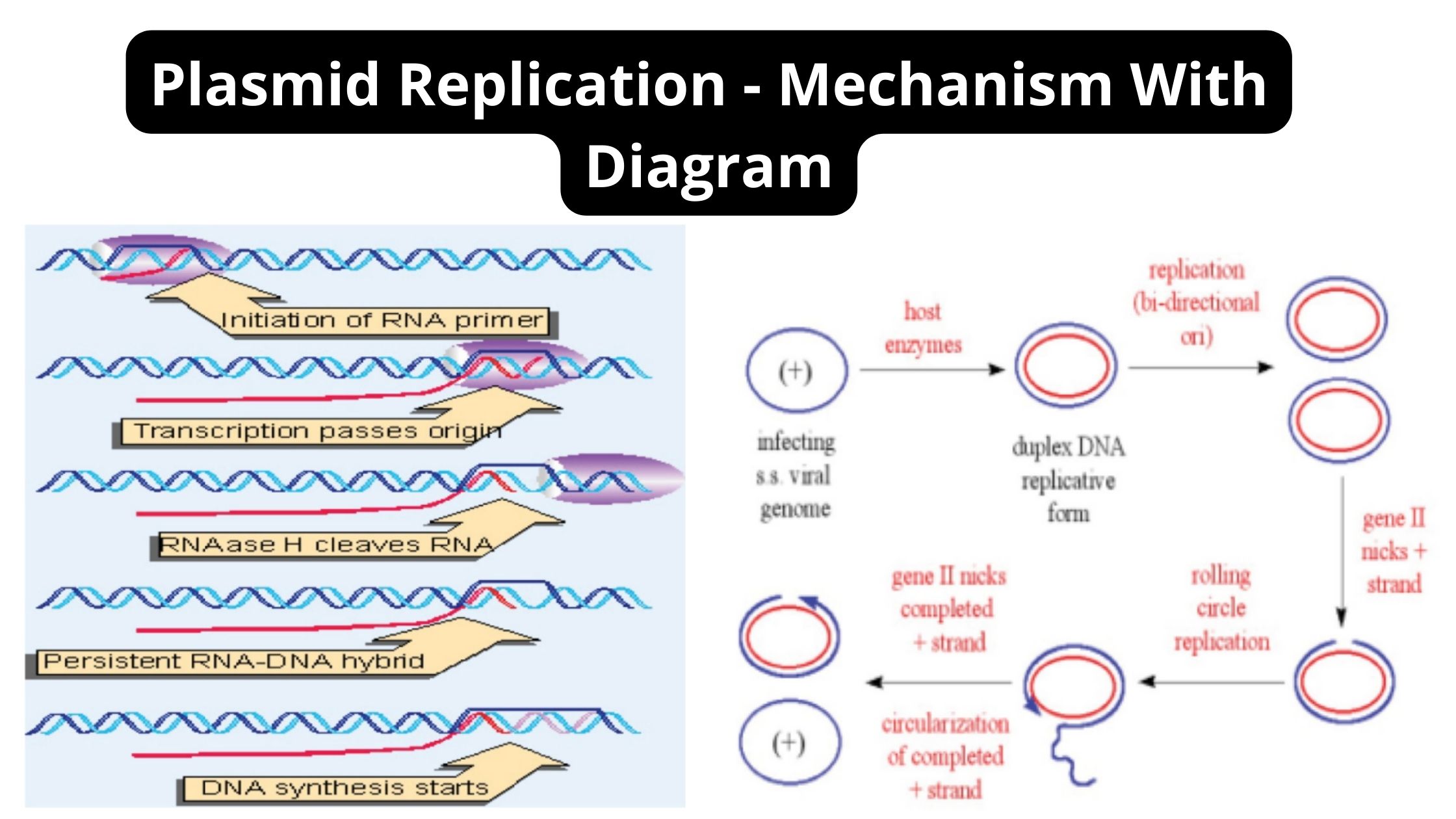
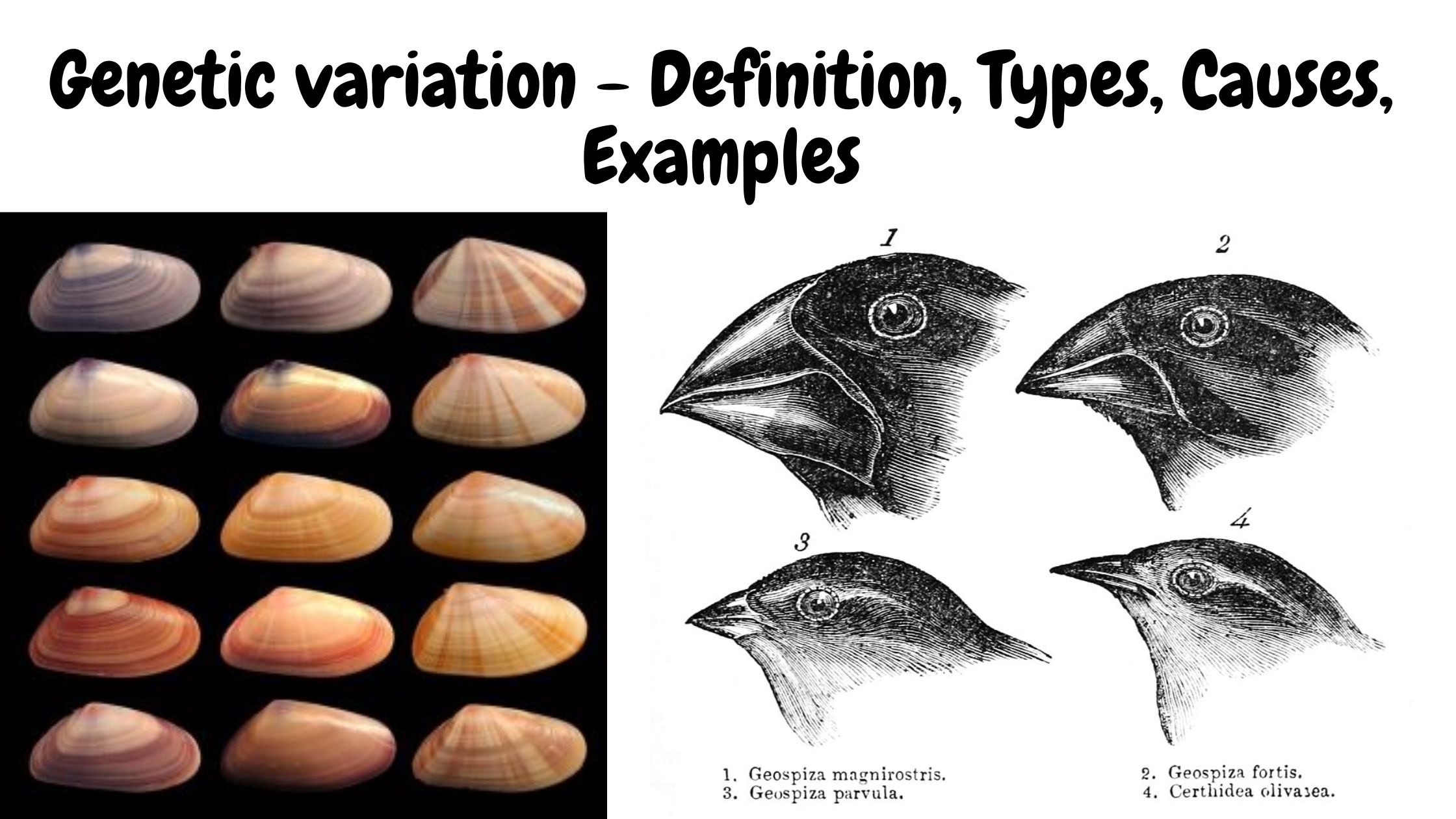
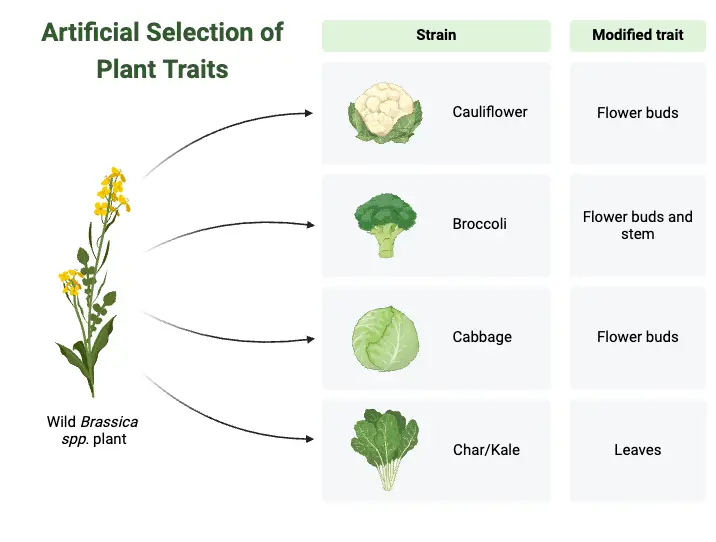
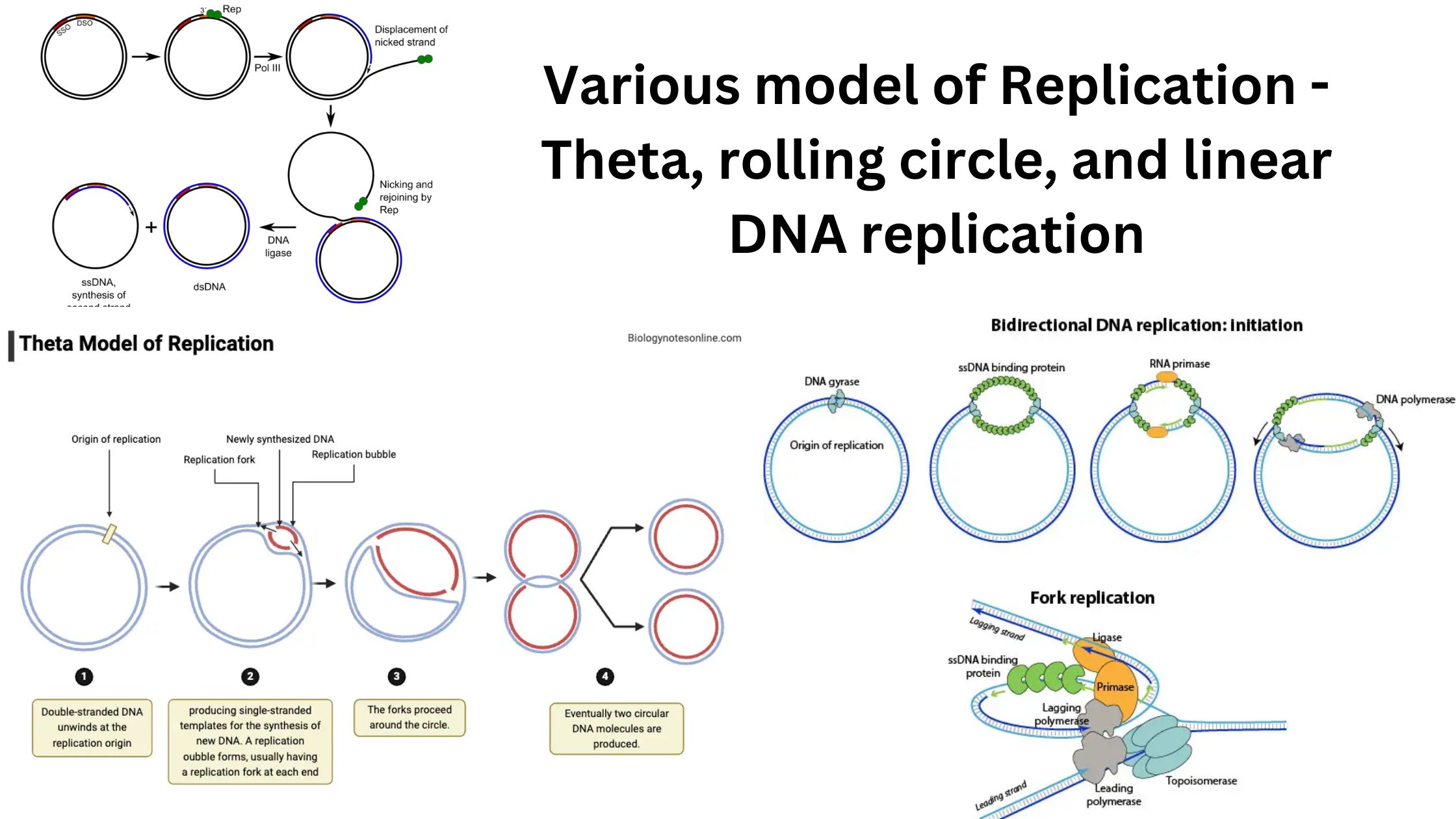
Transposition – Definition, Types, Mechanism
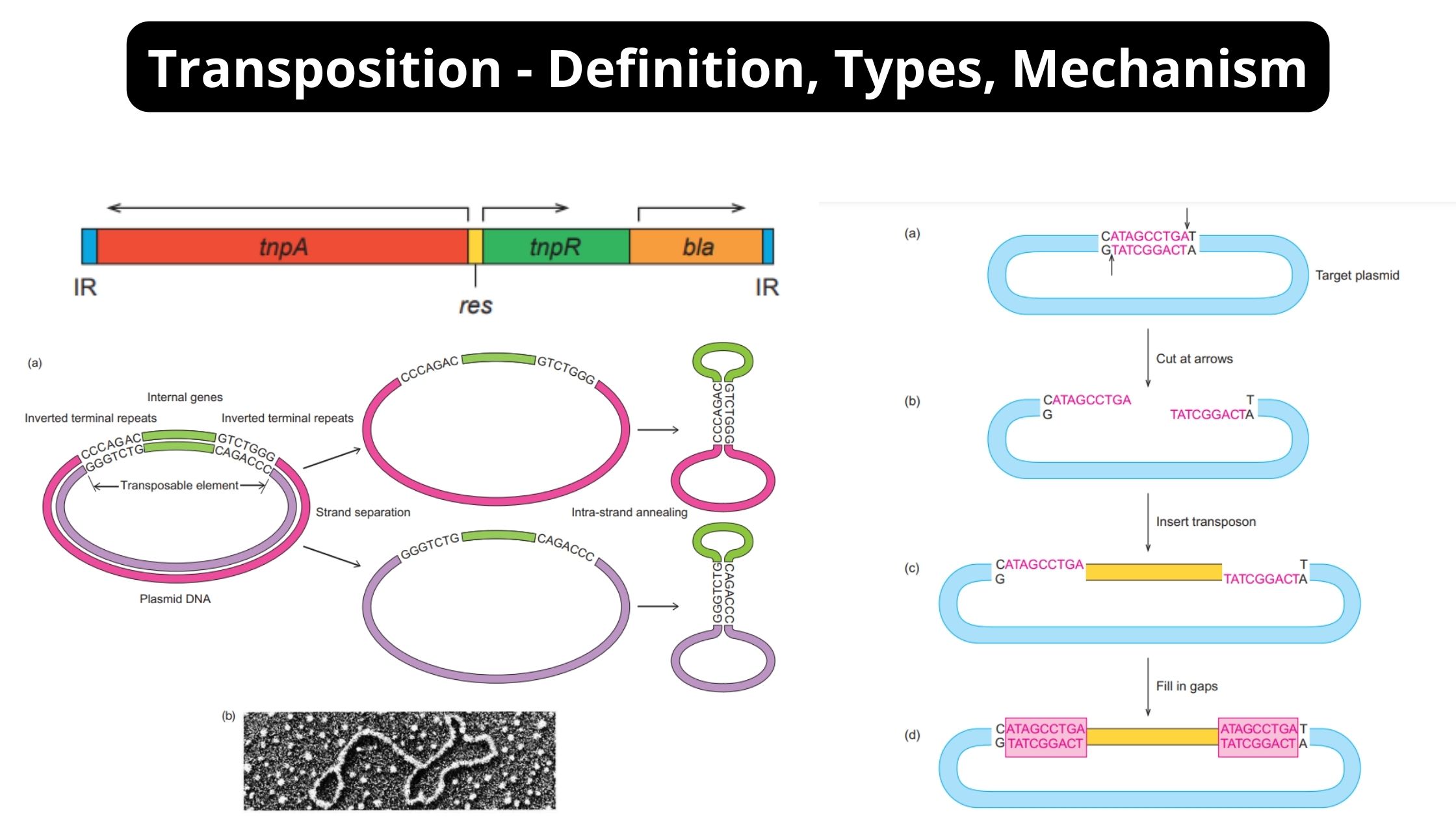
What is Transposition? Transposition is the process in which a particular DNA sequence is shifted from one position of the genome to another position. It is the movement of a transposable element or jumping gene, and it is not dependent on any homologous sequence at the target site. It is the process that may occur … Read more