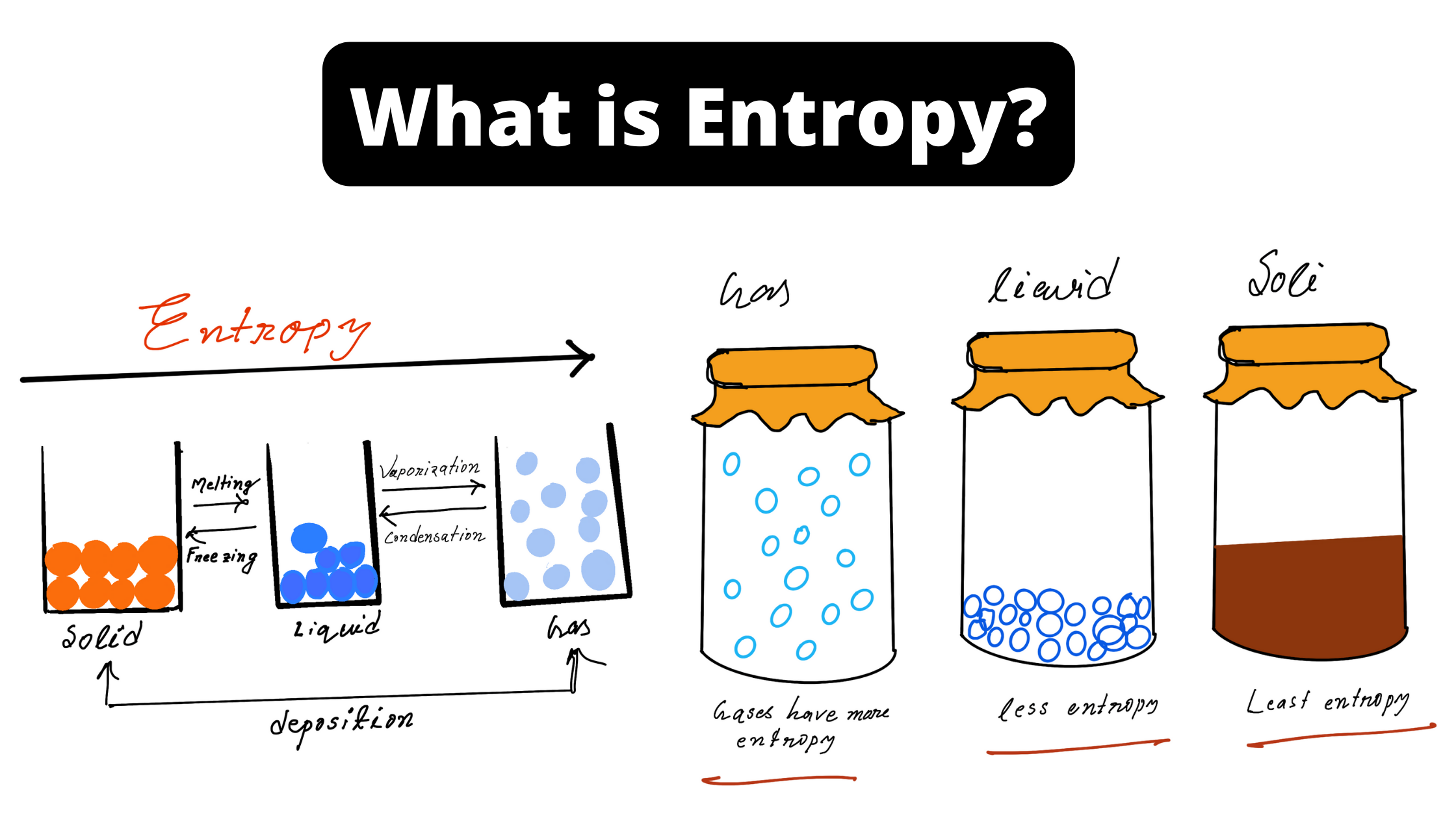
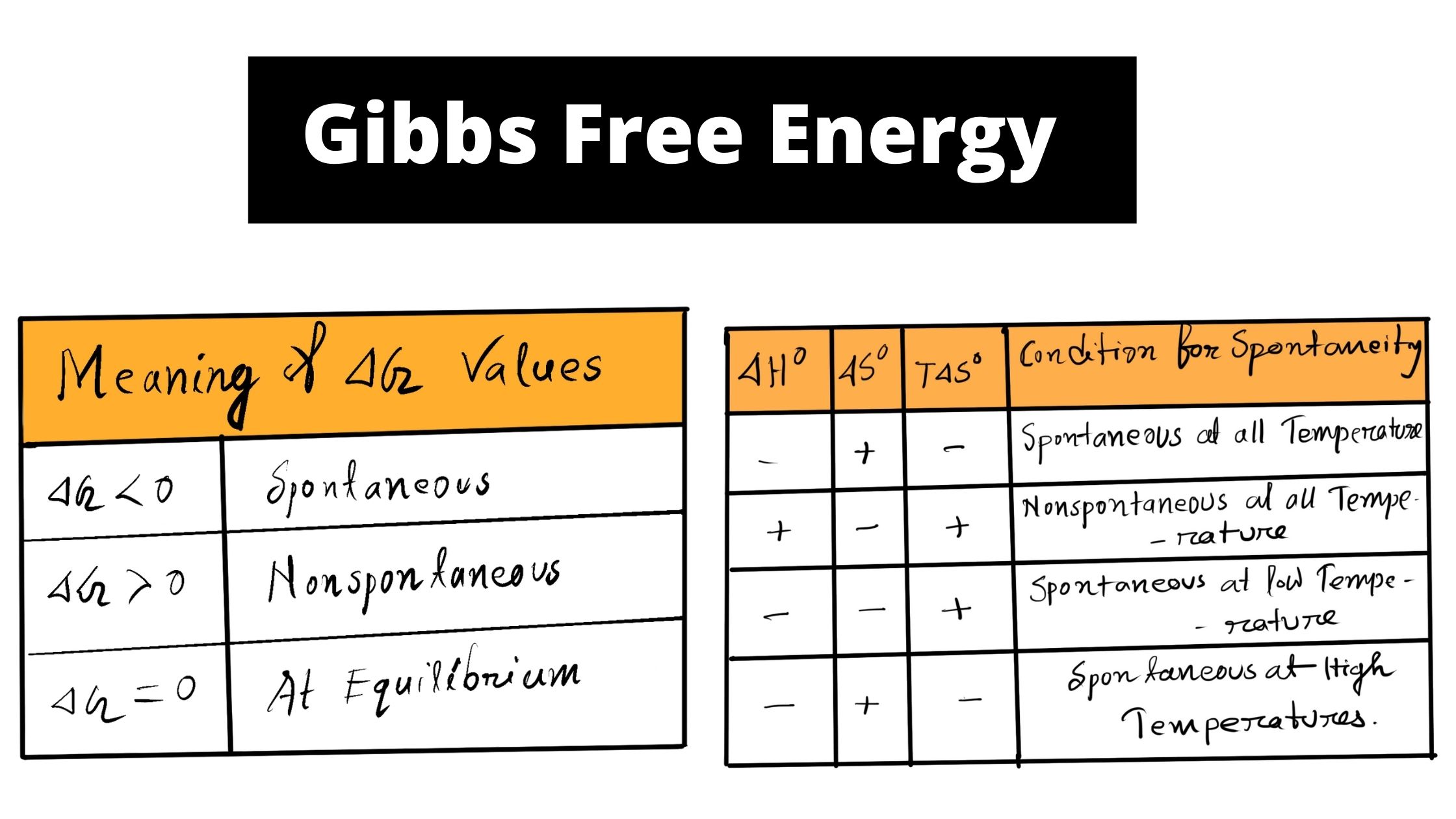
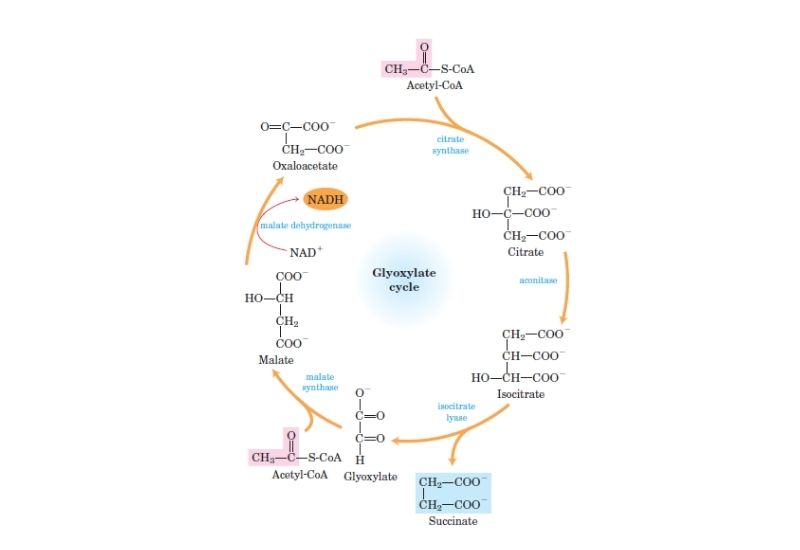
What is Entropy?
Entropy is among the most important concepts that students should be able to comprehend clearly when learning Chemistry as well as Physics. In addition, entropy may be described in a variety of ways, which means it can be used in a variety of stages or scenarios, like the thermodynamics stage, in cosmic cosmology, or even … Read more