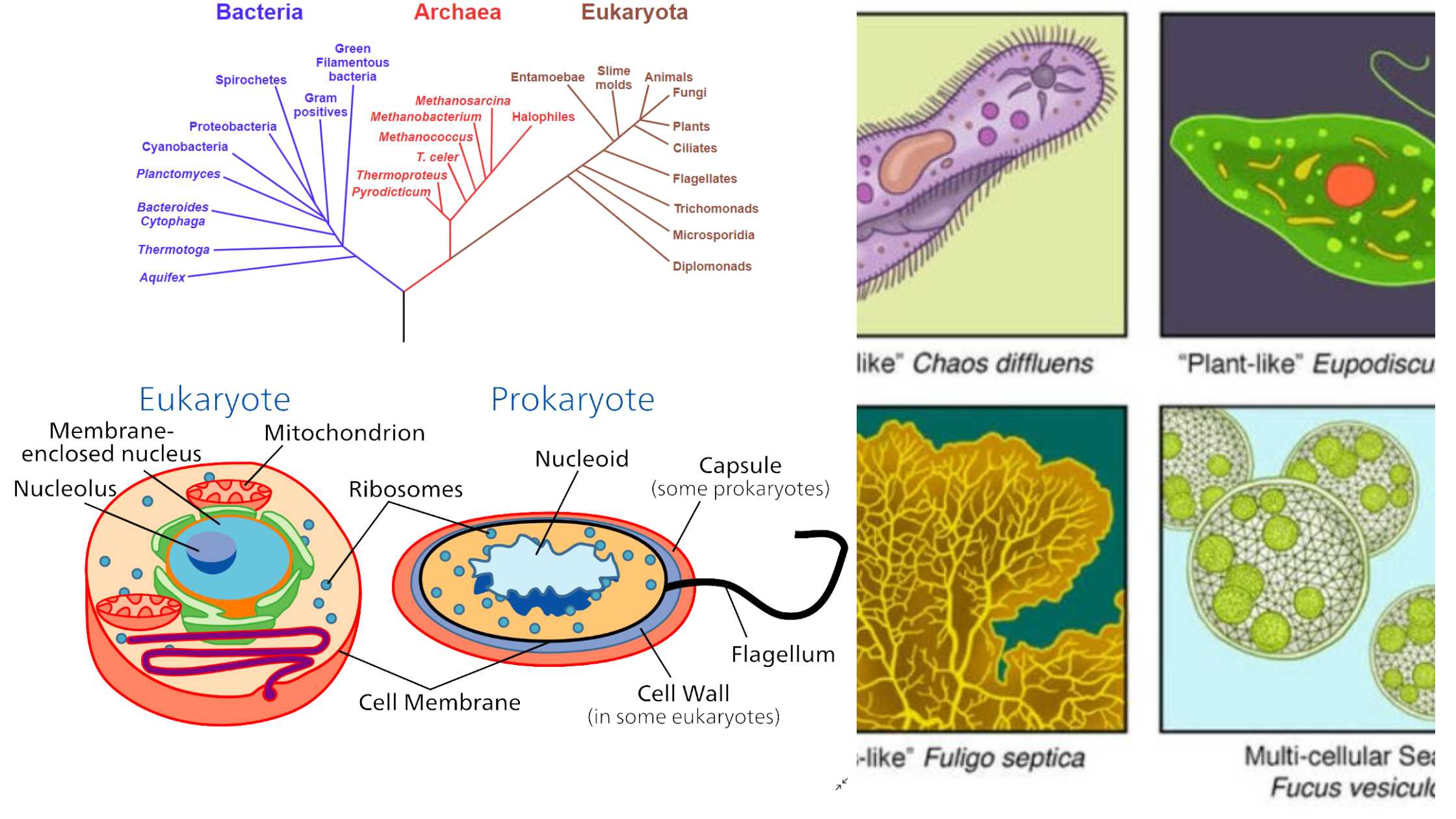
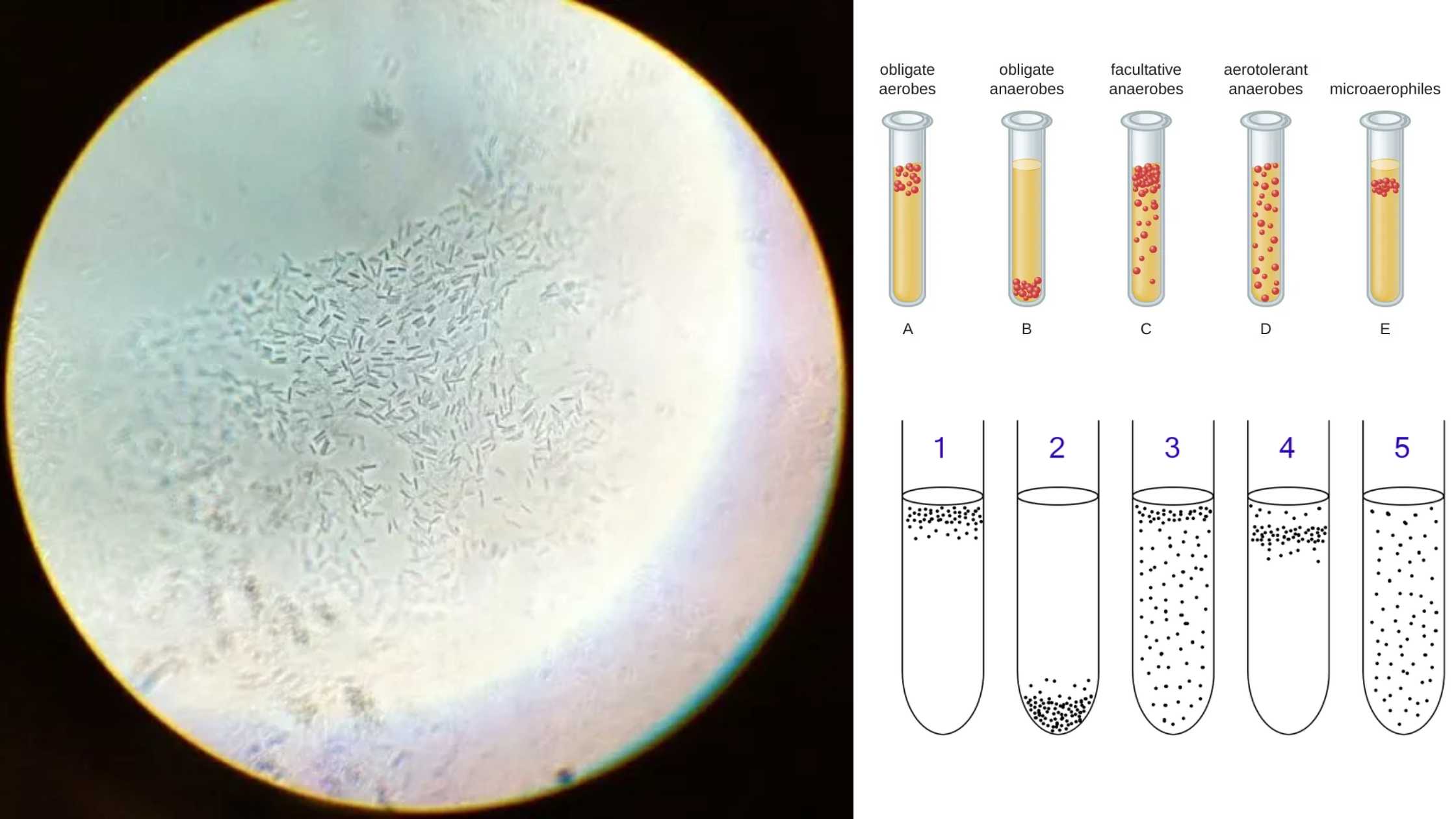
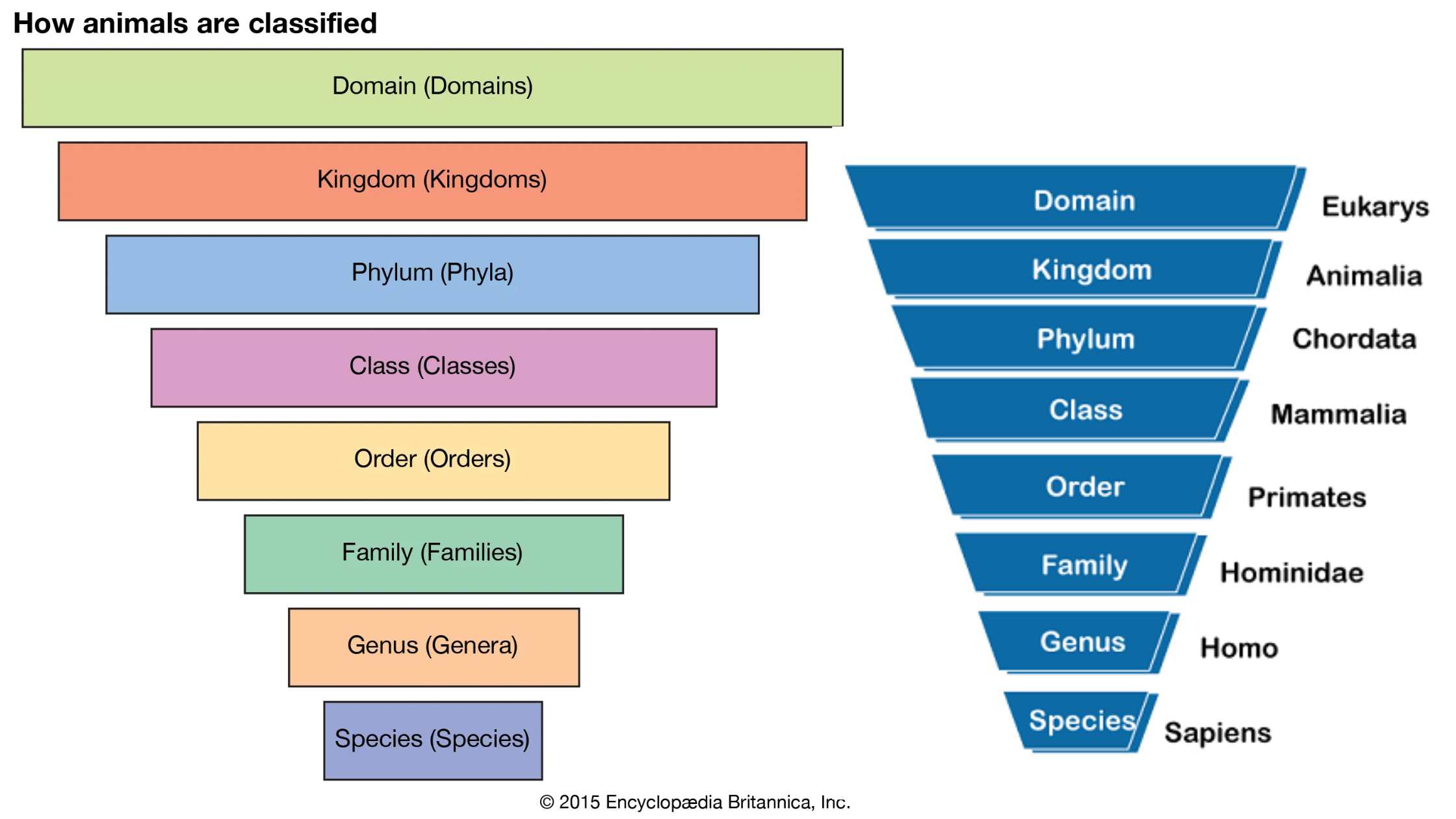
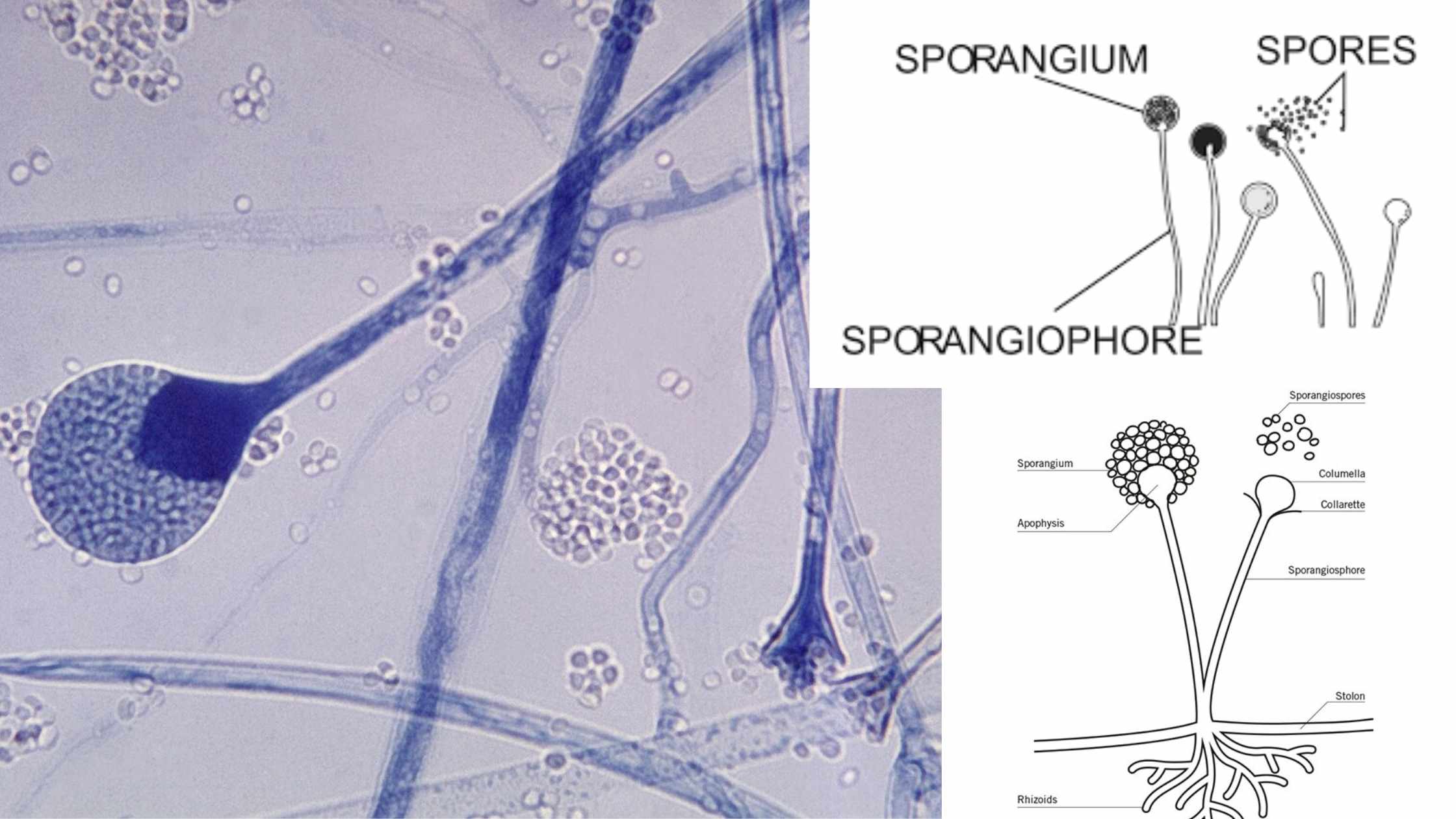
Microorganism – Definition, Types, Importance, Examples
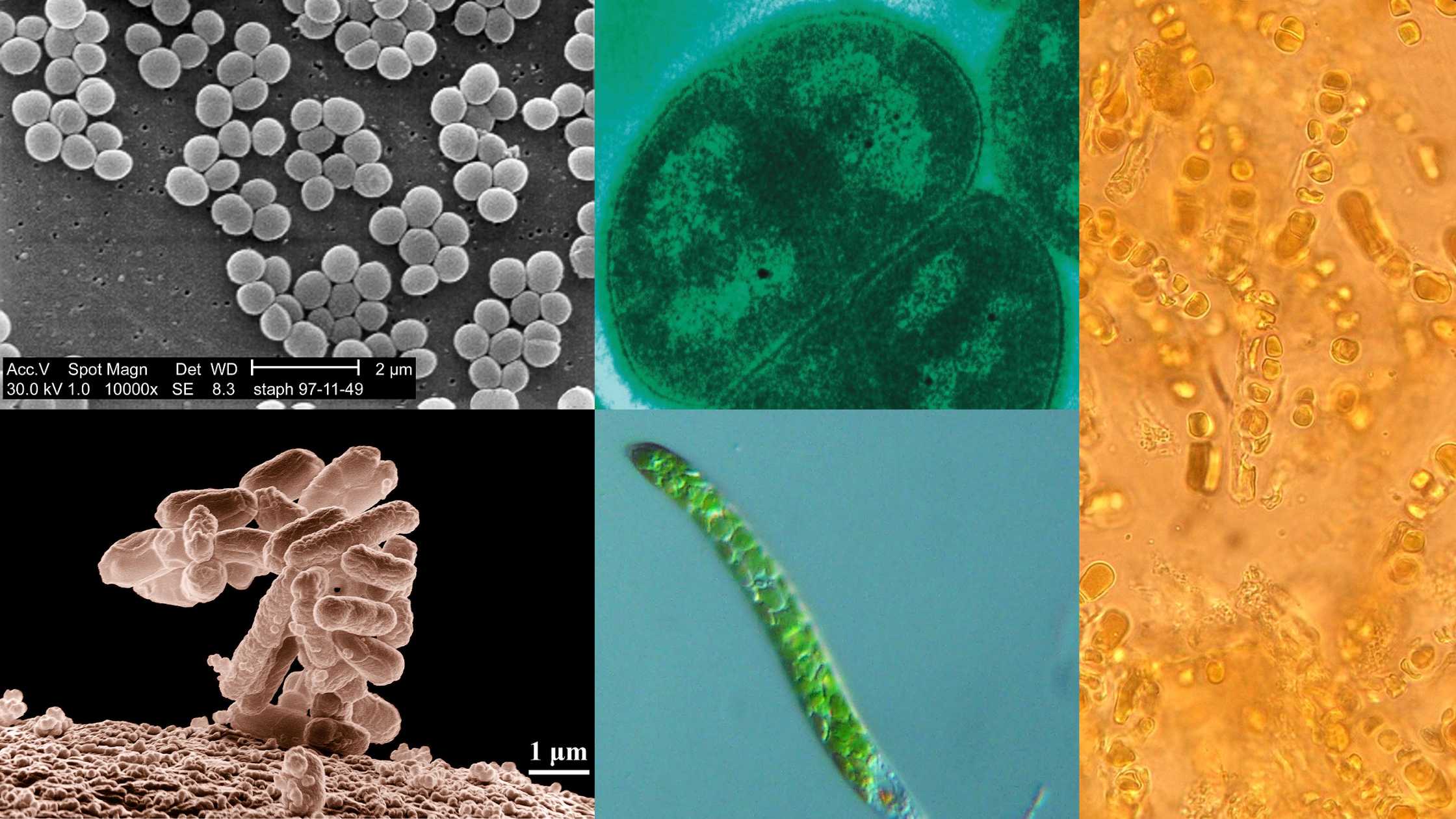
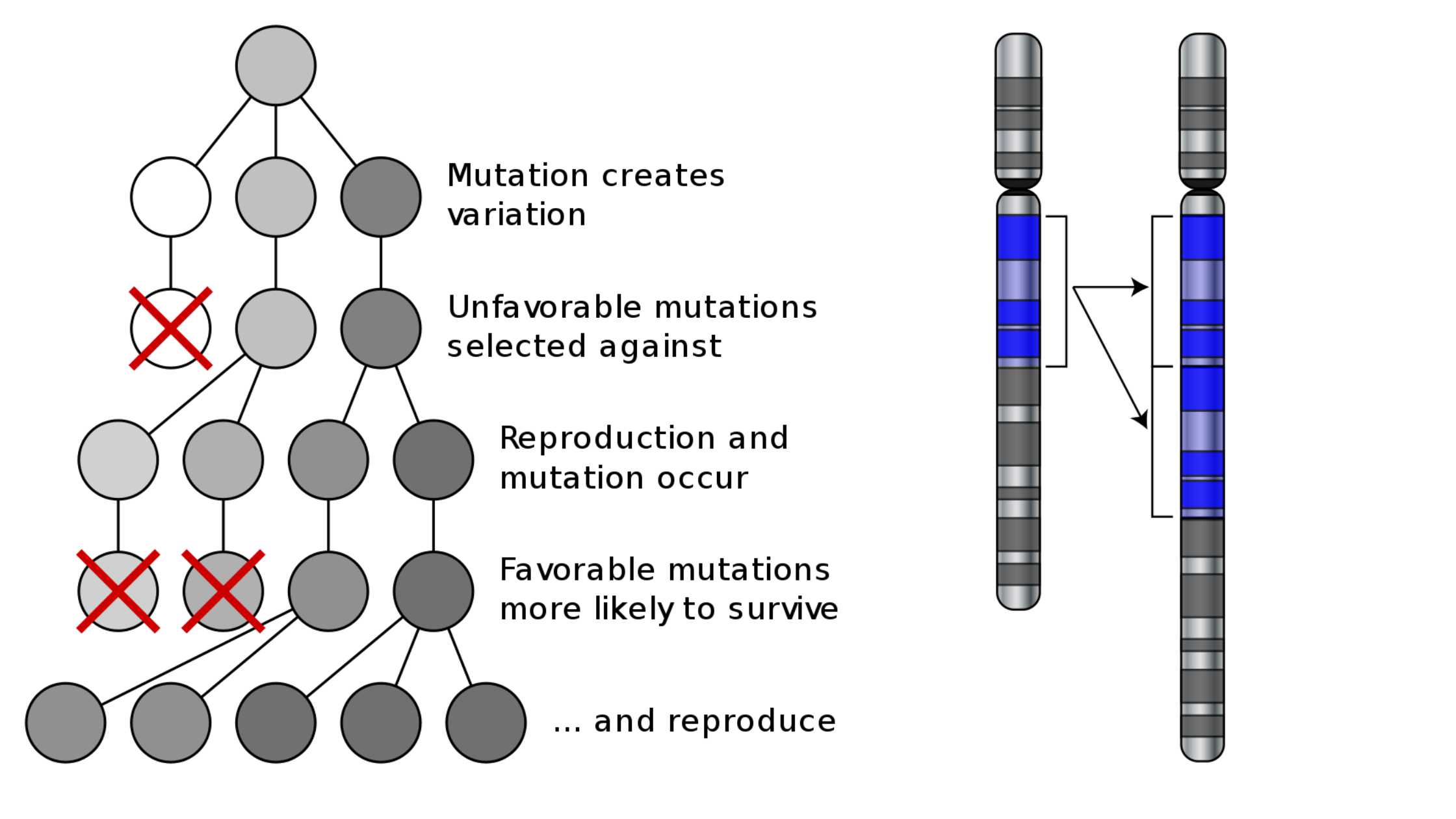
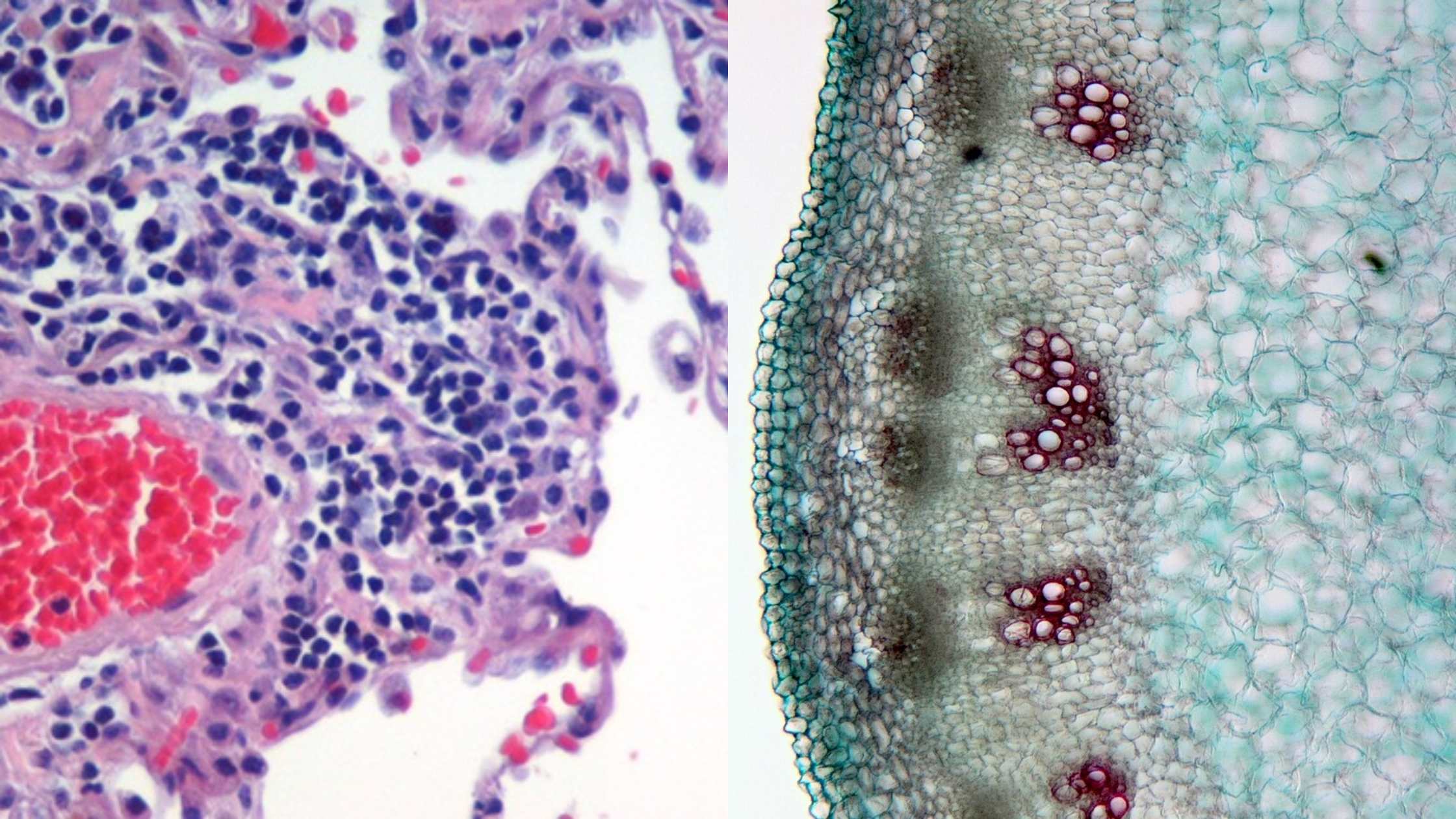
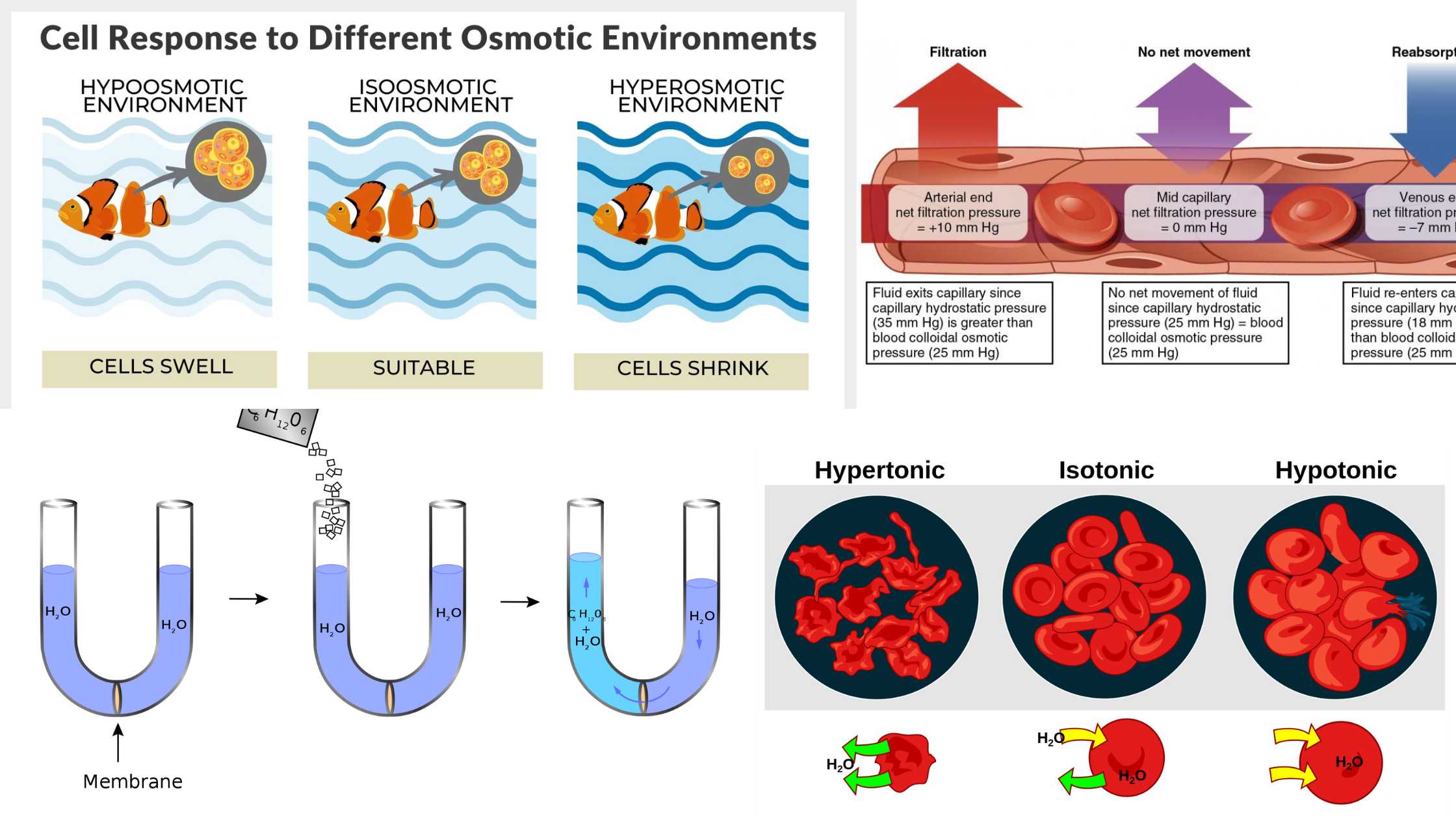
What is Microorganism? Definition of Microorganism A microorganism, or microbe, is a tiny living organism that is invisible to the naked eye and can exist as single-celled entities or colonies of cells. Discovery of Microorganisms Microorganisms, despite their minuscule size, have had a profound impact on our understanding of life and disease. The journey of … Read more