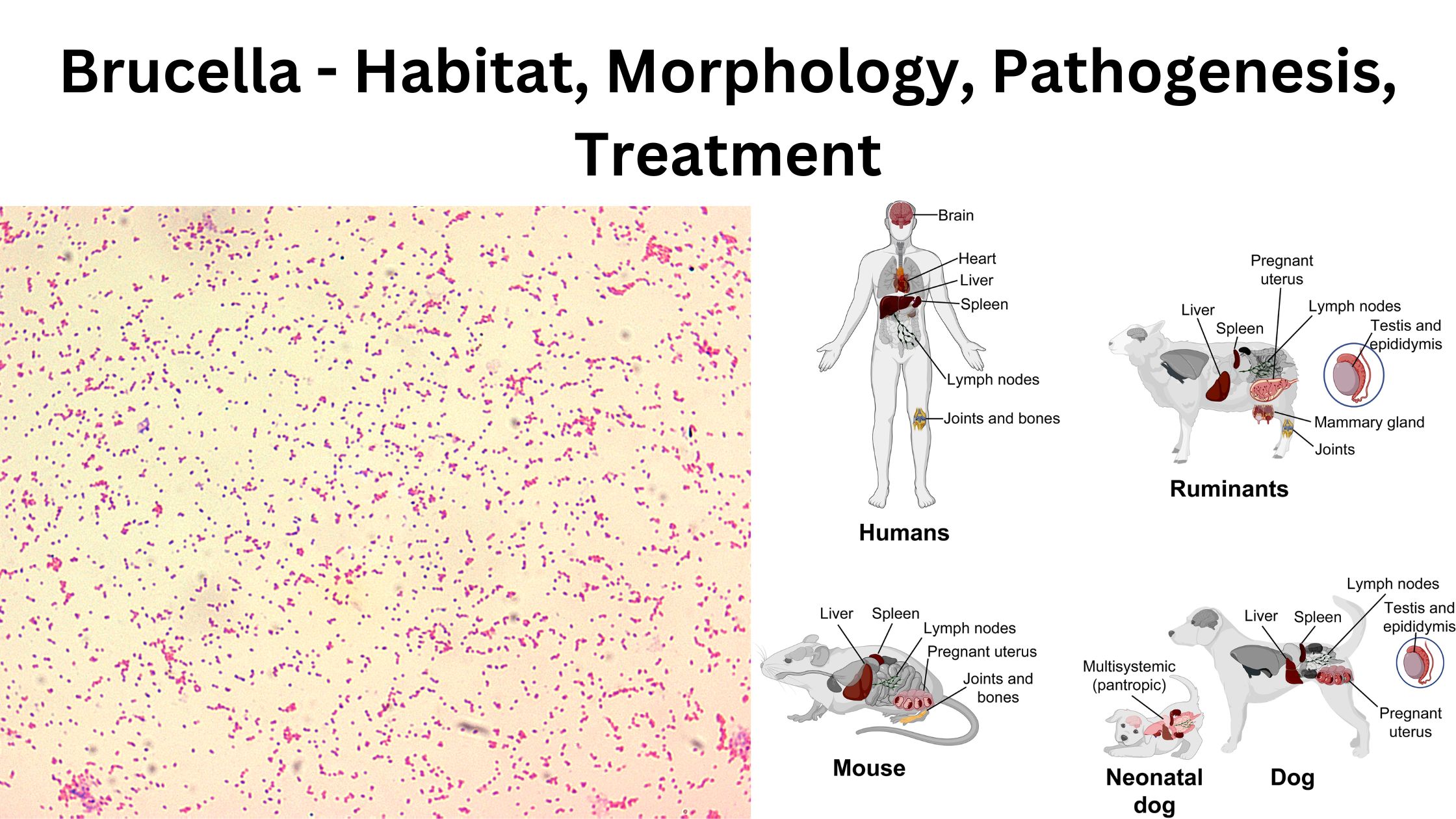
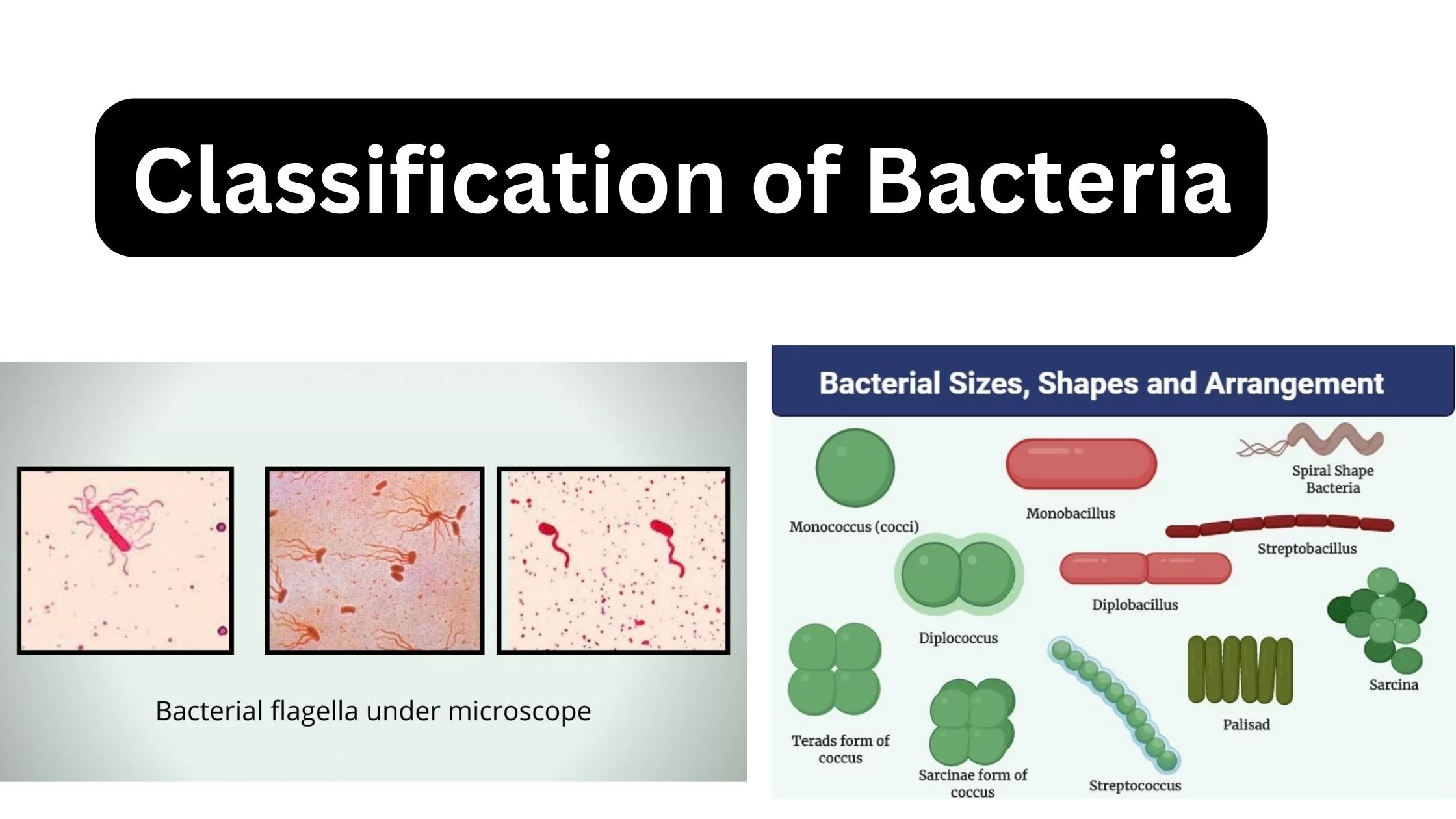
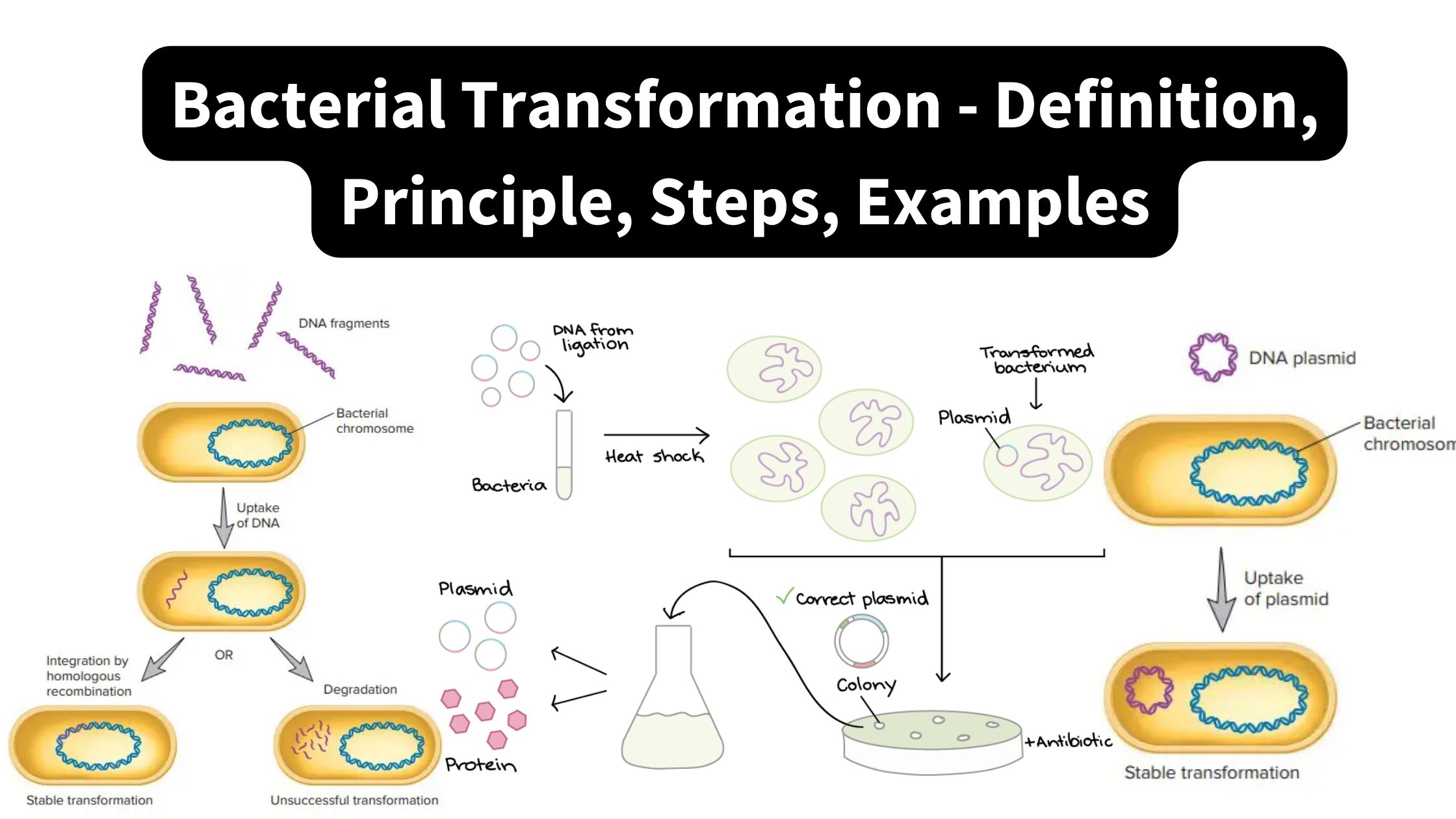
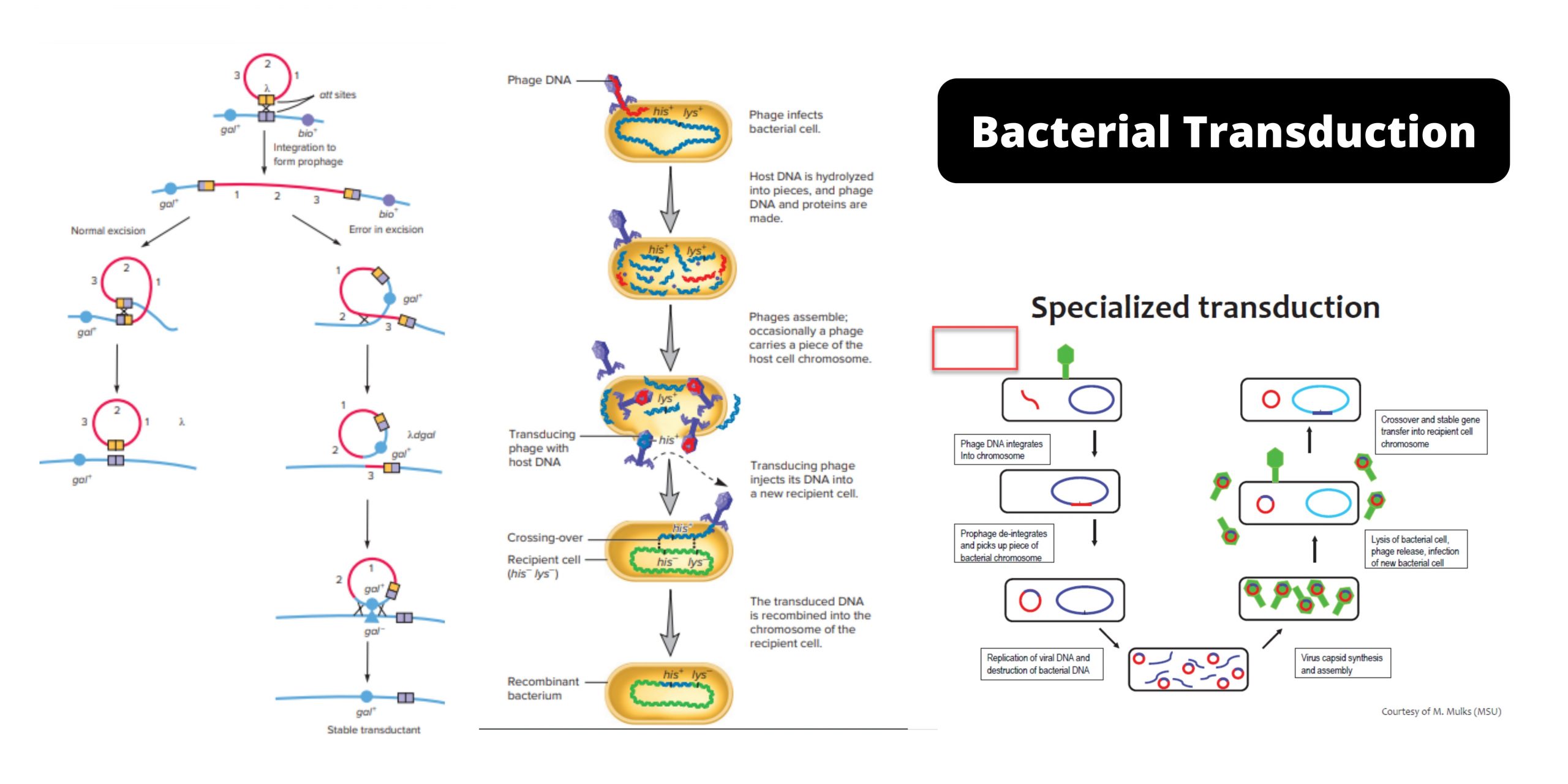
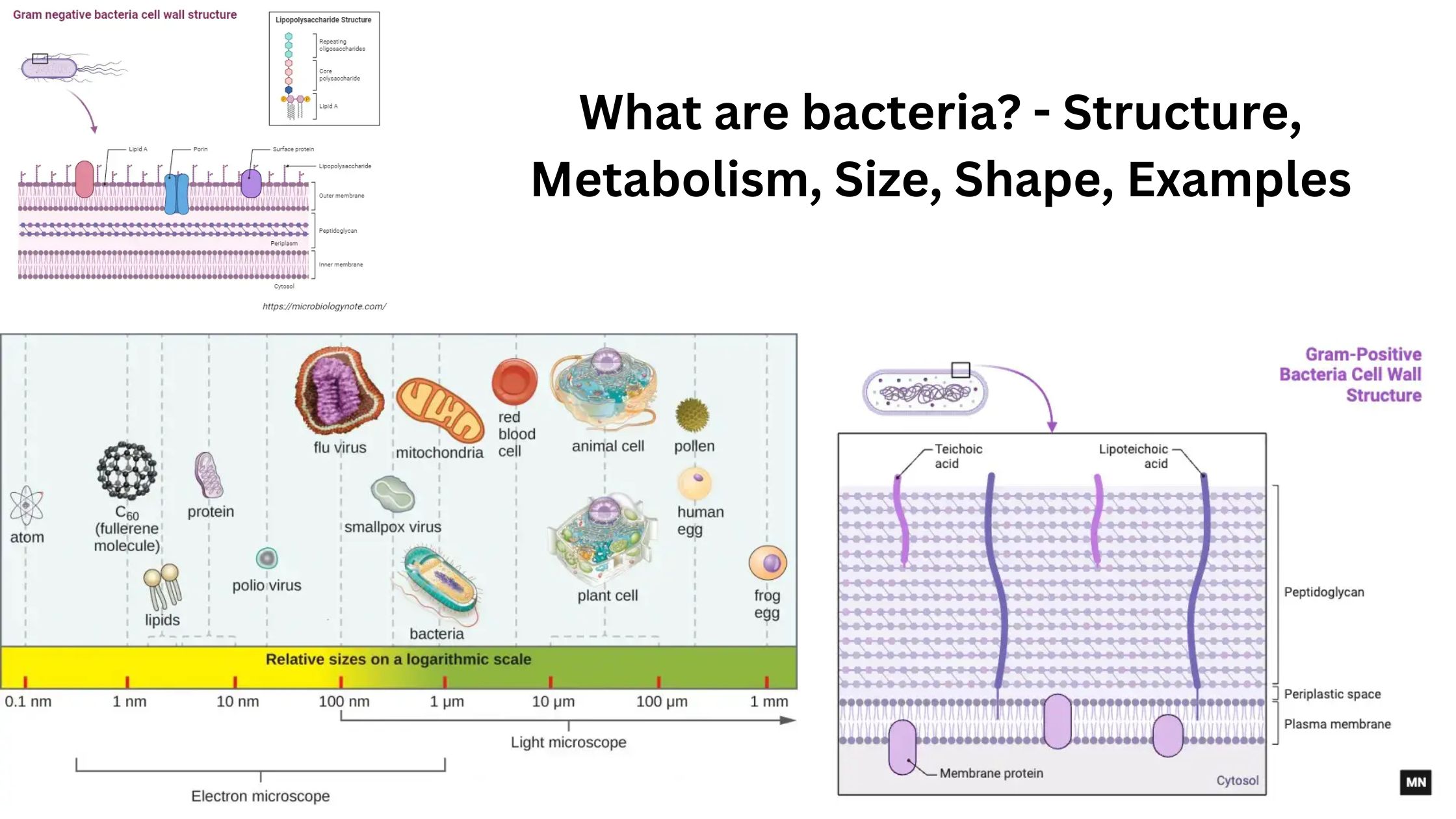
Brucella – Habitat, Morphology, Pathogenesis, Treatment
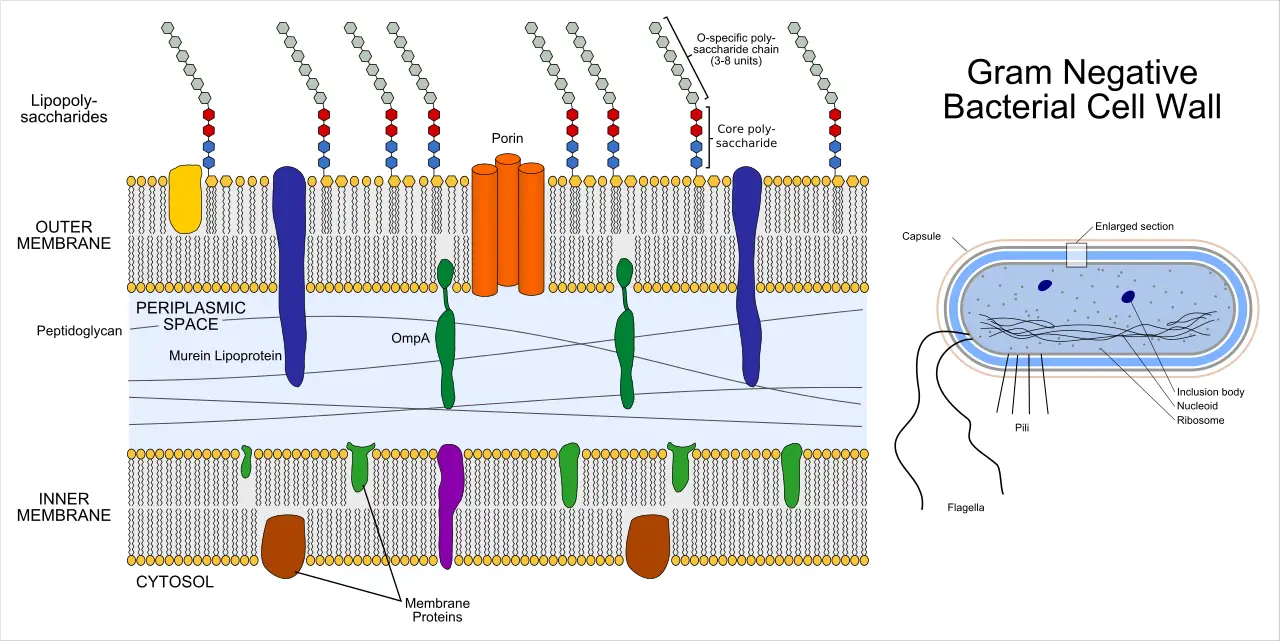
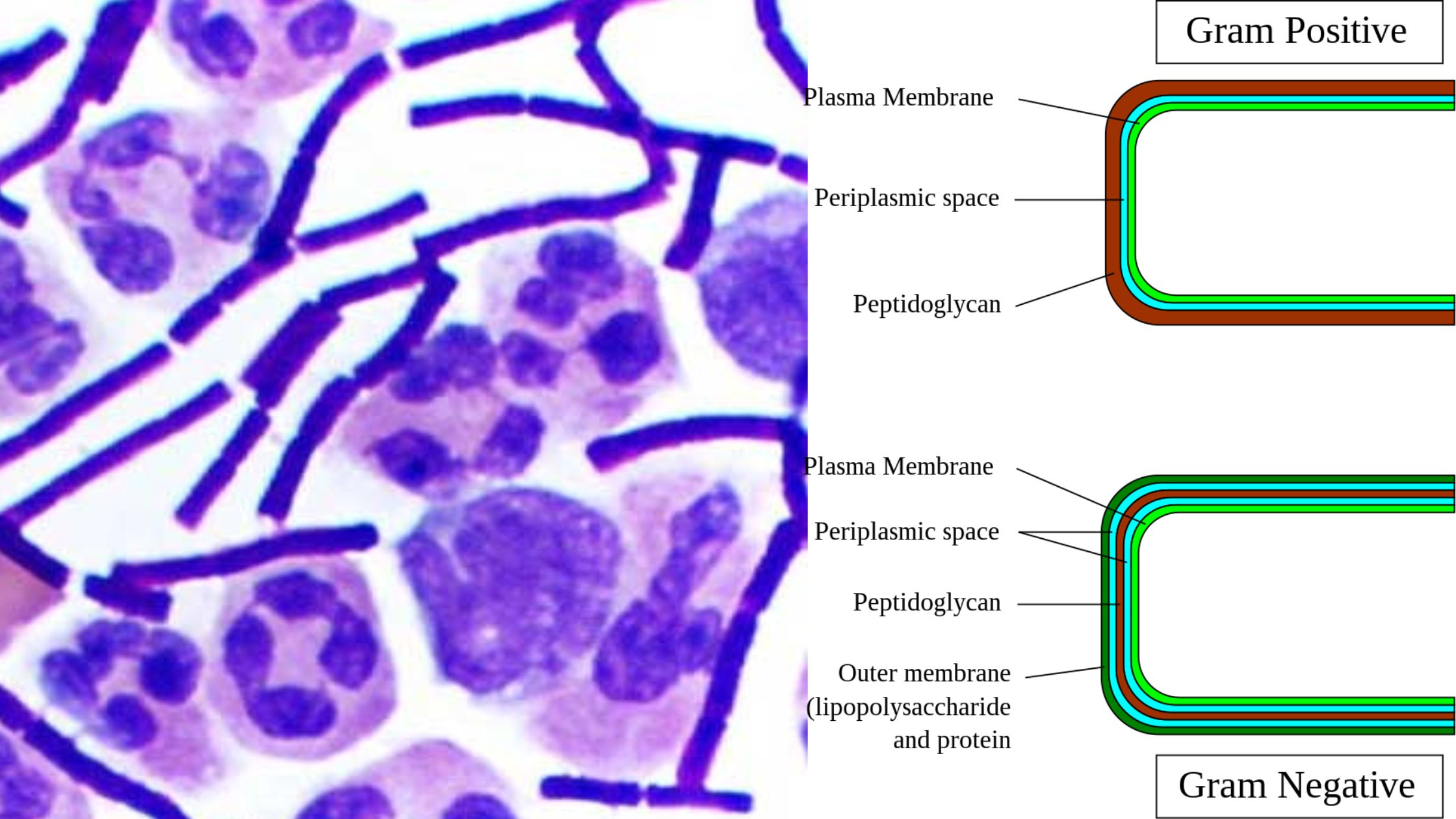
Brucella is a genus of small Gram-negative coccobacilli. It is non-motile and non-spore forming, and it is the organism responsible for a zoonotic disease called brucellosis. It is the process where the bacteria survive as facultative intracellular parasite inside different host cells. These organisms are named after David Bruce and are placed under the family … Read more