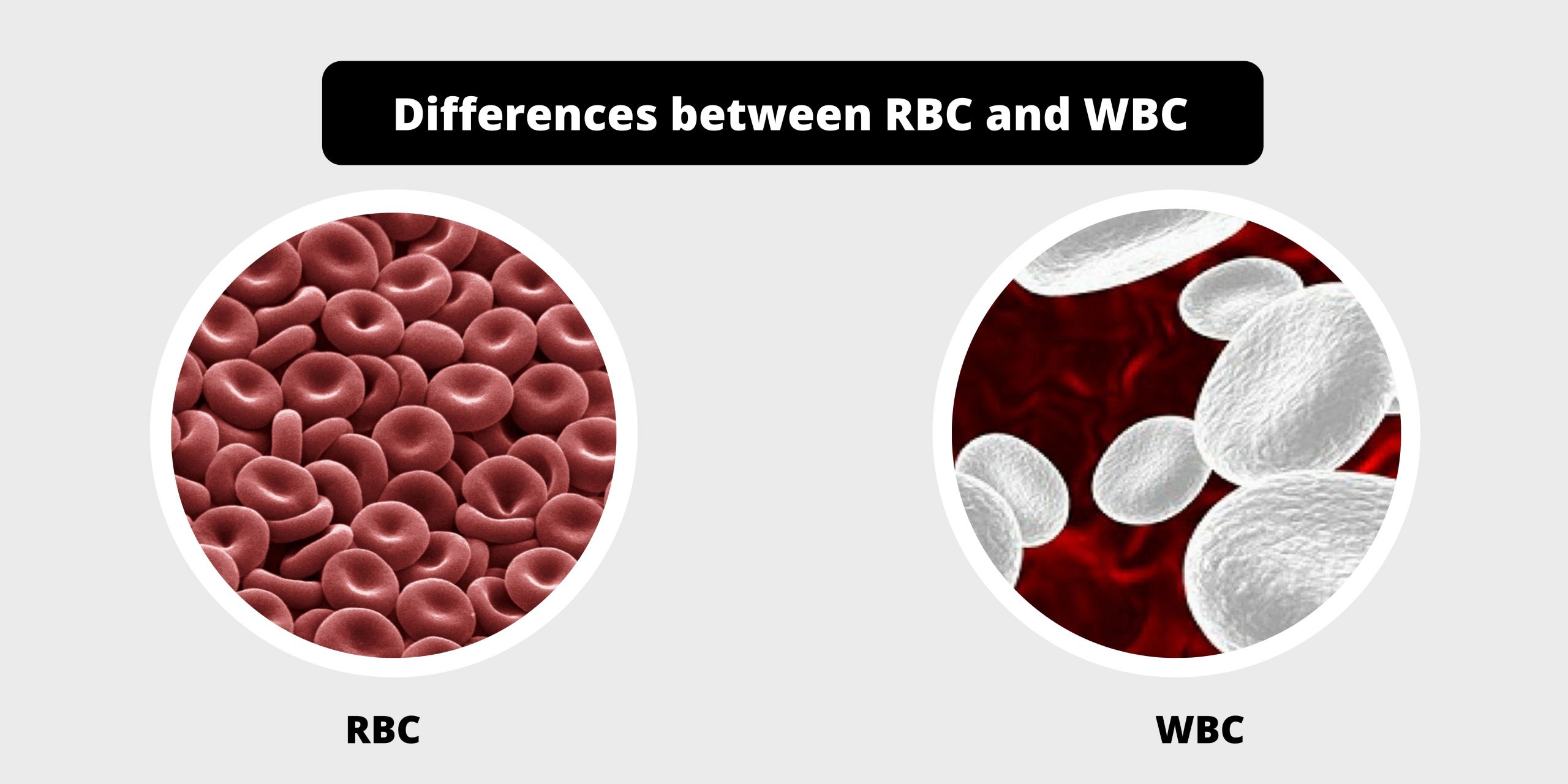
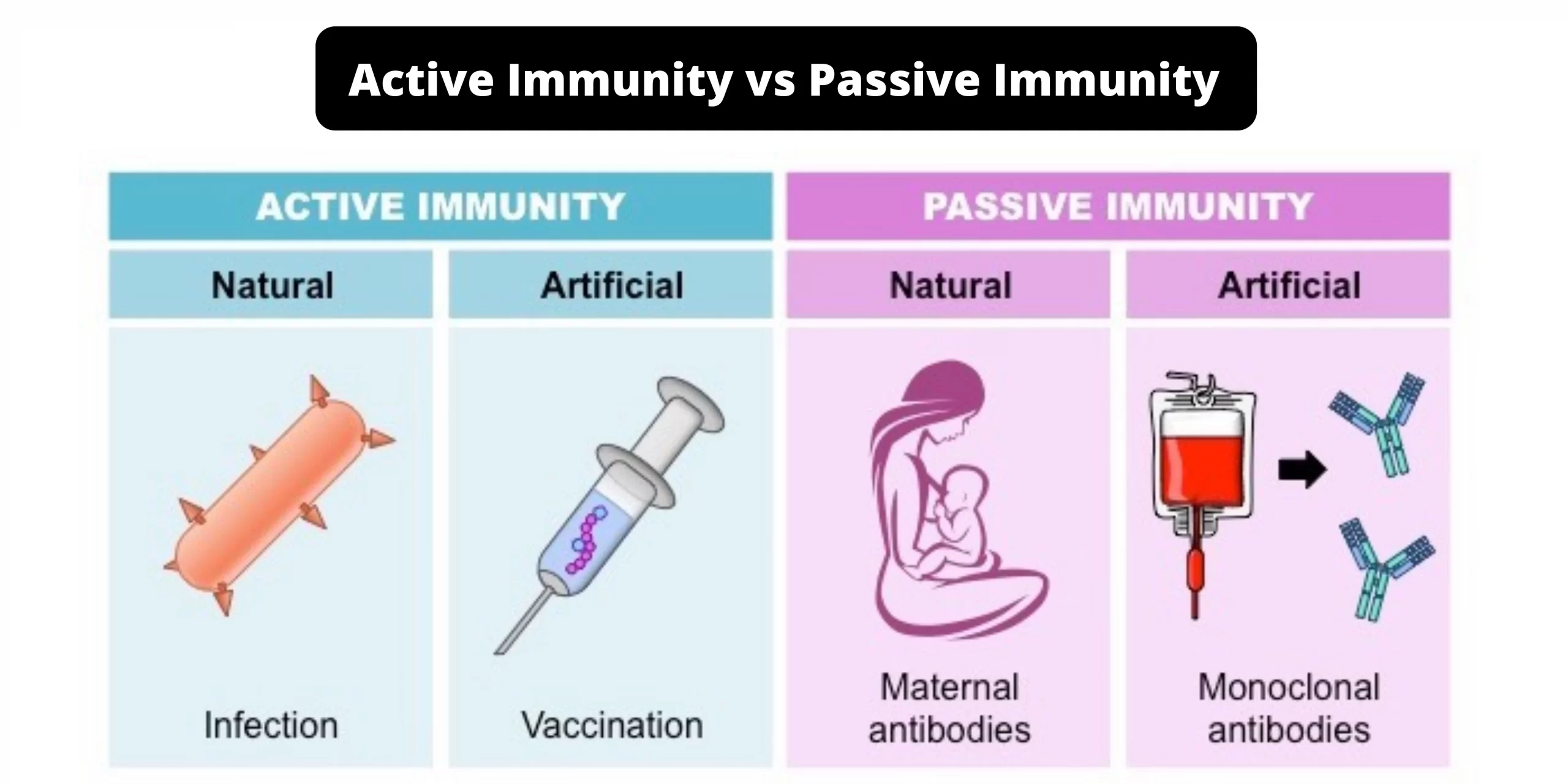
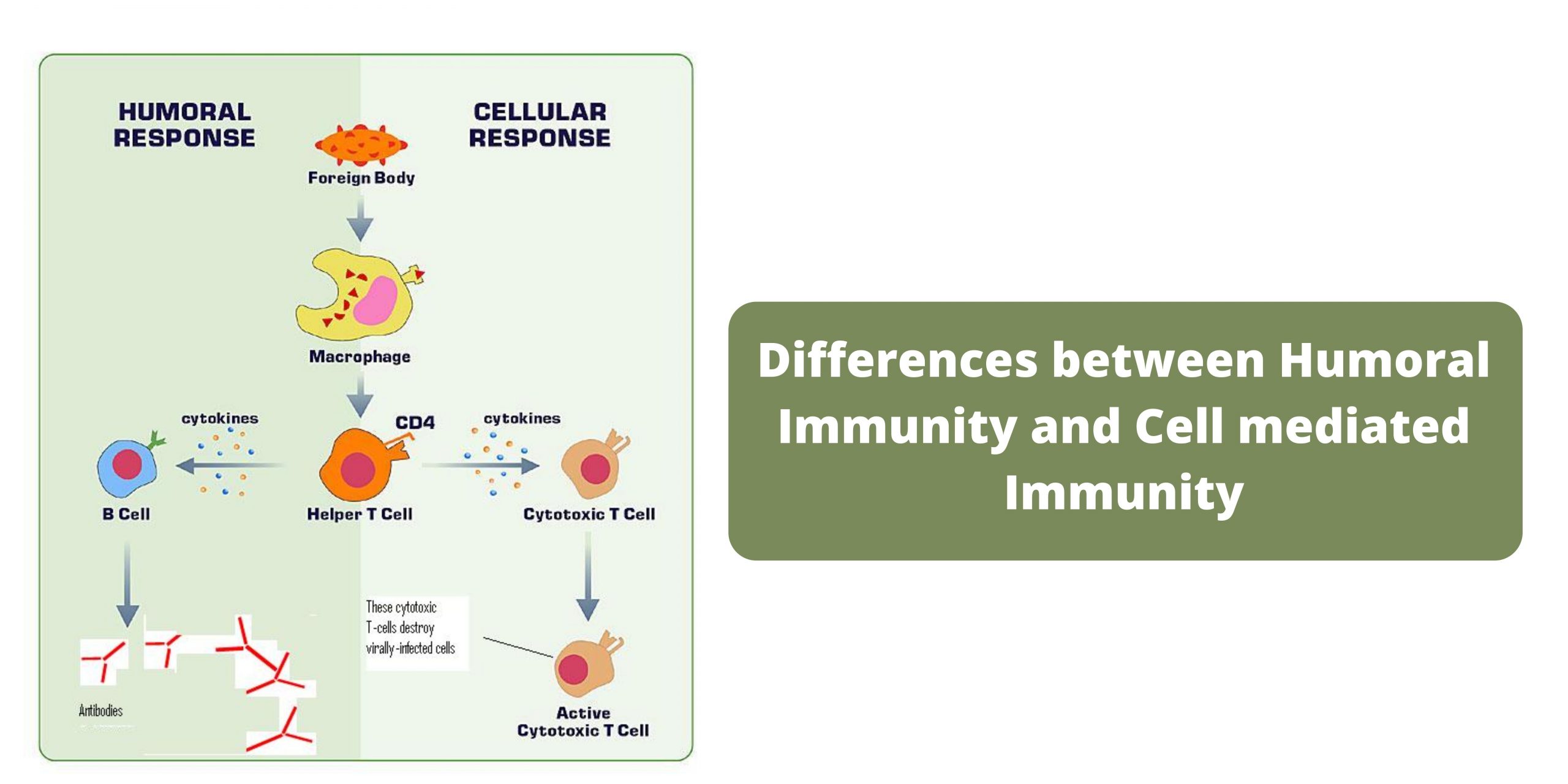
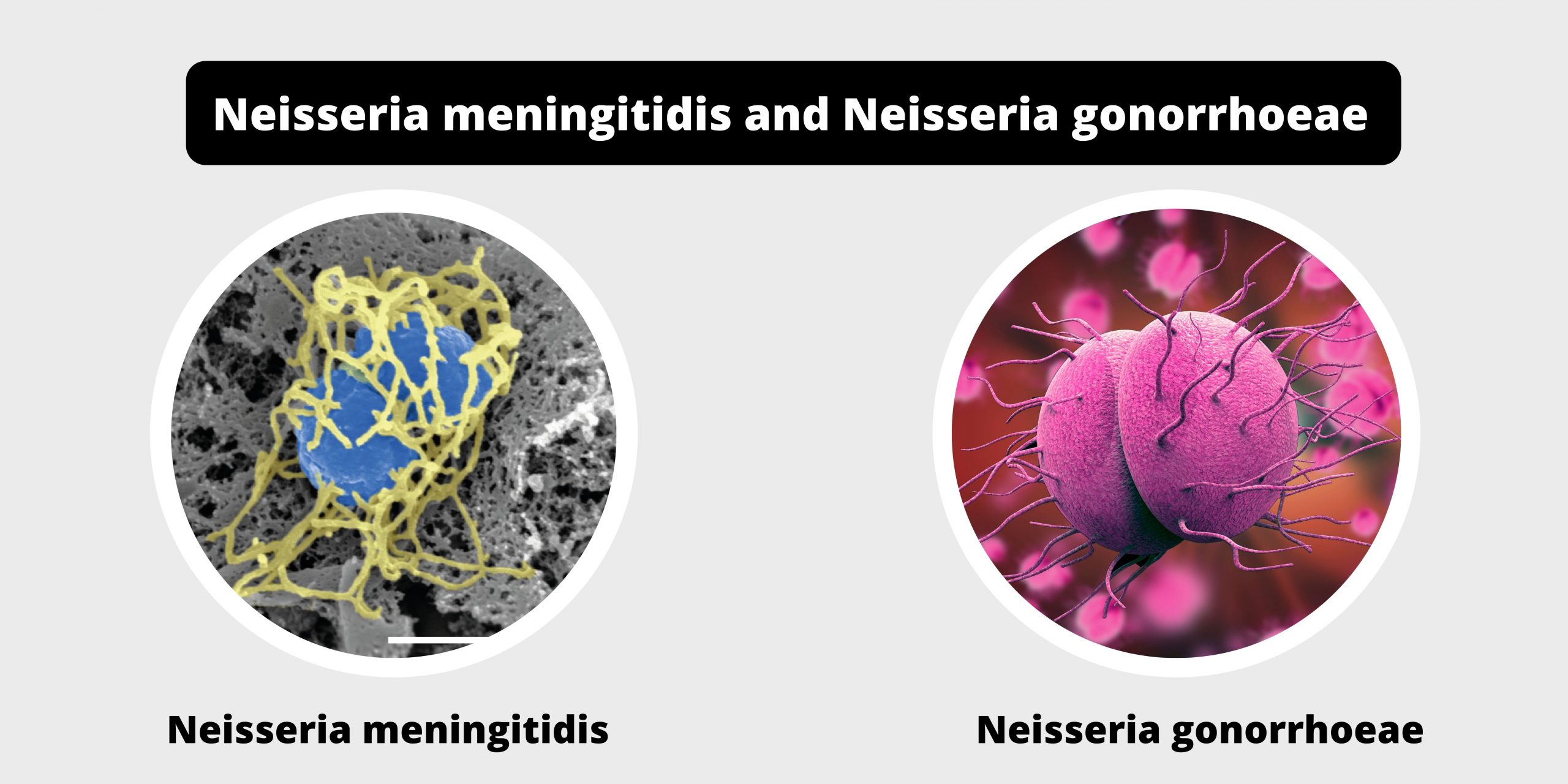
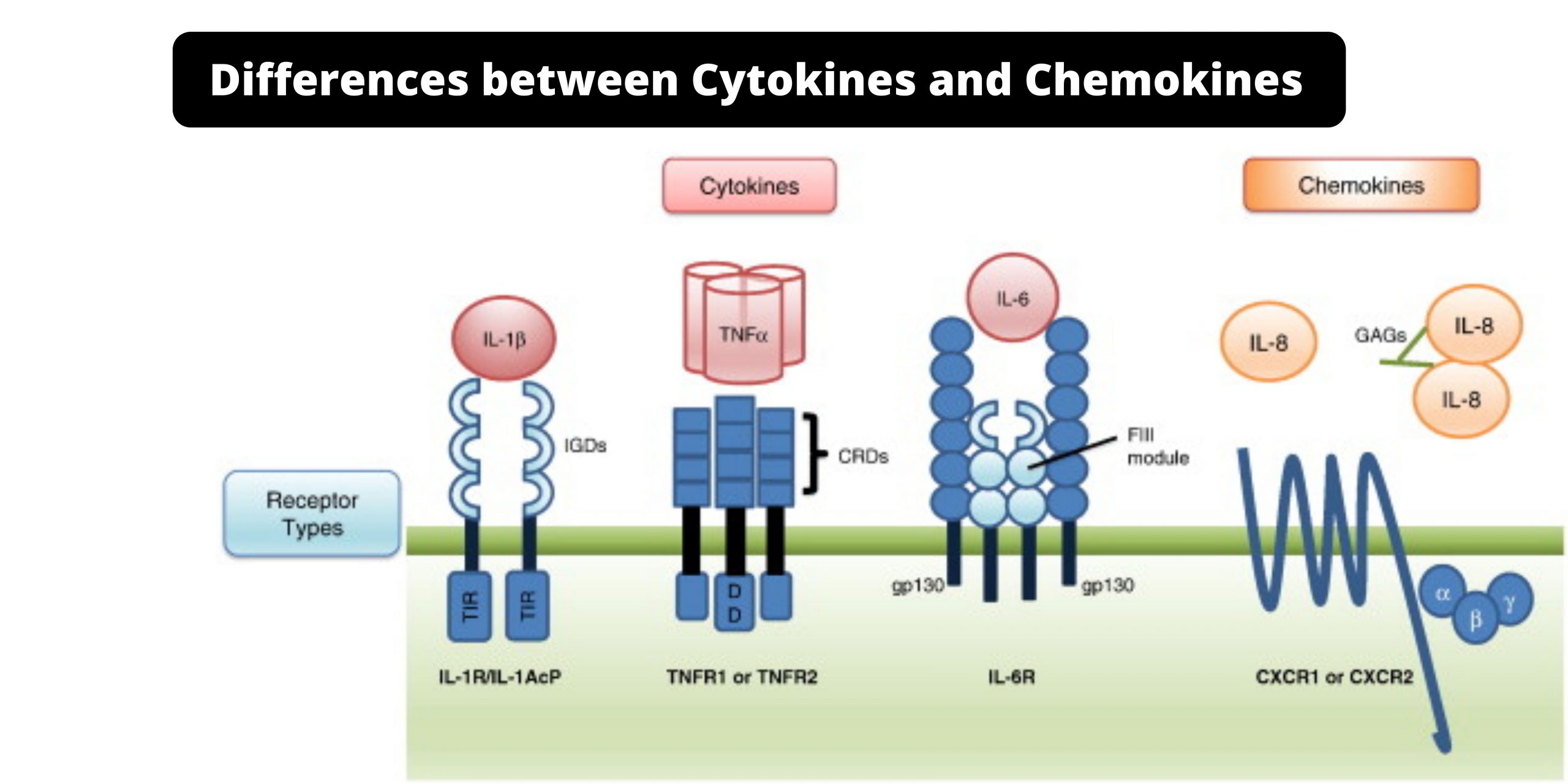
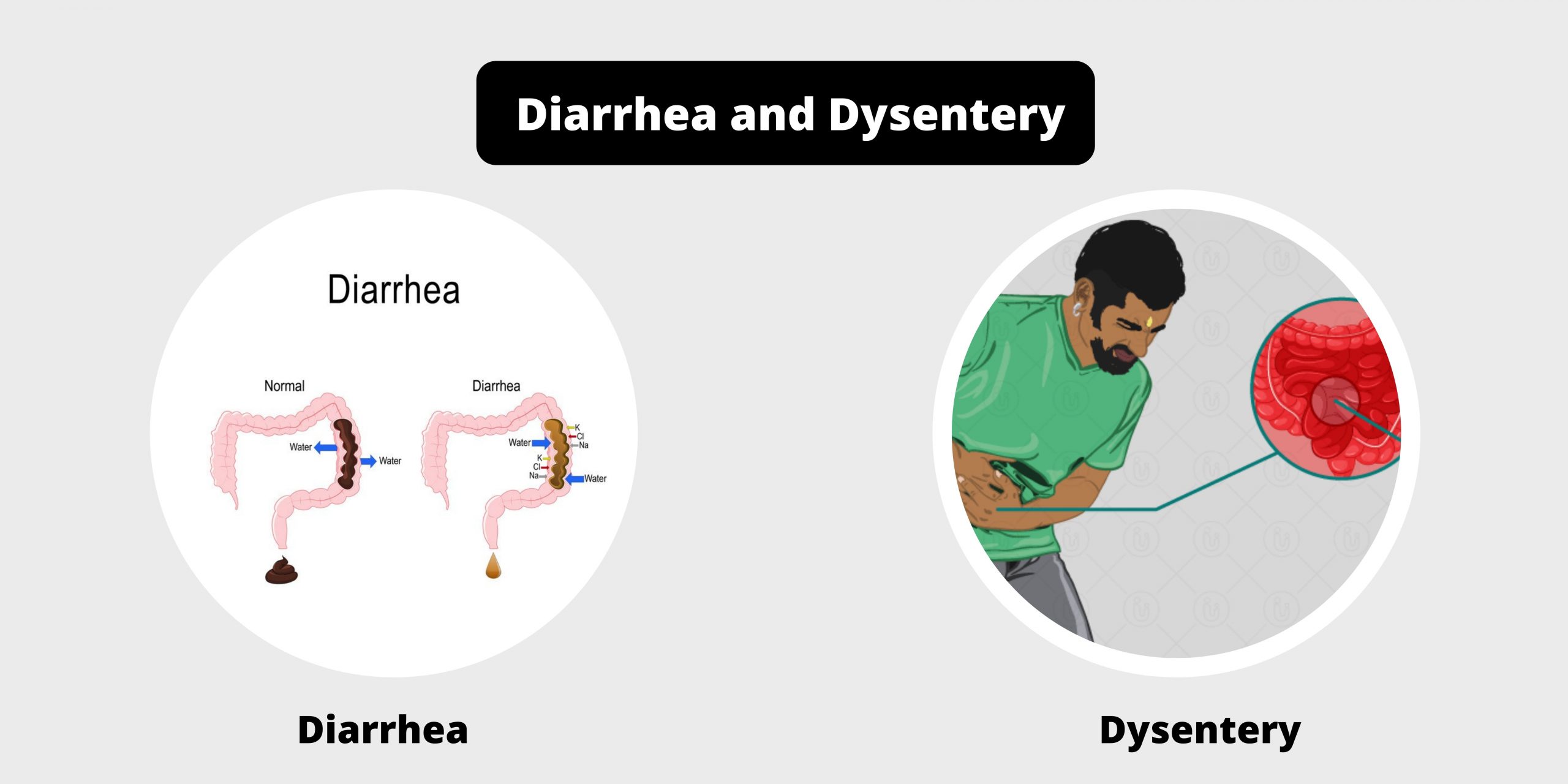
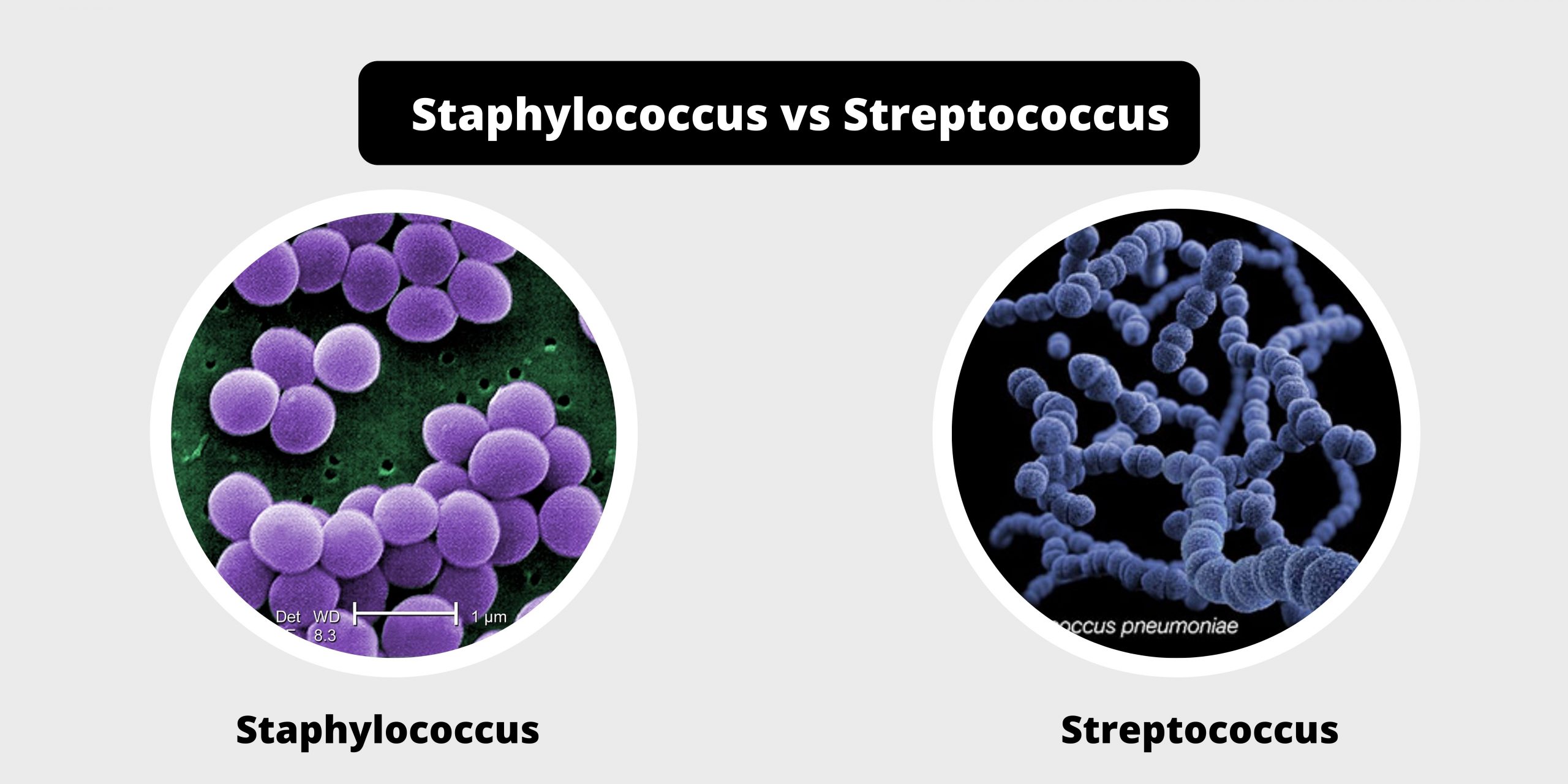
Differences between RBC and WBC – RBC vs WBC
White blood cells are two of the components of the blood supply in mammals. RBCs (RBCs) are biconcave discs that are circular in shape with hemoglobin-containing pigments to carry oxygen throughout the animal’s body. Oxygen is essential to the catabolism of cells within animals. A portion of carbon dioxide is transported through RBCs. They are created as a waste product in catabolism. They are also known as white blood cells. (WBCs) contain a range of types of cells like leukocytes neutrophils, and monocytes. They are able to differentiate into various defense mechanisms. The major distinction in red and white blood cells lies with their purpose that red blood cells transport oxygen around the human body, whereas white blood cells play a role with the protection of animals by destroying pathogens that attack the body’s cells.