A BOD incubator is a laboratory instrument that is used for maintaining a controlled temperature environment required for the estimation of Biochemical Oxygen Demand of water samples. It is designed to operate both at heating and cooling conditions which is different from ordinary incubators. It is mainly adjusted at a fixed temperature of 20°C which is essential for BOD analysis. The instrument provides a uniform and stable condition inside the chamber by continuous air circulation.
It is the process where microorganisms present in water sample consumes dissolved oxygen for the decomposition of organic matter. This oxygen consumption is measured after incubating the sample for a definite period generally five days. In this step the samples are placed inside the incubator under dark condition to avoid photosynthetic oxygen production. Apart from water analysis this incubator is also used for microbial culture studies pharmaceutical testing and plant tissue culture due to its ability to maintain low temperature conditions.
The history of BOD incubator is closely related with the development of water pollution monitoring systems. The concept of BOD testing was developed in England during the early studies on river water pollution. The standard temperature of 20°C and incubation period of five days was not randomly selected. It was based on the natural conditions of the River Thames.
It is observed that the average temperature of river water was around 20°C and the time taken for the river water to flow from London to sea was approximately five days. Hence these two conditions were adopted as standard for BOD determination. Initially the incubation was carried out in simple cupboards or chambers cooled with ice. Over time the incubator was modified with refrigeration units and temperature regulators.
Modern BOD incubators are now designed with digital controllers and compressor based cooling systems. These systems help in maintaining precise temperature irrespective of external laboratory conditions. The controlled environment ensures that the microorganisms remain active and the oxygen consumption process is consistent. Thus the BOD incubator has evolved from a simple chamber into an advanced temperature controlled laboratory equipment used widely in environmental and biological studies.
BOD incubator Definition
The BOD (Biological Oxygen Demand) Incubator is a specialized laboratory instrument designed to provide a controlled temperature environment, typically around 20 degrees centigrade, for microbial and biochemical studies, particularly for assessing the oxygen demand of microorganisms in water samples.
Principle of BOD Incubator
The principle of BOD incubator is based on maintaining a constant low temperature environment required for the growth and activity of aerobic microorganisms. It is generally standardized at 20°C which simulates the natural condition of aquatic systems. It is different from ordinary incubators as it consists of both cooling and heating mechanisms. The temperature inside the chamber is regulated by a control system where cooling operates when temperature rises above set point and heating functions when temperature falls below the required level.
This process is controlled by sensors and a temperature regulating unit which continuously monitors the internal condition of the chamber. Uniform temperature is maintained by continuous air circulation with the help of internal fan. This prevents formation of hot or cold zones inside the incubator. Under these controlled conditions microorganisms consume dissolved oxygen present in the water sample during decomposition of organic matter. The oxygen consumption takes place over a fixed incubation period usually five days which forms the basis for accurate BOD determination.
Parts of BOD Incubator
The main parts of BOD incubator are listed below–
- Outer cabinet– It is a double walled structure made of mild steel or stainless steel. It helps in protecting the internal chamber and reducing heat exchange with surroundings.
- Inner chamber -The inner chamber is generally made of stainless steel (S.S. 304 or 316). It provides space for keeping BOD bottles and is easy to clean.
- Insulation layer– An insulating material like polyurethane foam or glass wool is present between inner and outer walls. It prevents loss of temperature from chamber.
- Outer door– It is a solid insulated door fitted with locking arrangement. It helps in maintaining constant temperature inside incubator.
- Inner glass door– A transparent glass door is provided inside. It allows observation of samples without opening main door.
- Temperature controller– A digital microprocessor based controller is used for setting and regulating temperature. It maintains the required incubation condition.
- Temperature sensor -A temperature sensing device (PT-100) is fitted inside chamber. It continuously senses temperature and sends signal to controller.
- Refrigeration system– It consists of compressor and cooling coils. This system is responsible for lowering temperature below ambient level.
- Heating element– A tubular heating element is used for increasing temperature when required. It works along with cooling system to maintain set point.
- Air circulation fan– An internal fan is provided for uniform distribution of temperature. It avoids formation of hot or cold spots.
- Shelves or trays– Removable stainless steel wire shelves are present. These are used for placing BOD bottles during incubation.
- Safety thermostat– It acts as a protective device. It cuts off power supply if temperature exceeds safety limit.
- Control panel– The control panel contains switches indicators and digital display. It helps in monitoring and operating the incubator.
- Internal illumination– An internal light source is provided for visibility inside chamber. It is mainly used during sample arrangement.
- Caster wheels– Wheels are fixed at the bottom of incubator. They help in easy movement of the equipment.
BOD incubator Labeled Diagram
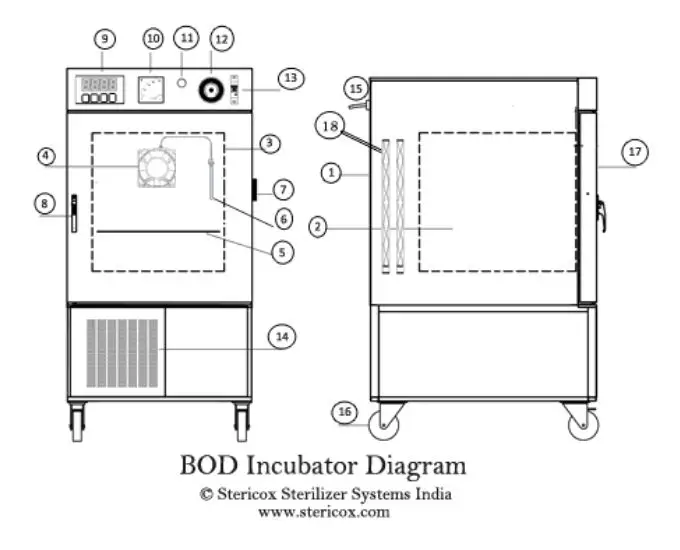
- Exterior
- Inner chamber
- Toughened glass window
- Air circulation fan
- Removable tray
- Temperature sensor
- Door hinges
- Door handle with lock & key
- PID temperature controller
- Analog ampere meter
- Pilot lamp
- Safety thermostat
- On/Off MCB
- Refrigeration system
- Power cord
- Caster wheels
- Solid door
- Heater
Operating Procedure of BOD Incubator
The operating procedure of BOD incubator is carried out in the following steps–
- Checking power supply– Ensure that the incubator is connected to a proper grounded power source. The main power supply should be stable before switching ON the unit.
- Cleaning of incubator– Check that the inner chamber shelves and surrounding area are clean. No moisture or spilled material should be present inside chamber.
- Position of incubator – The incubator should be placed away from direct sunlight and heat sources. Proper ventilation around the unit should be maintained.
- Switching ON the unit– Switch ON the main power switch present on control panel. The digital controller displays the present temperature and set temperature.
- Setting the temperature -Press the SET key on the controller to enter temperature setting mode. Adjust the set value using up or down keys and set the required temperature usually 20°C. Press SET again to confirm.
- Setting the timer (if provided)– Enter timer mode by pressing SET key. Adjust the required incubation time or set it to zero for continuous operation and confirm the setting.
- Stabilization of temperature– Allow the incubator to run empty until the set temperature is achieved and stabilized. This ensures proper condition before loading samples.
- Loading the samples– Open the door and place BOD bottles on shelves. The samples should be arranged with proper spacing to allow air circulation.
- Closing the door– Close the door properly and lock it if locking facility is provided. This prevents temperature fluctuation inside chamber.
- Monitoring during operation– Observe the digital display regularly to ensure temperature remains constant. Any alarm or deviation should be checked immediately.
- Recording observations– Temperature and incubation time should be recorded in log book at regular intervals during operation.
- Switching OFF the incubator -After completion of incubation period switch OFF the main power supply. Remove samples carefully.
- Cleaning after use -Remove shelves and clean inner chamber with disinfectant solution. Dry the chamber before next use.
Difference between Incubator and BOD Incubator
| Parameter | Incubator | BOD Incubator |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Regulation | Primarily offers heating capabilities. | Equipped with both heating and cooling functionalities. |
| Typical Operating Temperature | Set to operate at 37°C. | Operates at a broader temperature range, typically at lower temperatures such as 10°C and 21°C. |
| Functionality | Designed to foster the growth of microorganisms by providing a warm environment. | Tailored for studies related to Biological Oxygen Demand and other processes requiring cooler conditions. |
| Common Applications | Used in microbiology labs for routine cell culture processes. | Used to determine oxygen demand in decomposition processes and studies necessitating cooler conditions. |
Precautions for Operating a BOD Incubator
The precautions to be followed while operating a BOD incubator are given below–
- The incubator should be installed in a dry and well ventilated place. It should not be kept in direct sunlight or near heat sources.
- Sufficient space should be maintained between the incubator and the wall to allow proper heat dissipation.
- The incubator should be placed on a level surface to ensure proper functioning of compressor.
- The equipment should always be kept in upright position during movement to avoid damage.
- Proper earthing connection should be provided to prevent electrical shock.
- Extension cords should be avoided and a stable power supply should be used.
- The power supply should be disconnected before cleaning or maintenance work.
- The chamber should not be overcrowded with samples. Proper spacing should be maintained for air circulation.
- Air circulation vents and temperature sensors should not be blocked by samples.
- The door should not be opened frequently as it causes temperature fluctuation inside chamber.
- Temperature setting should not be changed repeatedly as it affects equipment life.
- After switching OFF the incubator sufficient time should be allowed before restarting.
- The temperature should be monitored daily to ensure proper incubation condition.
- The inner chamber and shelves should be cleaned regularly using suitable disinfectant.
- Corrosive cleaning agents should not be used on the incubator surface.
- Condenser and cooling system should be cleaned periodically for efficient operation.
- The temperature sensor should be handled carefully to avoid damage.
- Ice formation inside cooling system should be prevented by limiting door opening.
- The incubator should be kept in dark condition during BOD testing to prevent photosynthesis.
- The pH of water sample should be adjusted before incubation to support microbial activity.
- Residual chlorine should be removed from samples before placing them in incubator.
- Proper seeding should be done if microbial population is insufficient in sample.
Application of BOD incubators
The applications of BOD incubator are given below–
- It is used for determination of Biochemical Oxygen Demand of sewage industrial effluents and water samples.
- It is used in environmental laboratories for monitoring water pollution level and treatment efficiency.
- It is used for growth cultivation and storage of microorganisms like bacteria fungi yeast and molds at low temperature.
- It is used in pharmaceutical laboratories for stability testing of drugs vaccines and other pharmaceutical products.
- It is used in food and beverage industries for fermentation studies and shelf life analysis of food products.
- It is used in agricultural research for seed germination plant tissue culture and soil microbiology studies.
- It is used in insect breeding and zoological studies where controlled low temperature is required.
- It is used in biotechnology laboratories for enzyme studies biodegradation tests and microbial assays.
- It is used in medical and clinical laboratories for serum studies culture preservation and research work.
- It is used for storage of heat sensitive samples enzymes and biological reagents under controlled conditions.
Advantages of BOD Incubator
The advantages of BOD incubator are given below–
- It has both heating and cooling systems which helps in maintaining low temperature conditions.
- It can maintain required temperature independent of external laboratory temperature.
- It provides uniform temperature inside chamber due to continuous air circulation.
- It offers high accuracy and stability in temperature control which is required for sensitive tests.
- It is suitable for wide range of applications like water analysis pharmaceutical testing and microbial studies.
- It helps laboratories in following standard testing guidelines and quality control requirements.
- It is designed with stainless steel inner chamber which makes it durable and easy to clean.
- It reduces chances of contamination and ensures reliable experimental results.
Limitations of BOD Incubator
The limitations of BOD incubator are given below–
- It has high operational cost due to continuous use of heating and cooling systems.
- The BOD test requires a fixed incubation period of five days which makes the process time consuming.
- It requires regular maintenance like cleaning of condenser and checking of fan and compressor.
- Mechanical failure such as compressor damage refrigerant leakage or fan malfunction can affect operation.
- Improper loading of samples can block air circulation and cause uneven temperature distribution.
- Frequent opening of door leads to temperature fluctuation and condensation inside chamber.
- It is not suitable for samples containing toxic substances which inhibit microbial activity.
- Ice formation may occur in cooling system which reduces efficiency of temperature control.
FAQ
Q1. What is a BOD Incubator?
A. A BOD incubator is a laboratory equipment used for maintaining a controlled low temperature environment required for Biochemical Oxygen Demand testing. It is designed with both cooling and heating systems to maintain constant temperature during incubation period.
Q2. What is a BOD incubator used for?
A. A BOD incubator is used for incubating water and wastewater samples to determine the amount of dissolved oxygen consumed by microorganisms during decomposition of organic matter.
Q3. What is the main purpose of a BOD incubator?
A. The main purpose of a BOD incubator is to provide a stable temperature condition for accurate estimation of Biochemical Oxygen Demand of water samples.
Q4. What temperature range do BOD Incubators operate within?
A. BOD incubators generally operate within a temperature range of about 5°C to 60°C depending on model and requirement.
Q5. Why is a BOD incubator important?
A. It is important because it ensures precise and uniform temperature conditions which are essential for reliable BOD analysis and water quality assessment.
Q6. What is the difference between a BOD incubator and a normal incubator?
A. A BOD incubator has both cooling and heating systems whereas a normal incubator generally provides only heating. BOD incubator can maintain temperature below ambient level.
Q7. What is the working principle of a BOD incubator?
A. The working principle is based on maintaining a constant low temperature using controlled heating and refrigeration. This allows microorganisms to consume dissolved oxygen in water samples under standardized conditions.
Q8. What are the applications of a BOD Incubator?
A. It is used in water and wastewater analysis microbiological studies pharmaceutical testing food processing agricultural research and biological sample storage.
Q9. What are the general precautions you should take while using a BOD incubator?
A. Proper earthing should be ensured samples should not overcrowd the chamber frequent door opening should be avoided and regular cleaning should be done.
Q10. What factors should you consider when selecting a BOD Incubator?
A. Factors like temperature range accuracy chamber size energy consumption construction material and service support should be considered.
Q11. What are the advantages and disadvantages of a BOD Incubator?
A. Advantages include precise temperature control uniform conditions and wide application. Disadvantages include high cost regular maintenance and longer testing time.
Q12. What are the components of a BOD Incubator?
A. The main components are outer cabinet inner chamber insulation temperature controller sensor cooling system heating element shelves and air circulation fan.
Q13. What are the key features to look for in a BOD Incubator?
A. Key features include digital temperature controller uniform air circulation corrosion resistant chamber and safety thermostat.
Q14. What is the ideal temperature for a BOD incubator?
A. The ideal temperature for BOD incubation is 20°C which is standardized for BOD testing.
Q15. What are common mistakes to avoid when choosing a BOD Incubator?
A. Common mistakes include ignoring temperature accuracy selecting insufficient chamber size overlooking service support and choosing low quality insulation.
- American Public Health Association, American Water Works Association, & Water Environment Federation. (2001). 5210 Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD). In Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater.
- Biolab Scientific. (n.d.). BOD incubator BIBD-101 [Product catalog]. https://www.biolabscientific.com/BOD-Incubator/p/BIBD-101
- Biolab Scientific. (n.d.). Operating manual: BOD incubator BIBD-101, BIBD-102, BIBD-103, BIBD-104. https://biolabscientific.com/manual/BIBD-101_BIBD-102_BIBD-103_BIBD-104_Manual_Biolab.pdf
- Bionics Scientific Technologies. (n.d.). Top 10 powerful facts about BOD incubators – Principle, types, and uses explained. https://www.bionicsscientific.com/blog/what-is-the-bod-incubator/
- DwyerOmega. (n.d.). Introduction to Pt100 RTD temperature sensors. https://www.dwyeromega.com/en-us/resources/rtd-hub
- EPACK Prefab. (2018, October 31). Rockwool vs PU sandwich panels – A brief comparison. https://www.epack.in/rockwool-vs-pu-sandwich-panels-a-brief-comparison
- Gaoya Building Material Co., Ltd. (2024, January 7). What is the difference between rockwool and PUF?. https://www.building-mat.net/info/what-is-the-difference-between-rockwool-and-pu-90790529.html
- Harrier Groups. (n.d.). BOD incubator, principle, types and usage. https://www.harriergroups.com/bod-incubator/bod-incubator-principle-types-and-usage/
- Julabo USA. (n.d.). What is a Pt100, and do I need one for my temperature application?. https://julabo.us/what-is-a-pt100-and-do-i-need-one-for-my-temperature-application/
- Julabo USA. (n.d.). What is PID temperature control, and how does it enhance laboratory applications?. https://julabo.us/what-is-pid-temperature-control-and-how-does-it-enhance-laboratory-applications/
- Kesar Control Systems. (2021, October 7). What is a BOD Incubator and how does it work?. https://www.kesarcontrol.com/what-is-a-bod-incubator-and-how-does-it-work-
- Kesar Control Systems. (2022, September 3). The importance of BOD incubators in research and development. https://www.kesarcontrol.com/the-importance-of-bod-incubators-in-research-and-development
- Labotronics Scientific. (n.d.). BOD incubator LB-30BI catalog. https://www.labotronics.com/catalog/bod-incubator/lb-30bi
- Labstac. (n.d.). Operating manual: BOD incubator INC11-250. https://labstac.com/manual/INC11-250_Manual_Labstac.pdf
- Lakshmi N, B. (2011, March 2). Maintaining microbial precision: Crafting an SOP for operating and cleaning BOD incubators in the microbiology department. PharmaMax. https://pharmamax.org/Articles.aspx?ID=93&MID=93
- Mack Pharmatech. (2025, March 28). BOD incubator working principle and applications. https://www.mackpharmatech.com/blog-details/bod-incubator-working-principle-and-application
- Malhotra, V. (2025, May 17). Complete guide to BOD incubator: Working principle, types, and uses. Presto Group. https://www.prestogroup.com/articles/complete-guide-to-bod-incubator-working-principle-types-and-uses/
- Mishra, R. (2023, January 24). What is a BOD Incubator? Diagram, uses and principle. Testronix Instruments. https://www.testronixinstruments.com/blog/uses-and-importance-of-bod-incubator-in-industries/
- MRC Lab. (n.d.). Frequently asked questions (FAQs) – BOD (biochemical oxygen demand) testing. https://www.mrclab.com/frequently-asked-questions-faqs-bod-biochemical-oxygen-demand-testing
- MRC Lab. (n.d.). Incubators [Catalog]. https://www.obrnutafaza.hr/pdf/mrc/proizvodi/Incubators.pdf
- Narang Scientific Works Pvt. Ltd. (n.d.). NSW-152 Caltan B.O.D. incubator maintenance manual. https://www.nsw-india.com/download/NSW-152.pdf
- National Environmental Methods Index. (n.d.). Standard Methods: 5210B: BOD: 5-Day test. https://www.nemi.gov/methods/method_summary/5715/
- O’Driscoll, A. (2019, January 23). Possible reasons for temperature issues with your lab incubator. Laboratory Supply Network. https://labsup.net/blogs/blog/temperature-issues-with-lab-incubator
- Peak Sensors. (n.d.). What is a Pt100 RTD temperature sensor? [Complete guide]. https://peaksensors.com/what-is/what-is-a-pt100-sensor/
- PharmaJia. (n.d.). SOP for cleaning and operation of incubators 1. https://pharmajia.com/sop-for-cleaning-and-operation-of-incubators/
- PSI. (n.d.). B.O.D. Incubator [Brochure].
- RS Components. (2023, January 17). A complete guide to PID temperature controllers. https://uk.rs-online.com/web/content/discovery/ideas-and-advice/pid-temperature-controllers-guide
- Scitek Global. (n.d.). Best biological oxygen demand (BOD) incubator manufacturer. https://www.scitekglobal.com/bod-incubator.html
- Singh, J. (2020, December 16). BOD incubator – Cleaning, calibration, operation. Pharma Beginners. https://pharmabeginers.com/bod-incubator-calibration-cleaning-operation/
- Stericox India Private Limited. (n.d.). BOD incubator refrigerated low temperature incubator manufacturers India. https://www.stericox.com/incubator/bod-incubator.html
- Stericox Sterilizer Systems India. (2017). Standard operating procedure (SOP) of refrigerated incubator or BOD incubator. https://www.stericox.com/incubator/BOD-Incubator-SOP.pdf
- Sustainability Directory. (2025, November 29). What are the standard testing conditions (time and temperature) for the BOD5 test?. https://pollution.sustainability-directory.com/learn/what-are-the-standard-testing-conditions-time-and-temperature-for-the-bod5-test/
- TaiHongJun. (2025, May 21). Common biochemical incubator problems and how to solve them. https://taihongjun.com/biochemical-incubator-problems-solutions/
- Technopuff Solutions. (n.d.). PUF panels vs other sandwich panels. https://www.technopuffsolutions.in/puf-panels-vs-other-sandwich-panels/
- Thermolab. (n.d.). BOD & bacteriological incubators [Brochure]. Cuspor. https://cuspor.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/11/BOD-Incubators.pdf
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. (1999). Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD) Standard Method 5210 B (5-day BOD Test).
- Viraat Industries. (2025, February 27). Comparing PUF panels vs. traditional insulation materials. https://viraatindustries.com/comparing-puf-panels-vs-traditional-insulation/
- Web of Pharma. (2025, December 31). Incubators and BOD incubators. https://www.webofpharma.com/2025/12/incubators-and-bod-incubators.html
- Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources. (n.d.). BOD sample pre-treatment. https://dnr.wisconsin.gov/topic/labCert/BODPreTreatment.html
- Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources. (n.d.). BOD troubleshooting. https://dnr.wisconsin.gov/topic/labCert/BODTrouble.html
- Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources. (2023, November 17). Biochemical oxygen demand (BOD and cBOD) checklist. https://dnr.wisconsin.gov/sites/default/files/topic/LabCert/BOD_Final_2023-11-23.pdf