Difference Between Homologous Chromosomes and Sister Chromatids
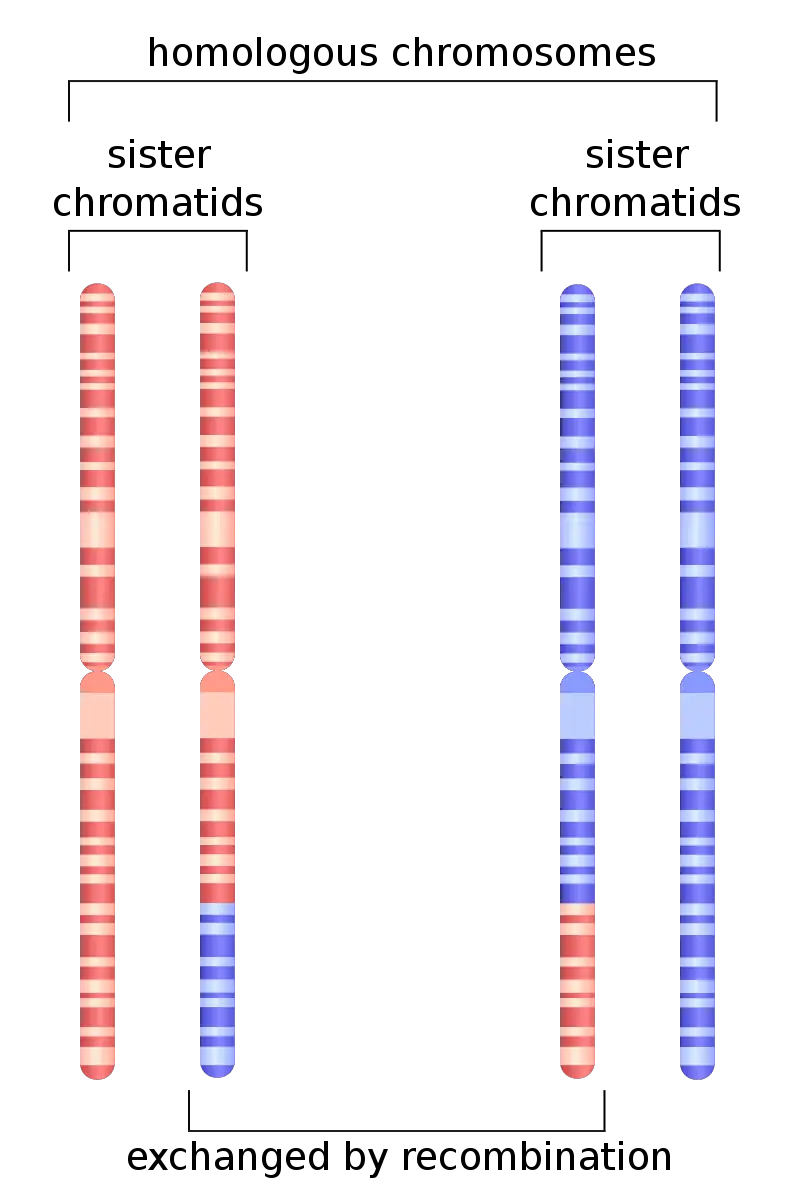
What are Homologous Chromosomes? Homologous chromosomes are fundamental components of the genetic architecture in diploid organisms, including humans. These chromosomes are pairs that have the same structure and genes, though they may carry different alleles, or variations, of those genes. Understanding homologous chromosomes is crucial for grasping the mechanisms of heredity and genetic variation. What … Read more