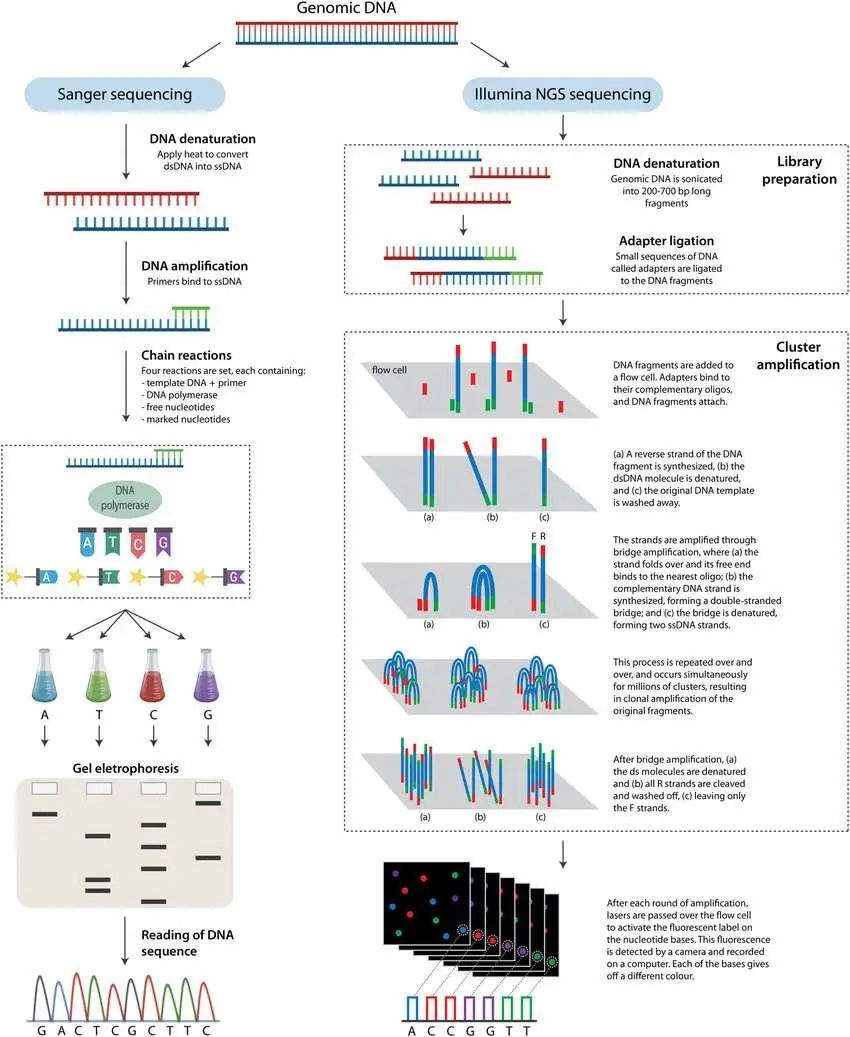
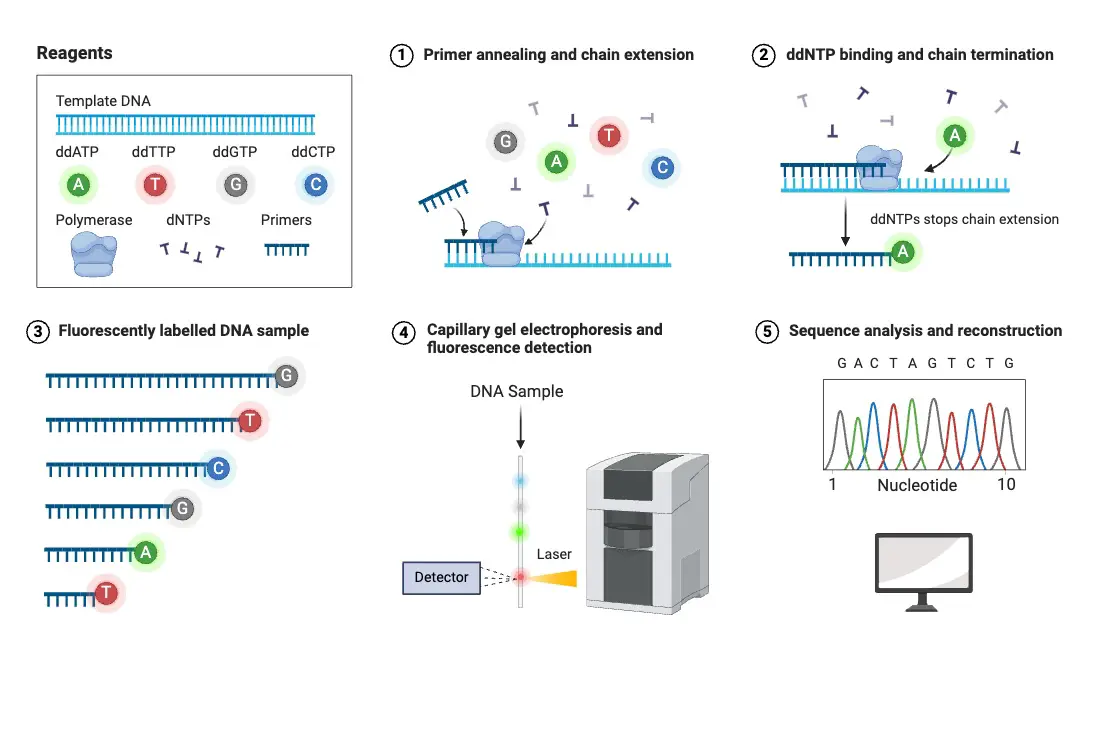
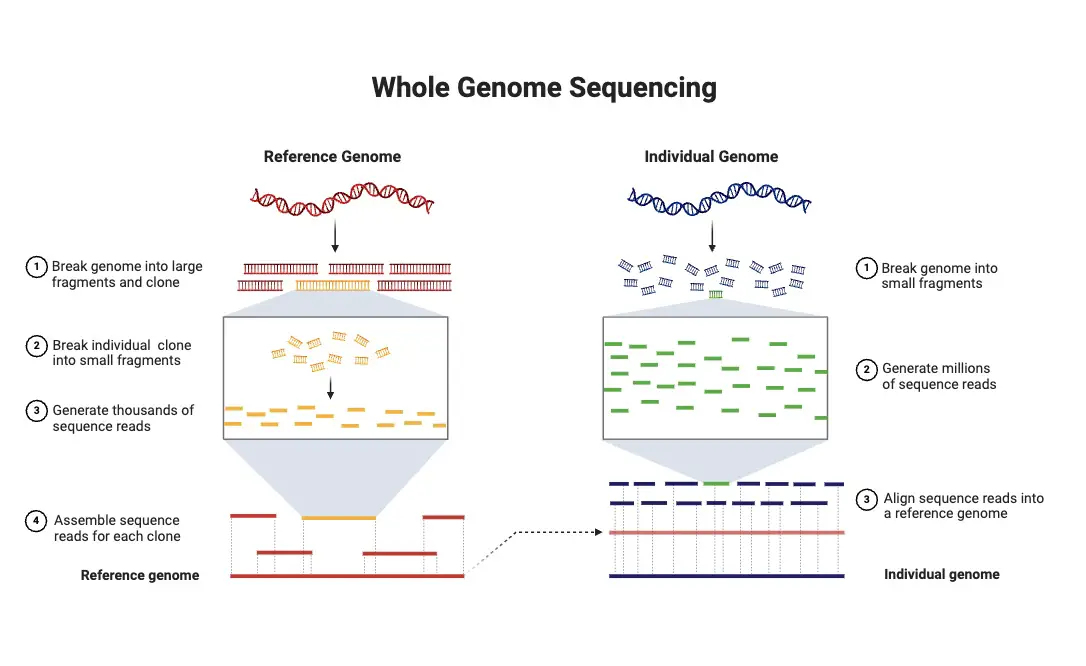
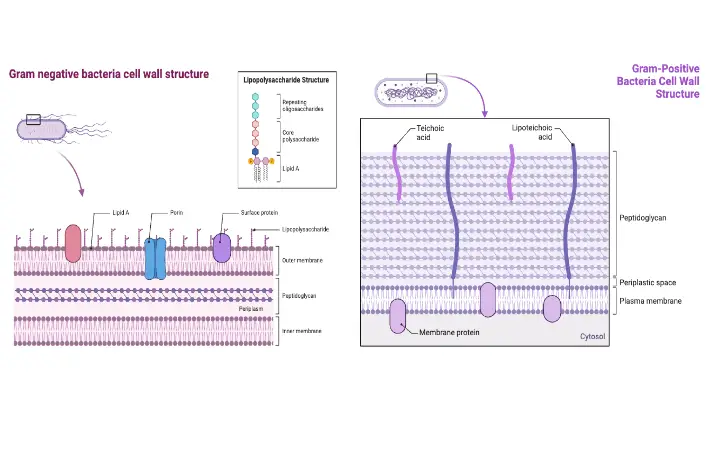
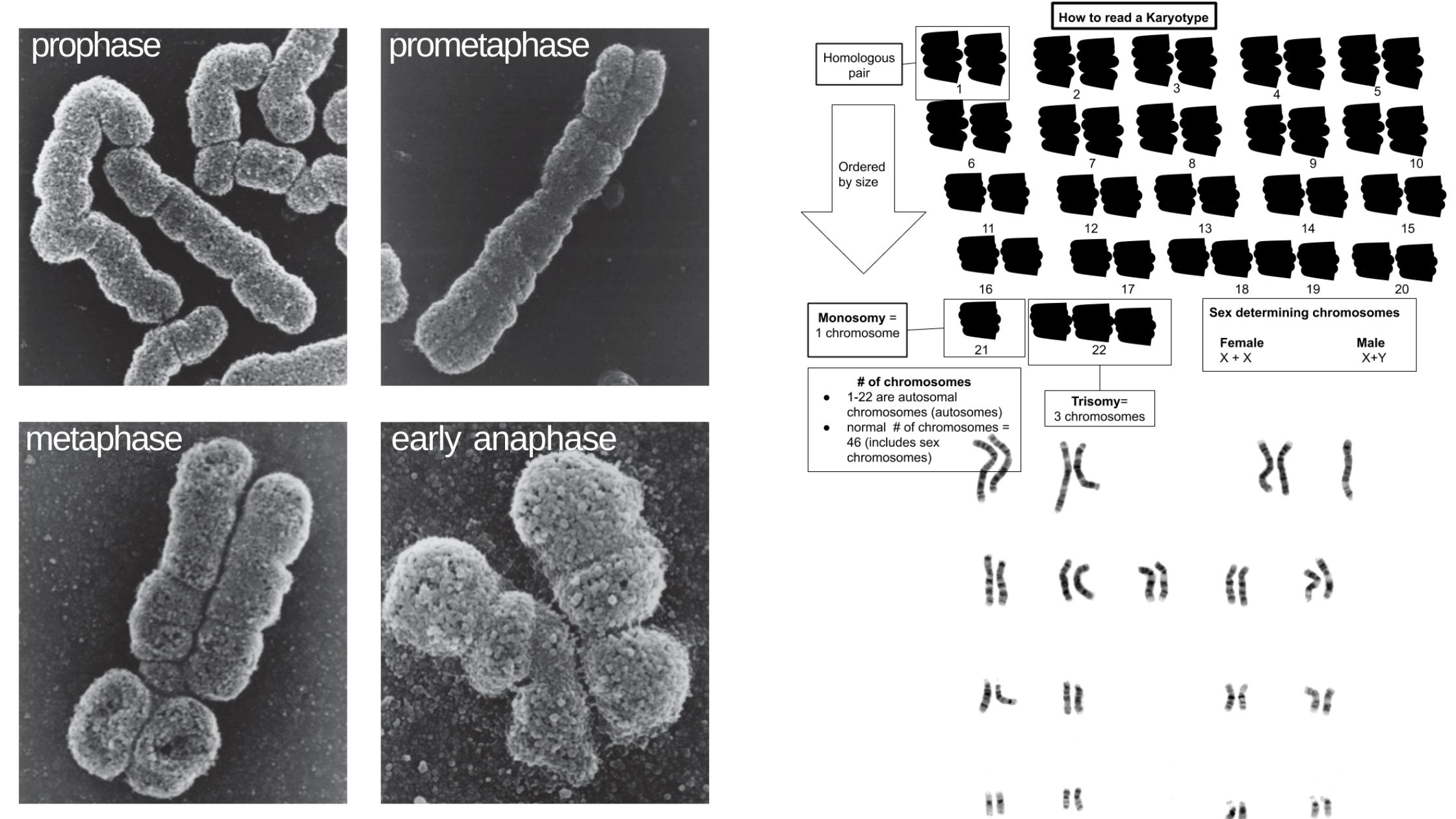
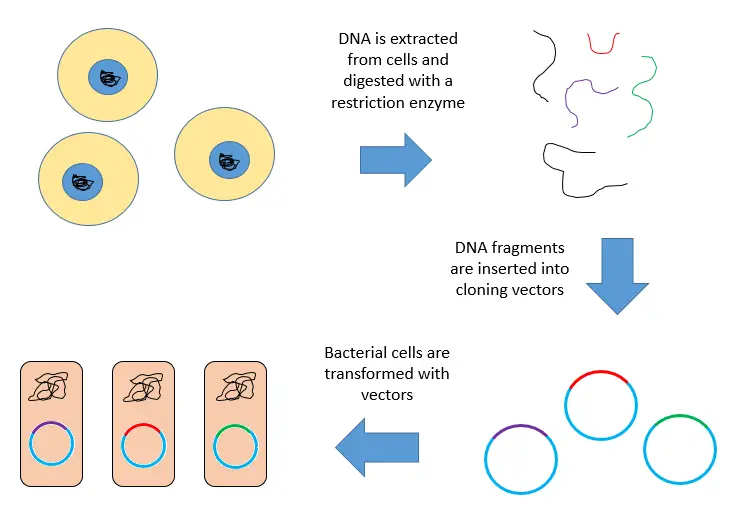
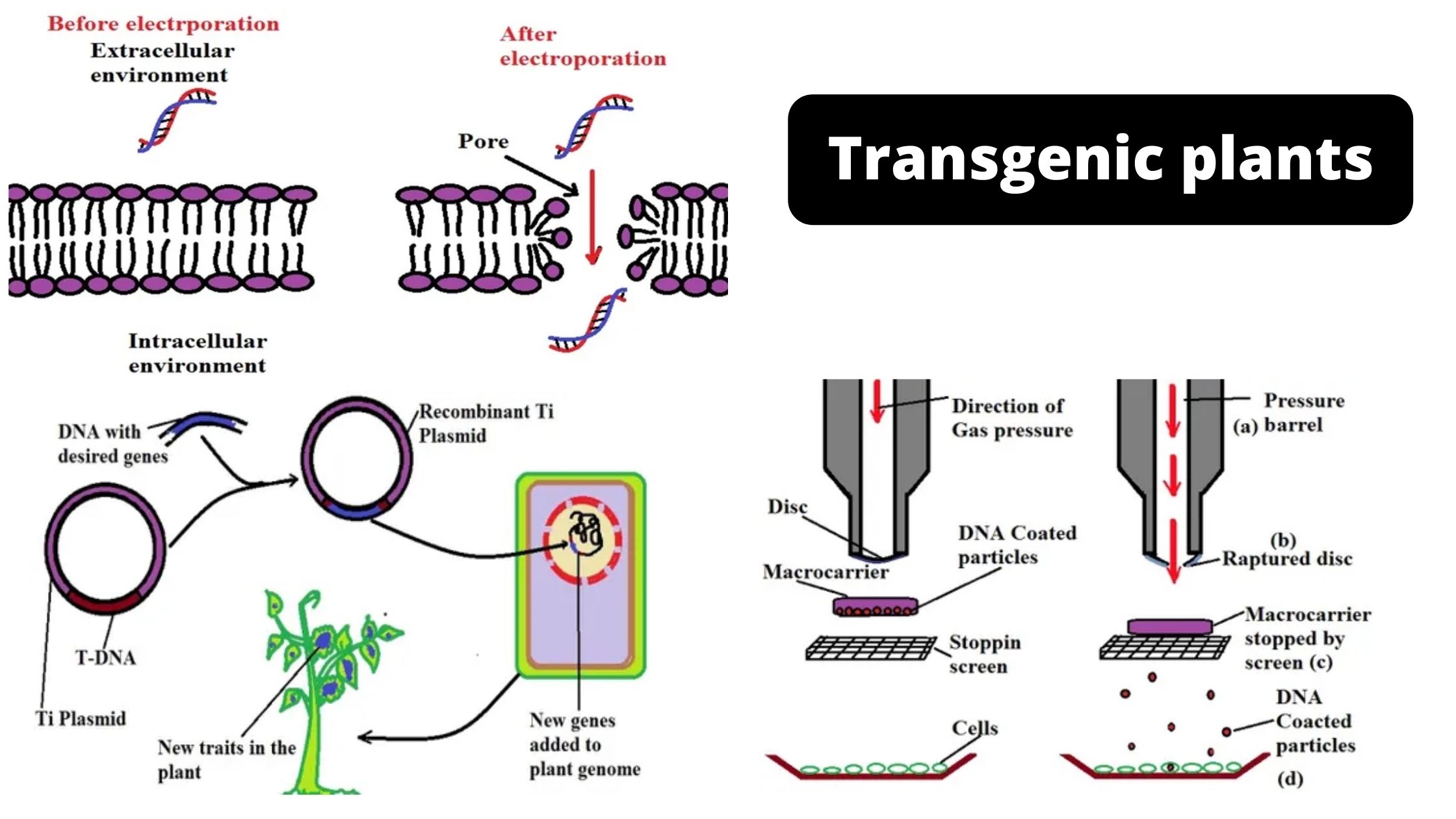
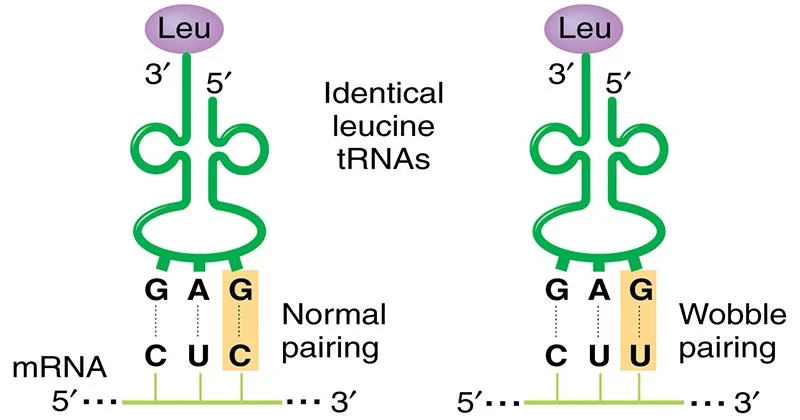
Sanger Sequencing vs Next Generation Sequencing (NGS)
What is Sanger Sequencing? Sanger Sequencing Workflow/Steps Sanger sequencing is a DNA sequencing method known for its reliability and accuracy. The process involves the formation of a reaction system, amplification of the target segment, gel electrophoresis, and sequence reading. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of the Sanger sequencing workflow: 1. DNA Sequence for Chain Termination PCR … Read more