Polygenic Inheritance (Quantitative inheritance) – Characteristics, Mechanism, Examples, Importance
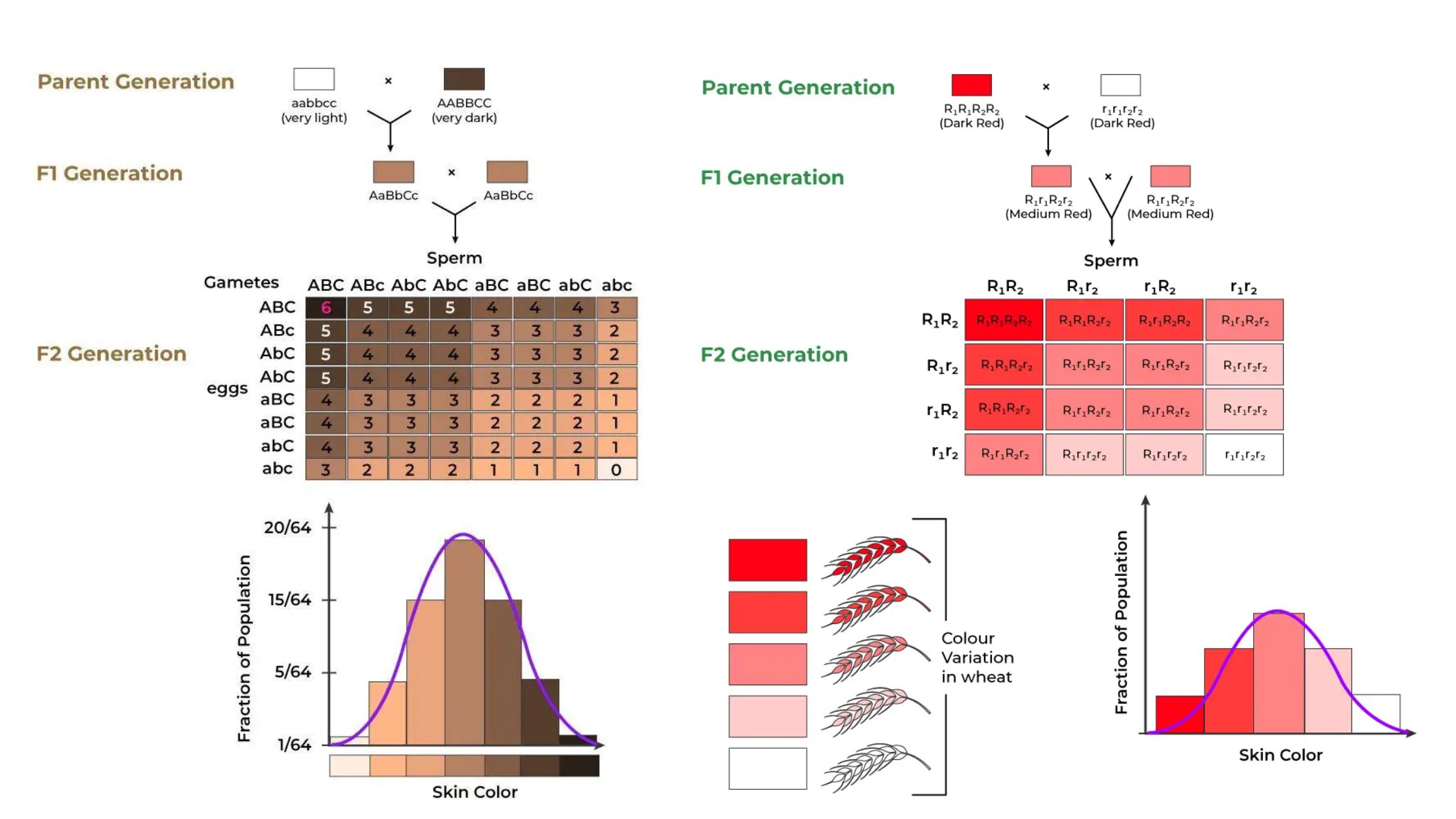
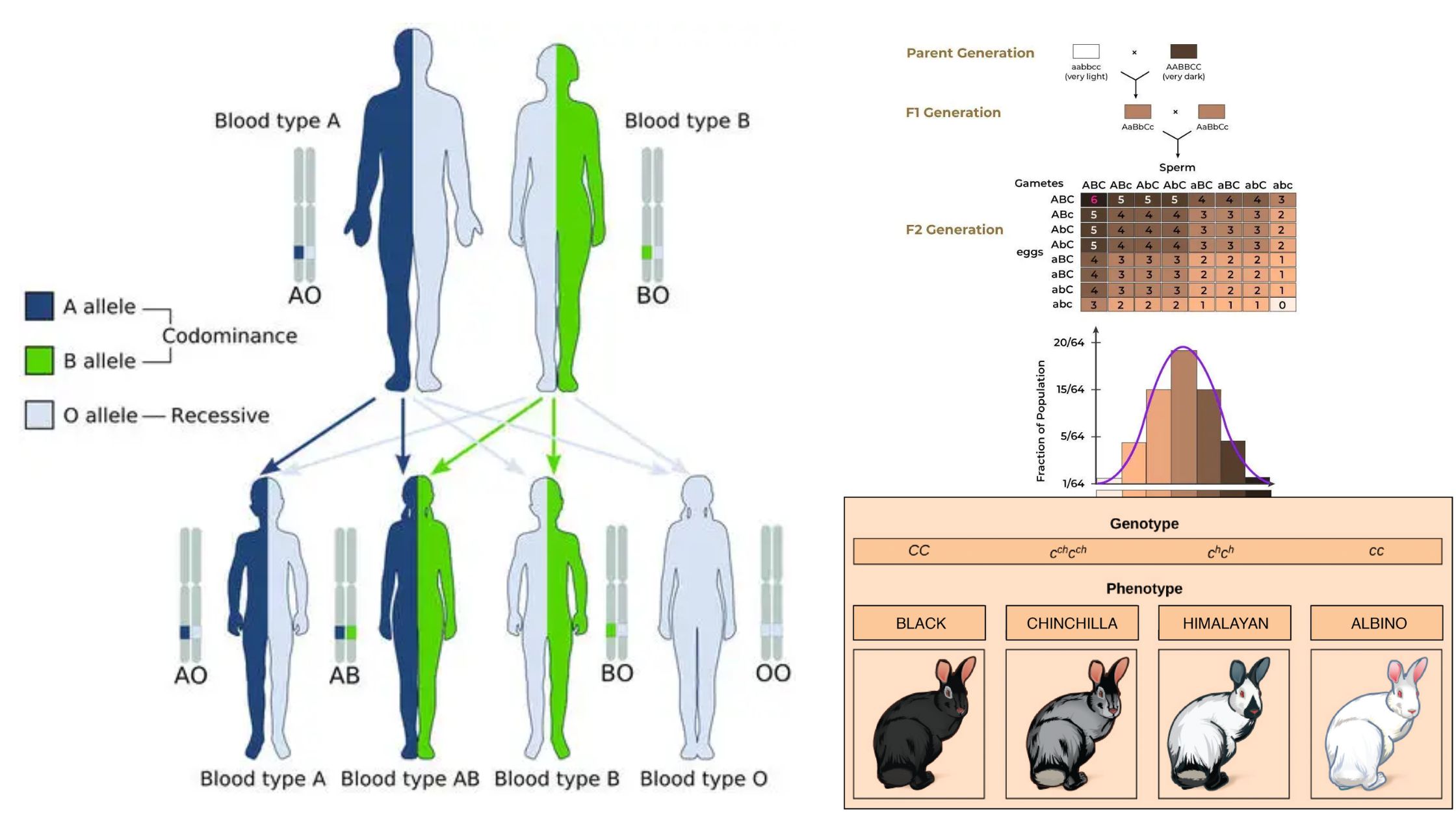
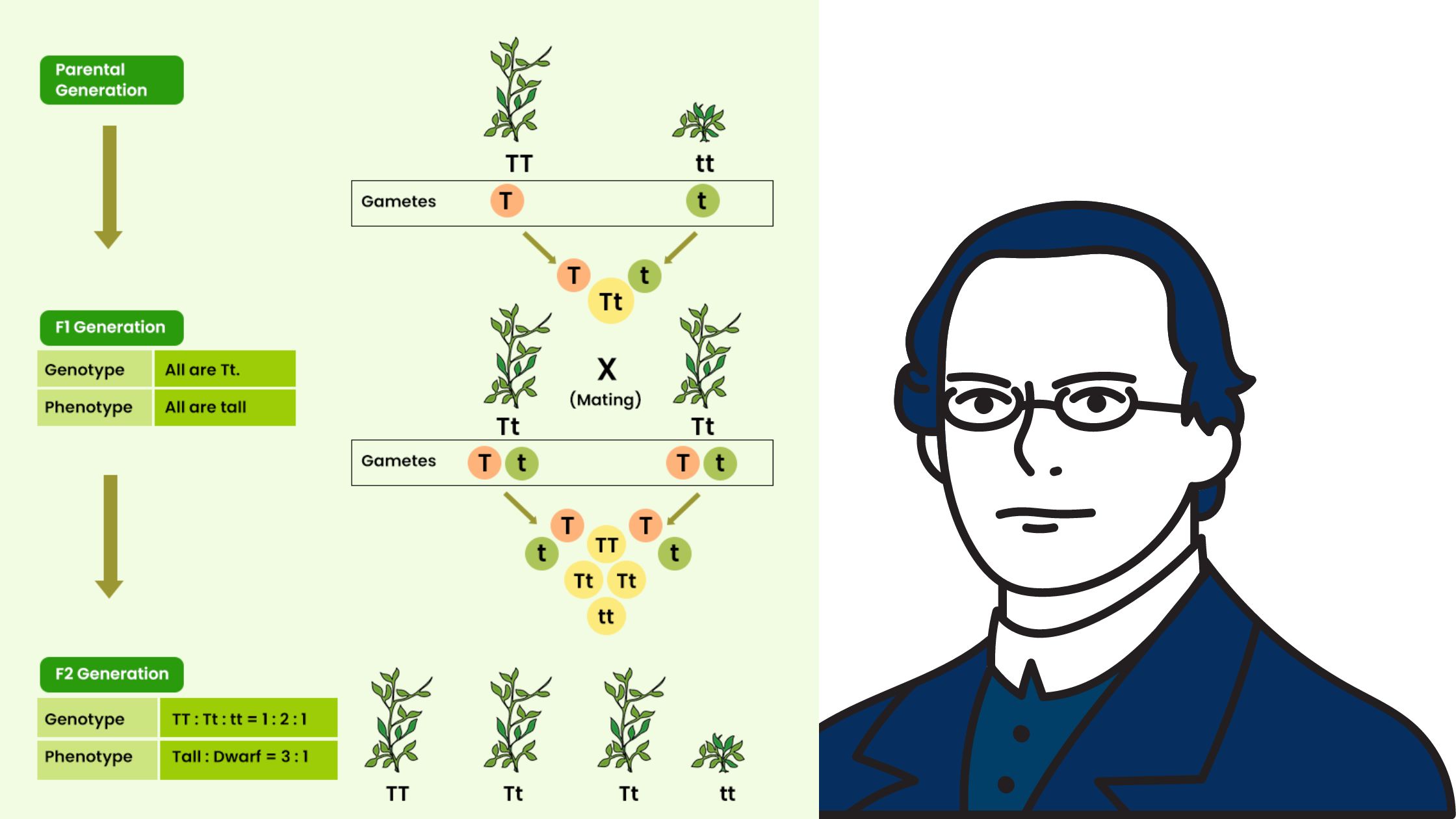
What is Polygenic Inheritance (Quantitative inheritance)? Definition of Polygenic Inheritance Polygenic inheritance is a genetic mechanism where a single phenotypic trait is controlled by the additive effects of multiple genes, resulting in continuous variation rather than discrete categories. Characteristics of Polygenic Inheritance Examples of Polygenic Inheritance in Humans This section explores how polygenic inheritance influences … Read more