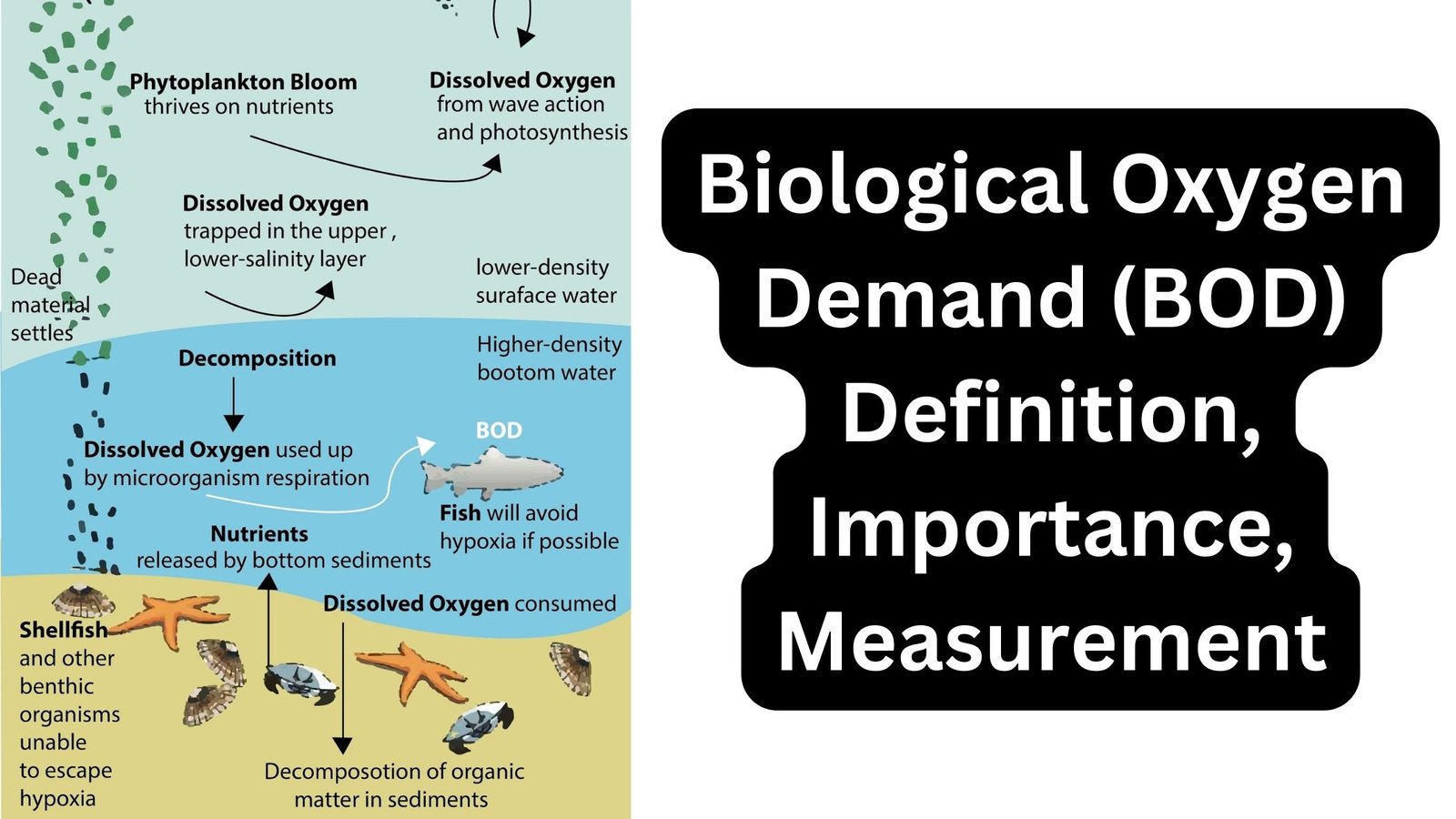
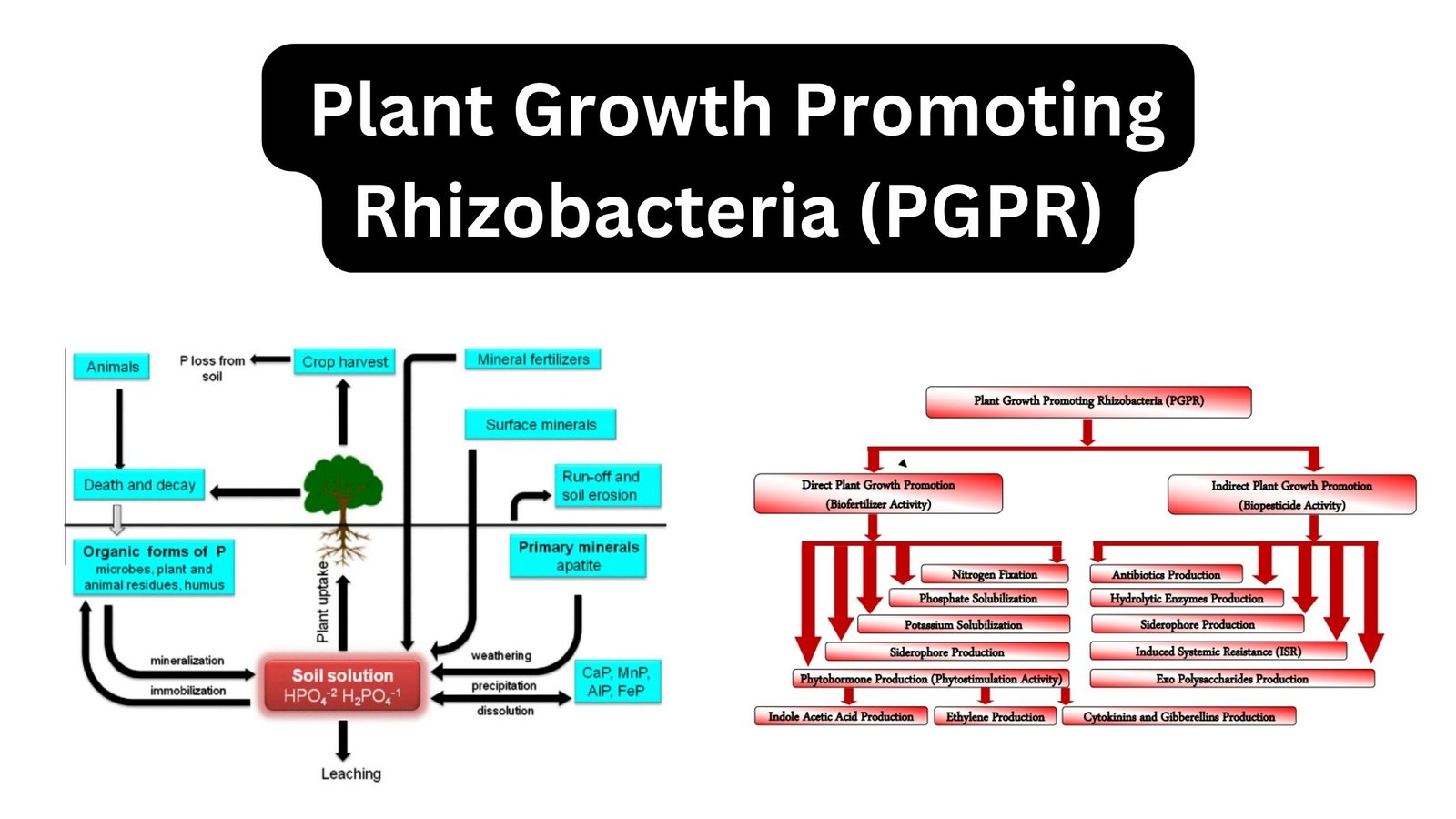
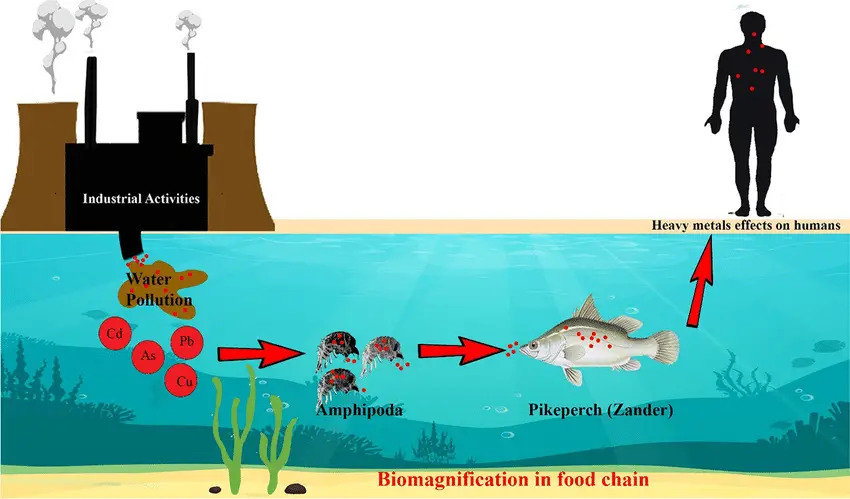
Biological Oxygen Demand (BOD) – Definition, Importance, Measurement
Biological oxygen demand refers to the amount of oxygen required by bacteria and other microorganisms to decompose organic matter under aerobic (oxygen present) conditions at a certain temperature (BOD). The greater the concentration of organic contaminants in the water, the greater the oxygen demand of the bacteria. Consequently, the level of contamination in a body … Read more