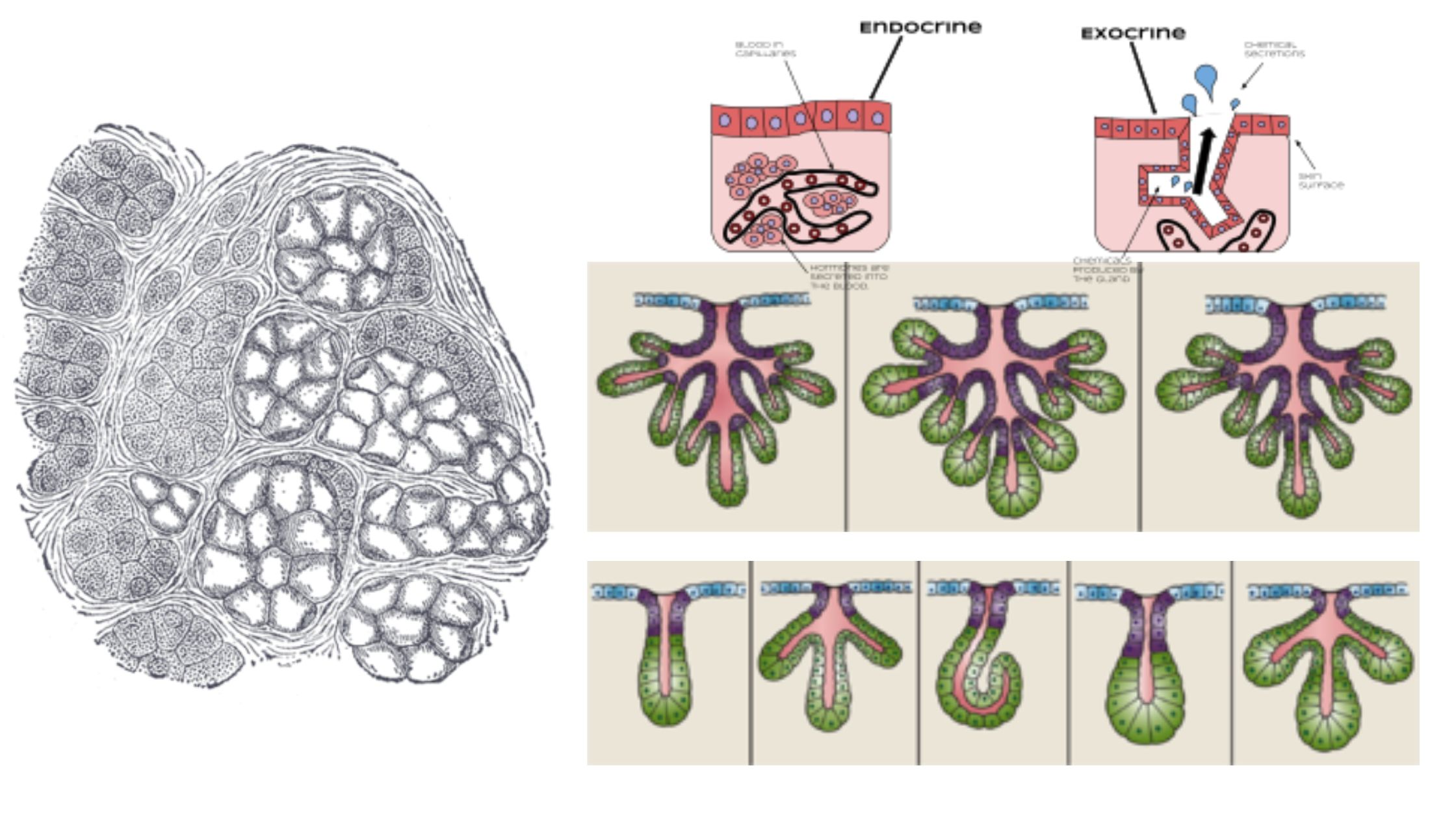
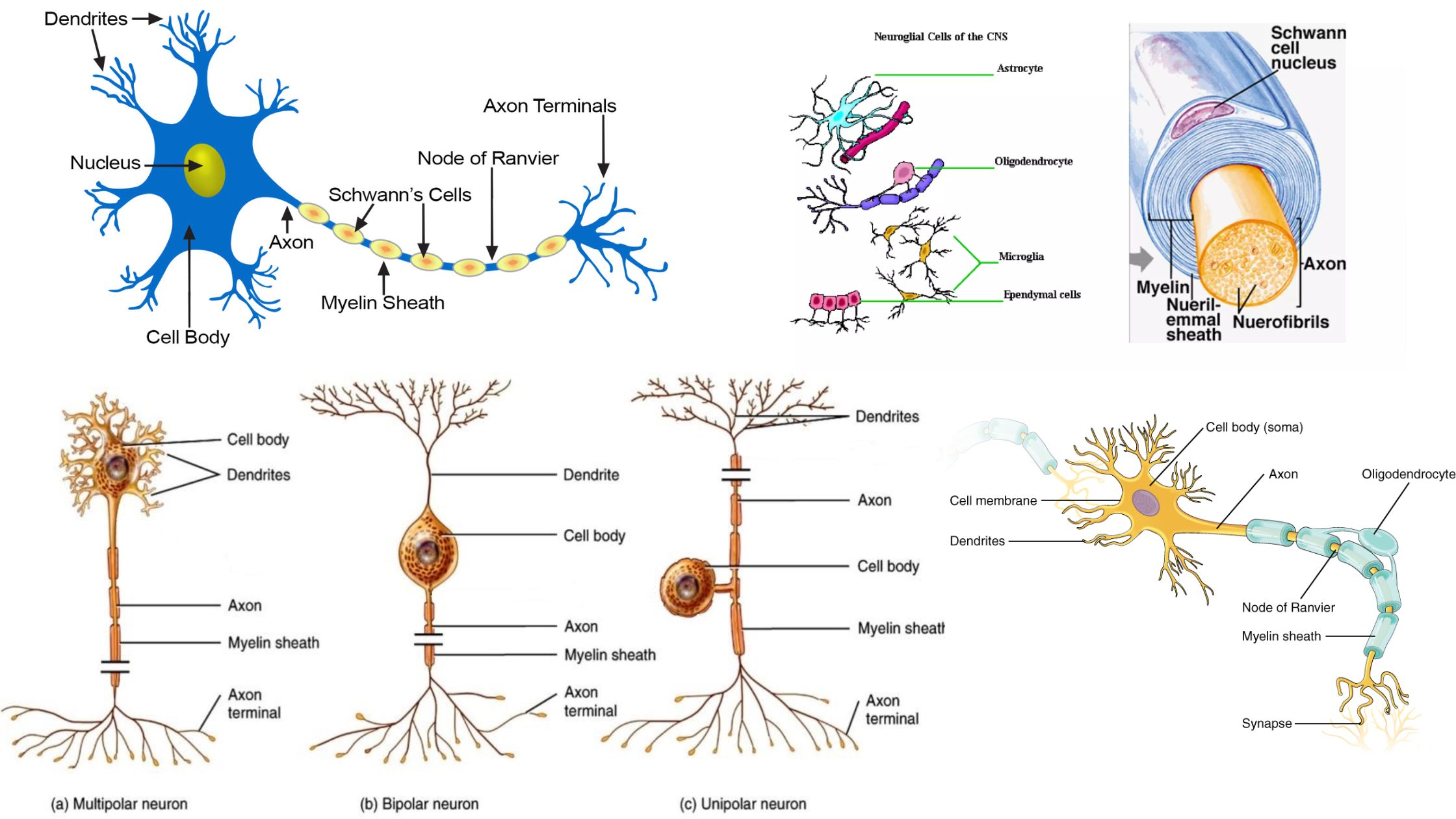
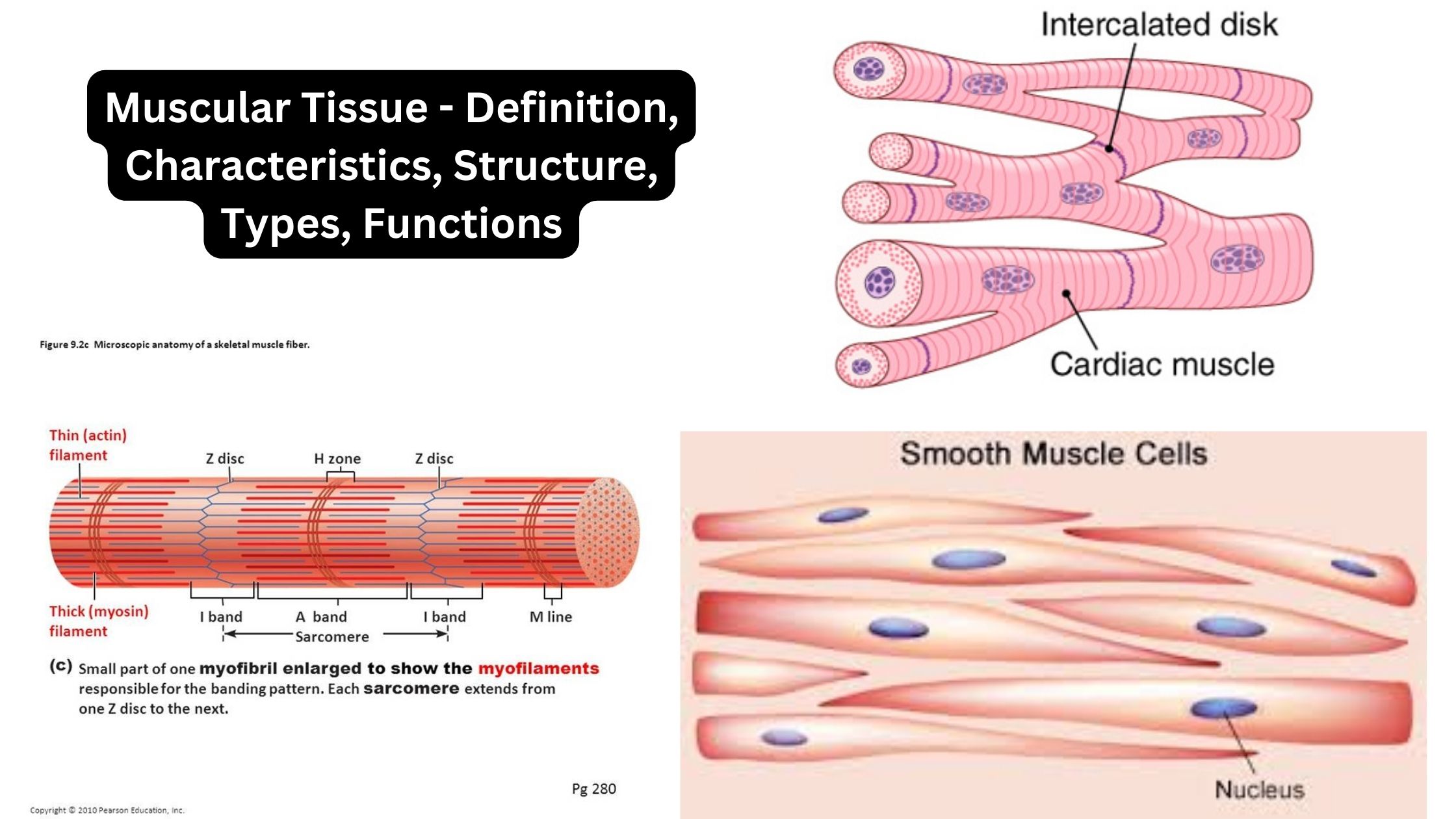
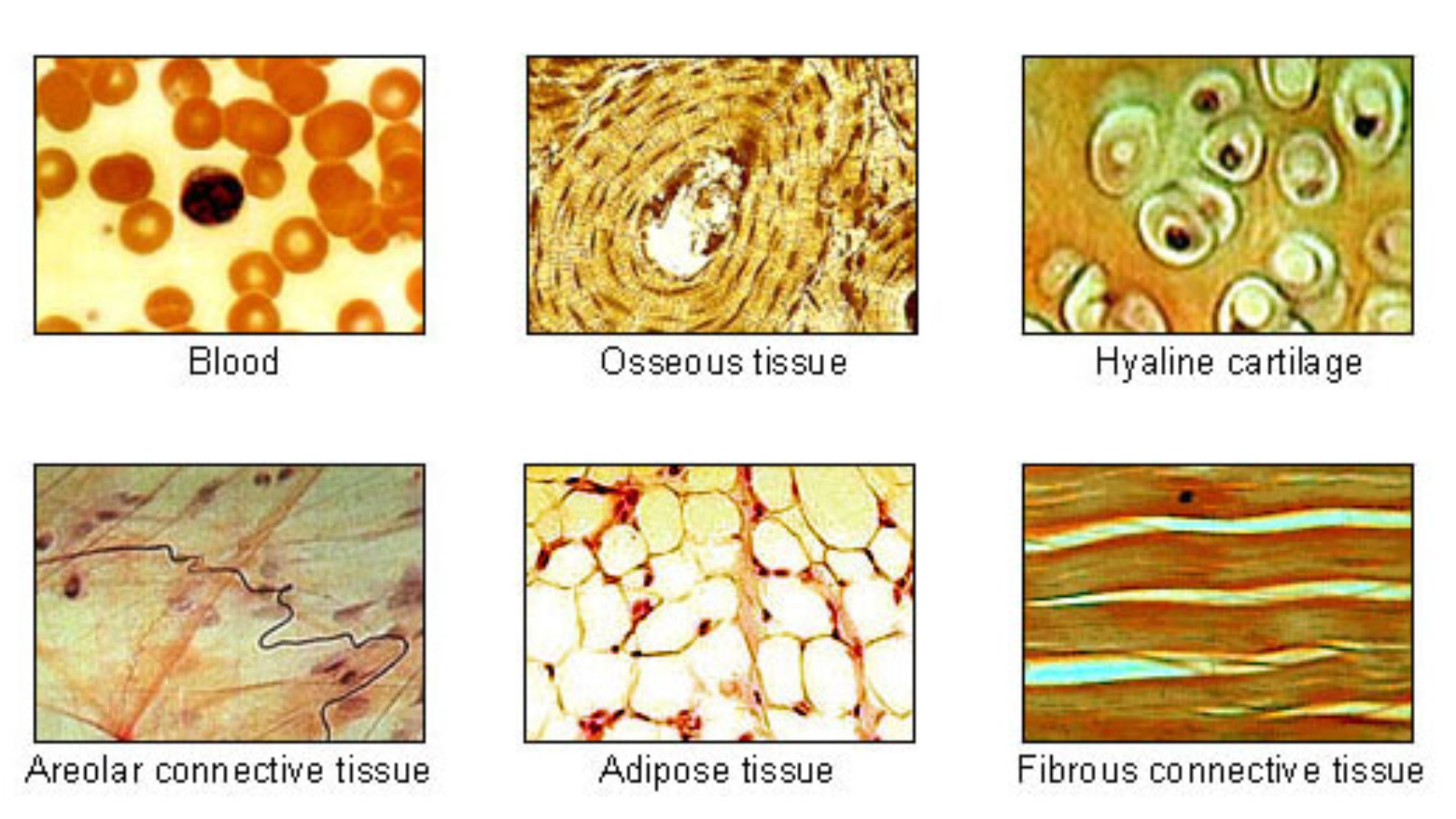
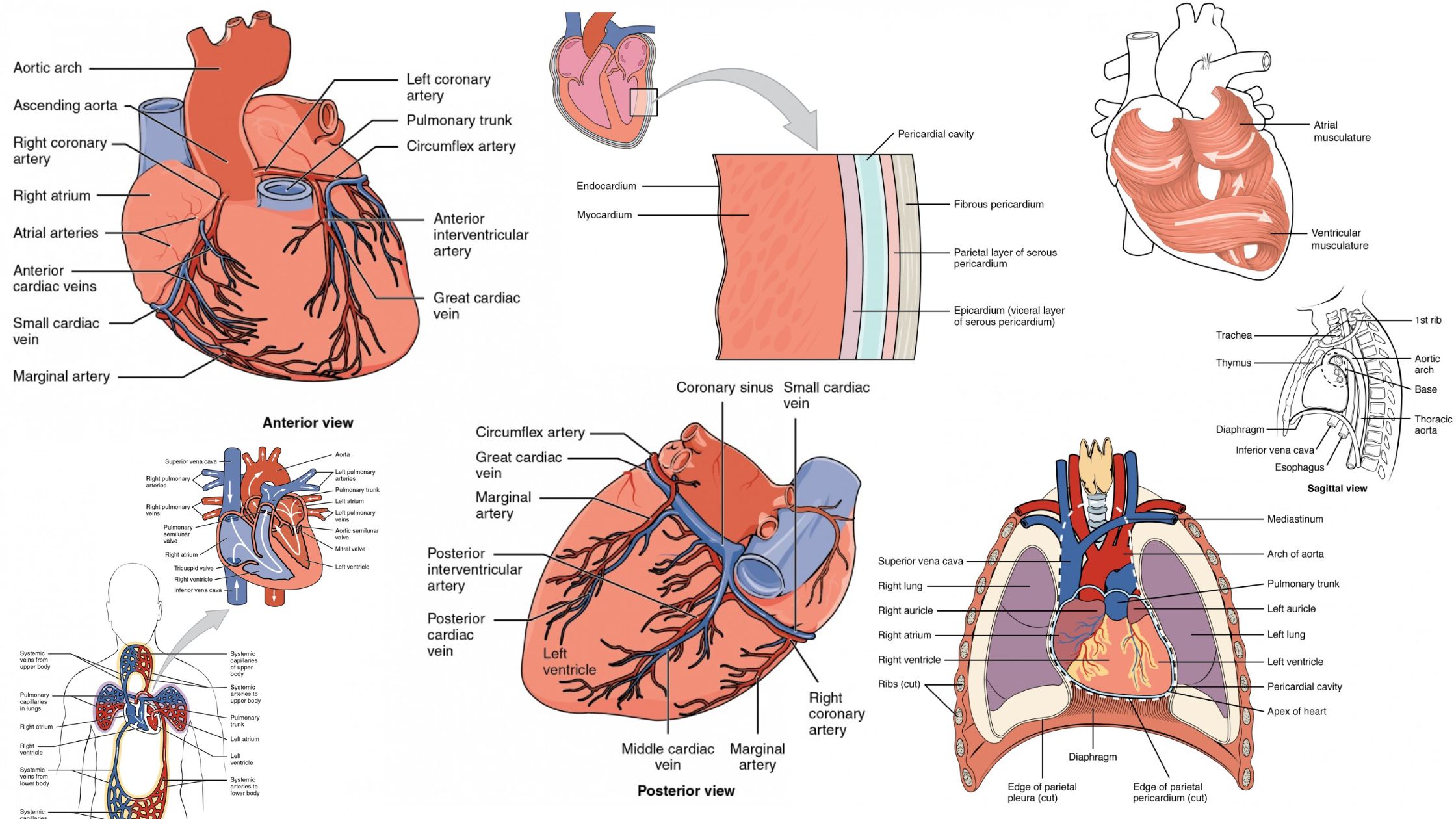
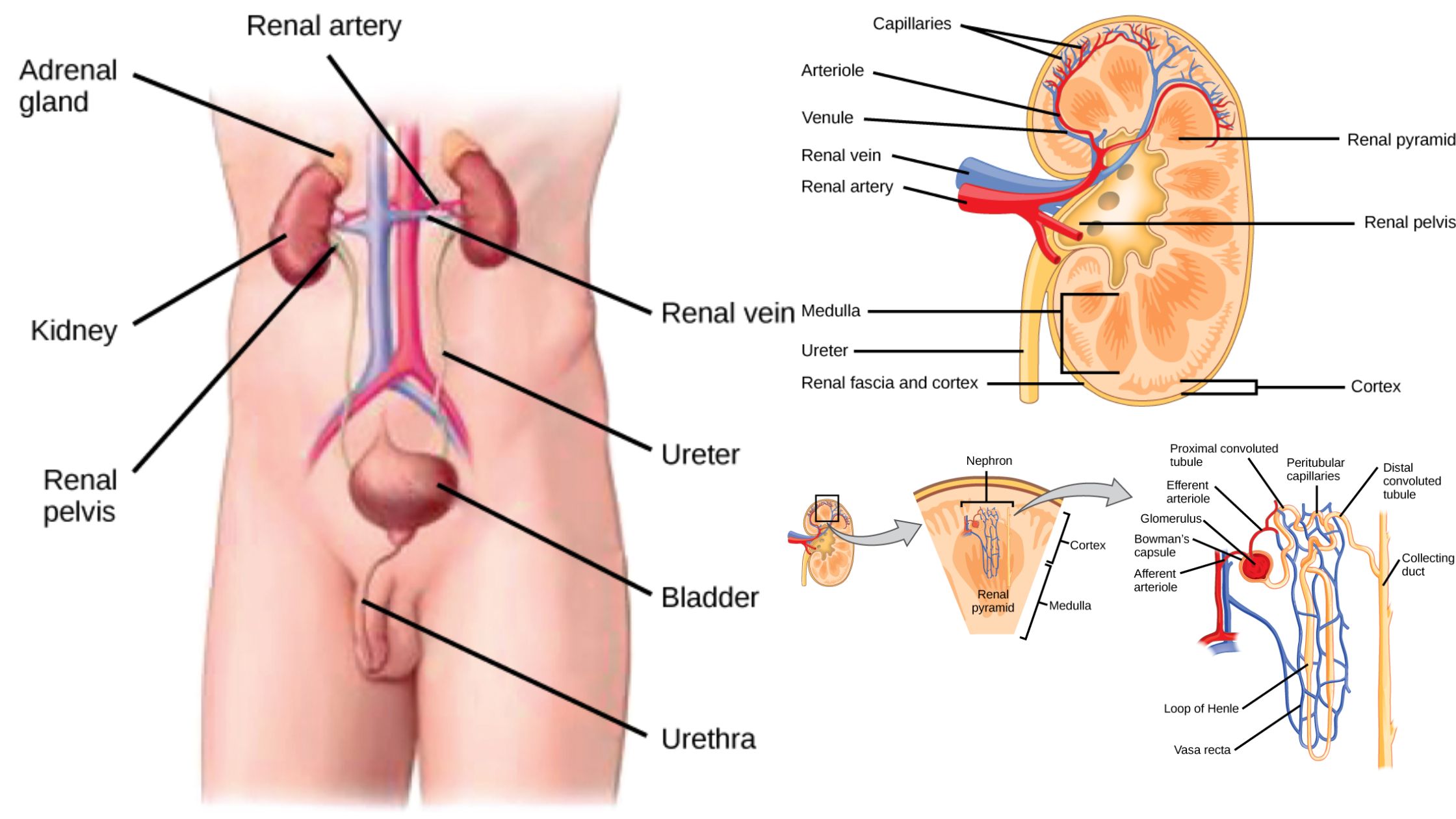
Cartilage – Definition, Structure, Types, Functions
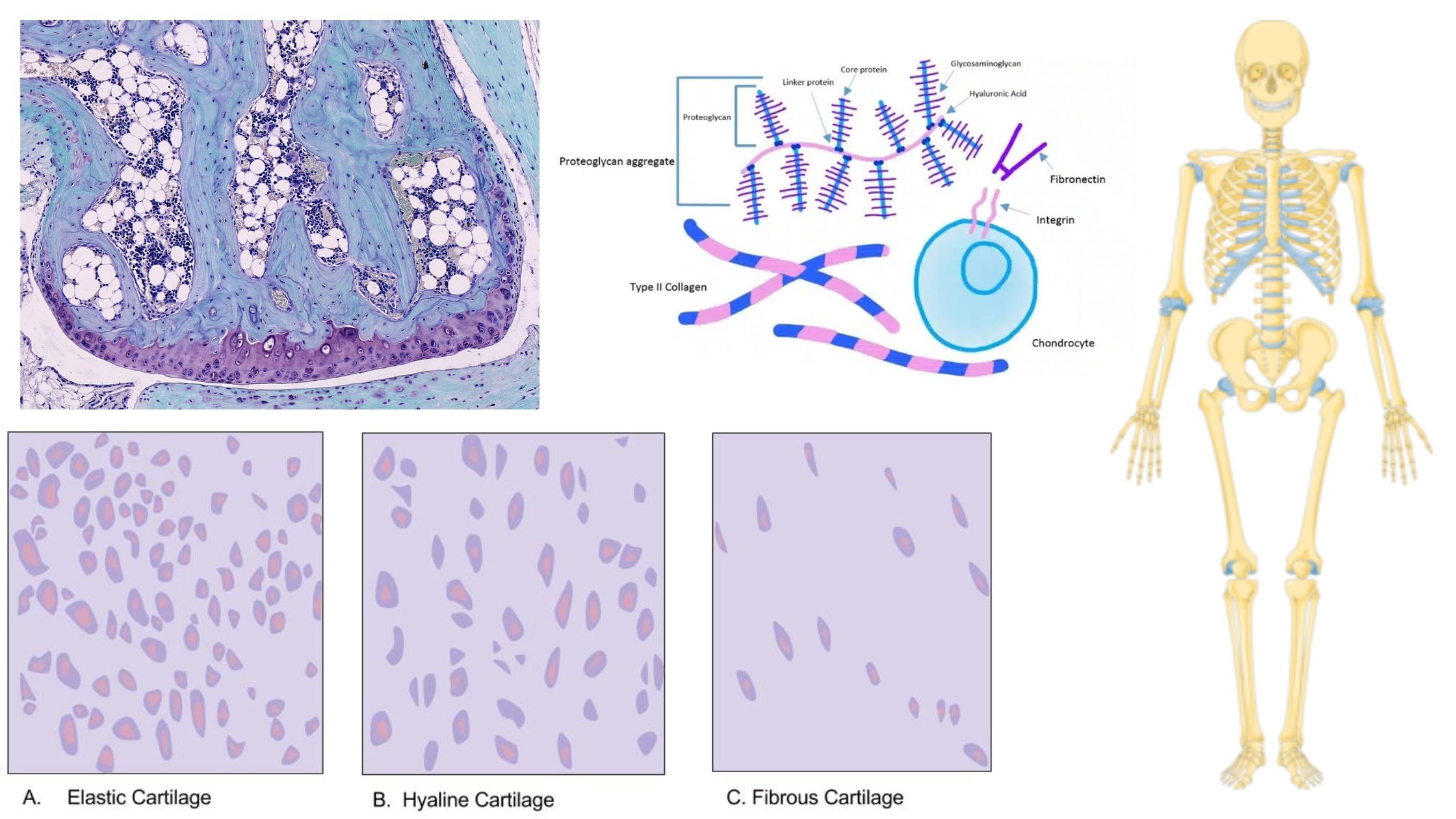
What is Cartilage? Definition of Cartilage Cartilage is a semi-rigid and flexible connective tissue found in various parts of the body, such as joints, nose, and ears. It is tough, yet pliable, and provides structural support, cushioning, and smooth surfaces for joint movement. Location of Cartilage Characteristics of Cartilage Structure of Cartilage Cartilage consists of … Read more