Embryonic Stem Cells – Definition, Properties, Applications
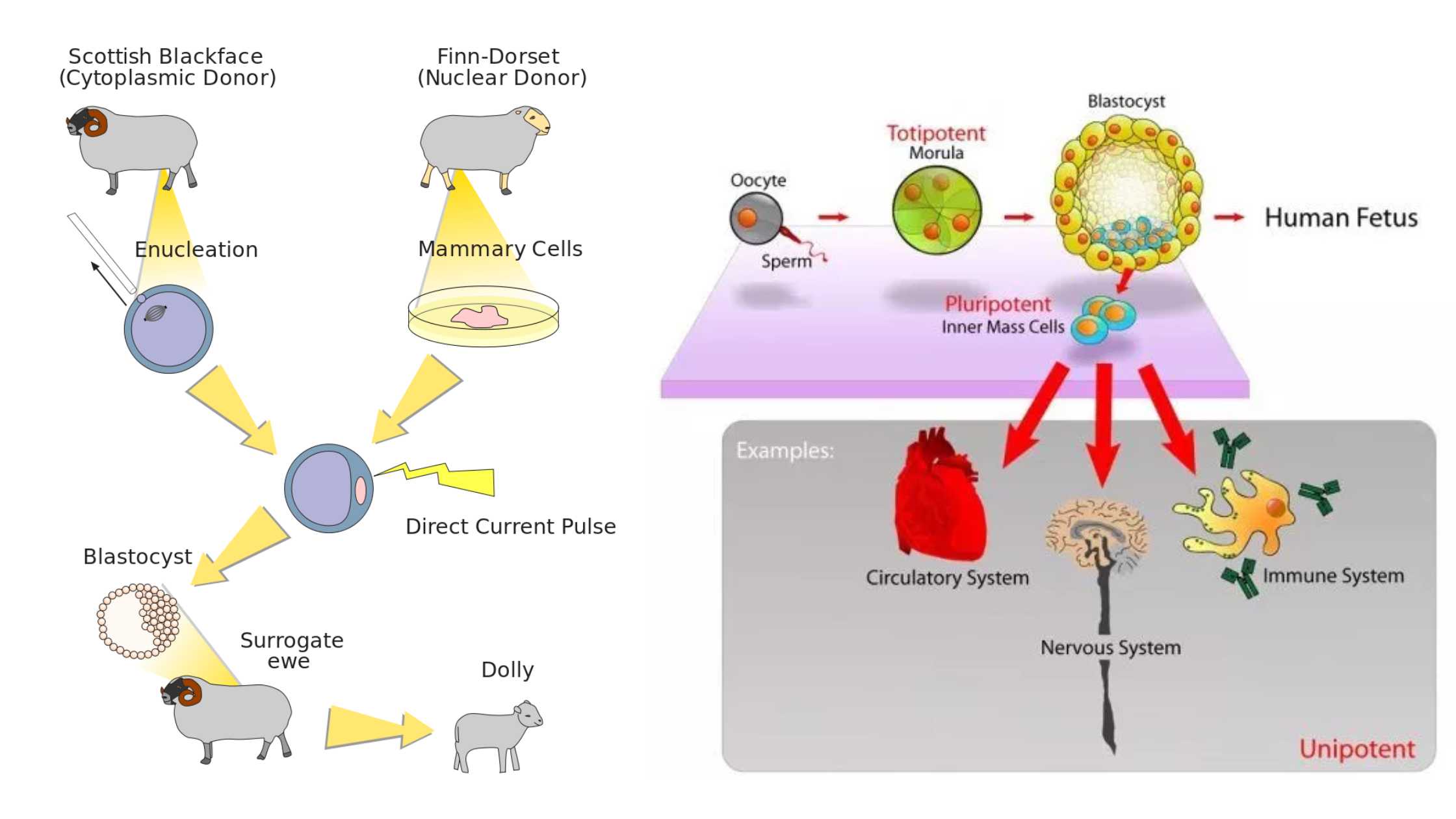
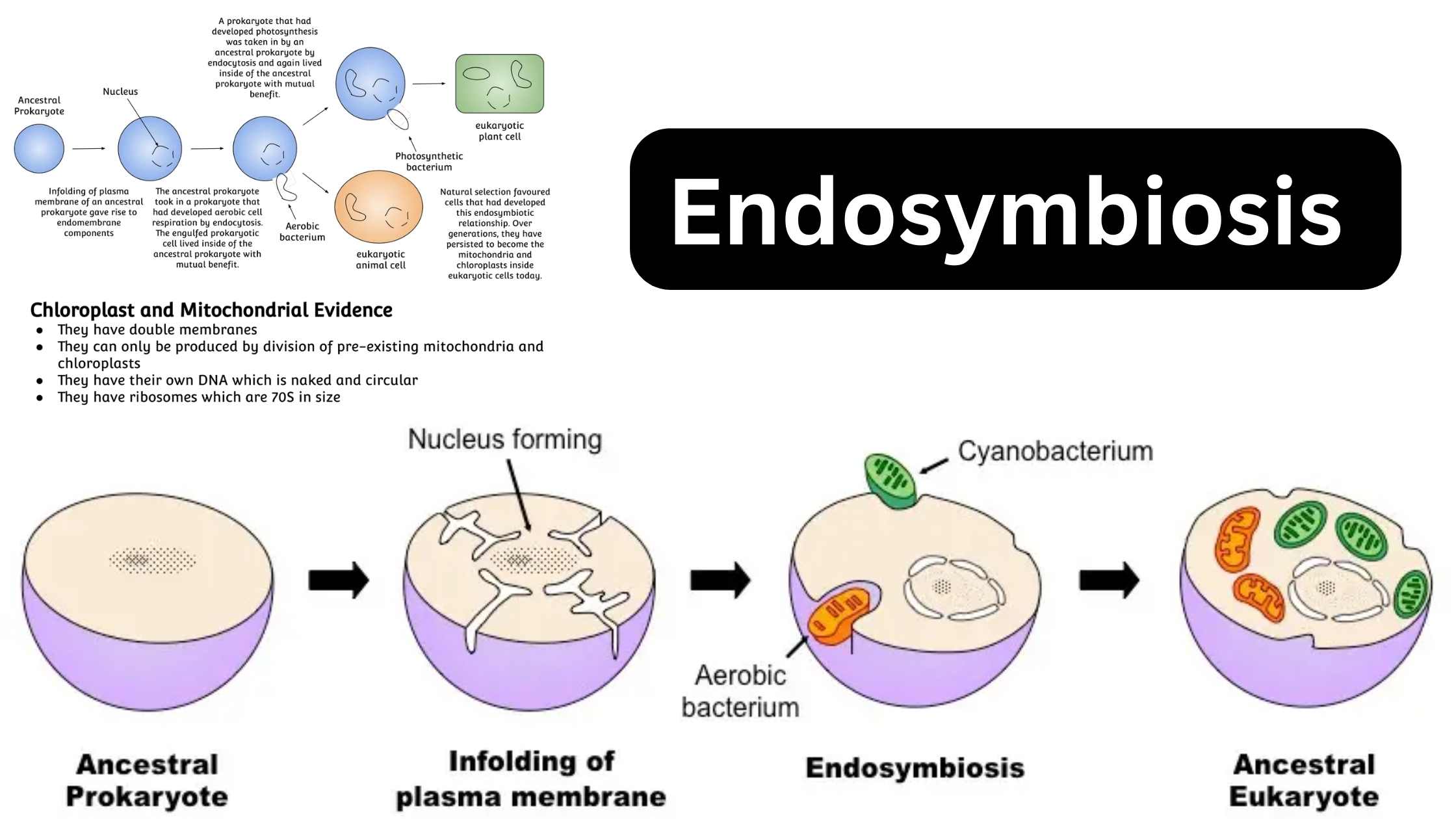
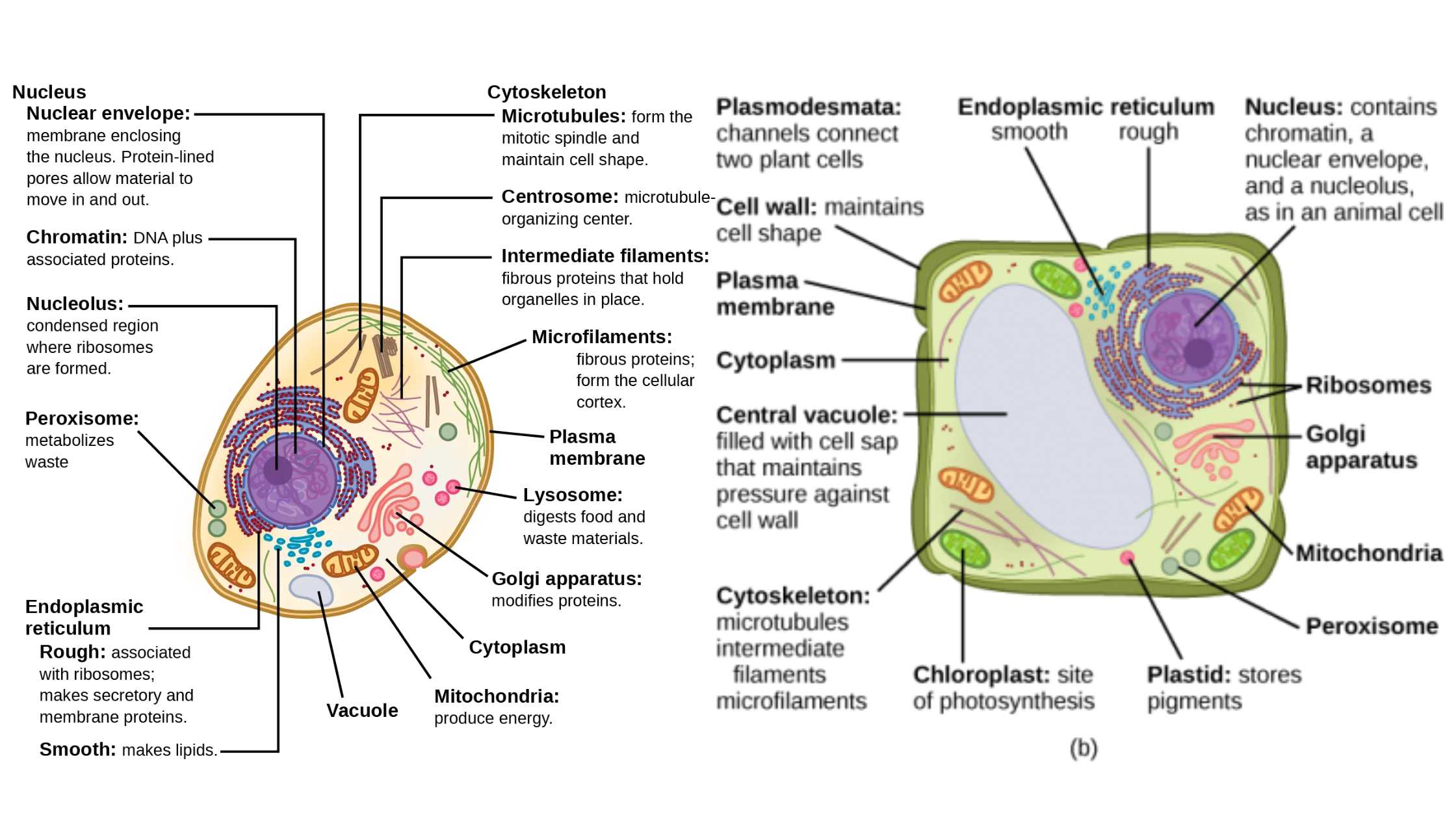
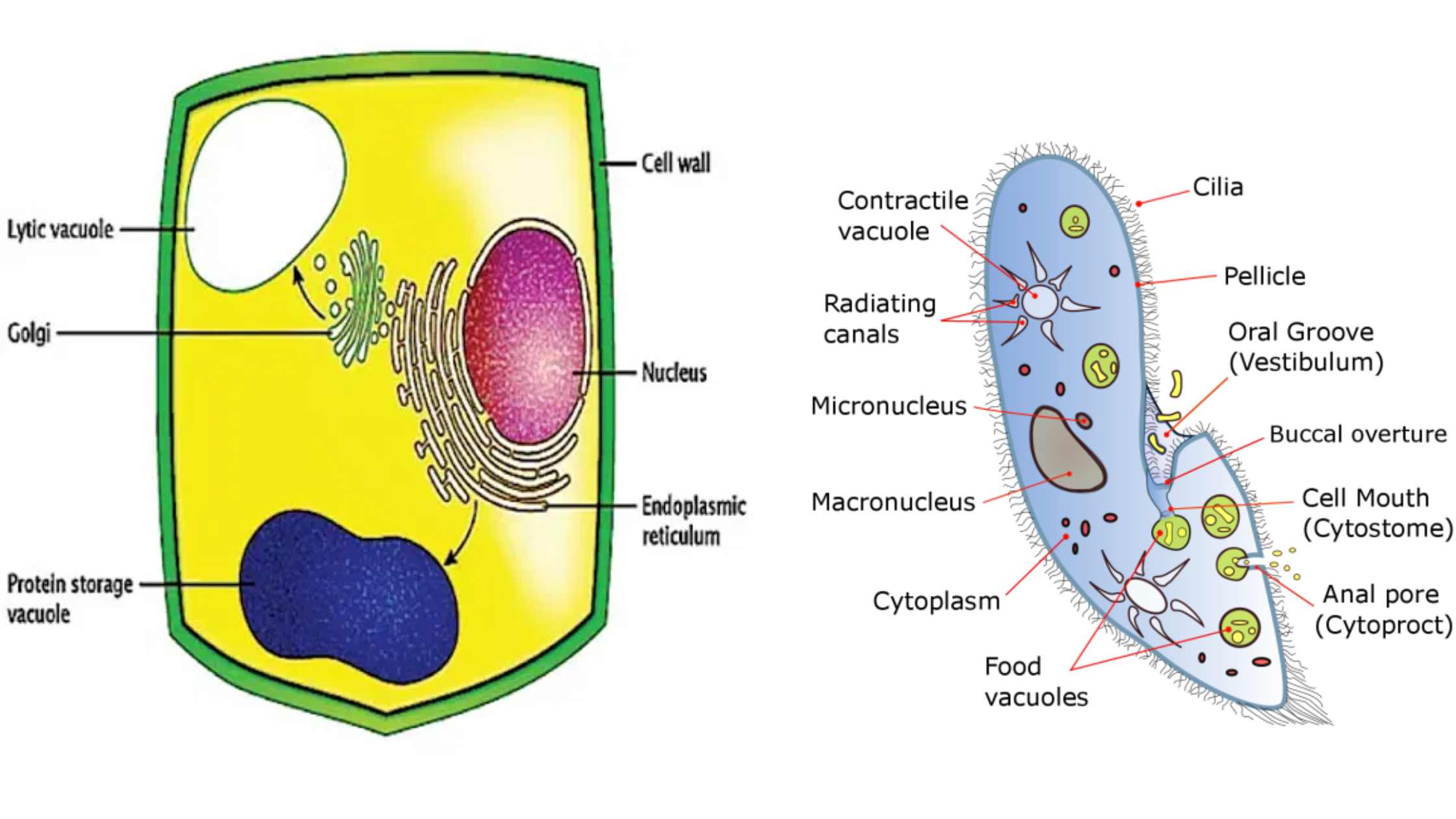
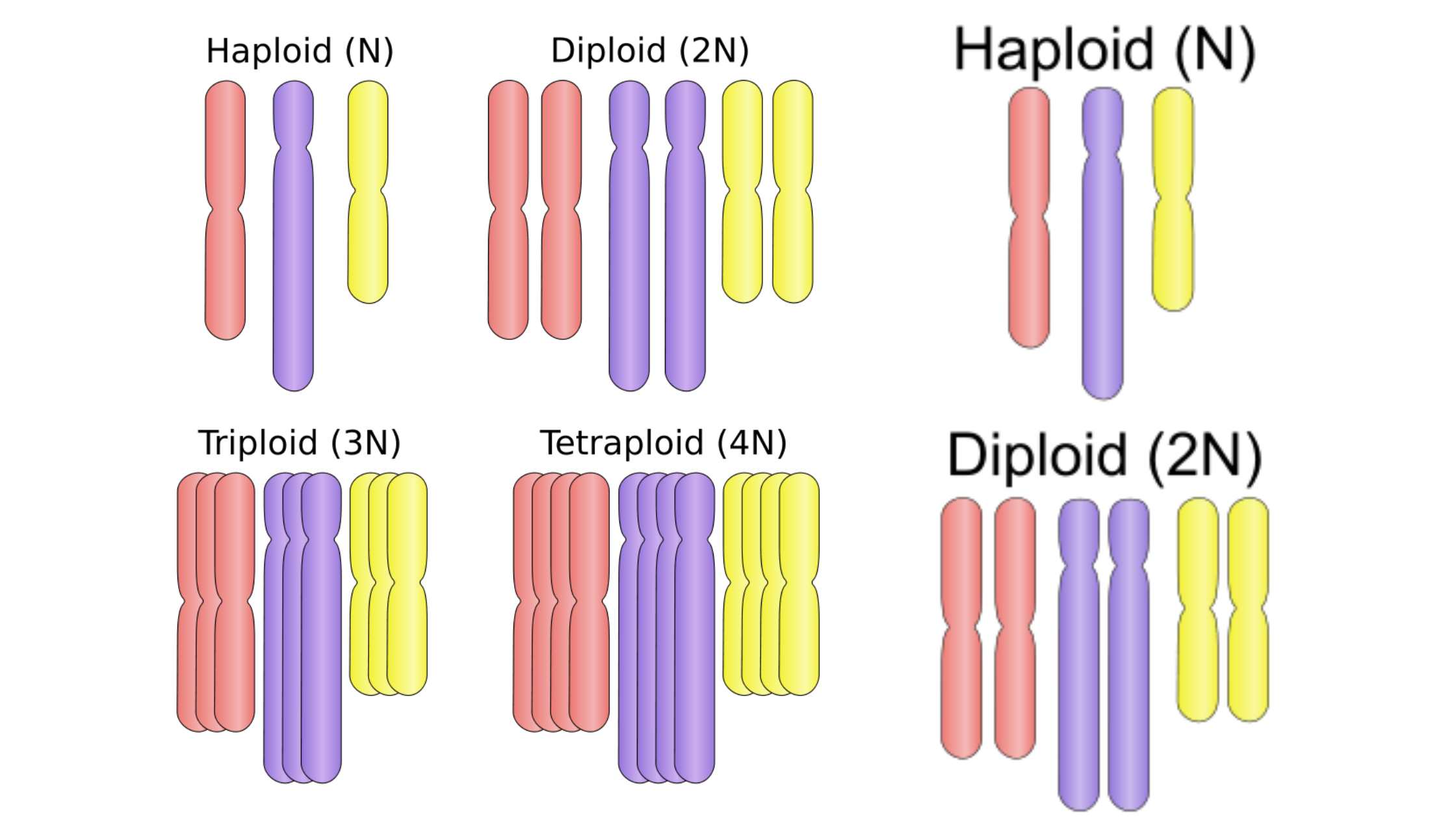
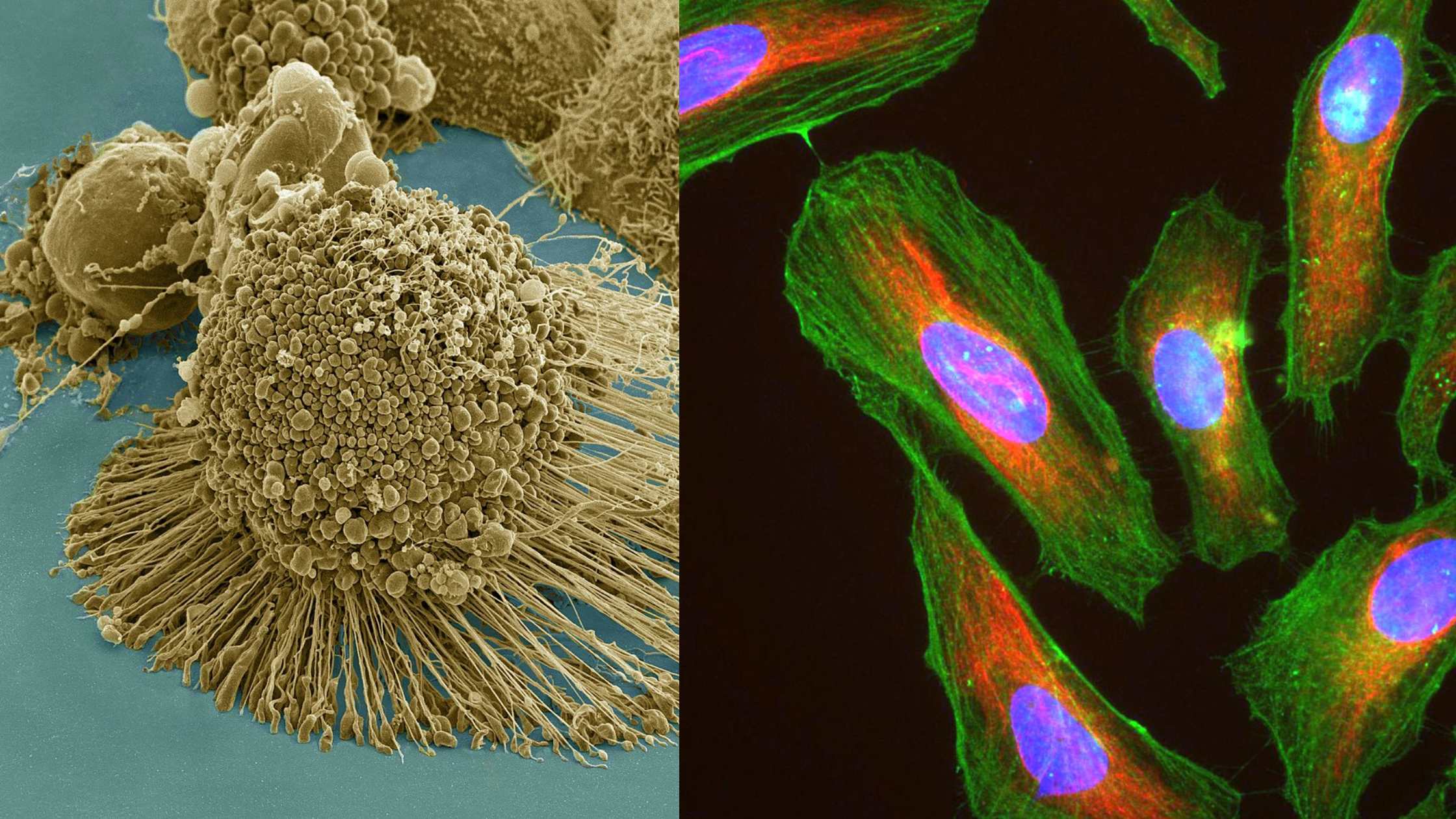
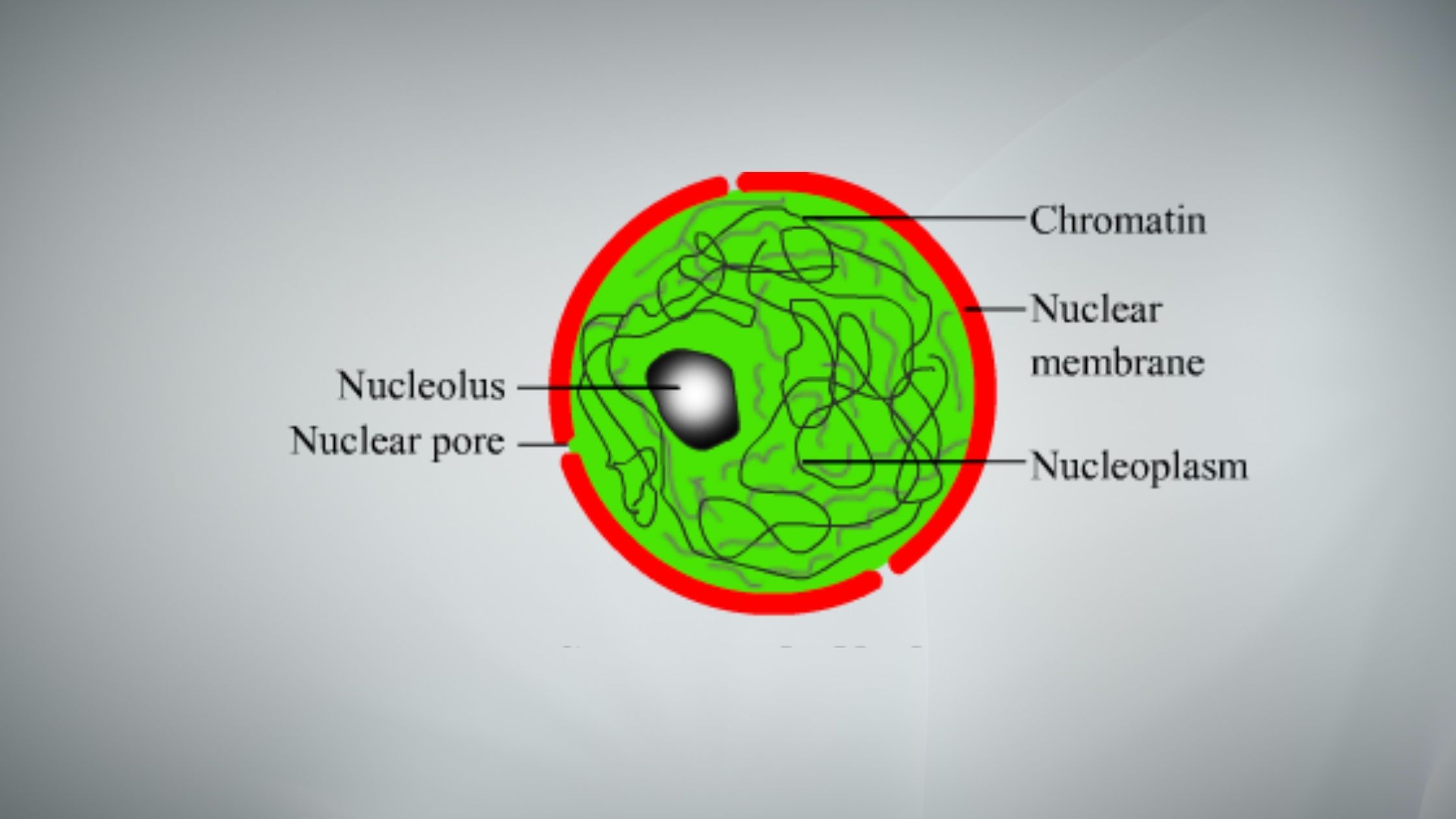
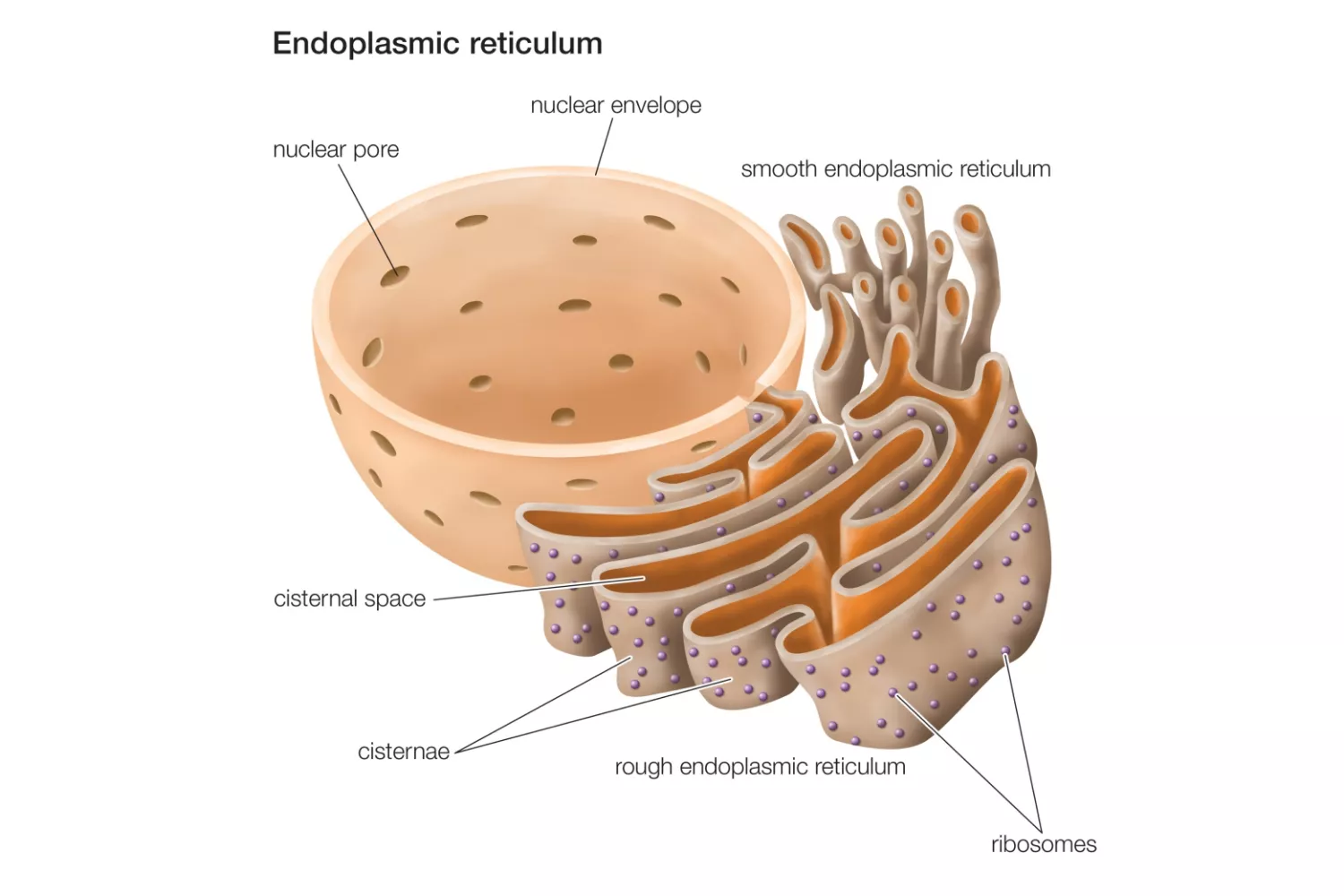
What is Embryonic Stem Cell? Definition of Embryonic Stem Cell Embryonic stem cells (ESCs) are pluripotent cells derived from the inner cell mass of a blastocyst, an early-stage embryo, capable of differentiating into any cell type within an organism. History of Embryonic Stem Cell The history of embryonic stem cells (ESCs) is marked by pioneering … Read more