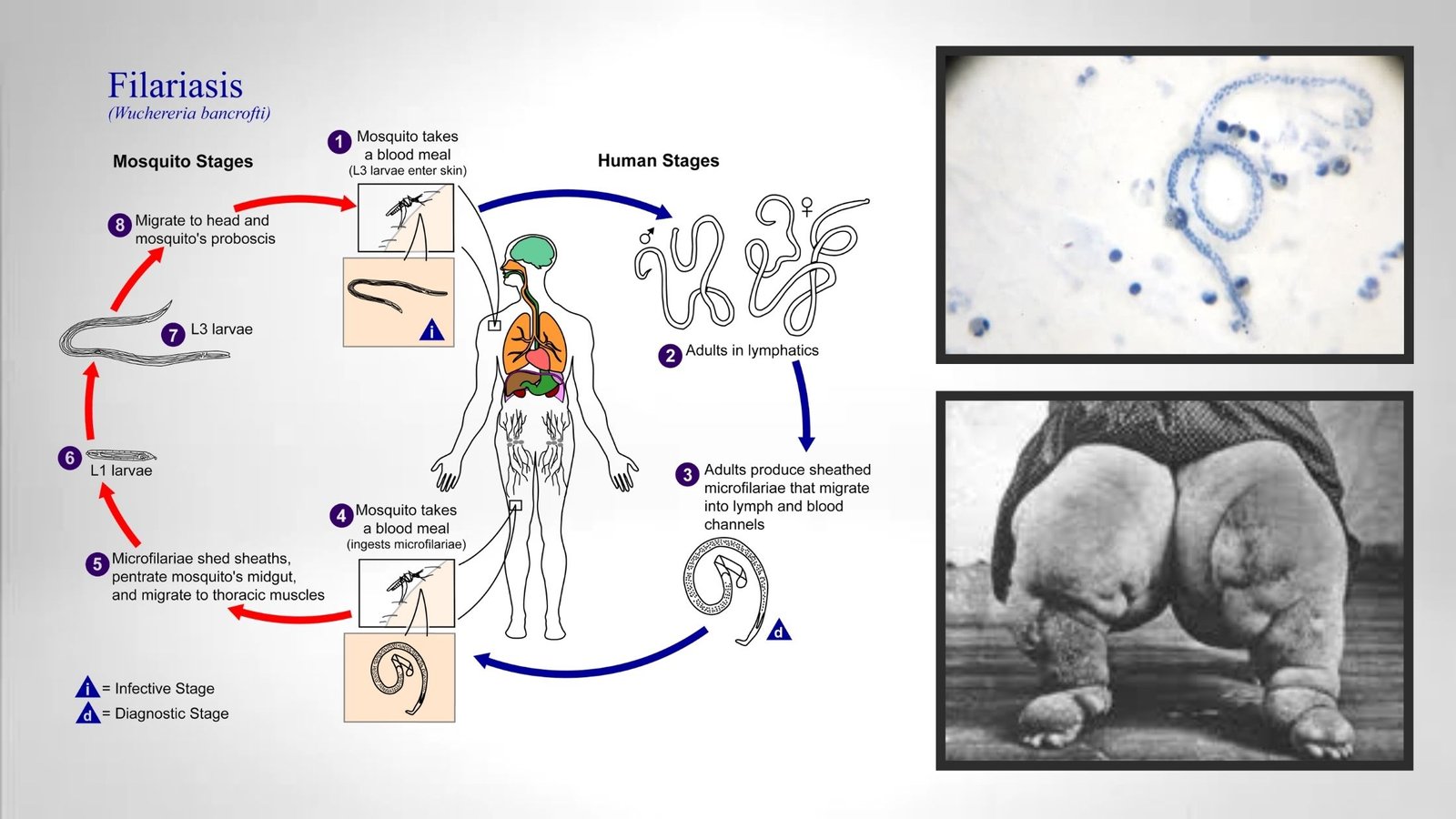
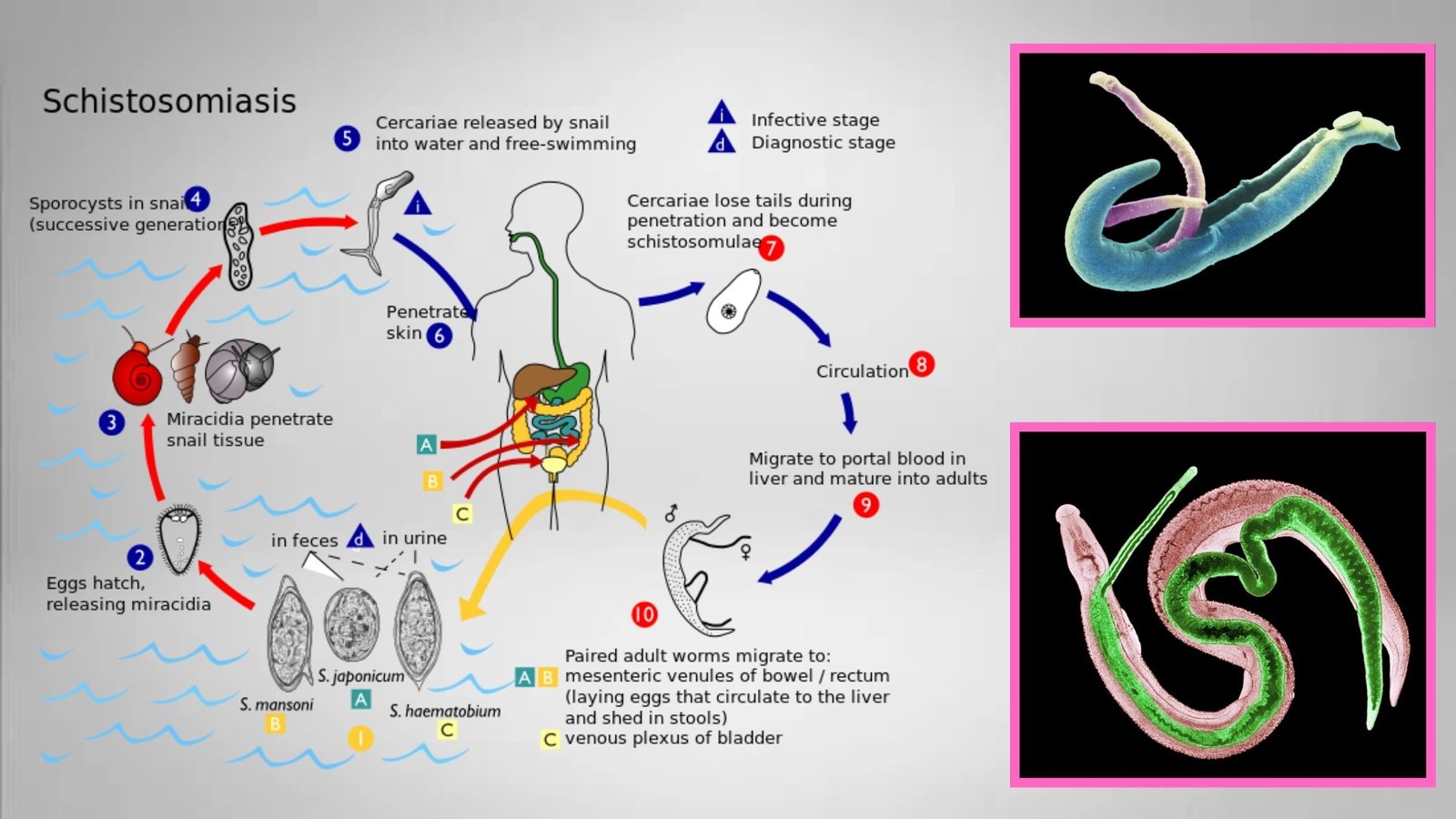
Wuchereria bancrofti – Morphology, Life Cycle, Epidemiology, Pathogenicity, Diagnosis, Prophylaxis and Treatment
Lymphatic filariasis is a parasitic disease caused by three microscopic, thread-like worms, called Wuchereria bancrofti, Brugia malayi and Brugia timori. These worms infect the lymphatic system and cause Lymphatic filariasis. The adult worm can be found in the human lymph system, this system helps to maintain the body’s fluid balance and fights against infections.