What is Pauly’s Test?
- There is a chemical assay called the Pauly reaction that can determine whether or not a protein contains the amino acids tyrosine or histidine.
- The German scientist Hermann Pauly is credited with describing this process, hence it bears his name. In alkaline circumstances, a coupling reaction between proteins containing tyrosine or histidine and diazotized sulfanilic acid yields a red colour.
- Highly coloured compounds can be formed when diazotized sulphanilic acid combines with amines, phenols, or imidazole.
- Since the diazonium component can only be produced at low temperatures, diazotization requires chilling the solution in ice.4, 6
Purposes of Pauly’s Test
- Tyrosine and histidine, aromatic amino acids, detection
Principle of Pauly’s Test
The presence of tyrosine and histidine can be determined with this test with high sensitivity. Sulphanilic acid is dissolved in hydrochloric acid and used as the reagent in this test. When being exposed to sodium nitrite and hydrochloric acid, sulphanilic acid forms a diazonium salt by the process of diazotization. To produce a red chromogen, the produced diazonium salt combines with either tyrosine or histidine in an alkaline media (azo dye).6,7
Reaction of Pauly’s Test
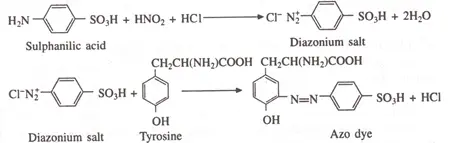
Sulphanilic acid + HNO2 + HCl → Diazonium salt + 2H2O
Diazonium salt + Tyrosine → Azo dye (red color)
Requirements for Pauly’s Test
- 1 % tyrosine, 1 % histidine, 1%glycine
- 1 % sulphanilic acid in 10 % HCI
- 5 % sodium nitrite
- 10 % sodium carbonate
- Ice bath
Procedure of Pauly’s Test
- Take 2 millilitres of test solution in a dry test tube.
- Take 2ml of distilled water in a separate test tube as a control.
- Add 1 ml of sulphanilic acid, stir thoroughly, and store in an ice bath.
- Add 1 millilitre of sodium nitrite solution to each test tube.
- Place in an ice bath for three minutes.
- Add 5 ml of sodium carbonate to create an alkaline solution.
- Watch for the formation of a red complex.
Result and Interpretation of Pauly’s Test
- Positive test: The presence of tyrosine or histidine is indicated by the formation of a red hue.
- Negative test: The absence of red colour production indicates the absence of tyrosine or histidine.

Limitations of Pauly’s Test
- The production of diazonium salt happens at low temperatures; hence, the test should be conducted with ice present.
- The test is incapable of distinguishing between histidine and tyrosine. Histidine produces a negative result in the Millon’s Test, hence the test can be performed.
FAQ
What is Pauly’s test?
Pauly’s test is a biochemical test used to detect the presence of tyrosine and histidine-containing proteins. It is named after the German chemist Hermann Pauly who discovered the test.
What is the principle behind Pauly’s test?
Pauly’s test is based on the principle of coupling between the amino acids and the diazonium ion formed in the reagent. The pauly’s reagent consists of sulphanilic acid dissolved in concentrated hydrochloric acid. The sulfanilic acid undergoes diazotization in the presence of sodium nitrate and hydrochloric acid. The result of the diazotization reaction is the diazonium salt (p-phenyldiazosulphonate).
How is Pauly’s test performed?
To perform Pauly’s test, 1 ml of chilled sulfanilic acid is added to a test tube, and a few drops of pre-chilled sodium nitrite are mixed in a vortex. One ml of amino acid sample is immediately added to the test tube and mixed in a vortex. Few drops of sodium carbonate are added to the test tube drop by drop until color begins to appear. A positive result is demonstrated by the appearance of a red-colored complex, indicating the presence of histidine and tyrosine in the solution.
What are the uses of Pauly’s test?
Pauly’s test is used to detect the presence of tyrosine and histidine-containing proteins. The test also allows the differentiation of histidine and tyrosine from other amino acids.
What are the limitations of Pauly’s test?
The formation of diazonium salt occurs at cold temperatures; thus, the test should be performed in the presence of ice. The test doesn’t allow the differentiation between histidine and tyrosine. Millon’s Test can be performed as histidine gives a negative result in Millon’s test.
References
- Tiwari, A. (2015). Practical Biochemistry. LAP Lambert Academic Publishing.
- https://vlab.amrita.edu/?sub=3&brch=63&sim=1094&cnt=1
- https://quizlet.com/96596357/pauly-test-flash-cards/
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pauly_reaction
- https://microbenotes.com/paulys-test/
- http://biocheminfo.com/2020/04/17/paulys-test-principle-reaction-reagents-procedure-and-result-interpretation/
- https://www.onlinebiologynotes.com/paulys-test-objective-principle-reagents-procedure-and-result/