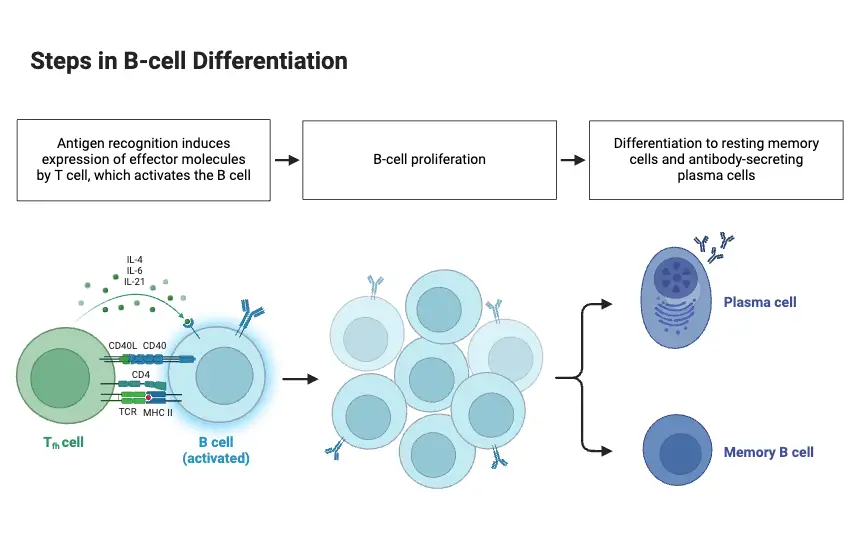
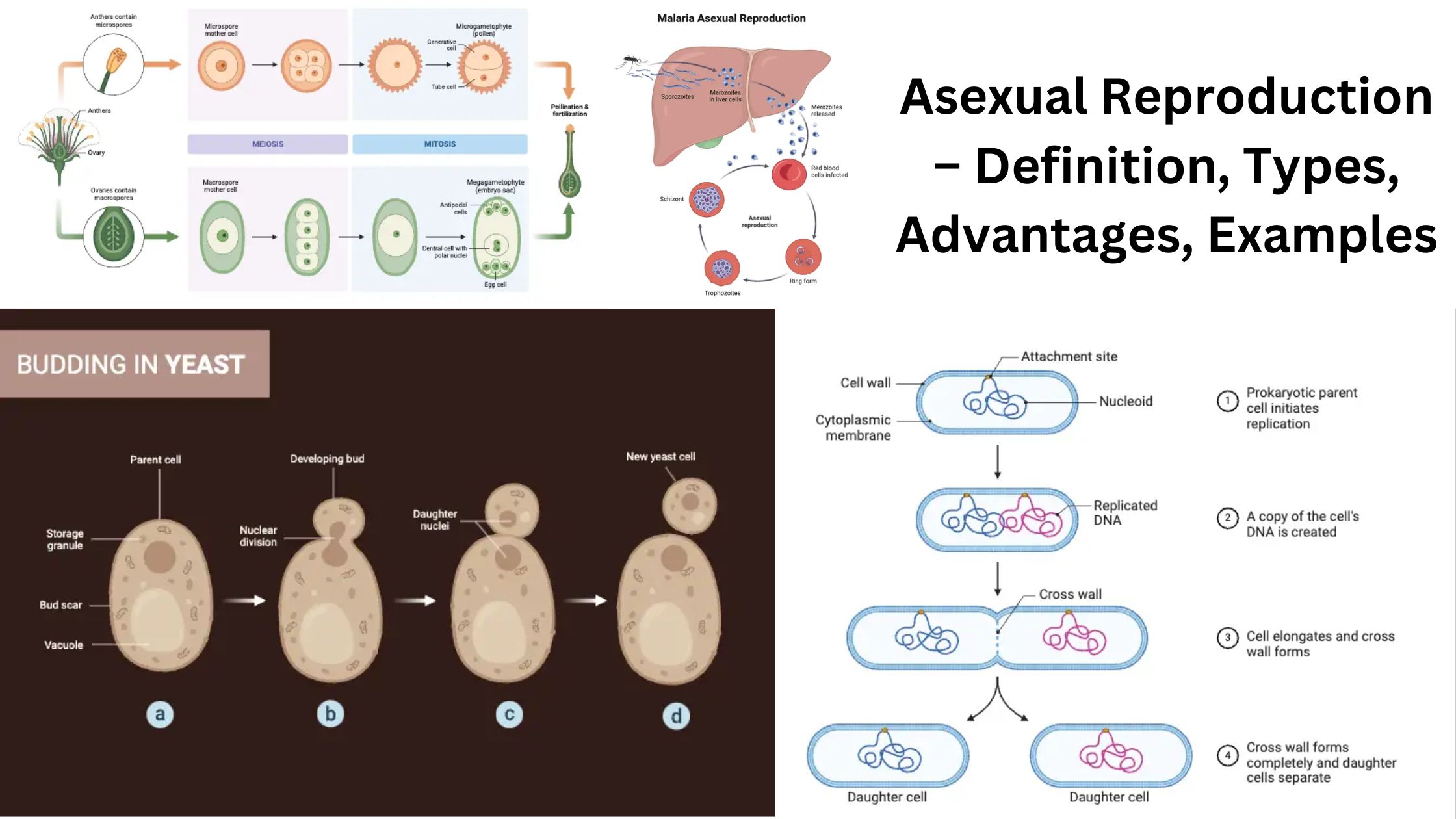
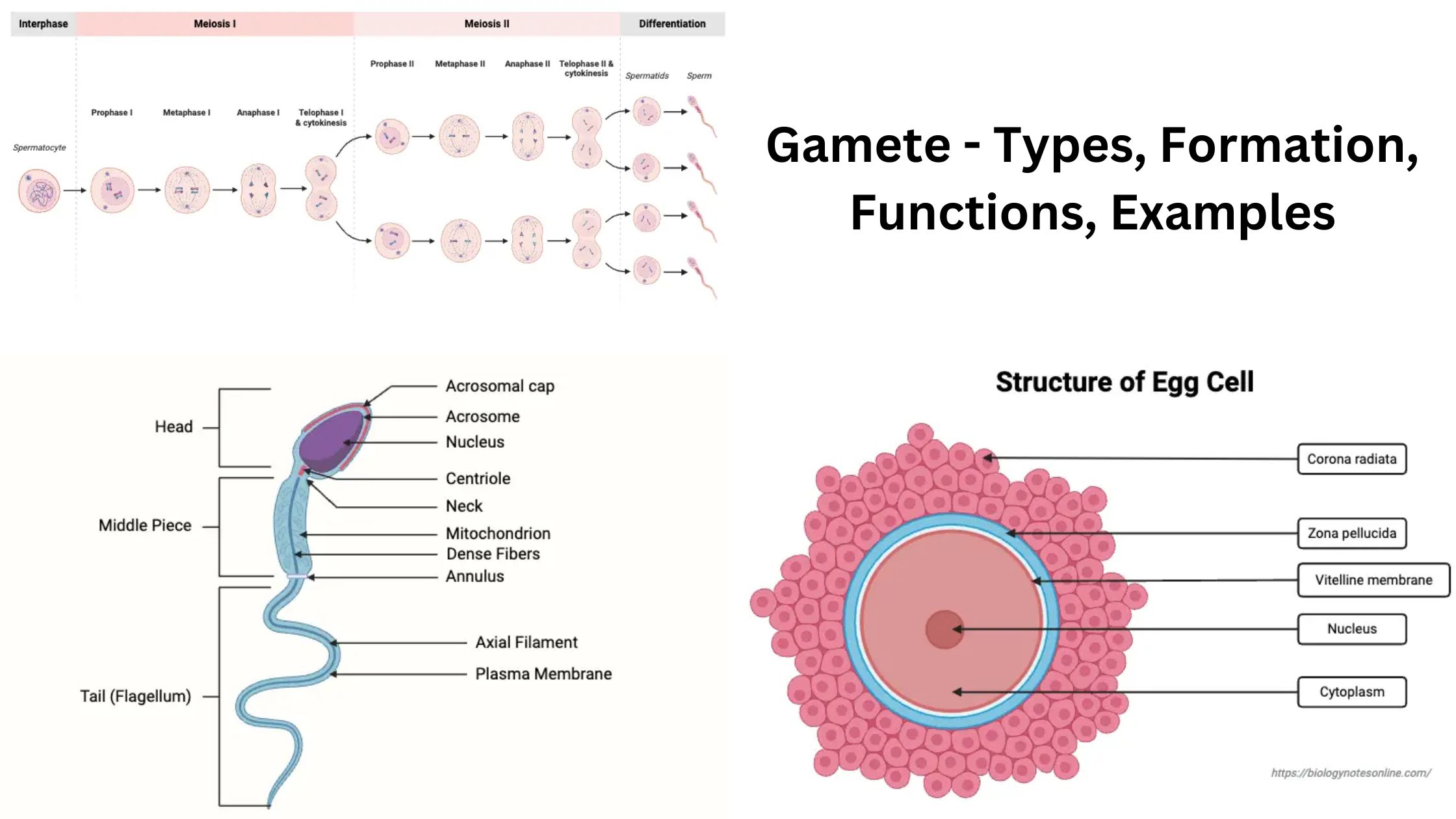
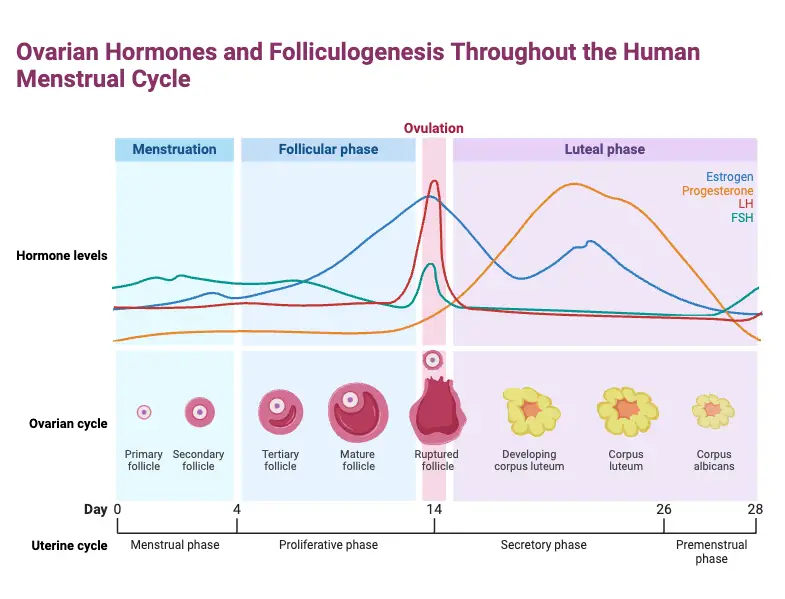
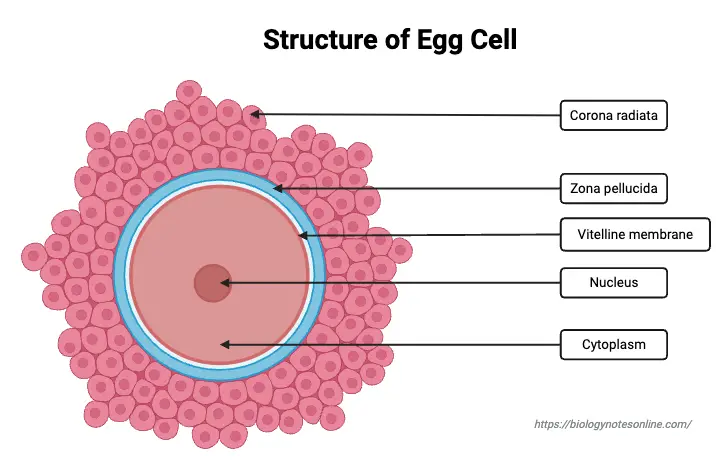
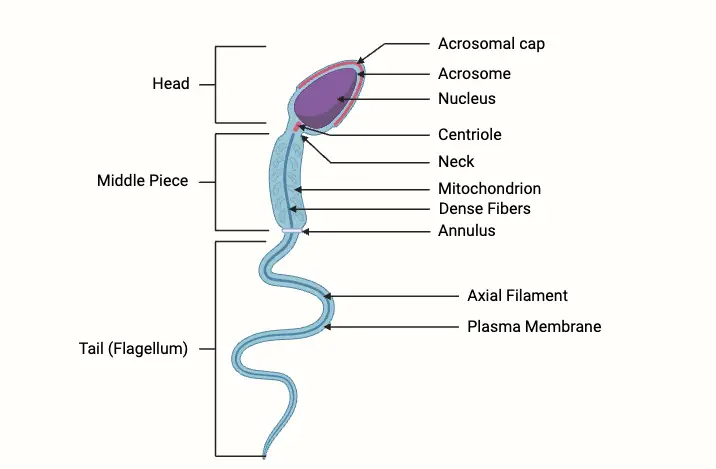
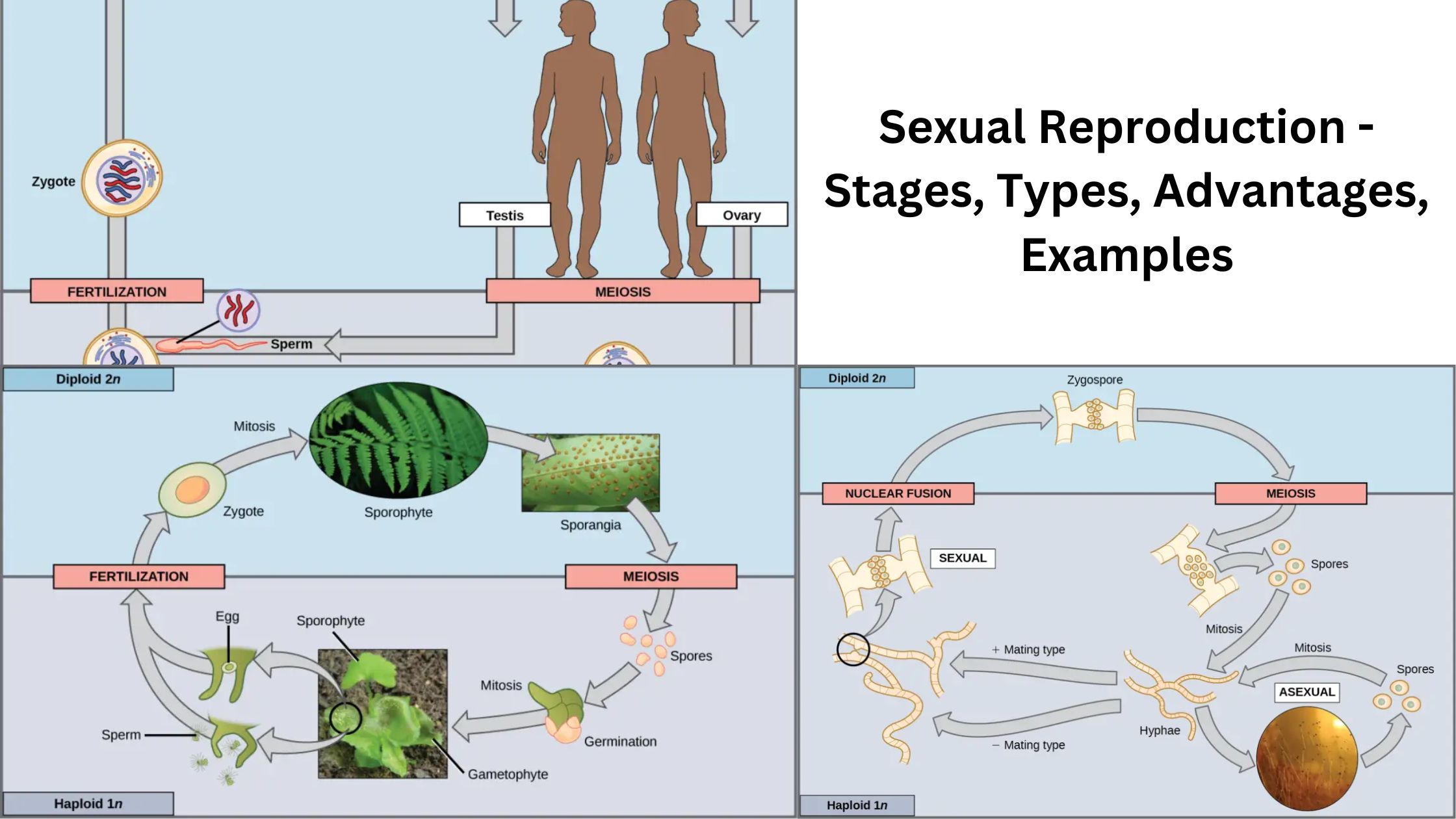
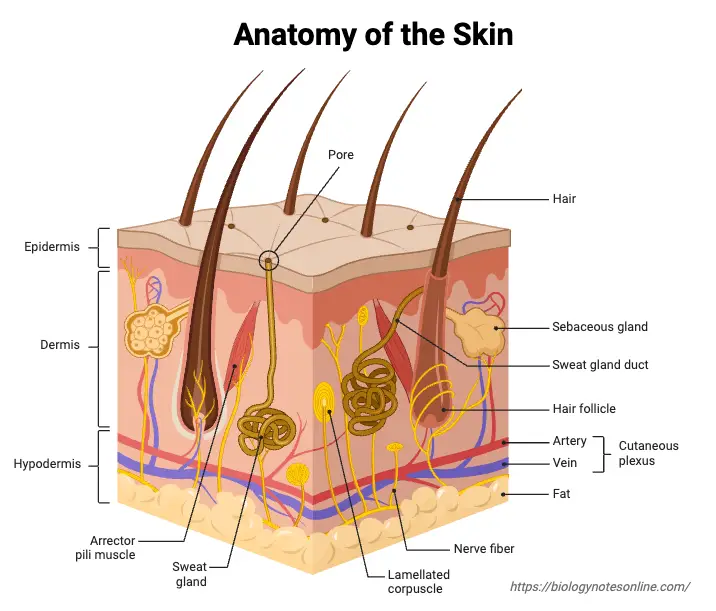
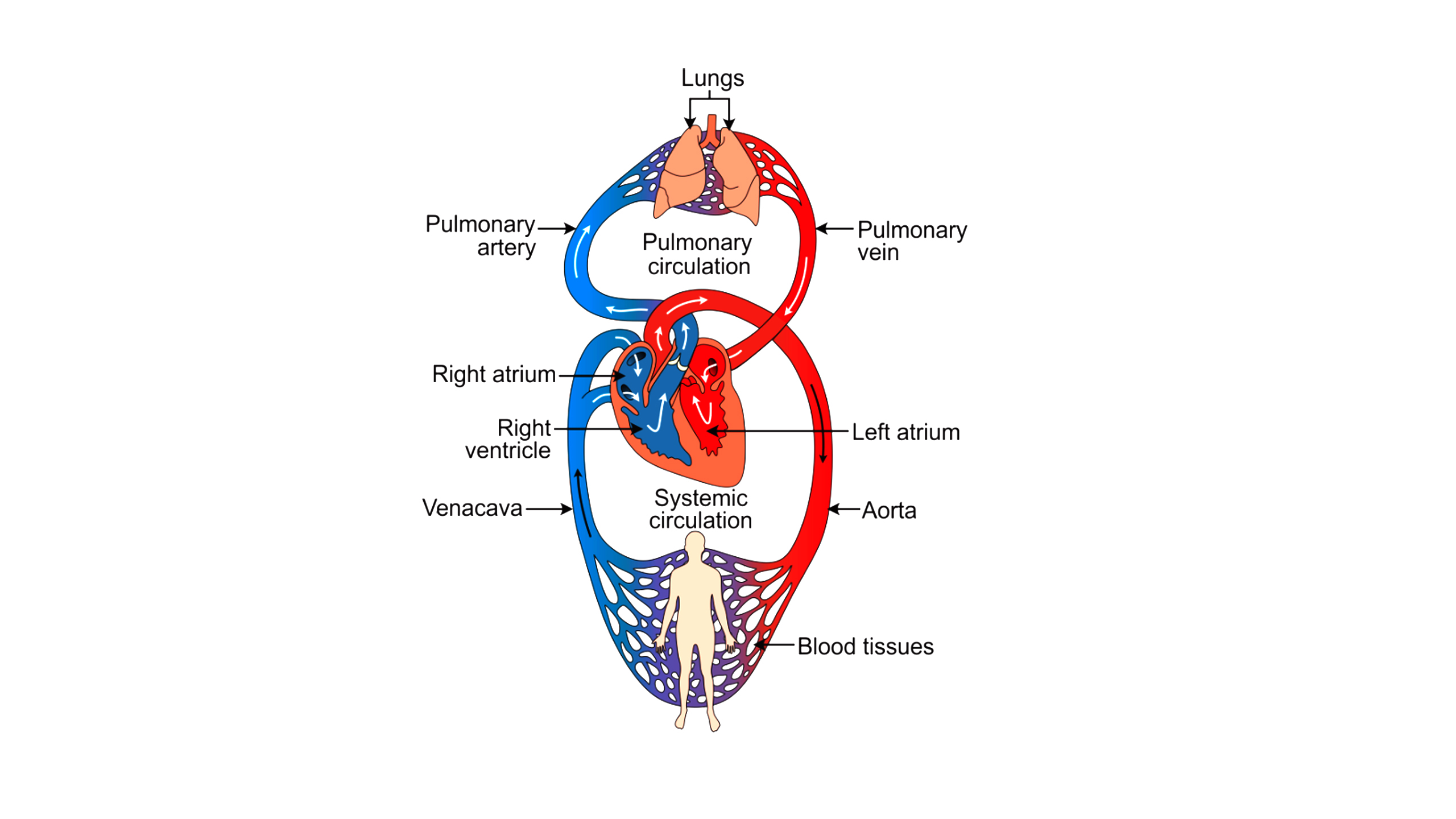
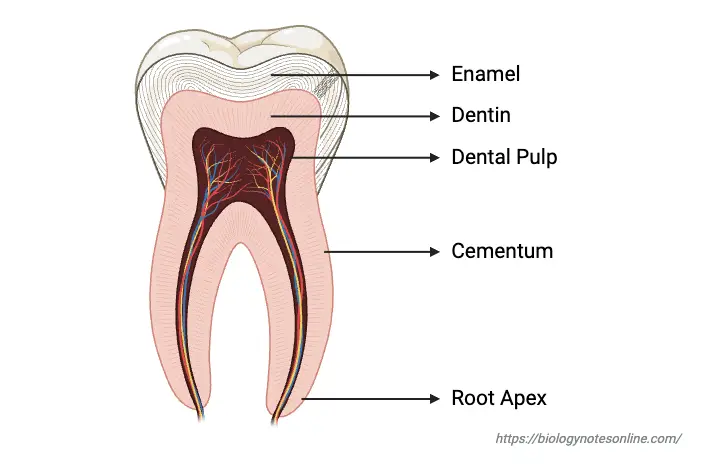
Cell Differentiation – Definition, Process & Examples
What is Cell Differentiation? Definition of Cell Differentiation Cell differentiation is the process by which unspecialized cells, like stem cells, transform into specialized cells with distinct structures and functions, enabling the development and maintenance of complex tissues and organs in multicellular organisms. Factors Influencing Cell Differentiation In multicellular organisms, several key factors influence cell differentiation, … Read more