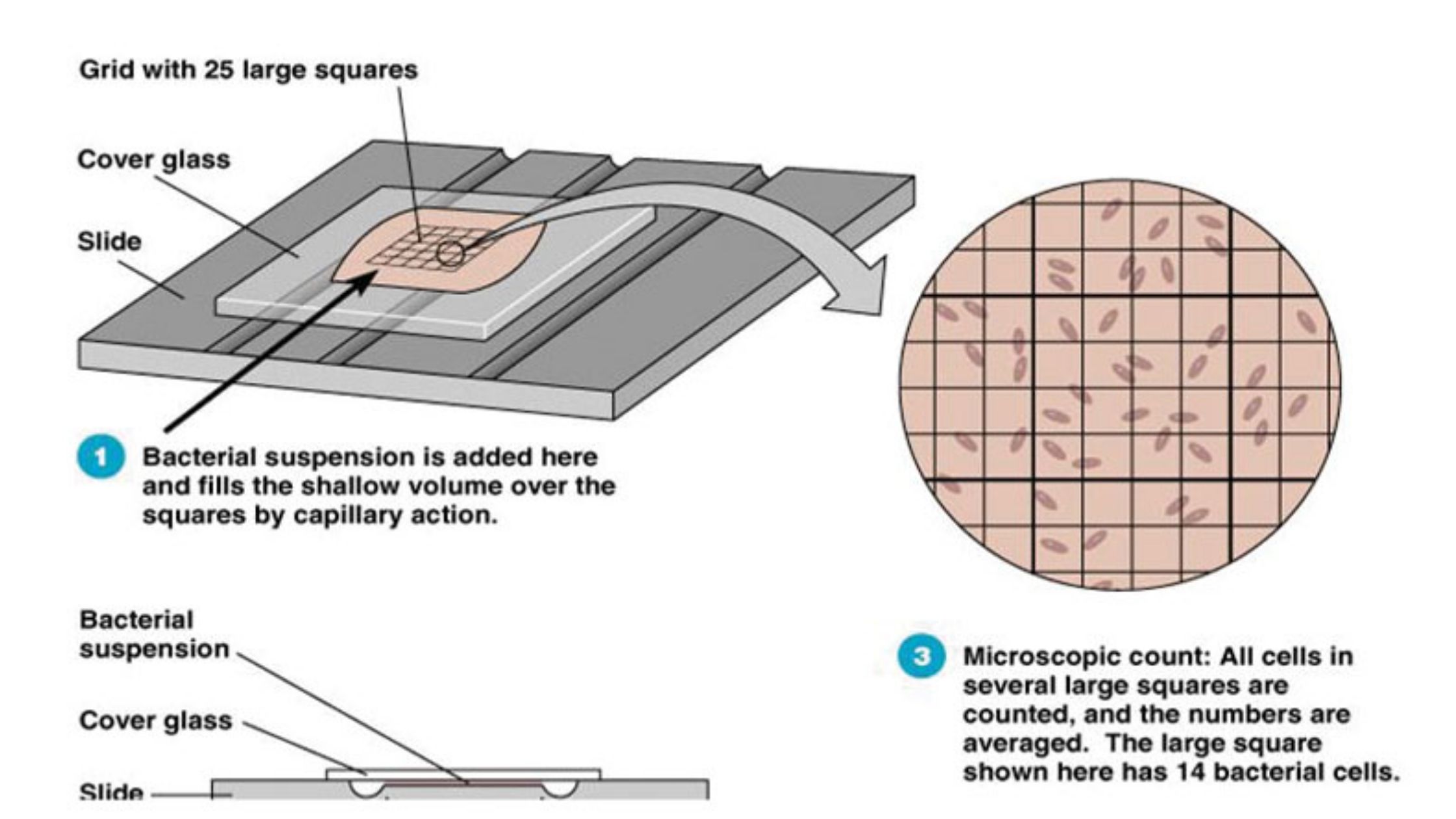
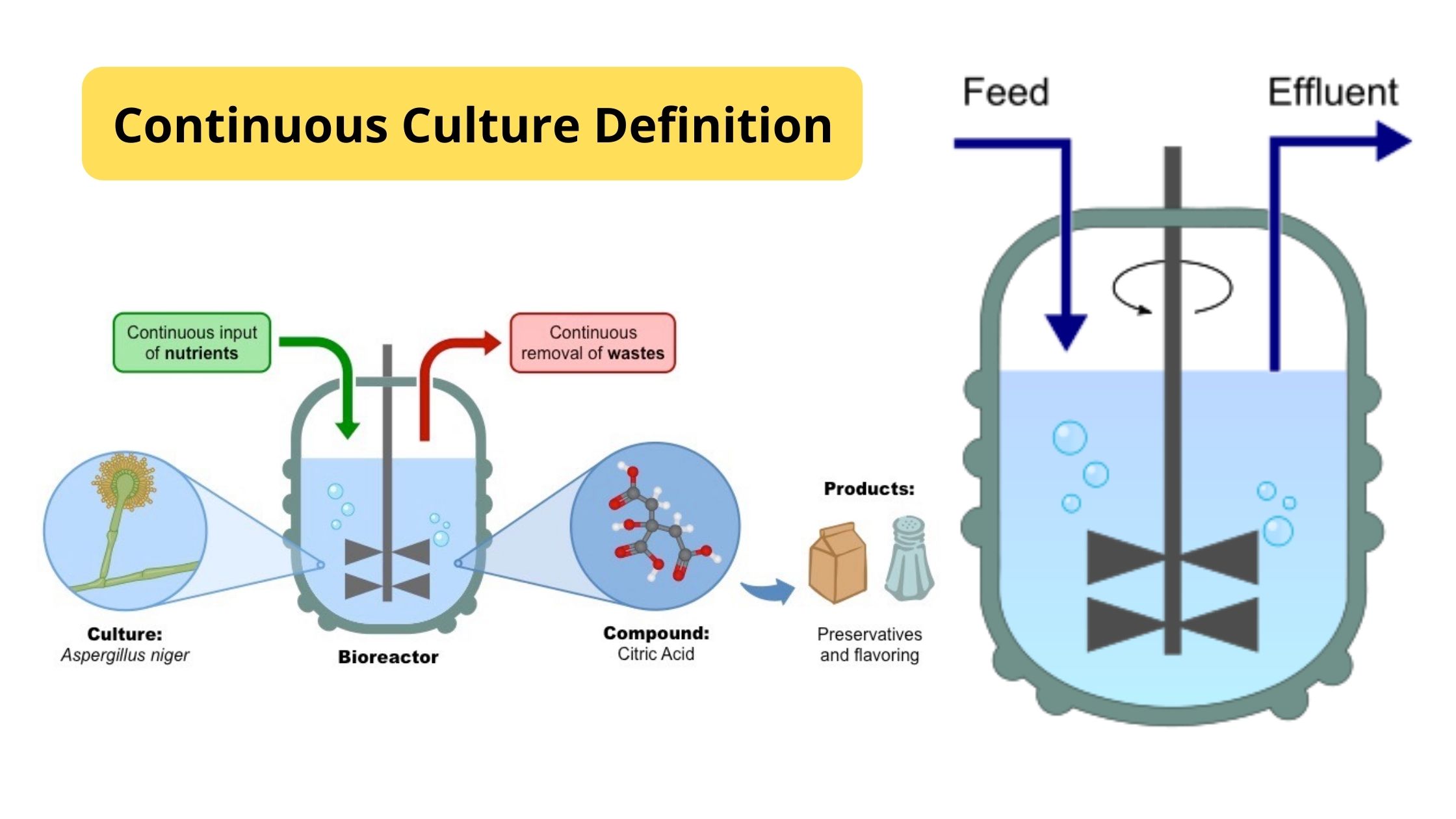
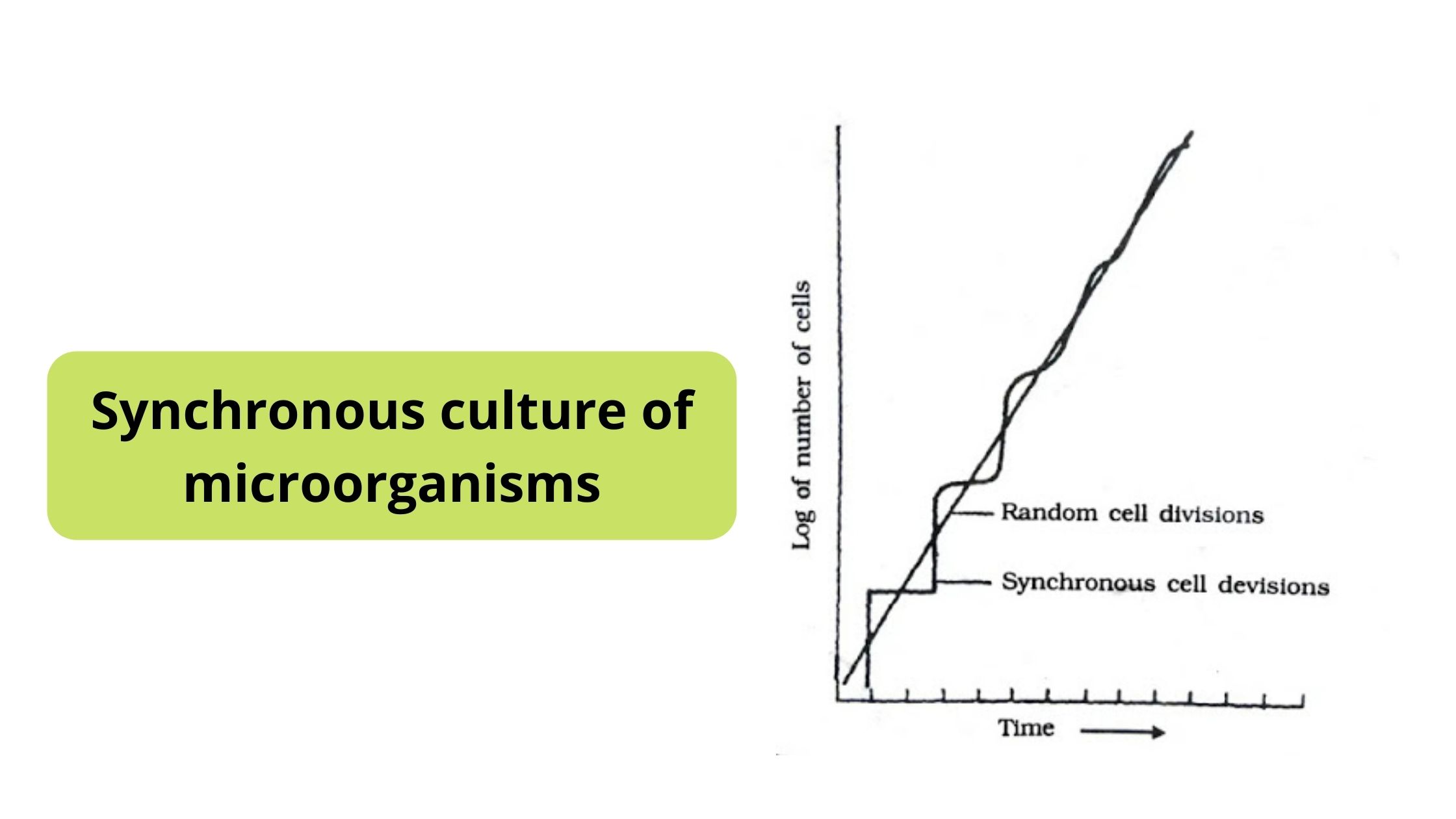
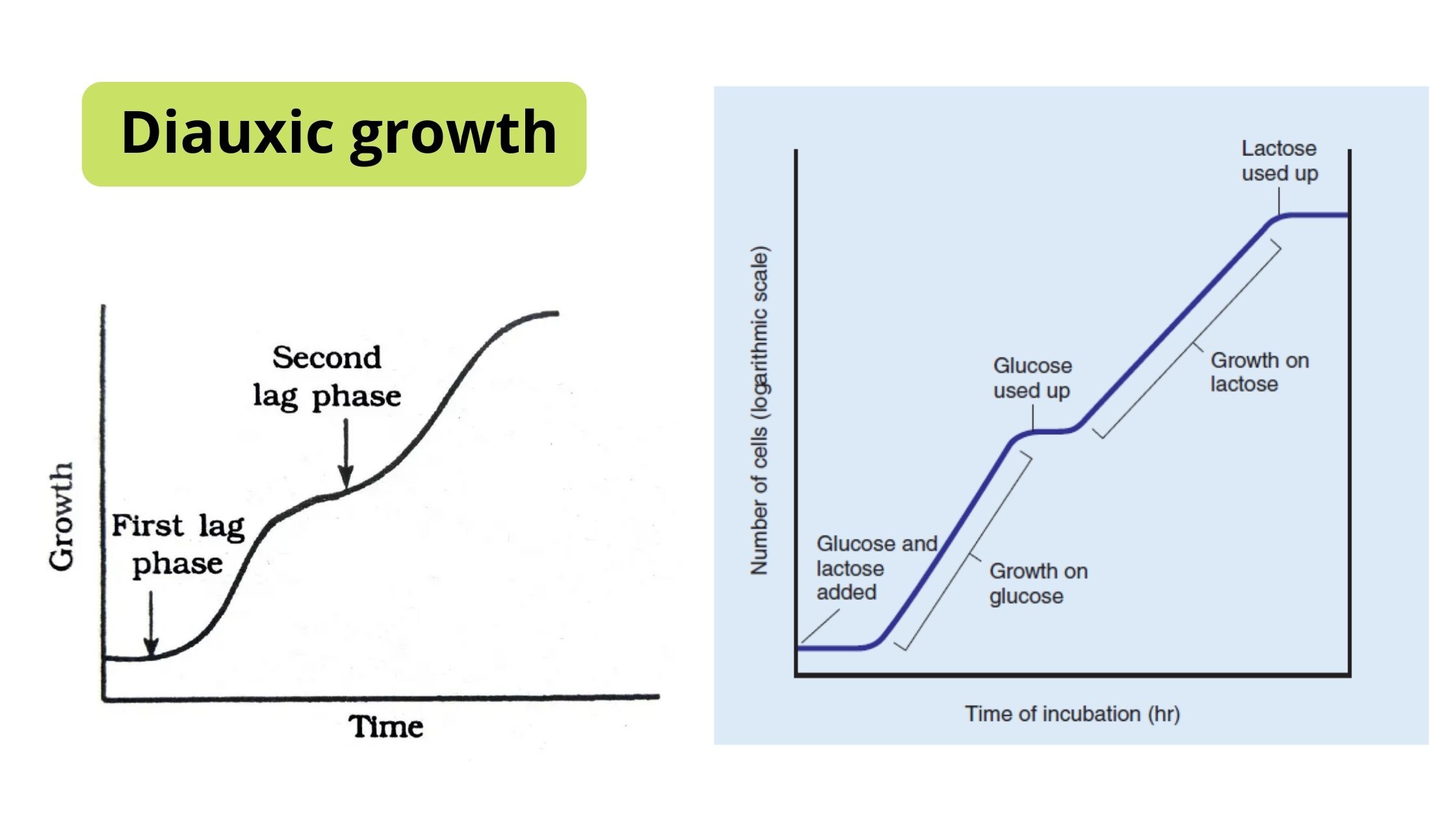
Sucrose Gradient Centrifugation
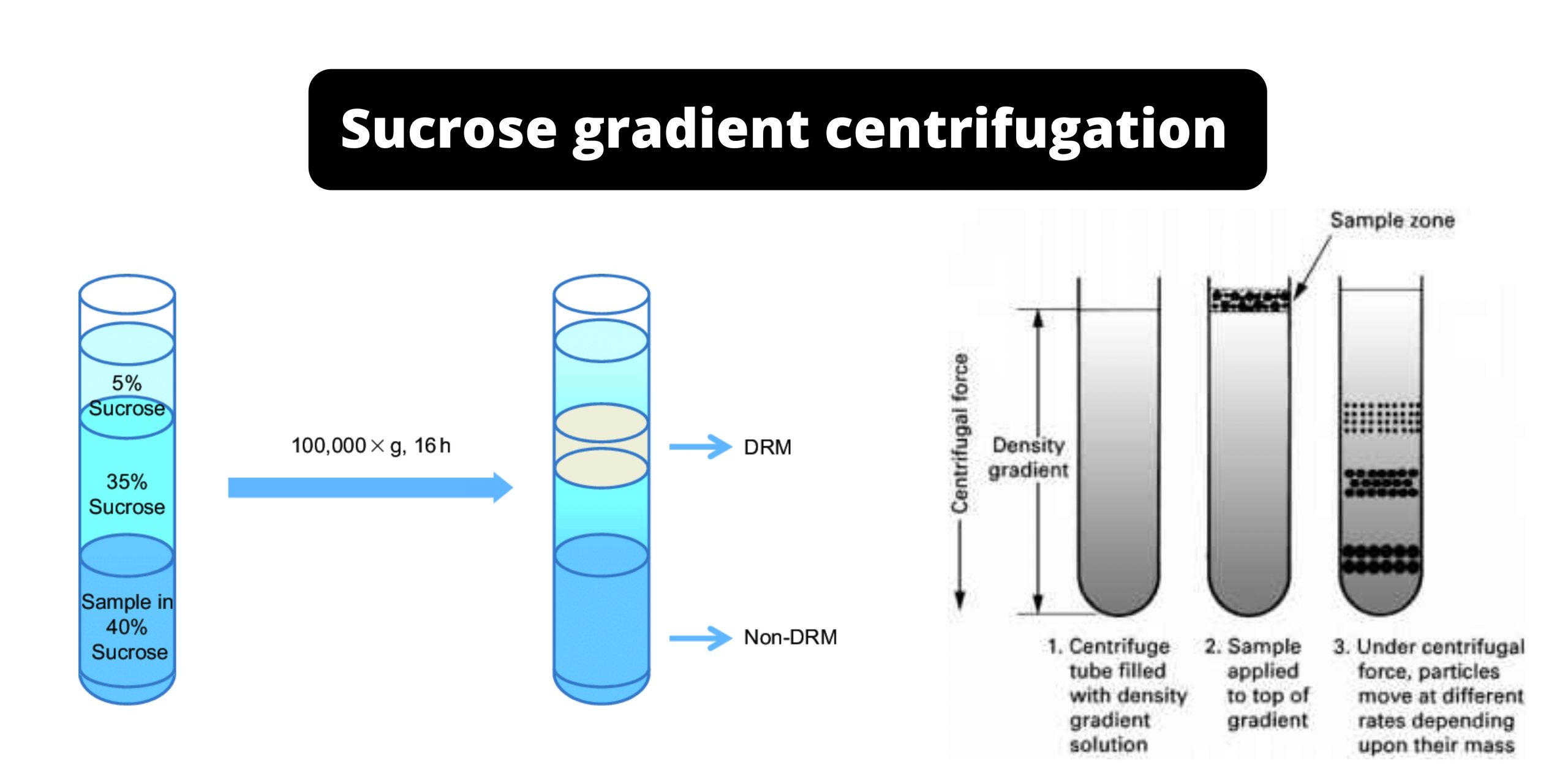
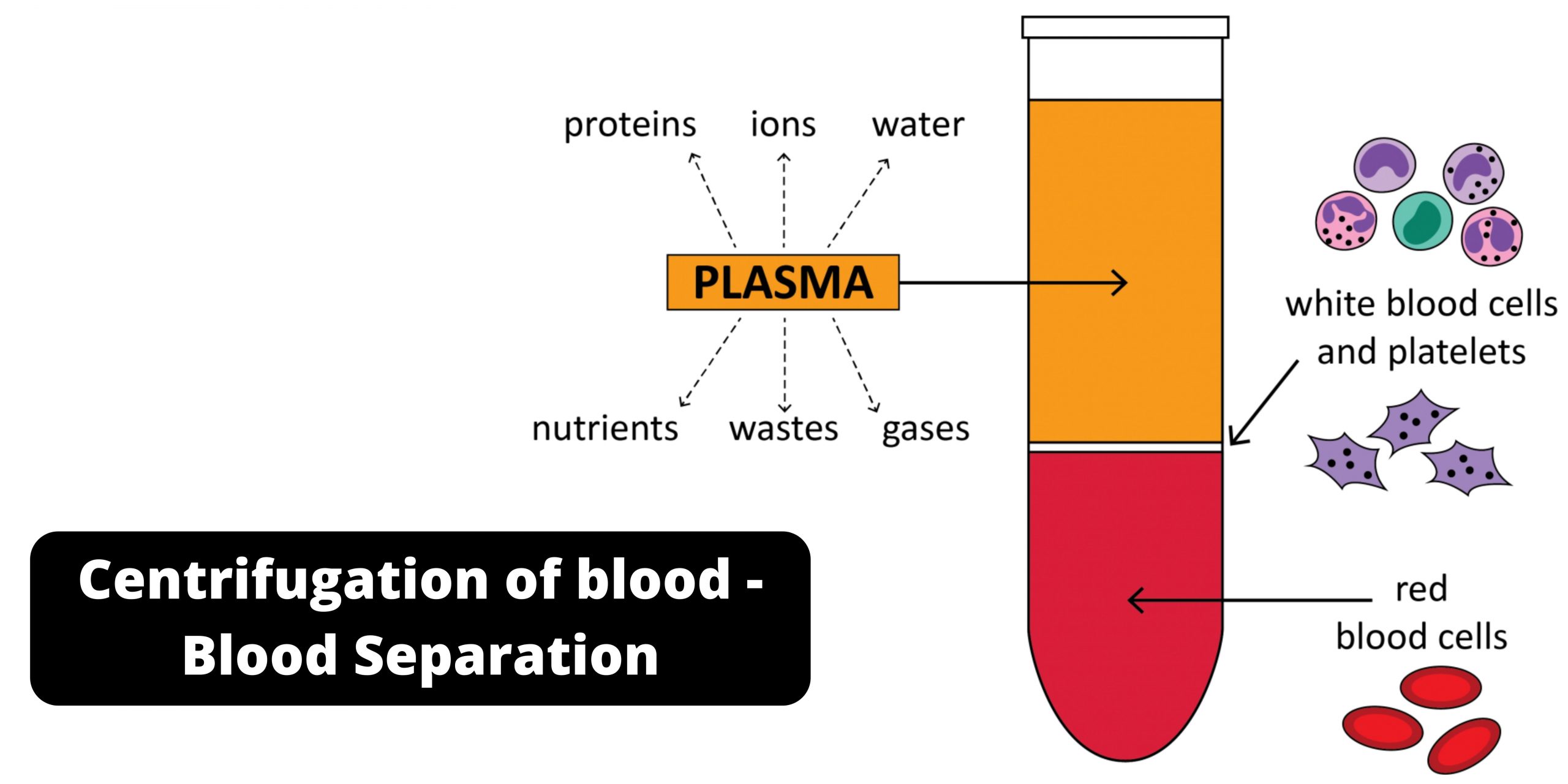
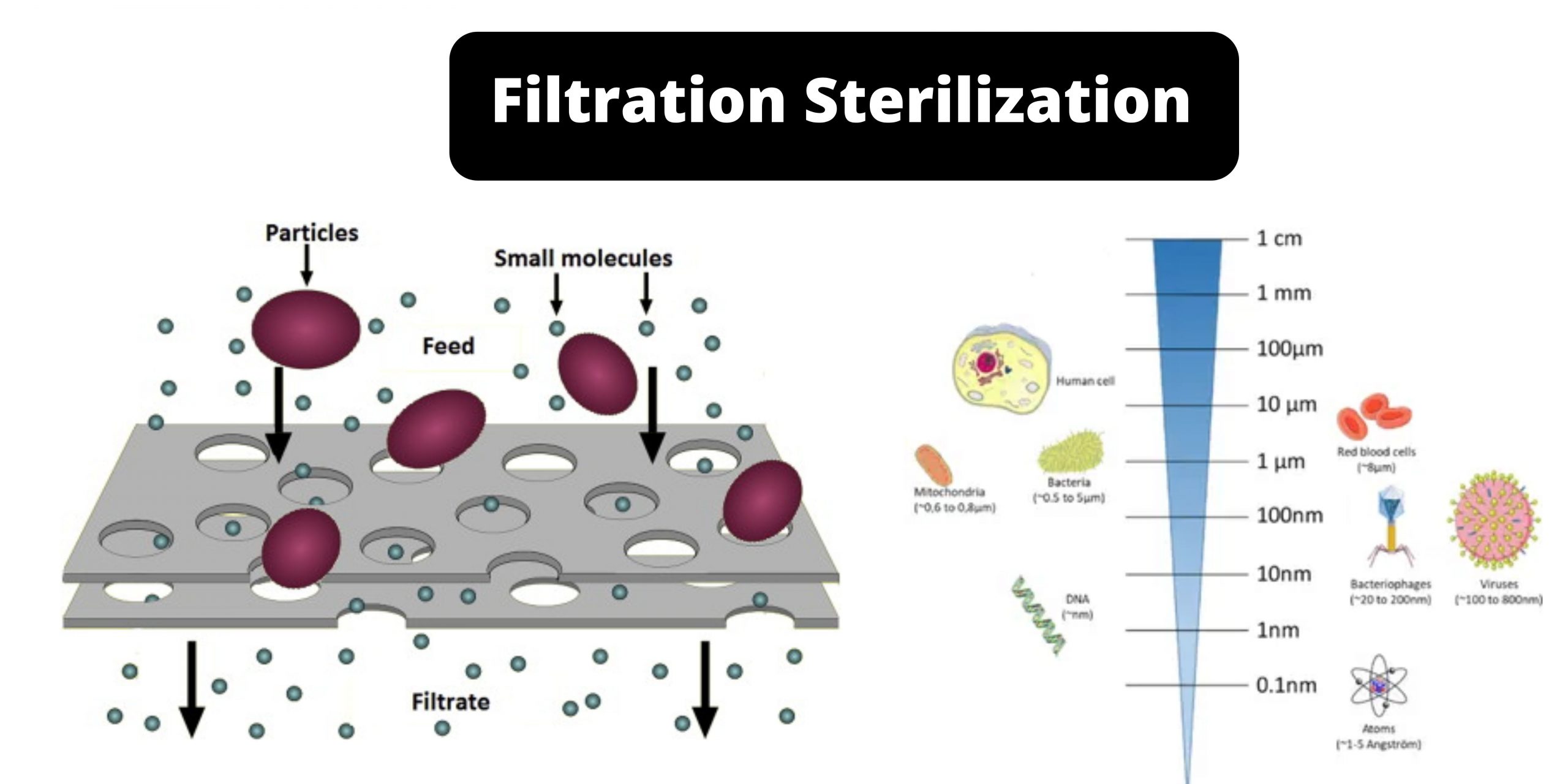
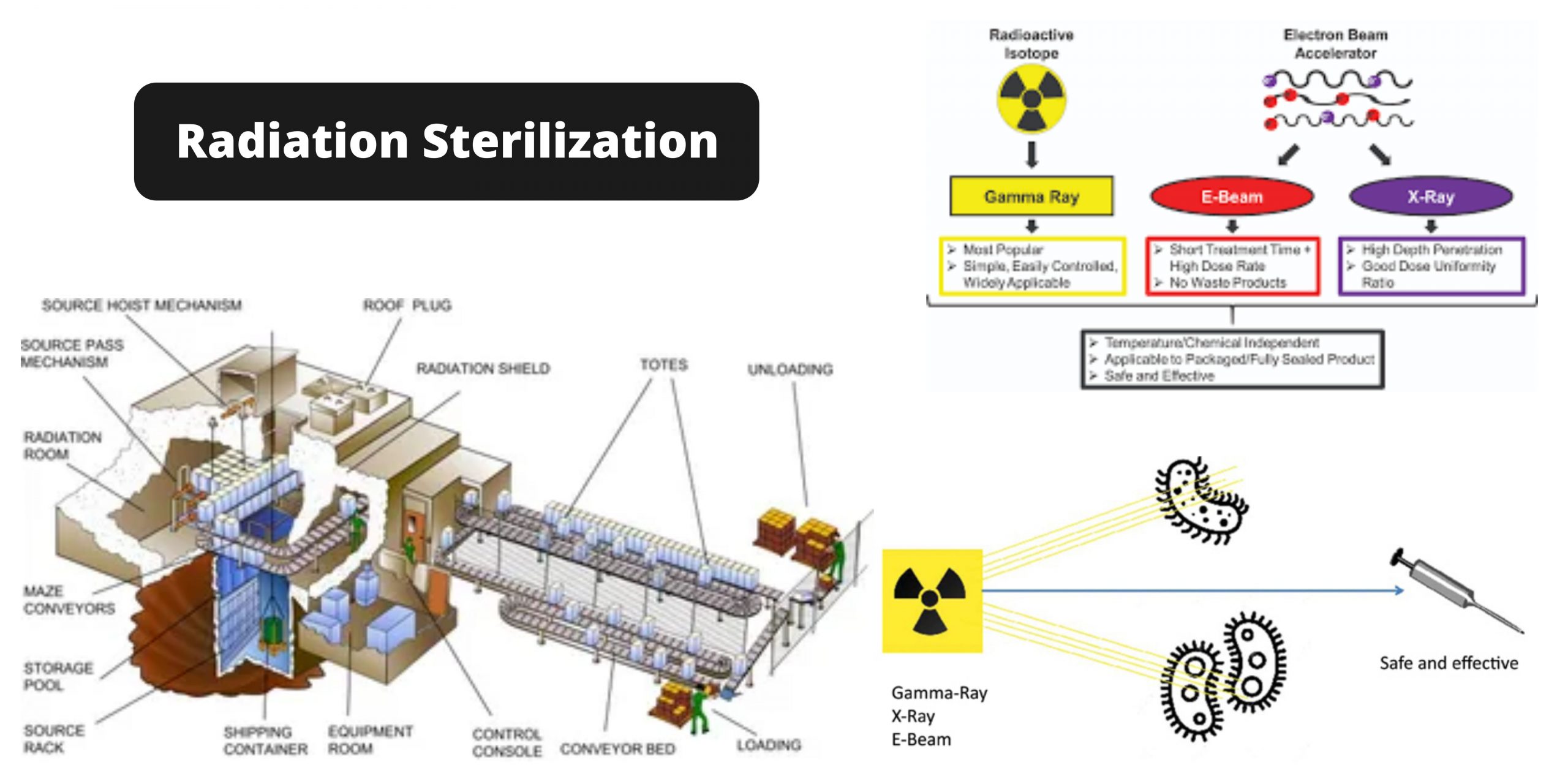
Sucrose gradient centrifugation Definition Technique for the characterization and preparation of subcellular particles. A sucrose gradient is used to fill a centrifuge tube of the type swinging-bucket design. The bottom is the most dense, and the top the least dense. The solution is then layered with a suspension of the particles. Centrifugation separates particles in … Read more