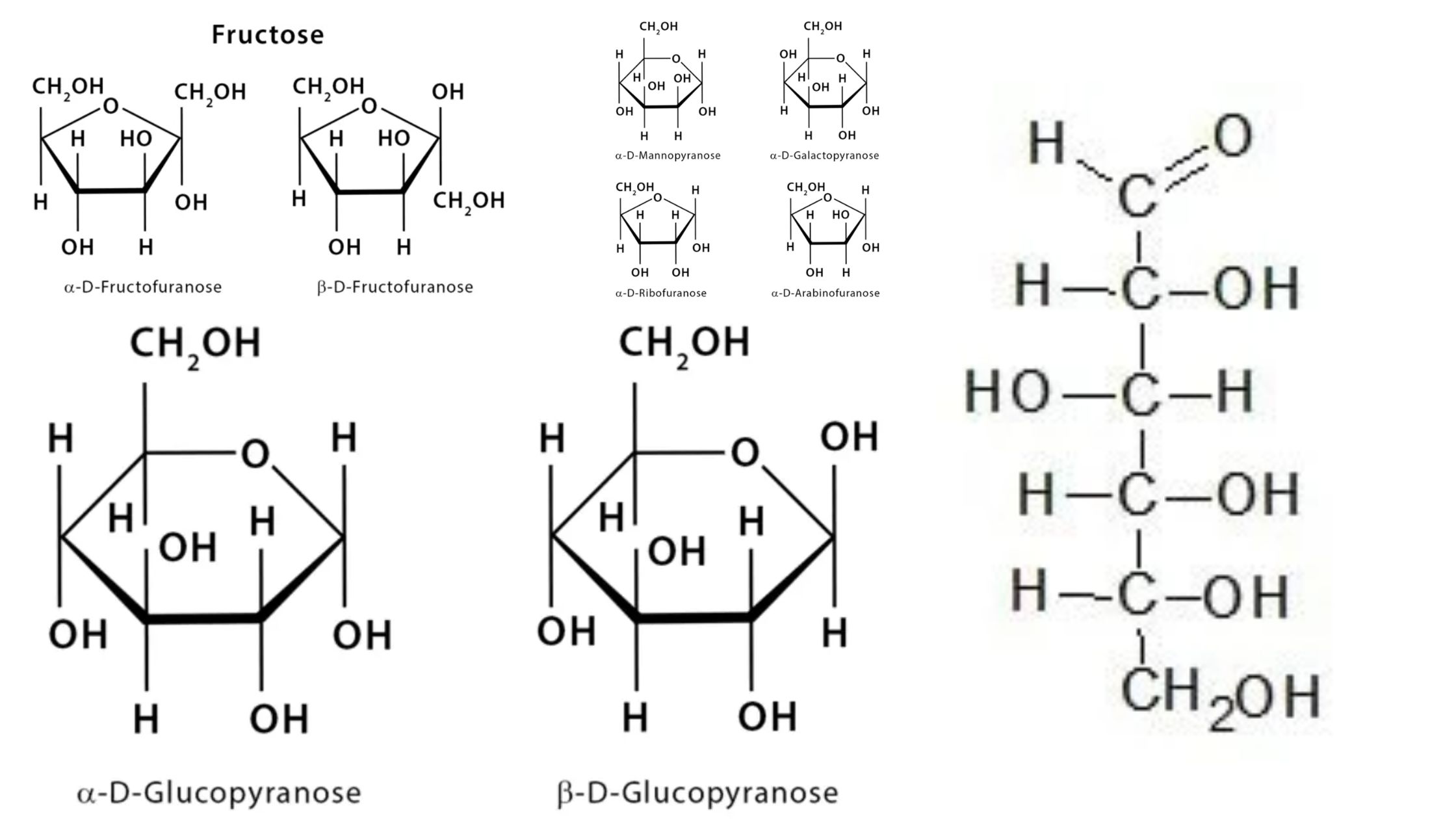
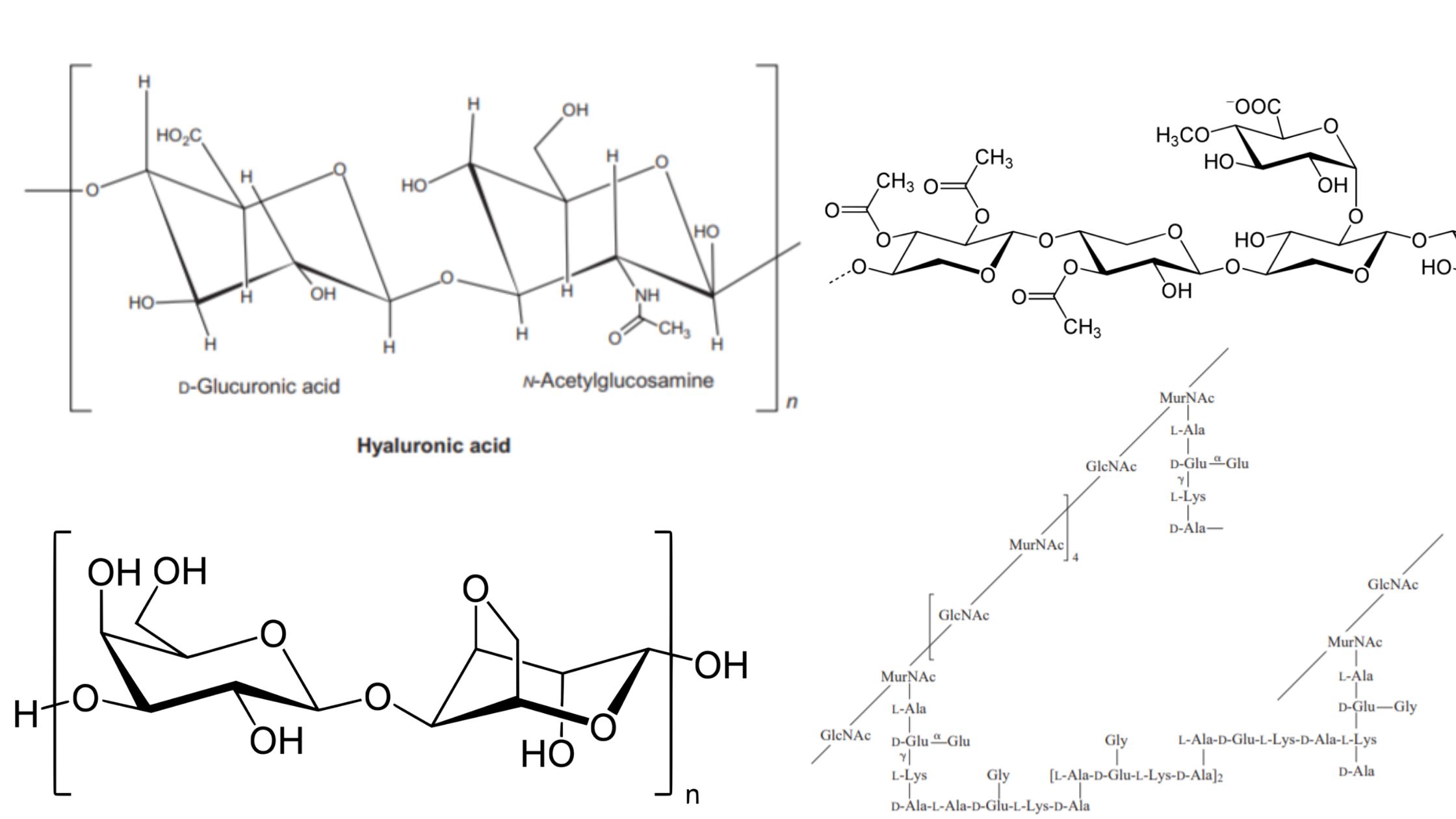
Epimers – Definition, Characteristics, Examples
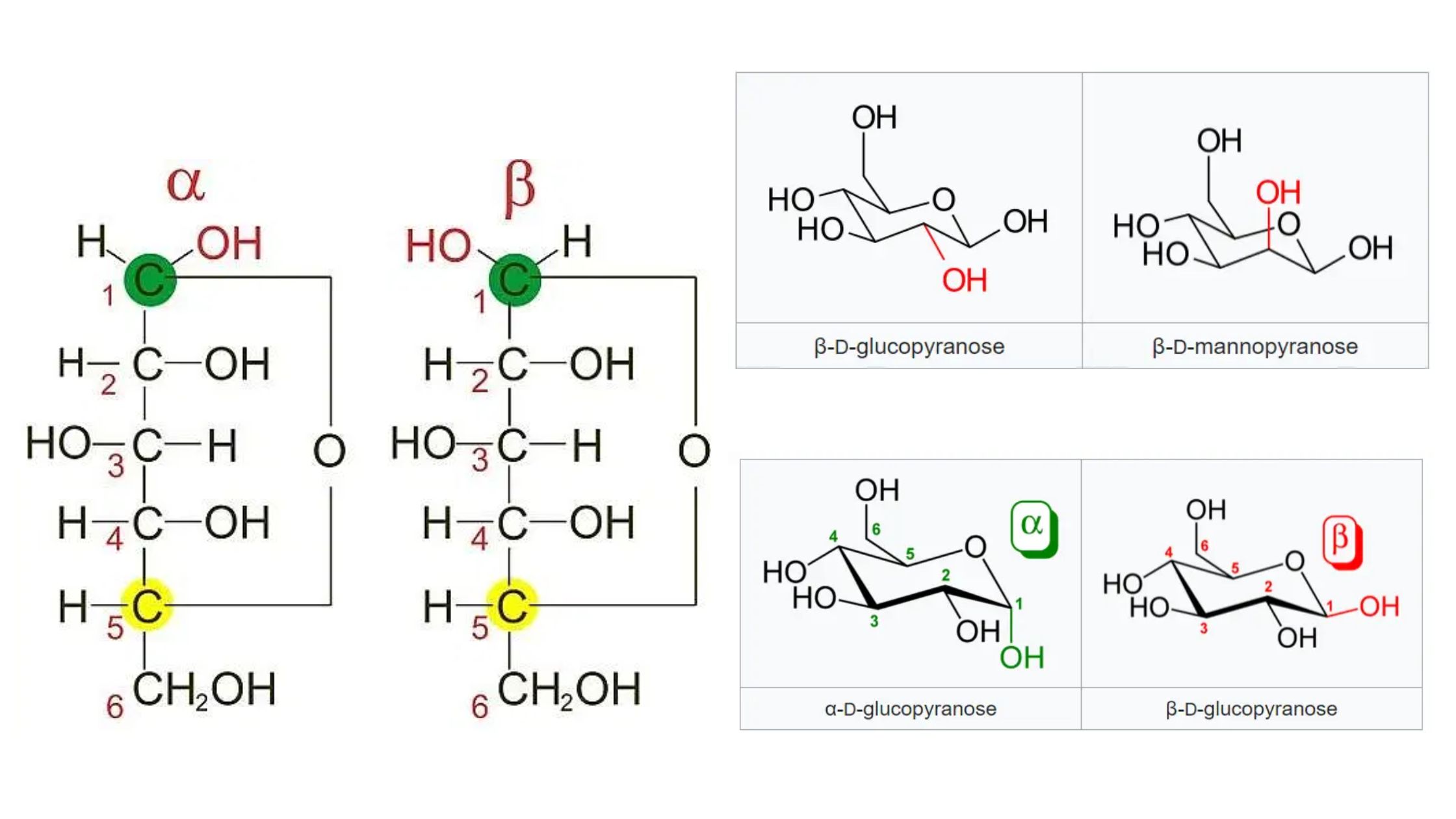
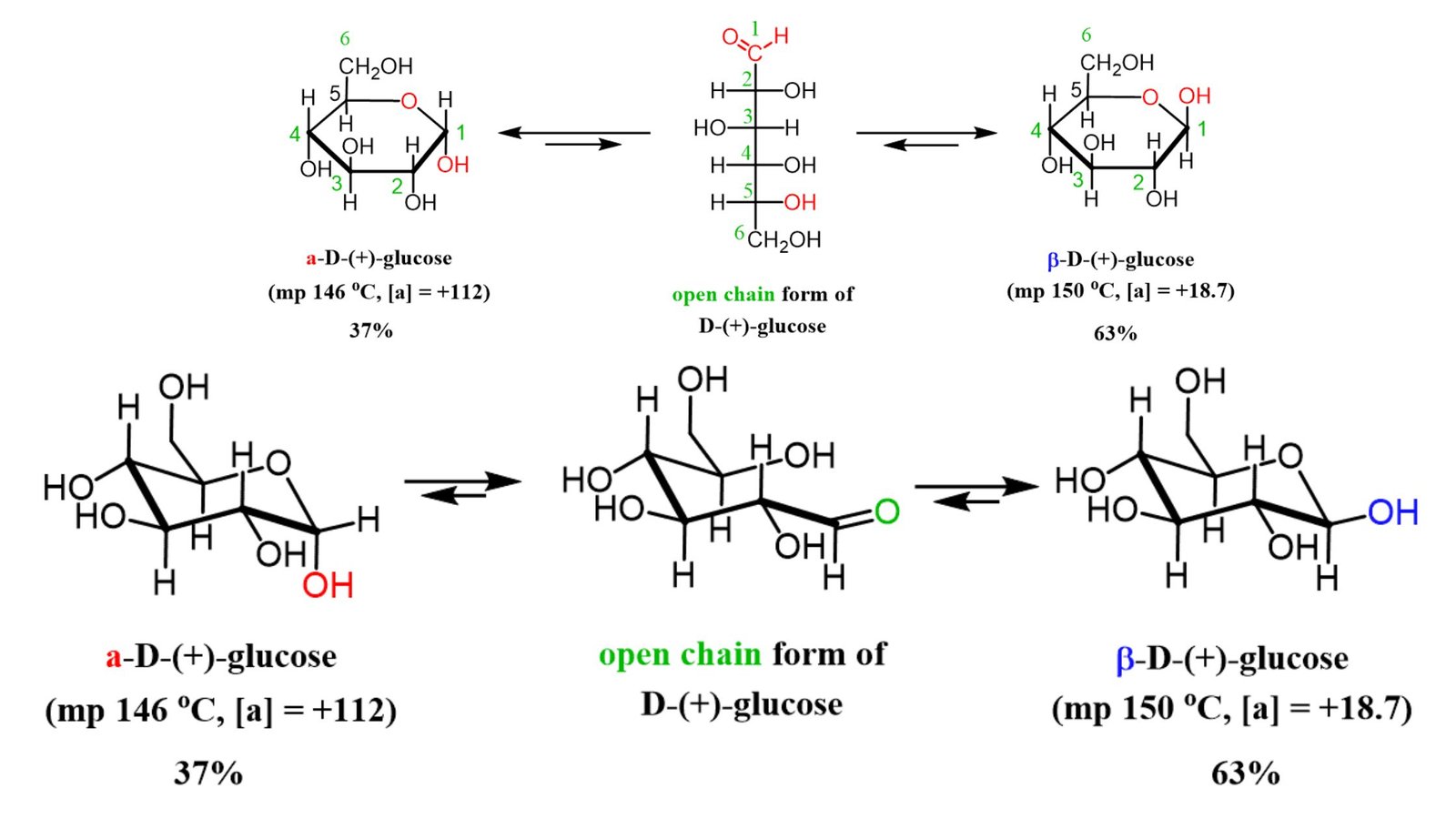
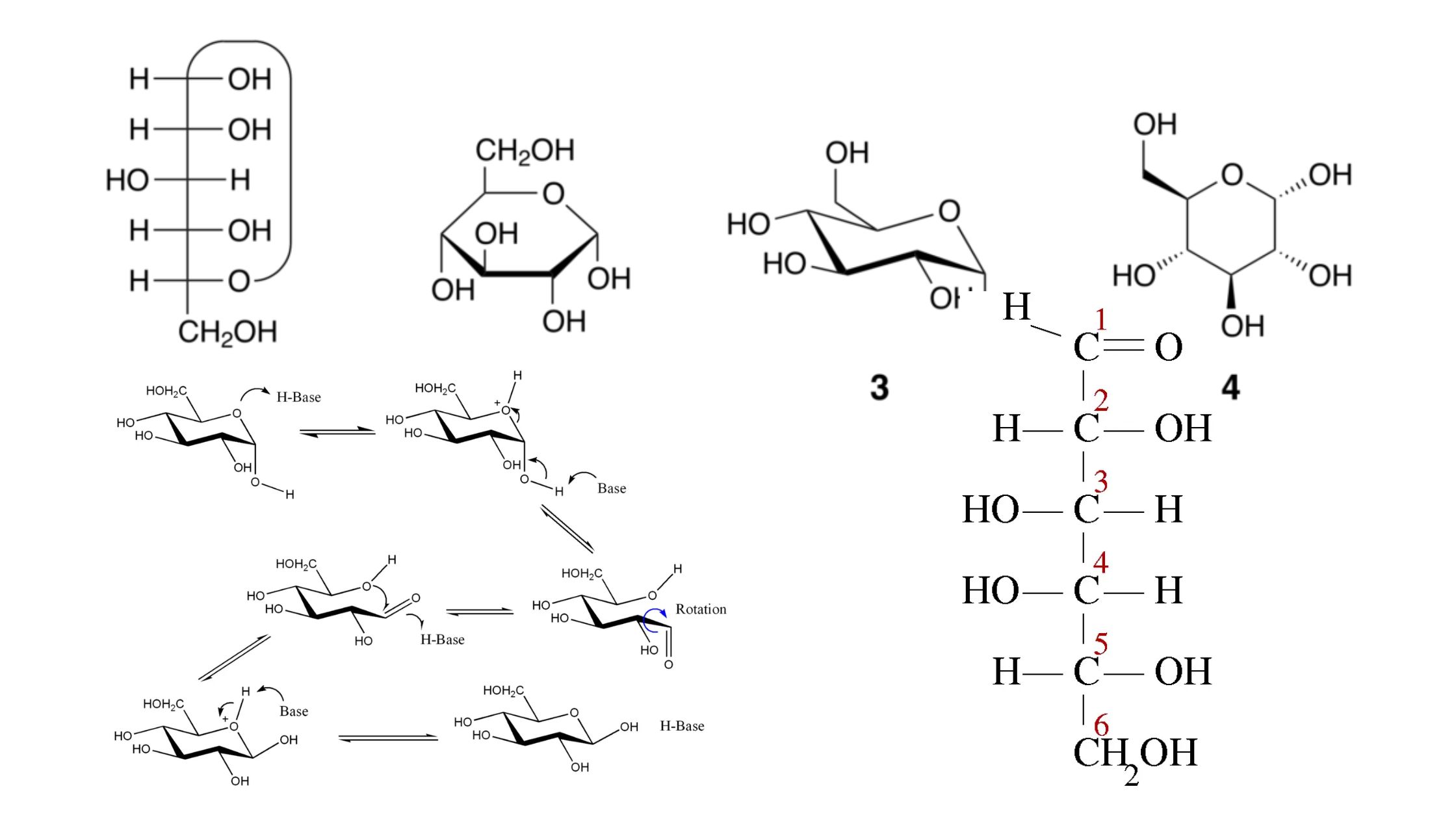
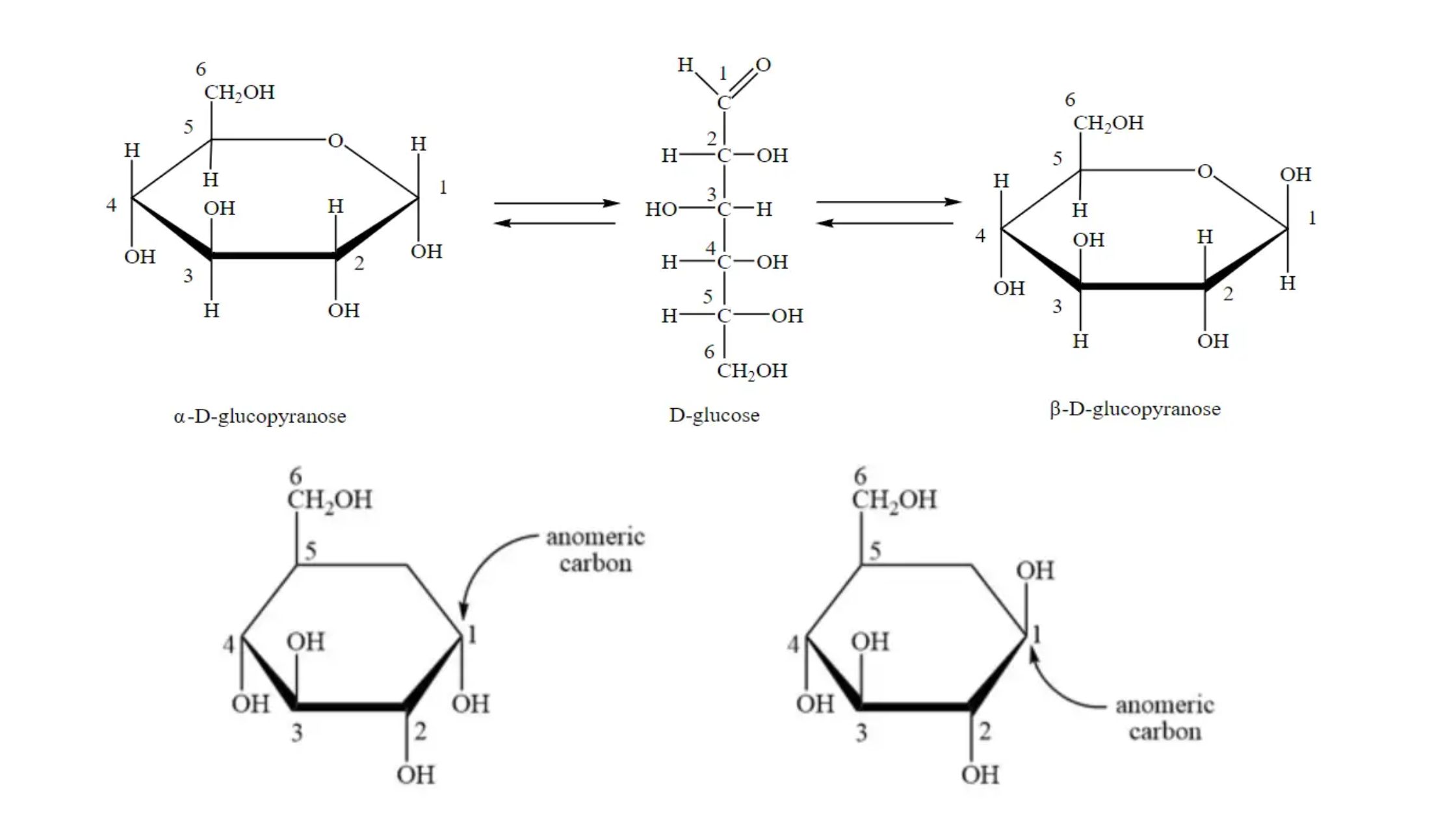
What are epimers? Epimer Definition Epimers are a type of stereoisomers that differ in configuration at only one stereogenic center while having the same configuration at all other stereogenic centers. Epimerization Main Characteristics of Epimers The main characteristics of epimers can be summarized as follows: How Do Epimers and Anomers Differ? Epimers and anomers are … Read more