- A laboratory hot plate is a device that is used to heat samples, solutions, or materials on a flat surface in a lab.
- The unit is constructed with a flat top plate (made of aluminium, ceramic or other durable material) and underneath it an electric heating element is located.
- The working principle is that an electric current flows through a resistive wire, heat is generated and then it is transferred to the plate surface and to the vessel being heated.
- In many models a magnetic stirrer is incorporated so that liquid samples can be both heated and stirred simultaneously, which improves uniformity of temperature and mixing.
- The device is preferred where an open flame (like a Bunsen burner) would pose hazard, and thus the hot plate reduces risk of ignition of flammable vapours (though hazards remain).
- Typical maximum temperatures can range up to about 300-400 °C (or even higher in some models) depending on the plate material and design.
- The selection of plate surface matters: for example a ceramic top is more resistant to corrosion and chemical attack, whereas an aluminium top gives good heat uniformity but may be less corrosion-resistant.
- Safe use is required: the operator must ensure the vessel is suitable (e.g., heat-resistant glassware), the surface is clean, cords are intact, and that the hot plate is not used with materials that may spark or give vapours into air.
Definition of Hot Plate
A hot plate is a portable heating device with a flat surface used to heat samples or materials in a controlled manner without the need for an open flame.
Principle of Hot Plate
The functional principle of a laboratory hot plate is that an electric current is passed through a heating element (resistive wire) and heat is generated by Joule heating, then the heat is transferred to the plate surface and to the vessel containing the sample.
In the case of a hot plate with magnetic stirrer, the principle also involves an electromagnetic field that interacts with a magnetic stir bar in the solution so stirring occurs while heating, thus the mixing and heat-distribution are combined.
With the heating element being embedded beneath a top plate made of materials like aluminium or ceramic, the heat conduction from element to surface is achieved, the vessel sits on that surface and the sample is warmed.
The temperature control is done by adjusting the current (or the thermostat) so that the plate reaches desired temperature (for example up to ~300-400 °C or higher depending on plate material) and that heat is uniformly delivered to sample.
In stirring- hot-plates the electromagnetic field rotates the stir bar by creating a revolving magnetic field under the plate which causes the liquid to motion, this promotes homogeneity of temperature and mixing.
The principle thus relies on both thermal conduction (from plate to vessel to sample) and magnetic induction / electromagnetic interaction (in models with stirrer), two mechanisms working together, though the primary heat generation is via resistive electric heating.
When the plate is turned off the surface remains hot for some time and residual heat conduction continues; thus caution is required as the device remains a heat‐source even after switch-off.
Types of Hot Plates
- Standard hot plate was defined as a heating device only (without stirring function) and it is used when simple warming of vessel contents is needed.
- Stirring hot plate integrates both a heating element and a magnetic stirring system and thus mixing and heating are combined in the same device.
- Magnetic hot plate (or hot-plate with magnetic stirrer) is a subtype where an electromagnet under the plate causes a magnetic bar in the liquid to rotate, so uniform heating + mixing is achieved.
- Aluminium-surface hot plate is one type of surface material variant and it was described as offering excellent heat uniformity but less corrosion resistance.
- Ceramic-surface hot plate is another material variant, which is resistant to chemical attack and higher temp shock (up to ~350 °C) though it may be more brittle.
- Stainless-steel surface hot plate is a further variation, designed for harsher environments (corrosive solvents, clean-rooms) and high durability.
- Polypropylene (plastic) surface hot plate is a less common variant for wet-chemistry use (e.g., acids / bases) where corrosion matters more than high temperature; its max temp is lower.
- Large-capacity / heavy-duty hot plate is a category where big top-plate size or high load/heavy vessel use are addressed, it’s chosen when heating large volumes or heavy items.
Parts of Laboratory Hot Plate
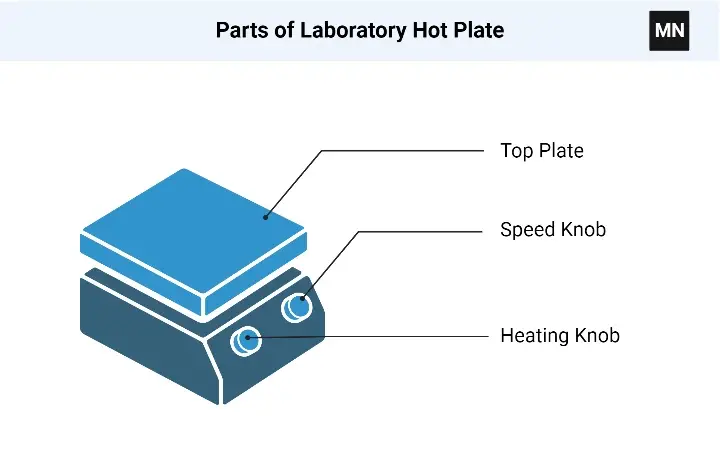
1. Base unit– The base unit is the fundamental housing that provides the unit with the heating element, wiring and control parts and it also supports the whole device.
2. Top plate / heating surface – The top plate is generally one of aluminum, ceramic or stainless steel and it is a flat surface where vessels are placed, the heating is by means of direct contact and the heat is conducted into the sample.
3. Heating element– The heating element that converts electrical energy into thermal energy is either under the top plate or embedded in it and after the heat transfer the surface is heated and the sample gets warm.
4. Temperature controller / heat control knob– This is the device by which the temperature is set and changed: a knob or digital controller, it regulates the amount of heat given to the workpiece, an arrow or pointer can be used to indicate the “hot top”.
5. Power switch/ power indicator light– The switch along with indicator light that works together to start the unit. When the light is on, you can tell that the appliance is in action.
6. Stirring motor / magnetic stir mechanism– A motor / electromagnet is located under the plate in the models with a stirring function and it is the one that drives the stir bar inside the vessel, hence mixing the liquid and heating can be done simultaneously.
7. Stir control knob / stirring speed display– The user changes the speed of mixing by means of the stir control knob; in more high-tech units a display shows the stir rate.
8. Connections / power cord input & external controller input– The power cord fits the machine; a few models may have a special input for a temperature probe or a controller.
9. Safety features /hot-top indicator– A visual indicator may become lit when the top plate is higher than a recommendable temperature threshold for touch (e.g., >60°C) and over-heat protection is there, thus safer operation is guaranteed.
10. Accessories / support rod & clamp– Besides the hot plate, the additional parts like vertical support rods, clamps or holder for glassware or probes can be obtained with the apparatus.
11. Insulation & casing – The housing encloses the heating element and plate, and the insulation is to limit the heat loss and for the user’s safety from the hot part inside.
12. Fuses/ power protection component– The base unit is equipped with a fuse or a circuit breaker that is there to protect the device from power surges or short circuit situations.
Operating Procedure of Hot Plate
- Before the equipment is plugged in, a check is made to see if it has any damages or if there are any loose cords.
- The hot plate unit is placed on a flat/stable surface and the surface is checked to ensure that it is free from dust and old residues.
- The power cord is plugged into the right outlet, the main switch is turned on, and the indicator light is checked to see if it is on.
- The temperature control knob or digital set-point is turned to the desired temperature and the top plate is left to stabilise (about 5-10 minutes) while the device is getting warm.
- The sample vessel is placed on the heated surface in the middle so that maximum contact is assured and heat transfer is efficient.
- If stirring is necessary, a magnetic stir bar is placed inside the vessel and the stir control is turned on so that mixing and heating can be done together.
- The temperature of the sample, the reaction progress or changes are looked at and any changes of heat/stir speed are made slowly to avoid a sudden overshoot and bumping.
- Once the heating/stirring is done, the temperature control is changed to “off” or the lowest setting, the power switch is turned off, the unit is unplugged (if necessary), and it is allowed to cool before cleaning.
- The surface is cleaned with a damp cloth (only once cool) and any spills or residues are removed; then the unit is checked for the next use.
- Safety checks are made: that no flammable material was next to the hot plate during its operation, that the appliance is of the correct voltage, and if there is any fault, it is recorded for the maintenance department.
Applications of Hot Plate
- Heating of glassware or solution is provided by a hot plate in laboratory settings for sample preparation or general warming.
- In chemical synthesis the hot plate is used to maintain a reaction mixture at desired temperature and sometimes stirring is added, enabling controlled reaction progress.
- Evaporation of solvents can be carried out on a hot plate when a more uniform heat-source is required rather than a flame.
- In materials science research thin-films or coatings are annealed on hot plates, and thus the hot plate plays role in substrate heating & solvent drying.
- Biological assays (like enzyme tests or DNA/RNA hybridization) are performed with hot plates helping maintain correct temperature, especially in biochemistry labs.
- Industrial tasks such as soldering electronics components onto circuit boards are carried out on specialized hot plates with corrosion-resistant surfaces.
- Pre-heating of materials, drying of parts, or sample digestion in environmental analysis labs are applications where hot plate use is common and necessary.
Advantages of Hot Plate Stirrer
- The hot plate is relatively affordable compared to many heating devices and it thus lowers equipment cost for labs.
- A unit is conveniently portable and it can be moved from bench to bench which gives flexibility in lab layouts.
- Because there is no open flame the risk of direct flame-contact is reduced and safer handling is allowed especially with flammable materials.
- Precise temperature control is offered by many hot plates, thus improved uniform heating of samples is enabled, which helps reproducibility of experiments.
- The surface of a hot plate is easy to clean (especially ceramic/stainless steel tops) so contamination is minimised and maintenance becomes simpler.
- Some models incorporate a magnetic stirrer and heating together, so simultaneous mixing and heating is provided which streamlines workflow.
- It is adaptable for many sample types and vessel formats, the device supports wide uses (liquid heating, evaporation etc) so versatility is enhanced.
Limitations of Hot Plate Stirrer
- The top surface often shows poor temperature uniformity when large vessels are used, and heat-hotspots may occur which reduce precision.
- A vessel stirring function is lacking in many basic units so mixing must be done externally which complicates operation, especially with viscous liquids.
- The heat output may be limited for very high-temperature operations (over 500°C) or for heavy sample loads, thus not all applications are supported.
- Older models can malfunction and run away heater-element may stay on even if switch is off, causing risk of fire or damage.
- Only surface heating is provided so indirect heating methods (like in-oil baths or block heaters) may give better temperature control and uniformity.
- The device is not ideal for highly flammable or volatile solvents because vapours may be ignited and no explosion-proof casing is usually provided.
- Maintenance demands are sometimes higher when chemical spills occur onto the plate, the corrosion and residue reduce lifetime and performance of the unit.
- Some complex experiments require very fine temperature control and high stability, and a standard hot plate may not satisfy those advanced needs, so an alternative equipment must be chosen.
FAQ
What is a laboratory hot plate?
A laboratory hot plate is a device used to heat substances or materials in a controlled manner in a laboratory setting. It typically consists of a heating surface, temperature controls, and sometimes a magnetic stirrer.
How does a laboratory hot plate work?
A laboratory hot plate uses electric heating elements beneath a surface to generate heat. The heat is then transferred to the objects or substances placed on the surface, allowing them to reach the desired temperature.
What are the common applications of a laboratory hot plate?
Laboratory hot plates are commonly used in various applications, including heating solutions, warming glassware, melting or evaporating samples, conducting experiments, and conducting chemical reactions that require controlled heating.
How do I select the right hot plate for my laboratory needs?
When selecting a hot plate, consider factors such as the required temperature range, heating capacity, stirrer capability, surface material compatibility, safety features, and the specific applications you intend to use it for.
Can I use a laboratory hot plate for flammable materials?
When working with flammable materials, it is crucial to ensure that the hot plate is designed to be used safely in such situations. Look for features like explosion-proof construction, spark-free operation, and compatibility with fume hoods for proper ventilation.
How do I clean a laboratory hot plate?
To clean a hot plate, allow it to cool down completely before wiping the surface with a damp cloth or using mild detergent if necessary. Avoid using abrasive cleaners or submerging the hot plate in water to prevent damage.
Can I adjust the temperature on a laboratory hot plate?
Most laboratory hot plates have adjustable temperature controls, allowing you to set and maintain specific temperatures based on your experimental requirements.
Is it safe to leave a laboratory hot plate unattended?
It is generally recommended not to leave a hot plate unattended, especially when heating volatile or flammable substances. Always follow safety protocols and guidelines provided by the manufacturer.
Can I use a laboratory hot plate for biological samples?
Yes, laboratory hot plates can be used for heating biological samples, but it is essential to ensure that the hot plate is compatible with the specific requirements of your biological samples and follow appropriate protocols to maintain sample integrity.
How can I ensure the safety of using a laboratory hot plate?
To ensure safety, always follow the manufacturer’s instructions, use appropriate protective equipment (such as heat-resistant gloves), avoid overloading the hot plate, keep flammable materials away, and be cautious when handling hot surfaces or substances. Regularly inspect and maintain the hot plate to ensure proper functioning and safety.
- https://studiousguy.com/hot-plate-stirrer/
- https://bionicsscientific.com/hot-plate-stirrer/laboratory-hot-plate.html
- https://conductscience.com/laboratory-hot-plates/
- https://www.mrclab.com/types-of-laboratory-hot-plates
- https://research.wayne.edu/oehs/pdf/factsheet-hot-plate.pdf
- https://conductscience.com/laboratory-hot-plates/
- https://chem.wisc.edu/wp-content/uploads/sites/1130/2019/12/HotPlateSafety.pdf
- https://neuationcentrifuges.wordpress.com/tag/what-is-hot-plate-used-for/
- https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/ed050p137
- https://microbenotes.com/hot-plate-principle-parts-procedure-types-uses-examples/
- https://www.laboratory-equipment.com/blog/hot-plate-comparison-for-digital-analog-magnetic-stirring-plates/
- https://lnf-wiki.eecs.umich.edu/wiki/Hot_Plate_Ettiquette
- https://www.nist.gov/system/files/documents/ncnr/Corning-Digital-Hot-Plate.pdf