Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) stain is the routine staining method used in histology and histopathology for observing the basic structure of tissues. It is the process in which two dyes are applied on colorless tissue sections so that the cellular parts become clearly visible under the microscope. Hematoxylin behaves as a basic dye and it is the dye that binds with the acidic components of the cell. The nucleus, ribosomes and other basophilic structures get a deep blue to purple color, and this reaction is referred to as nuclear staining. Eosin is an acidic dye and it binds with the basic components of the cytoplasm producing different shades of pink or red. The cytoplasm, cell boundaries and extracellular fibers like collagen are stained by eosin. It is this contrasting coloration that helps in identifying the normal tissue architecture and the changes occurring in different diseases.
Hematoxylin and eosin staining is used to recognize different types of tissues and it is the primary stain used in histopathology including sections from paraffin-embedded tissue and fine-needle aspiration biopsy. In this staining, hematoxylin gives a deep blue-purple color because it interacts with nucleic acids through a complex biochemical reaction. Eosin stains proteins in a nonspecific manner and this is why the cytoplasm shows variable degrees of pink staining. It is the process in which the strength of the nuclear staining also depends on the time of exposure of the sample to the dye. This is helpful in examining the nuclear content and the general morphology of the cells.
Hematoxylin and eosin are both classified as dyes and dyes naturally have an affinity for tissues depending on the acidity or alkalinity of the dye components. This staining creates a clear two-tone contrast that provides a general map of the tissue arrangement, and it is often the first step for detecting abnormalities such as cancer, inflammation, and degenerative changes.
Principle of Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) Staining
The principle of Hematoxylin and Eosin staining is based on the interaction of basic and acidic dyes with different cellular components, and it is the most widely used method for general tissue observation. It is the process in which two chemically opposite dyes are applied so that structures with different charges can be visualized separately. Hematoxylin acts as a basic dye that becomes positively charged after it is combined with a mordant, and this mordant–hemalum complex is responsible for binding with the acidic components of the cell. These are mostly the nucleic acids present in the nucleus and ribosomes, and they are stained in deep blue to purple. This reaction is referred to as basophilia which means attraction towards the basic dye.
Eosin acts as the counterstain, and it is an acidic dye carrying a negative charge. It binds with the basic components of the cytoplasm and extracellular matrix, and these structures take different shades of pink. This property is known as acidophilia. The cytoplasm, muscle fibers and connective tissue proteins are usually eosinophilic, and they provide the contrasting background needed for microscopic examination.
It is the differential staining property of these two dyes that creates the general pattern of dark nuclei and pink cytoplasm in H&E sections. The staining helps in understanding tissue organization, and it is used routinely because most cellular features show consistent affinity for either hematoxylin or eosin.
Requirements for Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) Staining
- Hematoxylin solution (Mayer’s, Harris, or Gill’s type) used as the nuclear stain.
- Mordant salts (commonly aluminum alum) required for forming the hematoxylin–mordant complex.
- Oxidizing agents (such as sodium iodate) used for ripening hematoxylin into its active form.
- Eosin Y solution used as the cytoplasmic counterstain (Eosin B or Phloxine B can also be present).
- Acetic acid added to eosin for sharpening the staining intensity.
- Differentiating solution prepared as acid alcohol (0.5–1% HCl in 70% ethanol) used to remove extra hematoxylin.
- Bluing agents like Scott’s tap water substitute, ammonia water, lithium carbonate or alkaline tap water.
- Alcohol series used for dehydration and rehydration (100%, 95%, 70%).
- Clearing agents such as xylene or xylene substitutes used before mounting.
- Clean glass slides or charged slides required for placing thin tissue sections.
- Coverslips used to make the stained preparation permanent.
- Mounting medium which is resinous and compatible with the clearing agent.
- Microtome used for cutting thin tissue sections (generally 2–7 µm).
- Oven or hot plate used to dry and fix sections on the slide.
- Staining jars, racks or automated staining apparatus for performing the staining steps.
- Water supply (tap water or deionized water) required for different rinsing steps.
Procedure of Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) Staining
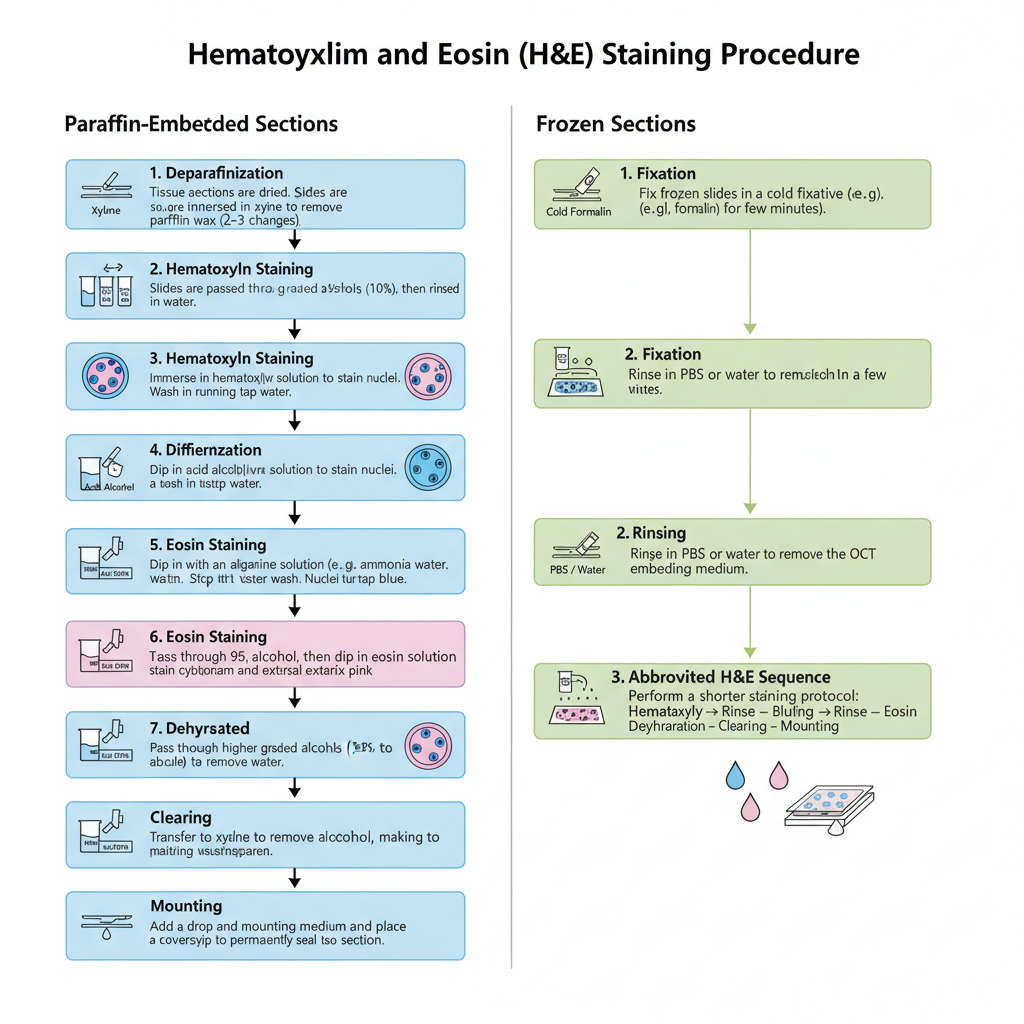
- Deparaffinization (Dewaxing). The paraffin sections on slides are dried properly in oven. Slides is kept in xylene which remove the wax, and usually 2–3 changes is used.
- Rehydration. Slides is passed through graded alcohols (100% to 95%). It is then rinsed in water which complete the hydration.
- Hematoxylin Staining. Slides is immersed in hematoxylin solution. It is then washed in running tap water to remove extra stain.
- Differentiation (in regressive method). In this step slides is dipped in acid alcohol which remove excess hematoxylin. A short water wash is done to stop the reaction.
- Bluing. Sections is treated with alkaline solution (like ammonia water). It is washed in tap water so that the nuclei become blue.
- Eosin Staining. Slides is passed quickly in 95% alcohol before eosin. It is dipped in eosin solution for a short period which stain cytoplasm.
- Dehydration. Slides is taken through higher graded alcohols (95% to absolute). This step also help in differentiating eosin if slides is kept longer.
- Clearing. Slides is transferred to xylene which remove alcohol and make the tissue clear.
- Mounting. A drop of mounting medium is added and coverslip is placed which seal the tissue section.
Procedure for Frozen Sections
- Frozen slides is fixed in cold fixative (formalin) for few minutes.
- Slides is rinsed in PBS or water which remove the OCT.
- Staining is done by a shorter H&E sequence (hematoxylin → rinse → bluing → rinse → eosin → dehydration → clearing → mounting).
Results and Interpretation of Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) Staining
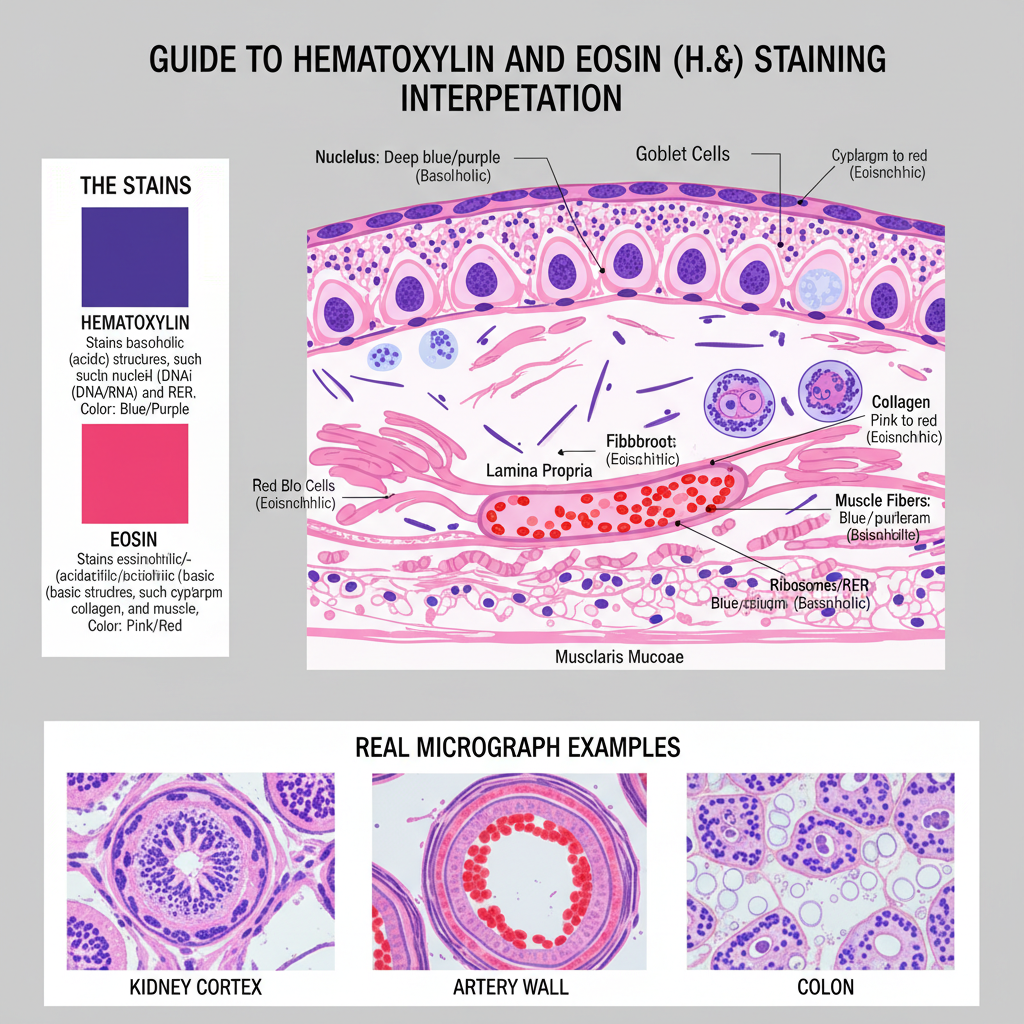
- Nuclei
- These stain deep blue or purple.
- It is due to basophilic nature of DNA and RNA which bind with hematoxylin.
- Cytoplasm
- Cytoplasm show pink to red color.
- The basic proteins bind with eosin which give the acidophilic reaction.
- Red Blood Cells
- RBCs appear bright red or orange.
- This is because of high affinity of eosin to hemoglobin.
- Muscle Fibers
- These stain pink to red.
- It is the result of eosin binding to the contractile proteins.
- Collagen Fibers
- Collagen show pink to red staining.
- It is the common eosinophilic reaction in connective tissues.
- Ribosomes and RER
- These stain blue or purple.
- It is because RNA content is high and it bind hematoxylin.
- Elastic Fibers
- Elastic fibers usually appear very light or almost unstained.
- Only faint pink color may be seen sometimes.
- Reticular Fibers
- These fibers remain unstained in H&E.
- Fibrin
- Fibrin is stained pink to red.
- This is referred to as an eosinophilic appearance.
- Mucin
- Mucin appear blue in progressive staining.
- In some cases it may show clear or unstained areas depending on pH of the stain.
- Calcium Deposits
- These appear dark blue or purple.
- It is the strong basophilic reaction in calcified regions.
- Bacteria and Fungi
- These structures may appear blue or purple.
- H&E is not specific for identification but it can show their general presence.
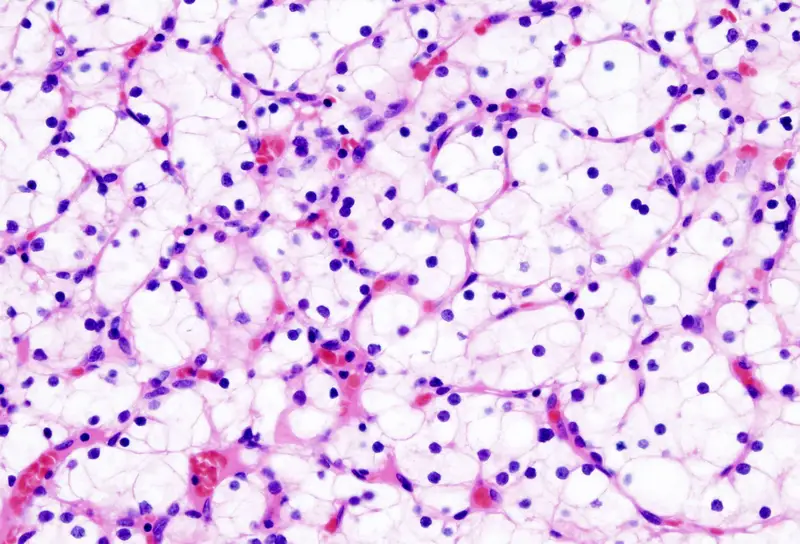
Uses of Hematoxylin and eosin staining
- It is used as the routine stain in general histopathology for examining tissue sections.
- It helps in observing the basic tissue architecture and cellular arrangement.
- The nuclei are clearly differentiated by hematoxylin, and cytoplasmic regions are seen by eosin.
- The stain is used for identifying structural changes in diseases, including abnormal nuclear features.
- It is important in tumor diagnosis because nuclear pleomorphism, hyperchromasia and mitotic activity is visible.
- The staining helps in assessing the degree of differentiation of different tumors.
- It is used for identifying muscle fibers, collagen and other connective tissue components based on their appearance.
- Red blood cells and fibrin are also seen clearly, and it is helpful in examining thrombus composition.
- It is used as a quality control step for checking fixation and processing issues in tissue sections.
- The stain is widely used in teaching because it shows most cellular and extracellular features clearly.
Advantages of Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) Staining
- It provides a clear structural view of tissues because nuclei and cytoplasm are stained distinctly.
- The stain is often enough for making many routine diagnoses based on general tissue architecture.
- It shows a strong contrast between basophilic and acidophilic components which helps in differentiation.
- The method is simple to perform and the staining steps are stable and reproducible.
- It can be adapted easily to automated staining machines for processing large sample numbers.
- Many hematoxylin preparations remain stable for long periods when stored properly.
- It acts as the baseline stain before performing advanced diagnostic tests since it shows overall morphology.
- It is also used as a quality control step for checking fixation and sectioning.
- Abnormal nuclear changes and other disease indicators can be recognized easily in stained sections.
Limitations of Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) Staining
- Different acidophilic components like collagen, muscle fibers and fibrin take similar eosin shades, so they cannot be chemically separated.
- Elastic fibers are poorly visualized because they do not take up the stain well, and reticular fibers also remain mostly unstained.
- The stain is not chemically specific and cannot detect particular carbohydrates or proteins like glycogen or mucins.
- Many microorganisms such as fungi or acid-fast bacteria are not clearly identified and need special staining.
- Counting mitotic figures on H&E sections is subjective, and there is difficulty in separating true mitosis from similar structures.
- Lipids are dissolved during paraffin processing and appear as empty spaces instead of stained components.
- It is a qualitative technique, and staining results may vary depending on reagent stability and timing.
- Basement membrane structures are not shown clearly and usually need special stains for proper visualization.
FAQ
Q. What is Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) staining?
A. It is the routine staining process used for observing tissue sections, and it uses hematoxylin for staining the nuclei and eosin for staining the cytoplasm.
Q. What does H&E staining show?
A. It shows the general tissue structure, where nuclei appear in blue to purple and the cytoplasmic regions appear in pink.
Q. What is the purpose of H&E staining?
A. The purpose is to provide a clear view of tissue architecture so that different normal and abnormal features can be examined.
Q. What do hematoxylin and eosin stain?
A. Hematoxylin stains the acidic nuclear components, and eosin stains the basic cytoplasmic and extracellular components.
Q. What colors do hematoxylin and eosin stain?
A. Hematoxylin gives a blue or purple color to nuclei, and eosin gives pink to red shades to the cytoplasm and connective tissues.
Q. How does H&E staining work?
A. It is the process in which hematoxylin bind with the acidic nuclei after forming a mordant complex, and eosin bind with the basic cytoplasmic parts, producing differential coloration.
Q. What are the components of H&E stain?
A. The main components are hematoxylin solution with a mordant, eosin solution, differentiating solution, bluing agents, alcohol series and clearing agents.
Q. Why is H&E staining important in histology?
A. It is important because it gives the fundamental information about tissue arrangement and helps in the first step of diagnosis.
Q. How is an H&E stain performed?
A. It is performed by dewaxing, hydrating, staining with hematoxylin, differentiating, bluing, staining with eosin, dehydrating, clearing and mounting.
Q. What are the different types of H&E stains?
A. Mayer’s hematoxylin, Harris hematoxylin and Gill’s hematoxylin are commonly used types depending on the staining method.
Q. What is the difference between progressive and regressive H&E staining?
A. In progressive staining, hematoxylin is applied until the desired intensity is reached, while in regressive staining the tissue is overstained and then differentiated using acid alcohol.
Q. What are the advantages of H&E staining?
A. It provides clear contrast, is simple to perform, it is stable, and it is suitable for routine diagnosis and teaching.
Q. What diseases can H&E staining help diagnose?
A. It helps in diagnosing many pathological conditions including cancers, inflammatory diseases, degenerative changes and general tissue abnormalities.
Q. What are alum hematoxylins?
A. These are hematoxylin solutions that use aluminum salts as mordants, forming the dye–mordant complex responsible for nuclear staining.
Q. What are the considerations for H&E staining?
A. Proper fixation, correct timing, reagent stability, water quality and controlled differentiation are important for getting consistent staining results.
- Anderson, J., & Rolls, G. (2025). An Intro to Routine and Special Staining in Histopathology. Leica Biosystems. https://www.leicabiosystems.com/us/knowledge-pathway/an-introduction-to-routine-and-special-staining/
- Brelje, T. C., & Sorenson, R. L. (2025). Collagen Fibers and Elastic Fibers | Connective Tissue. Histology Guide; University of Minnesota. https://histologyguide.com/slideview/MH-024-025-026-mesentery/03-slide-1.html
- Brown, S. (n.d.). The Science and Application of Hematoxylin and Eosin Staining. Robert H. Lurie Comprehensive Cancer Center, Northwestern University. https://www.feinberg.northwestern.edu/sites/mhpl/docs/the-science-and-application-of-hematoxylin-and-eosin-staining-6-5-2012.pdf
- Center for Musculoskeletal Research. (2020, March). Hematoxylin and Eosin Stain (H&E). University of Rochester Medical Center. https://www.urmc.rochester.edu/MediaLibraries/URMCMedia/musculoskeletal-research/core-services/histology/documents/CMSR-H-E.pdf
- Dunn, C., Brettle, D., Cockroft, M., Keating, E., Revie, C., & Treanor, D. (2024). Quantitative assessment of H&E staining for pathology: Development and clinical evaluation of a novel system. Diagnostic Pathology, 19(42). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13000-024-01461-w
- Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) Staining: Principles, Protocol, Morphology, and Applications in Diagnostic Histopathology. (n.d.). [Provided text].
- Henderson, T. (2025, November 7). Understanding the Differences Between Histology Stains: A Comprehensive Guide. Contract Laboratory. https://contractlaboratory.com/what-is-the-difference-between-common-histology-stains/
- Histology Equipment. (2025). The Difference Between Progressive & Regressive H&E Staining. Mercedes Scientific. https://histologyequipment.com/progressive-and-regressive-he-staining-what-are-the-differences/
- Ibrahim, A., Toss, M. S., Makhlouf, S., Miligy, I. M., Minhas, F., & Rakha, E. A. (2022). Improving mitotic cell counting accuracy and efficiency using phosphohistone‐H3 (PHH3) antibody counterstained with haematoxylin and eosin as part of breast cancer grading. Histopathology, 82(3), 393–406. https://doi.org/10.1111/his.14837
- IHC WORLD. (2024, January 20). Mayer’s and Gill’s hematoxylins. https://ihcworld.com/2024/01/20/mayers-and-gills-hematoxylins/
- Li. (2013, June 6). H&E staining. Xin Chen Lab; University of California San Francisco. https://pharm.ucsf.edu/xinchen/protocols/h-e
- Llewellyn, B. D. (2013, October). Hematoxylin Formulae. StainsFile. https://www.stainsfile.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/09/hematoxylin-formulae.pdf
- National Cancer Institute. (n.d.). Definition of H and E staining. NCI Dictionary of Cancer Terms. https://www.cancer.gov/publications/dictionaries/cancer-terms/def/h-and-e-staining
- Sampias, C. (2025). H&E Staining Basics: Troubleshooting Common H&E Stain Problems. Leica Biosystems. https://www.leicabiosystems.com/knowledge-pathway/he-basics-part-4-troubleshooting-he/
- Sampias, C., & Rolls, G. (2025). Hematoxylin & Eosin (H&E) Staining Intro: Procedures & More. Leica Biosystems. https://www.leicabiosystems.com/us/knowledge-pathway/he-staining-overview-a-guide-to-best-practices/
- Staessens, S., Denorme, F., François, O., Desender, L., Dewaele, T., Vanacker, P., Deckmyn, H., Vanhoorelbeke, K., Andersson, T., & De Meyer, S. F. (2020). Structural analysis of ischemic stroke thrombi: Histological indications for therapy resistance. Haematologica, 105(2), 498–507. https://doi.org/10.3324/haematol.2019.219881
- StainsFile. (2025). Ripening Hematoxylin. https://www.stainsfile.com/theory/methods/hematoxylin-eosin-staining/ripening-hematoxylin/
- University of Leeds. (n.d.). H&E staining. The Histology Guide. https://www.histology.leeds.ac.uk/what-is-histology/H_and_E.php
- University of Ottawa. (n.d.). Histological staining. Research and Innovation. https://www.uottawa.ca/research-innovation/histology/services/histological-staining