Economic Importance of Algae Overview
Algae is a photosynthetic, eukaryotic marine organism. Their size ranges from unicellular microalgae to giant kelp. Algae are characterized by their lack of flowers, formal roots, leaves, or even stems.
They can grow anywhere such as in the dirt or on rocks, marine water, freshwater, etc. Algae are variable in shapes, sizes, and colors.
There are several economic Importance of algae such as they are used as a food source, a fodder, in fish farming, as a fertilizer and they also used in medical industries.
1. Economic Importance of Algae in Food
- The algae provide proteins, vitamins, minerals, dietary fiber which make them good food sources.
- In many countries seaweeds (Porphyra, Laminaria, Ulva) are eaten in soups, salads, snacks and used as seasoning.
- The microalga Spirulina is consumed as supplement, because it contains high protein and essential amino acids.
- In processed foods, algal hydrocolloids (agar, carrageenan, alginates) are used as thickeners, gelling / stabilizing agents.
- From red algae agar is extracted, and it is incorporated into desserts, jellies, gels.
- Through gel / emulsifier roles, algal derivatives improve texture, stability and shelf-life of foods.
- The global demand for edible seaweeds is rising, so more economic value is generated by harvesting and farming them.
- In some marine aquaculture systems, algae grown are consumed as food by fish or shellfish, so food chain is supported.
- Algae are used to make functional / “health” foods, because they carry bioactive compounds (antioxidants, polysaccharides) which help human health.
- Edible seaweeds often contain iodine, calcium, magnesium; thus they supply these minerals in diet.
- In food security context, algae are considered as alternative food resource that can supplement terrestrial plants.
- Freshwater microalgae (after cell wall breakdown) are incorporated into powders / tablets / liquids, thus they become usable as food supplements.891011
Examples of Algal foods
- The Spirulina (a blue-green alga) is consumed as powder or tablet, because it packs high protein and vitamins.
- The Chlorella (a green microalga) is eaten in form of tablets / powder, often added to smoothies or health foods.
- The Porphyra (red seaweed) is used as nori sheets (for sushi wrap) and in soups / salads.
- Dulse (Palmaria palmata, red alga) is eaten dried as snack, or cooked in soups, vegetables.
- Laminaria (a brown alga, “kombu”) is used in broths / stocks (dashi) and as food seasoning.
- Wakame (brown seaweed, Undaria pinnatifida) is eaten in salads, soups or side dishes especially in East Asia.
- Ulva (green seaweed, “sea lettuce”) is consumed in salads, soups, or dried / shredded as garnish.
- Caulerpa racemosa (green seaweed, “sea grapes”) is used in salads in Philippines, Japan, Thailand etc.
- Gim (Korean dried seaweed sheets, genus Pyropia / Porphyra) is used to wrap rice or eaten as side dish.
- Green laver / Aonori (Ulva / Monostroma species) is sprinkled as seasoning or used in soups / snacks
- Cladophora (filamentous green alga) is eaten in parts of Asia (e.g. Mekong weed) either fresh or dried.1213
2. Economic Importance of Algae in Industries – Industrial applications of algae
- The algae are used to produce biofuels (biodiesel, bioethanol, biohydrogen) by converting lipid / carbohydrate rich biomass.
- In many industries, algal polysaccharides (agar, alginates, carrageenan) are extracted and used as thickeners, gelling / stabilizing agents in food, cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, textiles.
- The diatom shells (silica frustules) are used in filtration, abrasives, and as insecticide / desiccant powders (diatomaceous earth).
- In wastewater treatment, microalgae are applied to remove nutrients (N, P) and pollutants, and the treated water is reused or discharged.
- In the cosmetics / personal care sector, algal extracts (pigments, antioxidants, minerals) are incorporated in creams, masks, lotions for skin care benefits.
- Algal biomass is used in animal feed / aquaculture feed to improve nutrition, growth and health of fish, shrimp, livestock
- In biorefinery systems, multiple products (fuel, chemicals, food additives) are co-produced from a single algal cultivation to improve economic feasibility.
- In textile / leather / paper industries, alginate and other algal derivatives are used as sizing agents, in printing, and as coatings / adhesives.
- The species Auxenochlorella protothecoides is studied for its high lipid content and used in biofuel / industrial lipid production systems.
- In architecture / building materials, photobioreactors or algae facades are being developed to integrate algae cultivation for energy, carbon capture, and aesthetic use.14151617
Examples of commercial Products made from algae;
- The Spirulina supplement is sold as powder / tablets for human nutrition and in animal feed.
- The Dunaliella salina is commercialized for β-carotene production which is used as antioxidant / pigment in food & cosmetics.
- The carrageenan (from red seaweeds) is made into gelling / thickening agents used in ice creams, dairy, processed food.
- The alginate / alginic acid (from brown algae) is turned into food additives, dressings, wound care materials and industrial gels.
- The agar / agarose (from red algae) is manufactured for microbiological media, jellies, desserts, and biotechnological uses.
- The omega-3 algal oil is isolated from microalgae to make dietary / nutraceutical capsules (EPA / DHA).
- The Algenist alguronic acid is used in commercial skincare / anti-aging cosmetics as active ingredient derived from microalgae.
- The bioplastic MarinaTex is produced using red algae and fish waste as renewable plastic alternative.
- The polyurethane foams are made from algal residual oils (after omega-3 extraction) in industrial material production (e.g. in shoes, adhesives).
- The natural pigments / dyes from algae are sold for food coloring, cosmetics, textile coloring (e.g. phycocyanin, carotenoids)181929
3. Economic Importance of Algae in Agriculture
- Algae supply macro and micro nutrients (N, P, K, Fe, Zn etc.) which reduce dependency on chemical fertilizers.
- In paddy fields, cyanobacteria fix atmospheric nitrogen, and thus soil fertility is improved by their presence.
- Seaweeds / macroalgae are used as biofertilizers / soil conditioners, improving soil structure and water retention.
- Plant growth is stimulated by algal excreted substances (growth regulators, vitamins, amino acids) which are secreted by certain algae.
- In reclamation of saline / alkaline (usar) soils, blue-green algae are used to lower pH and improve soil productivity.
- Algae act as a reservoir of inorganic nutrients, which can be released slowly and sustain crops over time.
- Soil erosion is reduced when algae stabilize topsoil, binding particles together, especially in moist soils.
- In integrated farm systems, algae grown in wastewater or effluent can be harvested and recycled back to fields as fertilizer.
- Use of algal inputs leads to cost savings (less spending on synthetic fertilizers) and sometimes yield increases.
- Seaweed farming itself offers extra income for coastal farmers; it supports livelihoods, especially in developing regions.
- Carbon is sequestered by algae via photosynthesis; use of algal biomass in agriculture contributes to reducing atmospheric CO₂.
- In aquaculture systems, algae support fish culture by being food or improving water quality, which indirectly benefits agriculture where aquaculture and agriculture integrate.1234
4. Economic Importance of Algae in Medicine
- The algae produce bioactive compounds (polysaccharides, carotenoids, fatty acids) which are used in medicines and pharmaceutical industry.
- From red algae, cytarabine (an anticancer drug) is derived, and hence algae contribute to cancer therapy.
- In antiviral therapies, sulfated polysaccharides extracted from brown algae are tested for inhibiting viral entry or replication.
- Seaweed-derived compounds with anti-bacterial / antimicrobial effect have been isolated, and are used in drug development for infections.
- In anti-inflammatory treatments, algae components are exploited to reduce inflammation and oxidative stress in tissues.
- The algae are used to produce antioxidants, and these antioxidants are used as adjuncts / active agents in many therapeutic formulations.
- In drug delivery systems, algal polysaccharides / gels are used as matrices or carriers due to biocompatibility, and thus medicine release is controlled.
- With genetic engineering, algae are being used to express therapeutic proteins / recombinant pharmaceuticals, so cost of production may be lowered.
- The market demand for algal pharmaceuticals (nutraceuticals, medicines) is increasing, making algae a valuable economic resource in medical sector.567
5. Algae as nutrients
- The algae contain high-quality protein, sometimes up to 50-70 % of their dry mass, which includes all essential amino acids.
- They supply essential fatty acids (omega-3, omega-6) that are not made by body itself.
- In addition, algae provide vitamins (A, B complex, C, E, K etc.) which enrich diet and prevent deficiencies.
- Minerals (iron, calcium, magnesium, potassium, iodine and trace elements) are present in algae, and they improve mineral intake.
- Dietary fiber / polysaccharides in algae help digestion, slow glucose absorption, and support gut health.
- The algae are rich in antioxidants / bioactive compounds, which protect cells from oxidative damage.
- Because they grow fast and on non-arable land (saline / brackish water), algae are sustainable sources of nutrients, reducing pressure on farmland.
- It is noted that the content of nutrients vary by species, growth conditions, season, harvesting method etc., so consistency can be a challenge.
- The bioavailability (how well nutrients are absorbed) of some nutrients (e.g. vitamin B12 in some algae) is variable, and in some cases inactive forms are present.202122
6. Algae as biofuels
- The algae produce large amounts of lipids / oils which are extracted and processed into biodiesel (fatty acid methyl esters).
- In addition, algal carbohydrates and sugars are fermented to yield bioethanol or butanol which serve as liquid fuels.
- The residual biomass (after oil extraction) can be subjected to anaerobic digestion to produce biogas (methane + CO₂).
- The algae are used in hydrothermal liquefaction / thermochemical conversion (wet biomass → biocrude) to produce drop-in fuels similar to gasoline / diesel.
- In some tests, jet fuel / aviation biofuel is produced from specially tailored algal strains via lipid conversion and upgrading.
- The species Auxenochlorella protothecoides has been investigated because it accumulates high lipid under certain growth modes, so it is promising for biodiesel production.
- Microalgae growth is fast, and high photosynthetic efficiency allows more biomass per area, making fuel production potentially more productive than many terrestrial crops.
- The cultivation systems include open ponds and photobioreactors; in such systems CO₂ is bubbled / fed to maximize growth, and thereafter conversion steps are done.
- It has been estimated that algal oil yields (per hectare) can far exceed yields of conventional oil crops (e.g. 10–20 times more).
- The technology is still in development, as cost, energy inputs, harvesting / extraction remain challenges which must be overcome before large scale use is feasible.232425
7. Economic Importance of Algae in the cosmetic industry
- The algae yield antioxidants (carotenoids, phenolics etc.) which are used in skin care formulations to protect skin from radicals.
- In cosmetic products, algal polysaccharides (alginate, fucoidan) are used as moisturizers / hydrating agents, gels, thickeners, which improve texture.
- The algae extracts are applied as anti-aging agents, because they inhibit enzymes (MMPs) that degrade collagen, and stimulate collagen synthesis.
- Seaweed / microalgae provide natural colorants and pigments (phycobiliproteins, carotenoids) used in cosmetics, replacing synthetic dyes.
- Extracts from algae act as natural preservatives / antimicrobial agents, thus product shelf life is improved, contamination is reduced.
- The algae supply vitamins (A, C, E etc.) and minerals which nourish skin when incorporated in creams, masks, serums.
- In many commercial skincare lines, alguronic acid (a mixture of algal polysaccharides) is included as anti-aging / skin renewing ingredient.
- Because algae can be grown sustainably (without much land / freshwater), cost advantages can be gained over synthetic raw materials in cosmetics.
- The cosmetic / microalgae market is large; in 2023 it was valued at ~ USD 1.2 billion, showing strong economic potential.
- The algae biomass can be processed, fractionated, and high purity bioactives can be sold as premium cosmetic ingredients.343536
8. Importance of Algae as livestock nutrition
- The algae supply high quality protein, vitamins, minerals, fatty acids etc. which enrich livestock diets.
- In poultry, microalgae supplementation has been shown to raise omega-3 content in eggs, thus improving their nutritional value.
- The residual biomass / defatted algae can be used as feed ingredient, and it is digested / assimilated by animals.
- In ruminants, algae meals are employed to provide protein, trace minerals, vitamins and even prebiotic components for gut health.
- With some seaweeds (e.g. Asparagopsis) fed to cattle, enteric methane emissions are reduced, thereby improving energy efficiency of feed.
- In aquaculture and fish feed, algae are used as direct feed or feed supplement because fish accept them and they meet nutritional needs.
- Because algae can grow fast and on marginal land / saline water, the reliance on conventional feed crops (soybean, maize) is reduced, lowering feed cost pressure.
- In manure / waste nutrient recycling, algae are cultivated on nutrient-rich effluents and then harvested as feed, closing nutrient loop and reducing pollution.
- In trials, inclusion levels of 5-10 % algae in diets often yield improved growth, feed conversion, immunity without adverse effects (if used properly).
- The algae help supply essential amino acids and micronutrients that might be deficient in conventional feeds, thereby enhancing animal health and productivity.373839
9. Economic Importance of Algae in Aquaculture
- The algae serve as primary producers in aquaculture food chains, and thus larvae of fish, mollusks, crustaceans depend on them.
- In many aqua-feeds, microalgae are used to partially replace fish meal / fish oil, reducing cost and pressure on wild fish stocks.
- The water quality is improved when algae uptake excess nitrogen / phosphorus wastes, and thus pollution is lowered.
- In integrated multi-trophic aquaculture (IMTA), seaweeds / algae are co-cultured to absorb nutrients from fish or shrimp wastes, thereby enhancing system sustainability.
- Algal biomass provides pigments, carotenoids, fatty acids (like omega-3) that improve coloration, health and quality of cultured animals.
- The use of algal supplements enhances growth performance, immunity, disease resistance in aquatic species.
- The cultivation of macroalgae (seaweeds) itself is an economic product in aquaculture, giving value beyond fish / shellfish.
- Because algae grow fast with light / CO₂, biomass can be produced relatively cheaply, making them viable in aquaculture systems.
- The risk is reduced dependency on imported feeds / expensive inputs by substituting algae in diets.40
10. Economic Impacts of algal cultivation
- The cultivation of algae generates jobs and employment in farming, processing, harvesting, and downstream industries, thereby boosting local economies.
- Revenue from sale of algal biomass (for food, feed, biofuels, cosmetics) is earned, and economic value is realized by producers.
- In polluted or mine-impacted sites, algae cultivation is used to treat water and remove pollutants, and revenue is captured by selling the cleaned water or biomass.
- The farming of algae helps diversify income sources for coastal and rural communities, reducing dependence on a single crop or industry.
- With integrated systems, waste nutrients or CO₂ emissions are converted into algal biomass, which is sold — thereby reducing waste management cost and adding profit.
- Capital investment in cultivation infrastructure (ponds, photobioreactors) is required; thus large upfront costs are incurred before profit is realized.
- Operating costs (energy, nutrient supply, harvesting, drying) reduce net economic returns, especially when scale is small.
- The market price for algal products affects profitability — for biofuels especially, the economics is challenging unless byproducts are valorized.
- In biofuel scenarios, cost targets are tight; for example to compete in fuel markets, algal production cost must be kept low (e.g. ~$139.50 per ton for 30 % lipid biomass) in some models.
- In closed cultivation systems, capital & energy costs are higher, so they are often reserved for high-value products rather than bulk biofuels.
- When algal cultivation is scaled, economies of scale reduce per unit cost, making more products economically viable.
- If disruptions in market, climate, or regulations occur, the risk to investment is significant; stability of demand is key.
- Overall, algal cultivation can produce economic benefits, but success depends on optimizing costs, finding multiple revenue streams, and scaling.414243
11. Importance of algae in Environment
Importance of Algae in environmental management
- The algae absorb CO₂ by photosynthesis, and thus help in carbon sequestration, reducing greenhouse gases.
- In contaminated waters, algae are used to remove nutrients (nitrogen, phosphorus), thus preventing eutrophication of lakes / rivers.
- The algae accumulate heavy metals and toxic chemicals which are then removed when algae are harvested (bioremediation).
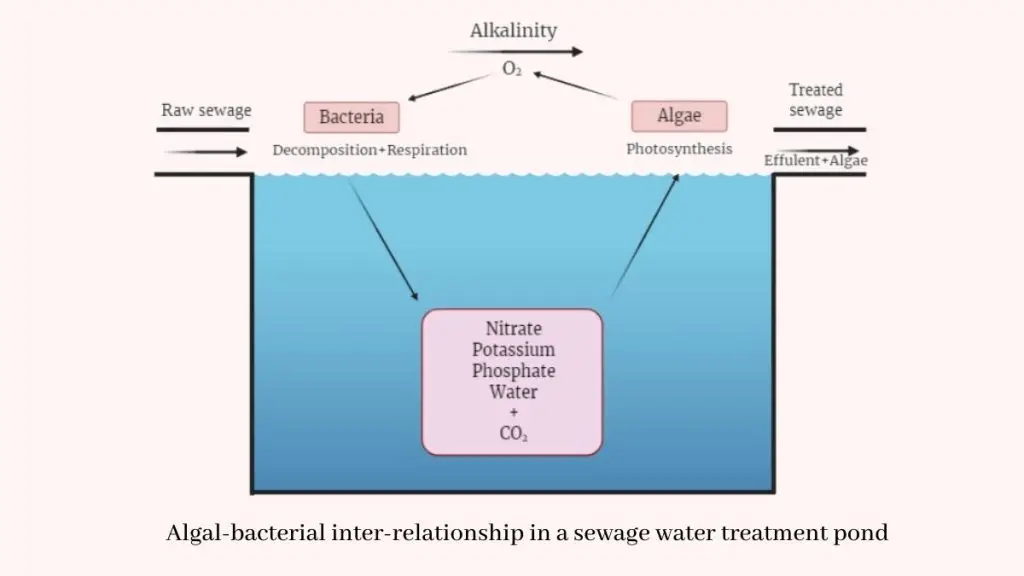
- In wastewater treatment systems, microalgae are used to treat sewage / industrial effluents, and the cleaned water is reused or safely discharged.
- In coastal / marine zones, seaweed farming helps buffer shorelines, reducing wave impact and erosion, and improving habitat for marine life.
- Algal biomass is converted into bioplastics, which reduce reliance on petroleum plastics and lower environmental pollution.
- In carbon capture projects, engineered algae strains are grown in ponds to trap CO₂, and biomass is then stored underground to lock carbon.
- Phycotechnology exploits algae in industrial / environmental roles, e.g. in sewage treatment, pollutant removal, and soil / water reclamation.
- In integrated systems, algae are used together with agriculture or aquaculture to recycle nutrients, reduce waste, and improve overall environmental balance.2627283031
Importance of Algae in carbon sequestration and climate change mitigation
- The algae absorb CO₂ during photosynthesis, convert it to organic carbon, and O₂ is released.
- In cultivation systems (ponds, photobioreactors) CO₂ from flue gases / atmosphere is supplied so that carbon sequestration is maximized.
- Some engineered algal strains have been made which capture more CO₂ (twice more) by improving carbon concentrating mechanisms
- Macroalgae (seaweeds) biomass that sinks into deep ocean or is buried in sediments carries carbon away from surface waters, so long-term sequestration is achieved.
- Harvested algal biomass can be converted into durable products (biochar, bioplastics) which lock carbon in solid form rather than letting it return to atmosphere.
- With large scale algae farming along coasts, the cumulative effect may reduce atmospheric CO₂, thereby helping climate change mitigation.
- The efficiency of carbon uptake is influenced by light, temperature, pH, nutrient supply, and algal species; optimizing these is essential.
- Some challenges remain: not all biomass is sequestered (much is decomposed), and quantifying how much CO₂ is permanently stored is difficult.
- Certain start-ups are scaling algal carbon capture systems (e.g. Brilliant Planet) to capture dozens to hundreds of tons of CO₂ per year, aiming lower cost vs direct air capture.
- By combining algae carbon capture with biomass utilization (fuel, materials) a circular system can be built that mitigates emissions while producing value.3233
Reference