Cell membrane staining is the process in which the plasma membrane of a cell is visualized with the help of dyes or fluorescent probes. It is the thin outer covering of the cell, and it is normally transparent, so it cannot be seen clearly under a simple light microscope. It is the process where special dyes bind with the lipid bilayer, surface carbohydrates, or membrane proteins, so the boundary of the cell becomes visible. It is used to study the cell outline, to see cell movement, and also to identify different cells in a tissue. It is important in experiments where the structure of the membrane or the position of the cell is required.
Different Methods of Cell Membrane Staining
There are different methods used for membrane staining, and each method is based on the specific property of the membrane.
1. Lipophilic Fluorescent Dyes
It is the method where fat-loving dyes are used which enter into the lipid bilayer of the membrane. These dyes include DiI (red) and DiO (green). The dyes insert into the hydrophobic region of the membrane without forming covalent bonds. It is used mainly in live cells because the dye stays inside the membrane for a long time. It is also used to track cell movement and neuronal pathways.
2. Lectin-Based Staining
This method is based on lectins which are proteins that bind with specific sugars present on the membrane surface. Wheat Germ Agglutinin (WGA) binds with N-acetylglucosamine present in the membrane. When WGA is attached with a fluorescent tag, it outlines the cell boundary clearly. It is used mainly in fixed tissues where the cell structure must be preserved, so this method is stable and reliable.
3. Immunofluorescence Staining
It is the process where antibodies are used to bind with specific membrane proteins. It identifies special receptors or channels like CD markers present on immune cells. It is used when the requirement is not only to see the outline but also to know which protein is present on the membrane. This method is highly specific.
4. Dye Exclusion Method
This is different from other methods because it is used to check membrane integrity. Dyes like Trypan Blue enter only into dead cells because live cells exclude the dye. If the membrane is intact the cell remains clear, and if the membrane is damaged the cell becomes blue. It is used for counting live and dead cells in a population and not for structural observation.
A. Lipophilic Fluorescent Dyes (The “Di” Family) Method
Principle
It is the method based on the special amphiphilic nature of the Di dyes where each molecule has a hydrophilic head and two long hydrophobic tails. It is these tails that have strong attraction toward the lipid region of the membrane, so when the dye is added to the cells the tails insert into the hydrophobic core of the lipid bilayer. The head portion stays exposed on the membrane surface. It is the process in which the dye behaves similar to the natural phospholipids present in the plasma membrane, so insertion occurs spontaneously without disturbing the membrane structure.
After entering the membrane, the behaviour of the dye changes due to its environment-sensitive fluorescence. In the aqueous medium the fluorescence is very low, but once the dye is present in the lipid zone, the conformation of the molecule becomes stable and strong fluorescence is produced. It is the reason that only the membrane area is visible while the surrounding medium remains dark. The molecules are not covalently attached with the membrane; instead, they remain floating inside the lipid layer. It is the process described by the fluid mosaic model where the inserted dye diffuses laterally in the membrane. This lateral spreading stains the entire cell uniformly and in neurons it also moves along the axons which is referred to as neuronal tracing.
Procedure
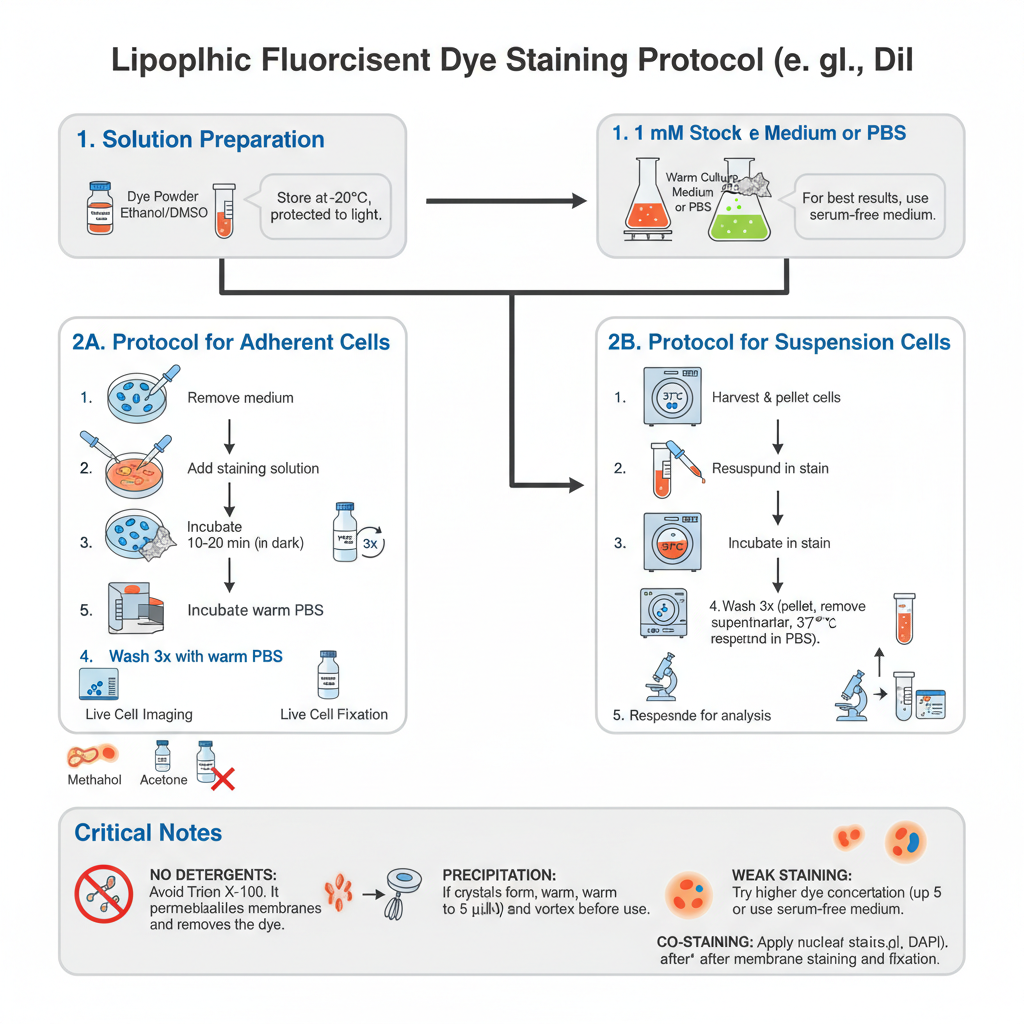
Preparation of Solutions
- Prepare Stock Solution. Dissolve the dye powder (e.g., DiI) in DMSO or Ethanol to obtain 1 mM stock. The tube is wrapped in aluminium foil (light sensitive) and stored at −20°C. It is stable for up to 6 months if kept frozen and dark.
- Prepare Working Solution. Dilute stock into warm culture medium (or PBS) to final 1–5 µM. Serum in medium can bind the dye and reduce efficiency. If staining is weak try serum-free medium or PBS for the staining step.
Steps — Protocol for Adherent Cells (coverslips or dishes)
- Remove medium. Carefully aspirate growth medium from the culture dish.
- Add stain. Gently add Working Solution (1–5 µM) until cells are covered.
- Incubate. Incubate at 37°C for 10–20 minutes. Keep protected from light (cover with foil) if incubator is not dark.
- Wash. Remove staining solution. Gently wash cells 3 times with warm PBS or medium. This removes excess dye which may have stuck to plastic and reduces background.
- Imaging or fixation. For live imaging add fresh warm medium and image immediately. Optional fixation: add 4% paraformaldehyde (PFA) for 10–15 minutes at room temperature. Do NOT use methanol or acetone as they strip lipids and wash away the dye.
Steps — Protocol for Suspension Cells (blood cells, lymphocytes)
- Harvest. Collect cells and centrifuge at 1000–1500 rpm for 5 minutes to pellet cells.
- Resuspend in stain. Aspirate supernatant and gently resuspend pellet in Working Solution (1–5 µM).
- Incubate. Incubate at 37°C for 10–20 minutes in dark.
- Wash. Centrifuge to pellet, remove dye, resuspend in fresh warm PBS or medium. Repeat wash 2 more times to remove unbound dye.
- Final resuspension. Resuspend in fresh medium for analysis (flow cytometry or microscopy).
Critical Notes
No detergents– Never use detergents like Triton X-100 or Tween-20 if membrane signal is required. These permeabilization agents poke holes in the membrane and wash away the lipophilic dye.
Precipitation– Bright red crystals or dots indicate dye precipitation. Warm staining solution to 37°C and vortex vigorously before use, or filter through 0.2 μm filter to remove particulates.
Weak staining– Try higher end of working range (up to 5 µM) or use PBS / serum-free medium for staining step. Prolonged incubation may increase background.
Co-staining– Nuclear stains (e.g., DAPI) should be applied after membrane stain and after fixation. This avoids dye transfer and spectral overlap.
Uses of Lipophilic Fluorescent Dyes (DiI, DiO)
- It is used in neuronal tracing to map long-distance connections because the dye diffuses along axons and dendrites in both anterograde and retrograde direction.
- It is used for live cell tracking to observe migration, fusion and movement since the dye is non-toxic and remains in the membrane.
- It is used for vesicle labeling where extracellular vesicles (exosomes) or liposomes are stained to study their uptake into cells.
- It is used in co-culture studies to distinguish two different cell populations by staining one cell group with red dye and the other with green dye before mixing.
Advantages
- It produces a very bright and stable fluorescent signal which does not fade quickly during imaging.
- It is non-toxic to live cells, so it is suitable for long-term tracking of cell movement or growth.
- It stains the lipid bilayer uniformly and forms an even ring around the entire cell surface.
- It works on almost all cell types because every cell has a membrane made of lipids.
Limitations
- It cannot be used with detergents like Triton X-100 since permeabilization removes the dye from the membrane.
- When cells are very close together, the dye can transfer between touching membranes and this may confuse cell tracking.
- Over time the dye may get internalized by endocytosis in live cells and appears as dots inside instead of a clear membrane ring.
B. Lectin-Based Staining (WGA) Method
Principle
It is the method based on specific binding between the lectin molecule and the carbohydrate residues present on the outer surface of the membrane. WGA is a lectin obtained from wheat and it has strong affinity toward N-acetylglucosamine and sialic acid which are abundant in the glycocalyx. It is the sugar-rich coating present outside the plasma membrane. When WGA is chemically linked with a fluorescent dye, it forms a WGA–fluorophore complex that attaches tightly with these sugars. It is the process in which the binding occurs only on the outer membrane surface because WGA does not enter the lipid bilayer.
After application to the cells, the fluorescent WGA binds uniformly with the exposed carbohydrate residues and outlines the entire cell boundary. It is stable because the interaction between the lectin and sugar residues is strong and remains intact even after fixation procedures. It is the reason that this method is preferred for fixed tissues where the cell shape and architecture must be preserved. The staining highlights the membrane surface clearly without disturbing the membrane structure.
Procedure
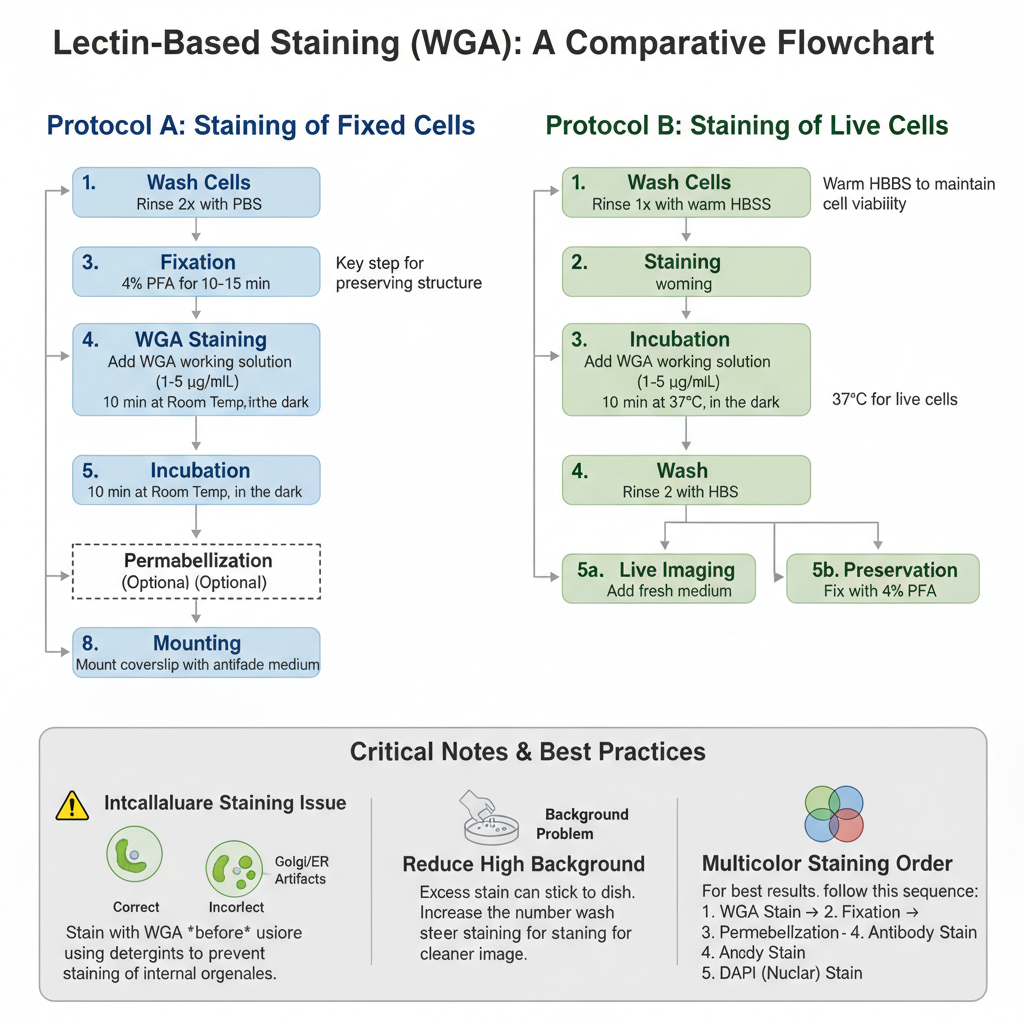
Preparation of Solutions
- Stock Solution– It is prepared by dissolving lyophilized WGA (conjugated with fluorophores like Alexa Fluor 488, 555, or 647) in PBS or distilled water. The concentration of the stock usually kept at 1 mg/mL. It is stored as aliquots at –20°C because repeated freeze–thaw cycle can reduce its activity.
- Working Solution– It is the process in which the stock is diluted with HBSS or PBS. The final concentration is kept around 1–5 µg/mL. HBSS is mostly preferred because it maintains cell morphology in better condition during staining of live cells.
Protocol A: Staining of Fixed Cells
This protocol is used when internal staining with other antibodies is also required. It is similar to the stepwise processes described in other laboratory protocols where washing, fixation, and staining are performed sequentially .
- Wash– The cells is rinsed 2 times with PBS for removal of culture medium.
- Fixation– The cells is fixed using 4% Paraformaldehyde (PFA) for 10–15 minutes at room temperature. Methanol fixation is not preferred as it destroys carbohydrate residues.
- Wash– It is rinsed 3 times with PBS.
- Staining– The WGA working solution (1–5 µg/mL) is added to cover the cells.
- Incubation– It is incubated for 10 minutes at room temperature in dark condition.
- Wash– Cells is washed 3 times with PBS for removing excess stain.
- Permeabilization (Optional)– This step is done only after WGA staining if internal proteins are to be stained. If permeabilization is done before staining, WGA enters inside and stains Golgi and ER which disturb membrane outline.
- Mounting– The coverslip is mounted using antifade mounting medium.
Protocol B: Staining of Live Cells
This method is used when membrane dynamics or live imaging is required.
- Wash– Cells is rinsed once with warm HBSS.
- Staining– WGA working solution is applied gently on the live cells.
- Incubation– It is incubated for 10 minutes at 37°C or room temperature in dark.
- Wash– Excess stain is removed by washing 2 times using HBSS.
- Imaging or Fixation
- For live imaging, fresh HBSS or phenol-red free medium is added.
- For preservation, fixation with 4% PFA can be done afterwards.
Critical Notes
Intracellular Staining Issue– If bright intracellular dots appear near nucleus, it indicates permeabilization was performed before WGA. It enters inside the cell and binds to Golgi membranes. So membrane staining must always be completed before using detergents. These types of process-dependent issues were also observed in several other biochemical techniques explained in uploaded files .
Background Problem– High background occurs when excess stain remains attached to plastic surface. Increasing number of washes after staining can reduce this.
Dual Staining– WGA is suitable for multicolor imaging. It can be used with DAPI for nuclear stain and red-fluorophore antibodies. The order usually followed is–
WGA stain → Fix → Permeabilize → Antibody stain → DAPI.
This order ensures that the stain is restricted to its correct location just like stepwise reactions maintained in different molecular assays discussed earlier .
Uses of Lectin-Based Staining (WGA)
- It is used for cell boundary visualization because it outlines the cell edges clearly in fixed tissues where other membrane stains may get removed.
- It is used for glycocalyx analysis to detect surface sugars like N-acetylglucosamine and to study changes during cancer or inflammatory conditions.
- It is used in bacteriology for staining the bacterial cell wall (peptidoglycan) to observe biofilms or infection patterns.
- It is used as a counterstain in fluorescence microscopy to show the cell surface position in relation to the internal organelles.
Advantages
- It is fixation resistant because WGA remains bound even after formaldehyde fixation and permeabilization, so it can be used together with intracellular antibody staining.
- It gives a sharp and clear outline of the cell borders which helps in automated image analysis.
- The binding between WGA and the sugar residues on the cell surface is very strong and stable.
Limitations
- When cells are permeabilized before staining, WGA stains the Golgi apparatus strongly and this can hide the membrane signal.
- The staining can vary because WGA binds to sugars and the glycosylation pattern may change during disease or stress conditions.
- It stains only the glycocalyx layer on the surface and does not show the lipid bilayer itself.
C. Immunofluorescence Staining Method
Principle
It is the method based on the specific recognition between an antibody and its antigen present on the cell surface. The antibody is a Y-shaped protein that binds only with a particular membrane protein such as receptors or channels. It is different from lipophilic dyes because it does not stain the entire membrane but detects only the selected protein. The antibody is linked chemically with a fluorophore, and when light of suitable wavelength falls on it, the dye absorbs the energy and emits visible fluorescence. It is the process in which this emitted light makes the location of the antigen clearly visible.
The method can be direct when the fluorophore-labelled primary antibody binds with the target in one step. Indirect immunofluorescence uses an unlabeled primary antibody followed by a fluorescent secondary antibody that attaches with the primary one. It is the process where signal amplification occurs because several secondary antibodies bind to a single primary antibody, making the stained region brighter. For membrane staining, the cells are usually not permeabilized so that the antibodies bind only to the external surface proteins. It gives a sharp outline of the membrane without staining the internal cell components.
Procedure
Preparation of Reagents
Some of the main reagents are prepared before starting the staining steps. These are similar as other laboratory buffers which maintain protein structure and antigen stability.
- Fixation Buffer– It is prepared by using 4% Paraformaldehyde (PFA) in PBS. Methanol or acetone is not used because these dissolve the lipid membrane and the surface antigens is damaged.
- Blocking Buffer– This buffer contains 1–5% BSA or 5% normal goat serum in PBS. No detergents like Triton X-100 or Tween-20 is added because these increase membrane permeability and allow antibody to bind internal structures.
- Antibody Dilution Buffer– It is the process of diluting antibodies in 1% BSA in PBS. This buffer helps in reducing non-specific sticking of antibodies during the staining.
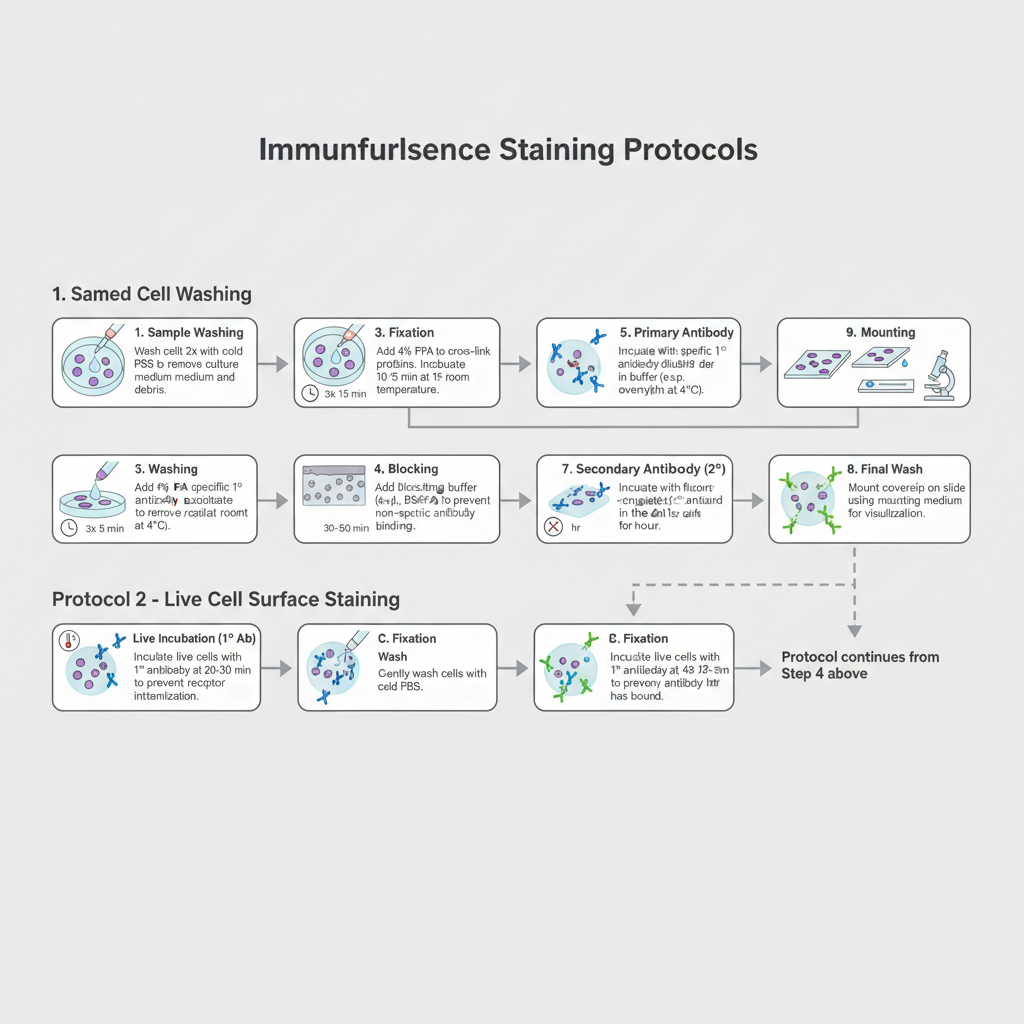
Steps of Immunofluorescence Staining (Fixed Cells)
The following are the steps used for staining fixed cells. The sequence follows washing, fixation, blocking, and finally antibody treatment, similar to other multi-step protocols explained in the PDFs.
1. Sample Washing
The culture medium is removed from the coverslip. Cells is washed gently 2 times with cold PBS for removal of debris.
2. Fixation
4% PFA solution is added to cover the cells. It is incubated for 10–15 minutes at room temperature. Over-fixation more than 20 minutes can mask the epitope and the antibody will not bind properly.
3. Washing
The PFA is removed. Cells is washed 3 times with PBS for 5 minutes each.
4. Blocking
Blocking buffer (without detergent) is added. It is incubated for 30–60 minutes at room temperature. It is the process that covers non-specific sticky sites so that the antibody binds only the targeted protein.
5. Primary Antibody Incubation
Primary antibody for the membrane protein (for example Anti-EGFR) is diluted in antibody dilution buffer. The diluted antibody is added on the cells. It is incubated overnight at 4°C or 1 hour at room temperature.
6. Washing
The antibody solution is removed. Cells is washed 3 times with PBS for 5 minutes each. These washes remove the unbound antibodies.
7. Secondary Antibody Incubation
Fluorophore-conjugated secondary antibody (for example Goat Anti-Mouse Alexa 488) is diluted in antibody dilution buffer. It is added to the cells and incubated for 1 hour at room temperature in dark. From this step the sample must be protected from light to avoid bleaching.
8. Final Wash
Cells is washed 3 times with PBS for 5 minutes each.
9. Mounting
The coverslip is mounted on slide using antifade mounting medium. Sometimes DAPI is used for nuclear staining during mounting. The edges of coverslip can be sealed with nail polish and the slide is kept at 4°C.
Alternative Live Cell Surface Staining
Some receptors lose antibody binding after fixation. In this case staining can be done on live cells.
- Live Incubation– Primary antibody is added on living cells in cold culture medium at 4°C for 20–30 minutes. Cold temperature prevents receptor internalization so the stain remain on the cell surface.
- Wash– Cells is washed with cold PBS gently.
- Fixation– 4% PFA is added after the primary antibody binding step.
- Secondary Antibody– All further steps like blocking and secondary staining are same as in fixed cell protocol.
Uses of Immunofluorescence Staining
- It is used for receptor mapping to identify the location of specific surface receptors or ion channels on the cell membrane.
- It is used in diagnostic pathology to detect markers on tumour cells, such as HER2, which helps in identifying the type and stage of disease.
- It is used for pathogen detection by showing the presence of viral or bacterial antigens on infected cell surfaces.
- It is used in drug studies to observe whether a drug molecule has bound to its target receptor on the membrane.
Advantages
- It is highly specific because it can identify a particular membrane component such as a defined receptor or channel.
- It is used for cell identification where different cell types in a mixed sample can be recognized by their surface markers.
- It allows multiplexing since it can be combined with other fluorescent dyes for multi-colour imaging.
Limitations
- The method is complex because the protocol involves several steps like blocking, primary antibody and secondary antibody incubation.
- Antibodies are costly compared to simple chemical dyes, making the method expensive.
- The epitope is sensitive to fixation and sometimes the target site is hidden or damaged, preventing proper antibody binding.
D. Membrane Exclusion Method (Trypan Blue) – Dye Exclusion Method
Principle
It is the method based on the selective permeability of the plasma membrane and the integrity of the living cell. In a normal cell, the membrane functions as a strong barrier that prevents the entry of large and negatively charged dye molecules such as Trypan Blue. It is the process in which the intact membrane excludes the dye completely, so the live cell appears clear when observed under the microscope. The ability of the membrane to keep the dye out is the key principle of this method.
When the cell is dead or when the membrane is damaged, the permeability is lost and the membrane becomes porous. In this condition the dye enters into the cytoplasm and binds with the internal components, and the cell becomes blue in colour. It is the difference between live and dead cells that allows the technique to determine cell viability. The method does not stain the membrane itself, but it depends on the membrane acting as a gatekeeper, so the presence or absence of staining shows whether the cell is alive or dead.
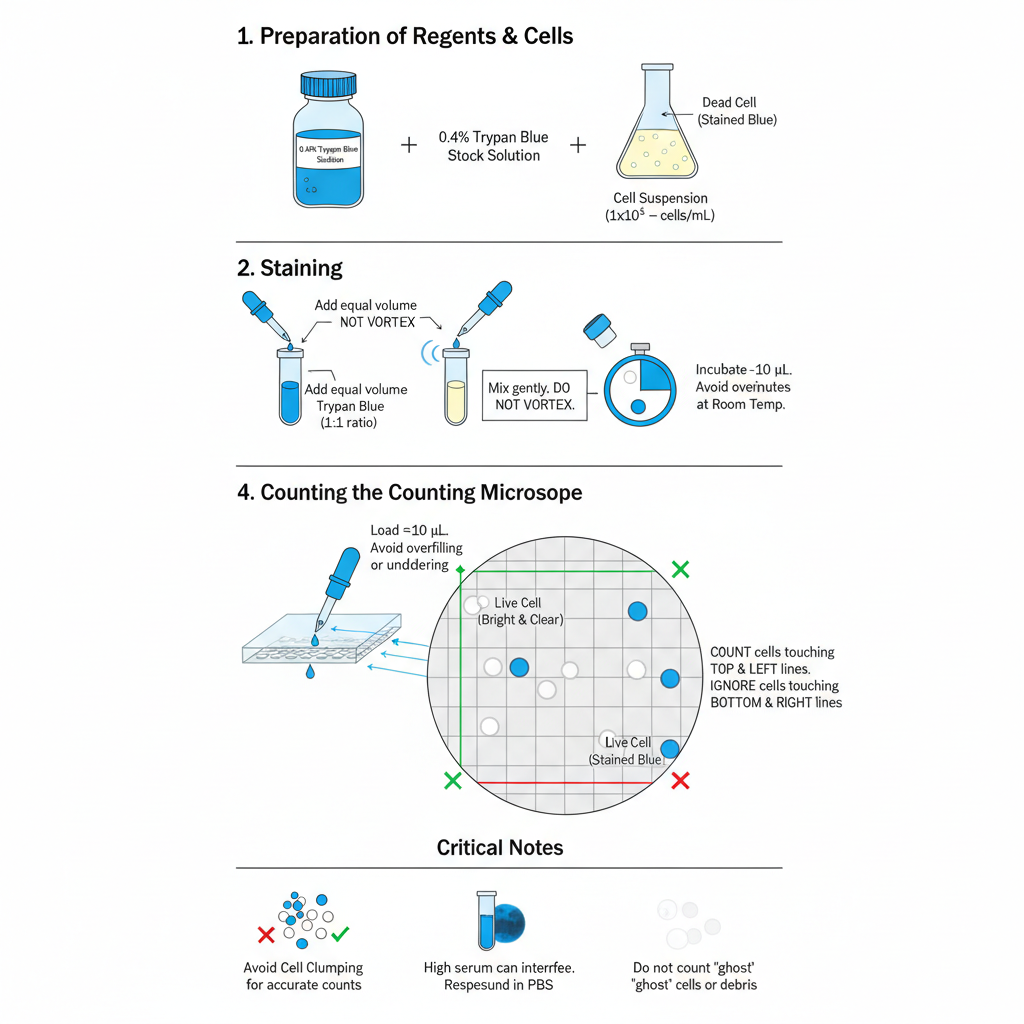
Procedure
Preparation of Reagents
- Trypan Blue Stock Solution (0.4%)– It is prepared by using 0.4% Trypan Blue dissolved in PBS or normal saline (0.85% NaCl). If the solution is stored for a long period, it must be filtered through 0.2 µm syringe filter because crystals may form which looks like cells during counting.
- Preparation of Cell Suspension– Suspension cells is mixed well and taken directly. For adherent cells, they are detached using Trypsin–EDTA and centrifuged. The pellet is resuspended in medium or PBS to form a uniform single-cell suspension. Usually a concentration between 1×10⁵ to 1×10⁶ cells/mL is suitable for counting.
Staining Procedure
- Aliquoting– About 10 µL (or 20 µL) of the cell suspension is transferred into a small tube or plate well.
- Addition of Dye– Equal volume of 0.4% Trypan Blue is added to the cells (1:1 ratio).
- Mixing-It is mixed gently by pipetting 3–5 times. Vigorous vortexing is avoided because it may damage delicate cells.
- Incubation-It is incubated for 1–3 minutes at room temperature. Incubation more than 5 minutes is not preferred as Trypan Blue is slightly toxic and it may cause viable cells to lose membrane integrity.
Hemocytometer Counting
- Preparing the Chamber– The hemocytometer and cover glass is cleaned using 70% ethanol and dried. The cover glass is placed correctly on the counting chamber.
- Loading the Sample– Nearly 10 µL of the stained cell mixture is pipetted at the edge of the cover glass. The liquid is pulled inside by capillary action. Overfilling or underfilling disturb the counting accuracy.
- Microscope Setup– The chamber is placed under brightfield or phase contrast microscope. Usually the 10× objective (100× total magnification) is used for focusing on grid lines.
- Counting of Cells– Cells is counted in the four large corner squares.
– Live cells appear bright, clear, and refractile.
– Dead cells appear blue and non-refractile.
Cells touching the top and left boundary lines are counted, and those on the bottom and right lines are not counted to avoid repetition.
Calculations
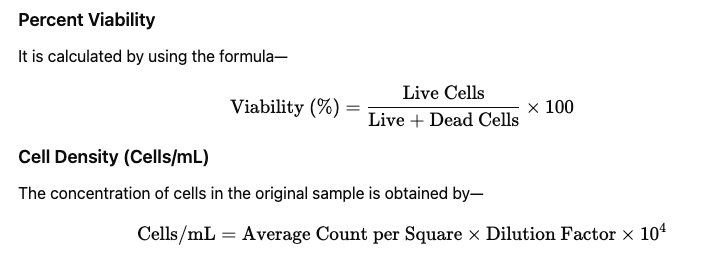
Average count is calculated by dividing total cells counted in 4 squares by 4. Dilution factor is usually 2 because cells and dye are mixed in equal volume. The factor 10⁴ converts the hemocytometer chamber volume into mL.
Critical Notes
Serum Interference– High amount of serum can bind Trypan Blue and produce dark background. Cells is resuspended in PBS before staining to reduce this problem.
Cell Clumping– Clumped cells cannot be counted properly. The suspension must be mixed thoroughly or passed through cell strainer.
Ghost Cells– Sometimes burst dead cells leave faint debris, which is not taken in counting because they do not represent intact cells.
Uses of Membrane Exclusion Method (Trypan Blue)
- It is used for viability counting to separate live clear cells from dead blue cells during routine culture handling.
- It is used in cytotoxicity assays to measure how toxic a chemical or drug is by checking the number of cells that turn blue after treatment.
- It is used for quality control to determine the health percentage of a cell population before performing costly experiments, where viability above 90% is generally required.
Advantages
- It is very fast and gives the viability result within a few minutes.
- It is cost-effective because only a normal light microscope is needed and no costly reagents are required.
- It is simple to perform since no special buffer or incubation step is used.
Limitations
- It gives only a binary result showing cells as alive or dead and cannot differentiate apoptosis or necrosis.
- The dye is toxic, and when cells remain in Trypan Blue for more than a few minutes, live cells begin to take up the dye leading to false readings.
- It does not provide structural details of the membrane and only indicates whether membrane integrity is lost.
Result of Cell Membrane Staining
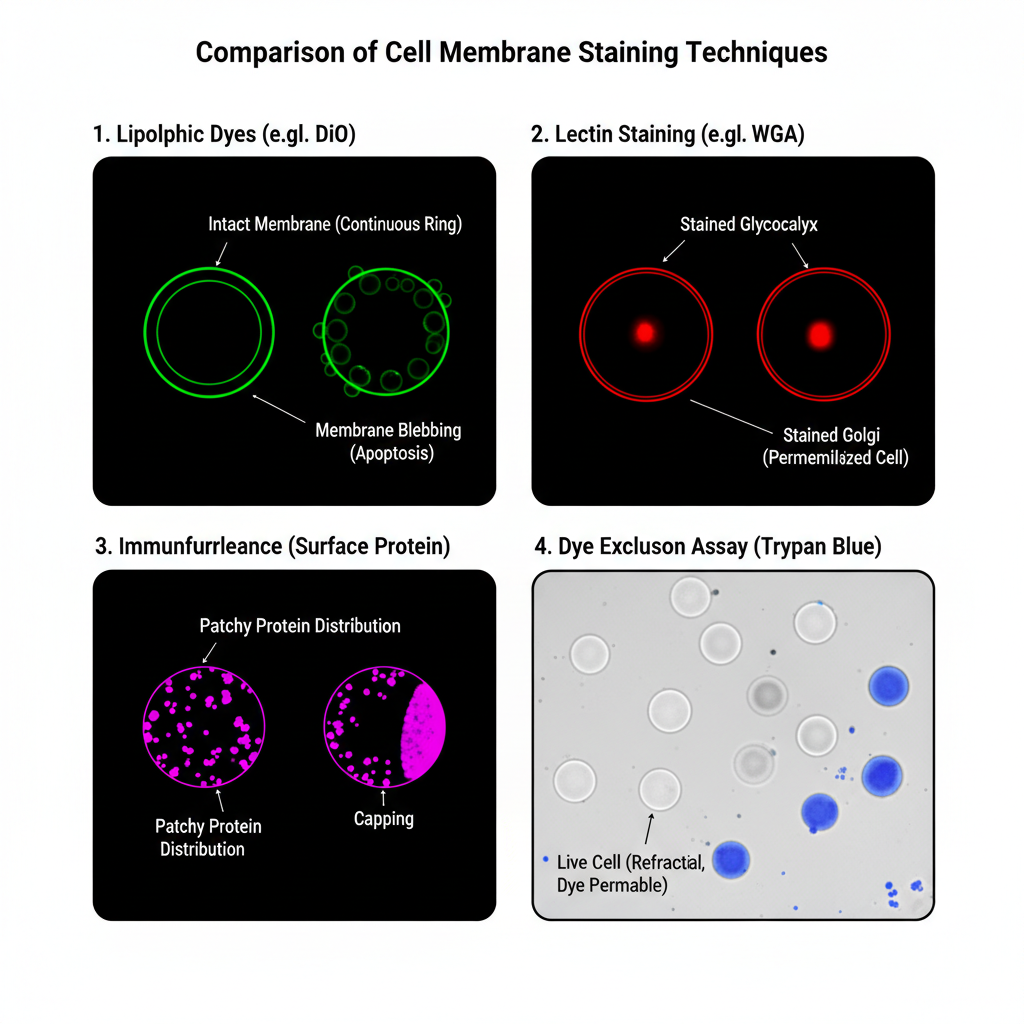
1. Lipophilic Fluorescent Dyes (DiI, DiO)
It is observed that the cell membrane forms a continuous fluorescent ring around the cell surface. This ring appears bright and uniform showing a clear outline of the cell boundary. DiI generally shows an orange-red colour while DiO appears green under the fluorescent microscope. The cytoplasm and nucleus remains dark because these dyes do not stain the internal structures. In live cells the dye may show slight movement due to membrane fluidity and some dots may appear inside the cytoplasm when endocytosis is occurring.
A clear and continuous ring indicates that the membrane is intact. When the ring appears with bubble-like structures (blebbing), it is the sign of membrane stress or apoptosis.
2. Lectin-Based Membrane Staining (WGA)
In this method the cell boundary is marked by a sharp and thick fluorescent outline. It is the glycocalyx region that is stained so the line sometimes appears thicker compared to lipophilic dyes. The colour depends on the fluorophore like WGA-Alexa 488 showing green fluorescence and WGA-Alexa 594 showing red fluorescence. Mostly the staining remains on the surface. If the cell was permeabilized, then a bright internal spot may appear near the nucleus which is the Golgi body because WGA binds strongly there.
This pattern of staining shows that N-acetylglucosamine and sialic acid residues are present on the cell surface. The outline is very distinct and suitable for measuring cell size or counting cells.
3. Immunofluorescence Staining of Surface Proteins
Result
The appearance is not a smooth ring. It is generally patchy, dotted or irregular depending on the distribution of the target protein. When the protein is clustered, bright patches can be seen. When the protein is evenly distributed, a faint ring may appear. The background between the cells remains completely dark. The fluorescent signal means that the specific antigen is present on the membrane. Absence of fluorescence means the antigen is not present or binding has not occurred.
Sometimes a bright cap is formed at one side of the cell which is referred to as capping. This occurs when surface proteins cluster after binding with the antibody.
4. Dye Exclusion Method (Trypan Blue)
Under the brightfield microscope the live cells appear clear, transparent and refractile. These cells show a shiny halo when the focus is adjusted. The shape remains round and smooth. Dead cells appear blue in colour. These cells look swollen, dull and non-refractile. Small blue particles that do not resemble cells are debris and are not counted.
Clear cells indicate that their membrane is intact and the dye is excluded actively. Blue cells indicate that the membrane is damaged and the dye has entered by passive diffusion. If 90 clear cells and 10 blue cells are counted, then the viability is 90%.
Summary Table: Results of Cell Membrane Staining Methods
| Staining Method | Appearance Under Microscope | Colour / Signal | Internal Staining | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lipophilic Fluorescent Dyes (DiI, DiO) | Continuous bright ring around the membrane; uniform outline; cytoplasm and nucleus remain dark | DiI – Orange-red; DiO – Green | No internal staining, except few dots during endocytosis | Clear ring shows intact membrane; blebbing indicates stress or apoptosis |
| Lectin-Based Staining (WGA) | Sharp and thick fluorescent outline of cell boundary; stains glycocalyx | Depends on fluorophore (e.g., Alexa 488 – Green, Alexa 594 – Red) | Surface staining mainly; Golgi spot appears if permeabilized | Indicates presence of N-acetylglucosamine/sialic acid; borders are distinct for morphometry |
| Immunofluorescence for Surface Proteins | Patchy, dotted or irregular pattern; may show clusters or faint ring | Depends on antibody fluorochrome | No cytoplasmic signal; background remains dark | Positive fluorescence shows antigen presence; capping indicates receptor clustering |
| Dye Exclusion Method (Trypan Blue) | Live cells are clear, refractile and round; dead cells are blue and swollen | Blue staining only in dead cells | Not applicable | Clear cells show intact membrane; blue cells show membrane damage; used for viability (%) |
- Abcam. (n.d.). Immunocytochemistry (ICC) and immunofluorescence (IF) protocol. Retrieved December 1, 2025, from https://www.abcam.com/en-us/technical-resources/protocols/icc-protocol
- Strober, W. (2015). Trypan blue exclusion test of cell viability. Current Protocols in Immunology, 111(1), A3.B.1–A3.B.3. https://doi.org/10.1002/0471142735.ima03bs111
- Thermo Fisher Scientific. (n.d.-a). Trypan blue staining protocol. Retrieved December 1, 2025, from https://www.thermofisher.com/cn/zh/home/references/gibco-cell-culture-basics/cell-culture-protocols/trypan-blue-exclusion.html
- Thermo Fisher Scientific. (n.d.-b). Vybrant™ DiI cell-labeling solution. Retrieved December 1, 2025, from https://www.thermofisher.com/order/catalog/product/in/en/V22885
- Vector Laboratories. (n.d.). Wheat germ agglutinin (WGA), fluorescein. Retrieved December 1, 2025, from https://vectorlabs.com/products/fluorescein-wheat-germ-agglutinin-wga/
- Atlantis Bioscience. (2025, September 30). 3 types of cell surface stains: Lipophilic dyes, lectins & protein labels explained. Blog.
- BOC Sciences. (n.d.). Cell staining: Definition, principles, protocols, dyes, and uses.
- Chan, C. Y., Faragalla, Y., & Wu, L.-G. (2022). Illuminating membrane structural dynamics of fusion and endocytosis with advanced light imaging techniques. Biochemical Society Transactions, 50(4), 1157–1167. https://doi.org/10.1042/BST20210263
- Clayton, E. L., & Cousin, M. A. (2008). Differential labelling of bulk endocytosis in nerve terminals by FM dyes. Neurochemistry International, 53(3-4), 51–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2008.06.002
- Cummings, R. D., & Etzler, M. E. (2009). Antibodies and lectins in glycan analysis. In A. Varki, R. D. Cummings, J. D. Esko, et al. (Eds.), Essentials of glycobiology (2nd ed., Chapter 45). Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK1919/
- Fang, Y., Malik, M., England, S. K., & Imoukhuede, P. I. (2022). Absolute quantification of plasma membrane receptors via quantitative flow cytometry. Methods in Molecular Biology, 2475, 61–77. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-2217-9_4
- Frick, M., Schmidt, K., & Nichols, B. J. (2007). Modulation of lateral diffusion in the plasma membrane by protein density. Current Biology, 17(5), 462–467. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2007.01.069
- Glover, M. (2025, March 7). Tech tip: Staining membranes in fixed cells (CytoLinerTM protocol). Biotium.
- Kothari, S. S., Heineman, R. E., & Harrison, R. E. (2023). Optimizing lectin staining methodology to assess glycocalyx composition of Legionella-infected cells. Undergraduate Research in Natural and Clinical Science and Technology (URNCST) Journal, 7(7), 1–10. https://doi.org/10.26685/urncst.490
- Malínská, K., Jelínková, A., & Petrášek, J. (2014). The use of FM dyes to analyze plant endocytosis. Methods in Molecular Biology, 1209, 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-1420-3_1
- Moe, S. (n.d.). Considerations for selecting a fluorescent dye or ligand. Promega Corporation.
- Sigma-Aldrich. (n.d.). Cell tracking with lipophilic membrane dyes.
- The comprehensive analysis of cell membrane staining techniques: Principles, probe chemistry, and advanced applications in molecular imaging. (n.d.).
- Thermo Fisher Scientific. (n.d.). BestProtocols: Staining intracellular antigens for flow cytometry.
- Thermo Fisher Scientific. (n.d.). Tracers for membrane labeling—Section 14.4. The Molecular Probes Handbook.
- Weigert, R. (2014). Imaging the dynamics of endocytosis in live mammalian tissues. Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Biology, 6(4), a017012. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a017012