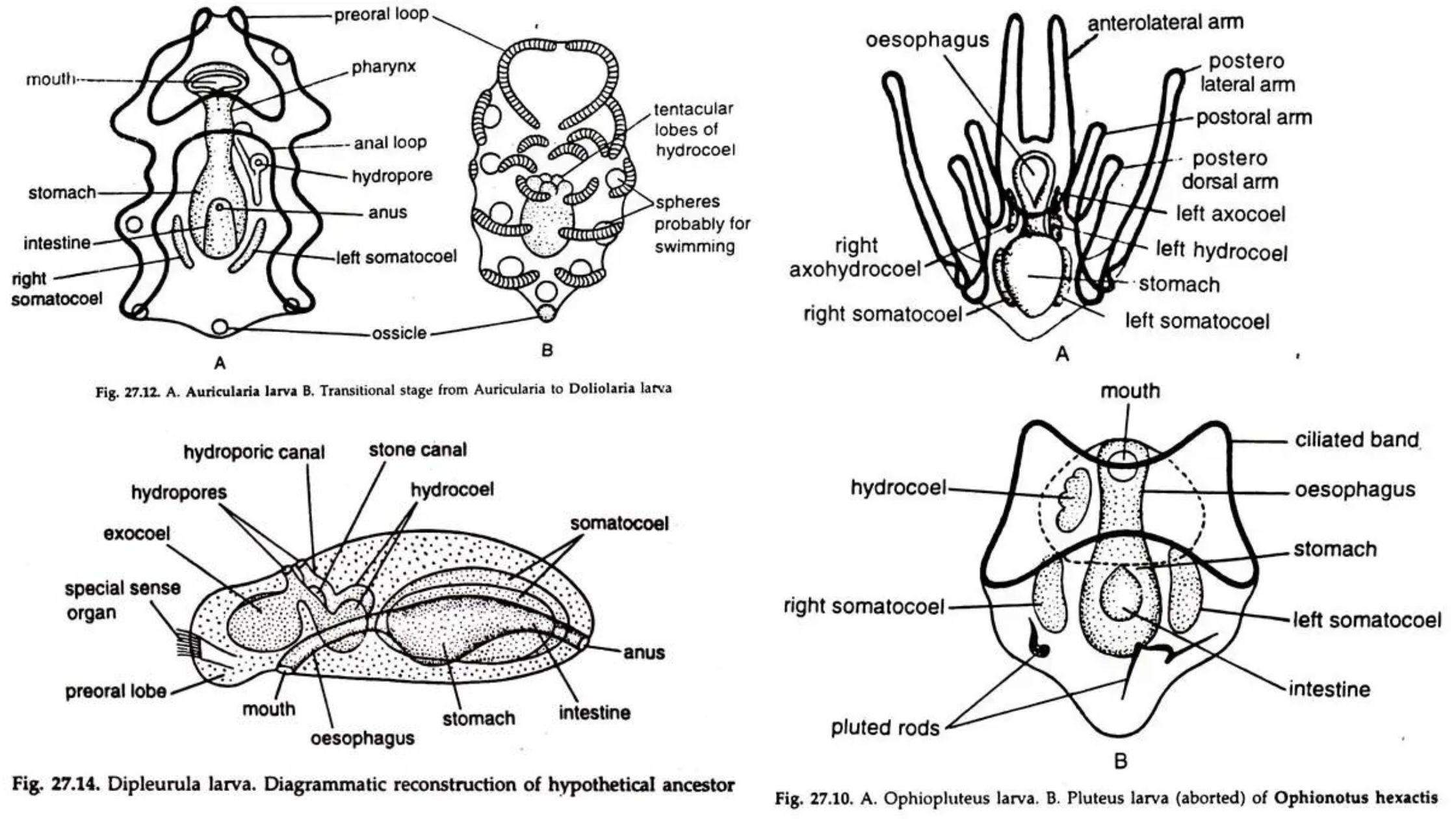
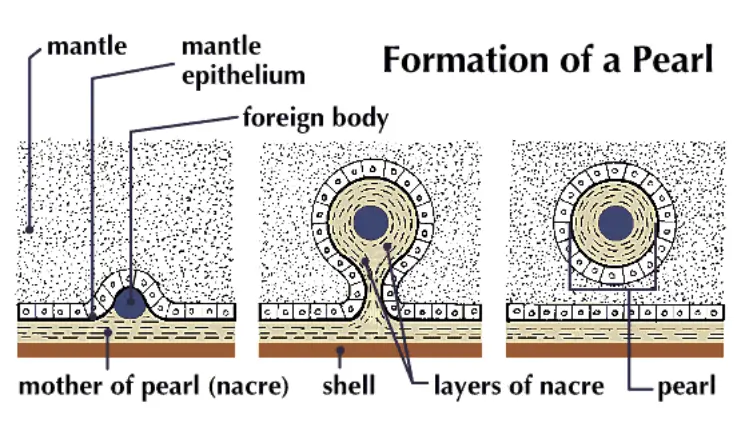
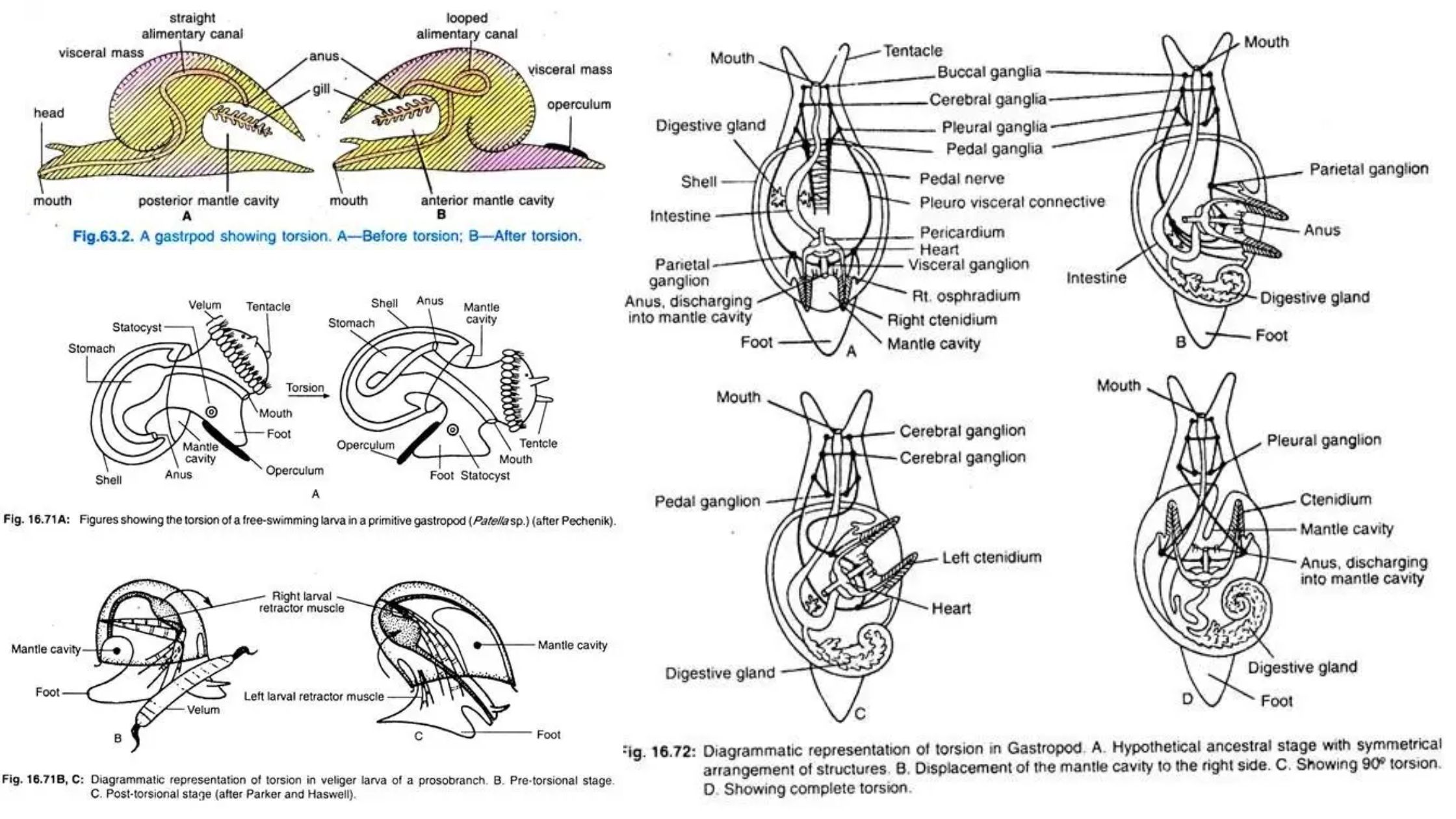
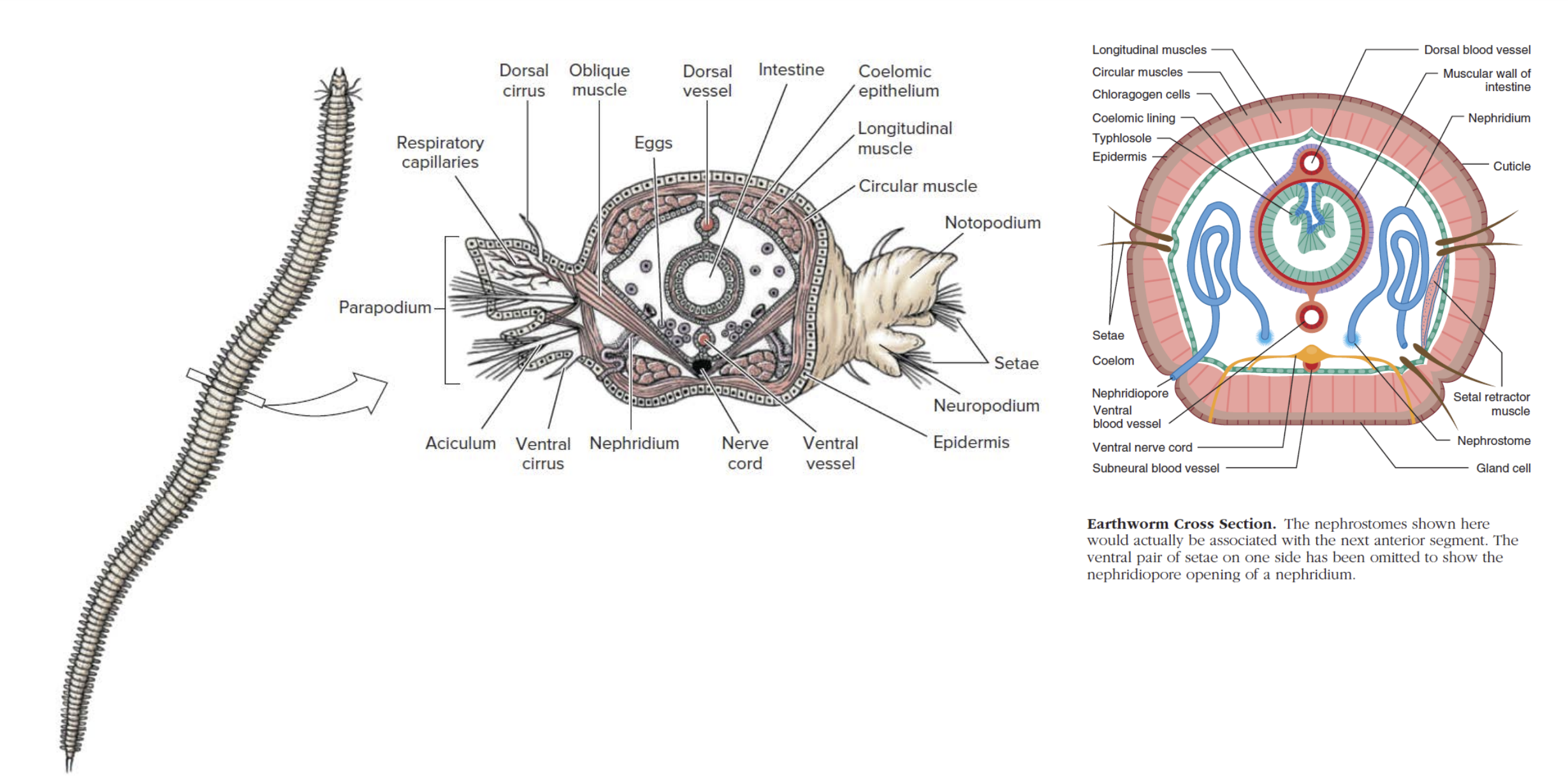
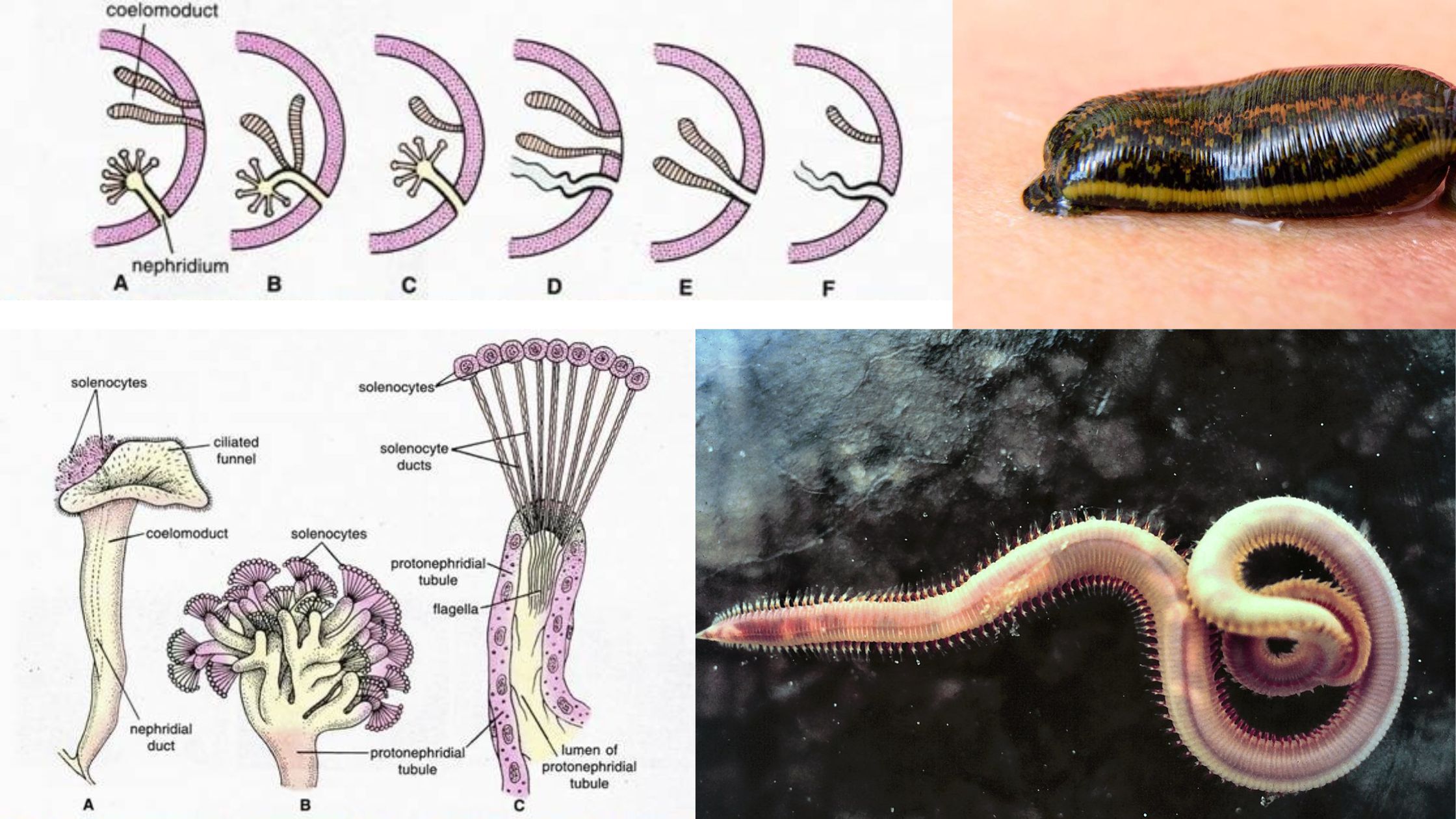
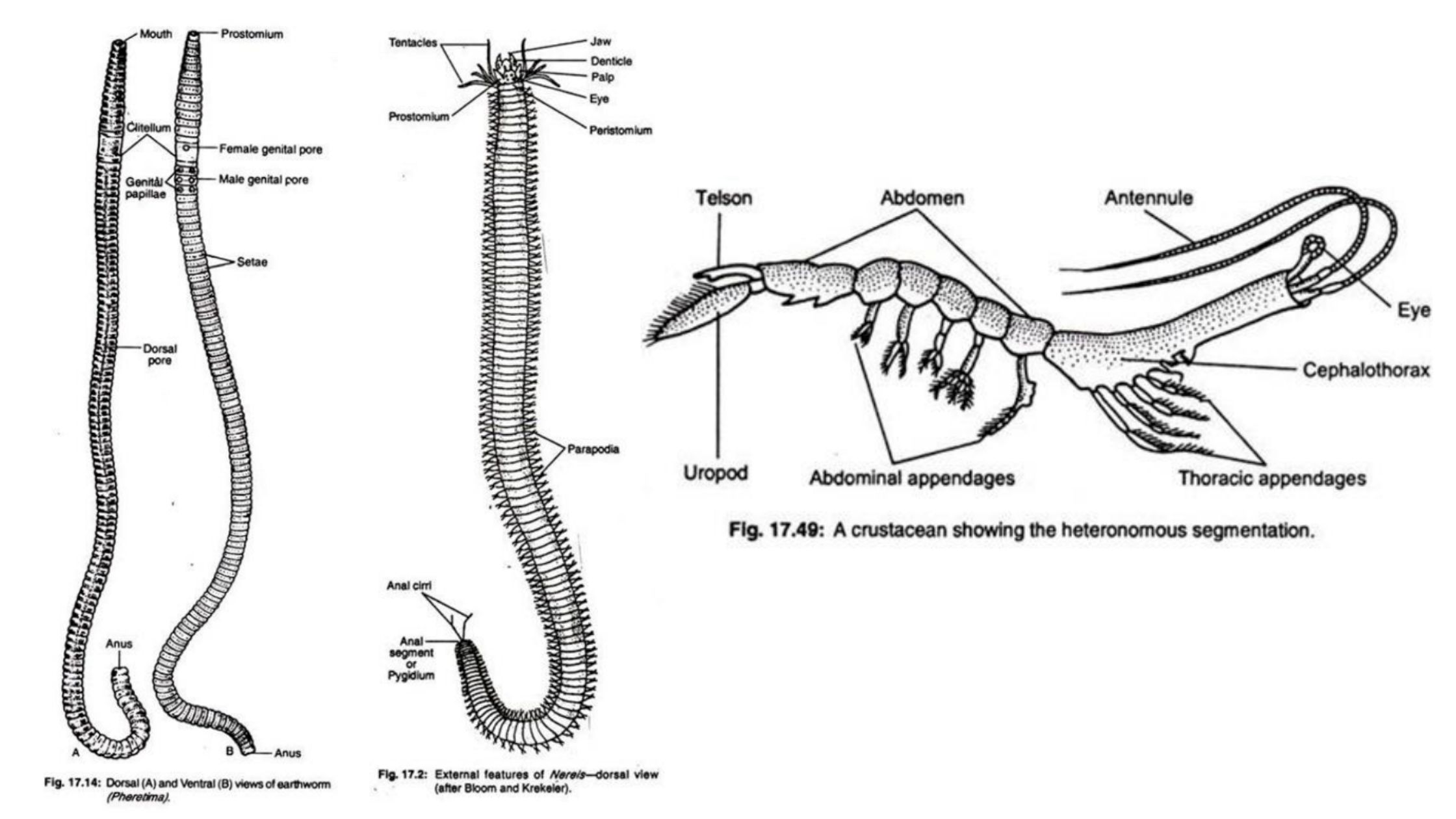
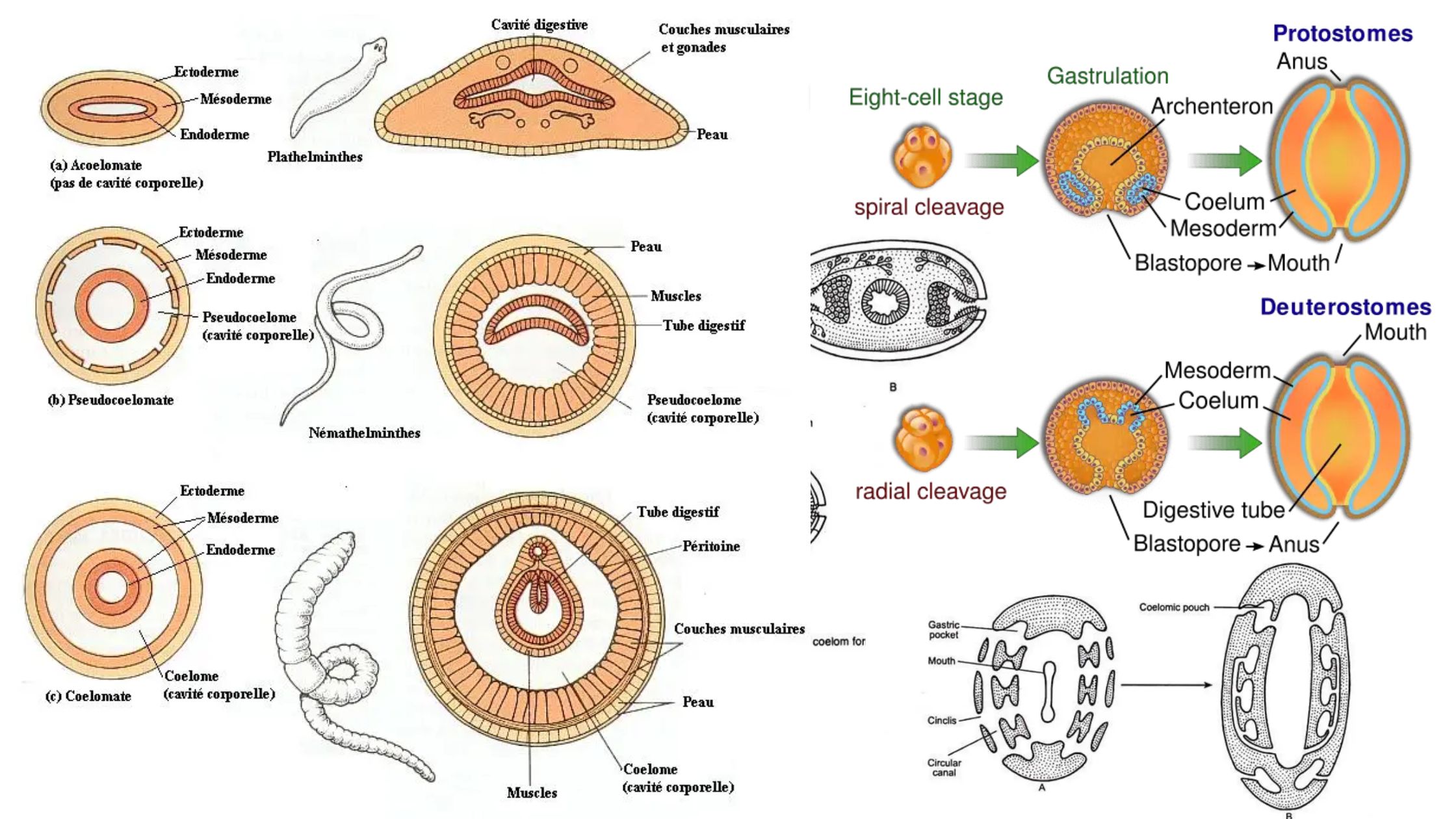
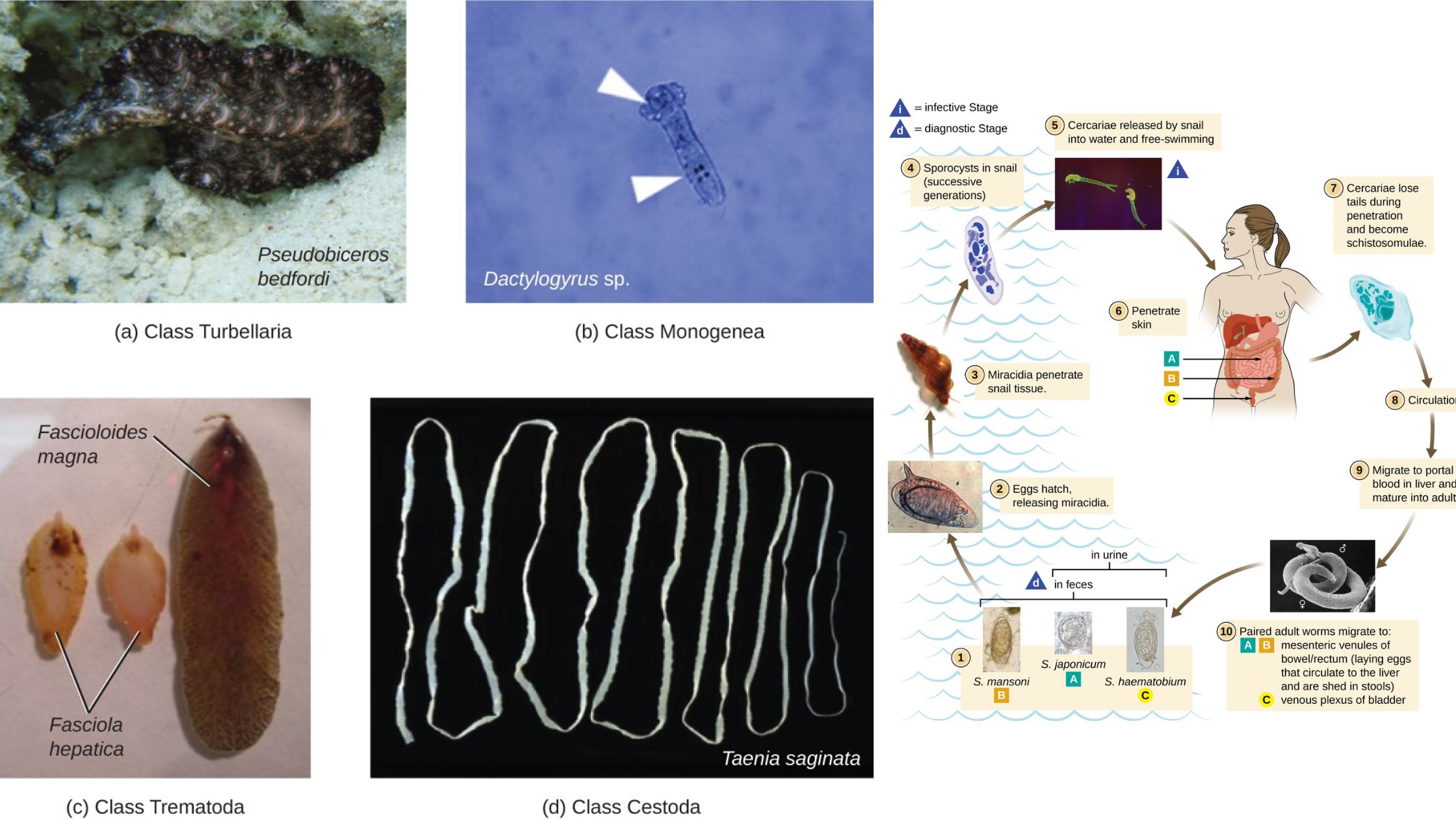
Phylum Echinodermata – Definition, Classification, Characteristics, Examples
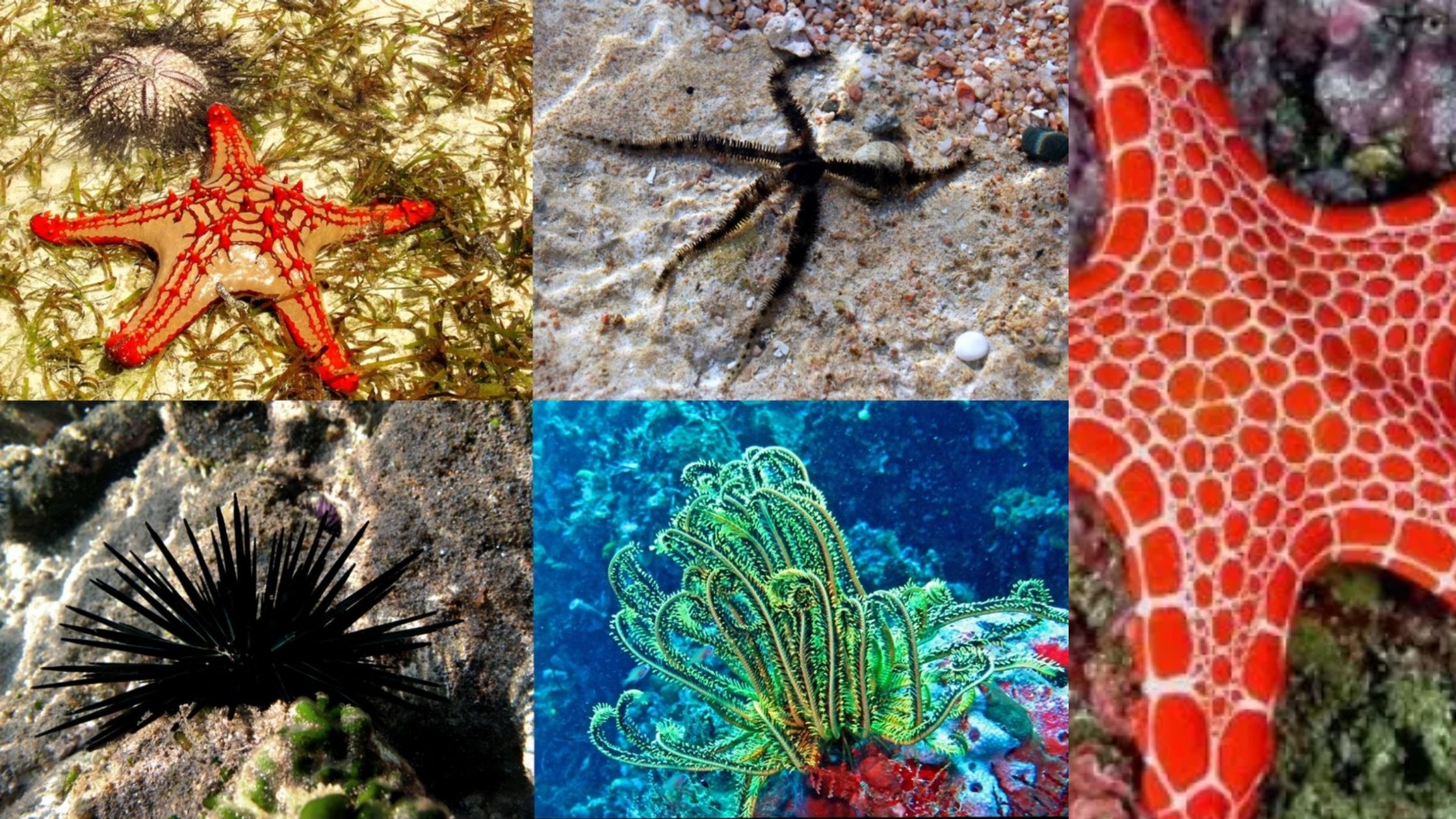
What is Phylum Echinodermata? Phylum Echinodermata Definition Phylum Echinodermata encompasses marine organisms characterized by a calcareous endoskeleton, pentamerous radial symmetry in adulthood, and a specialized water vascular system, with notable members including starfish, sea urchins, and sea cucumbers. Characteristics of Phylum Echinodermata In essence, Phylum Echinodermata represents a diverse group of marine organisms, distinguished by … Read more