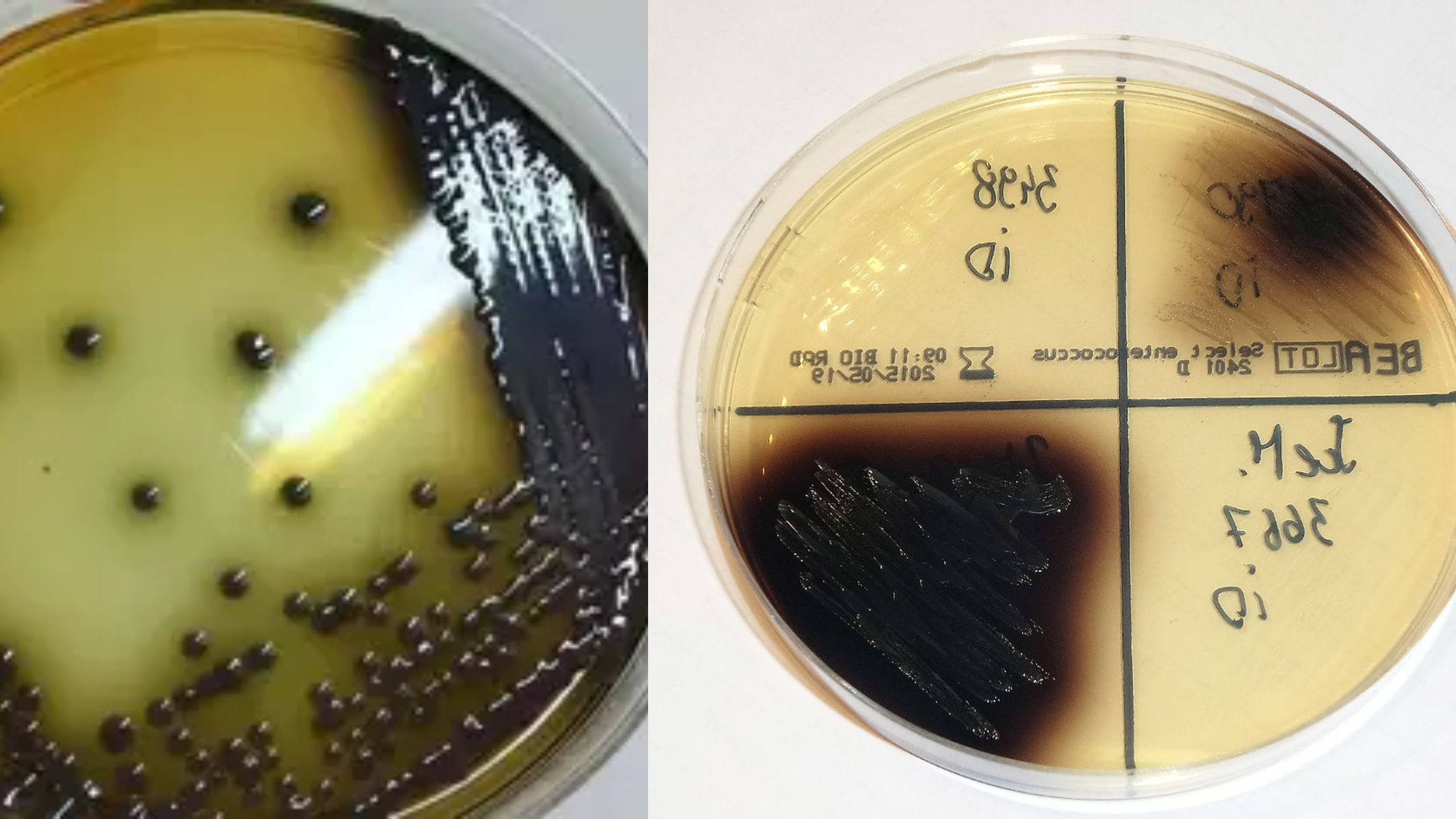
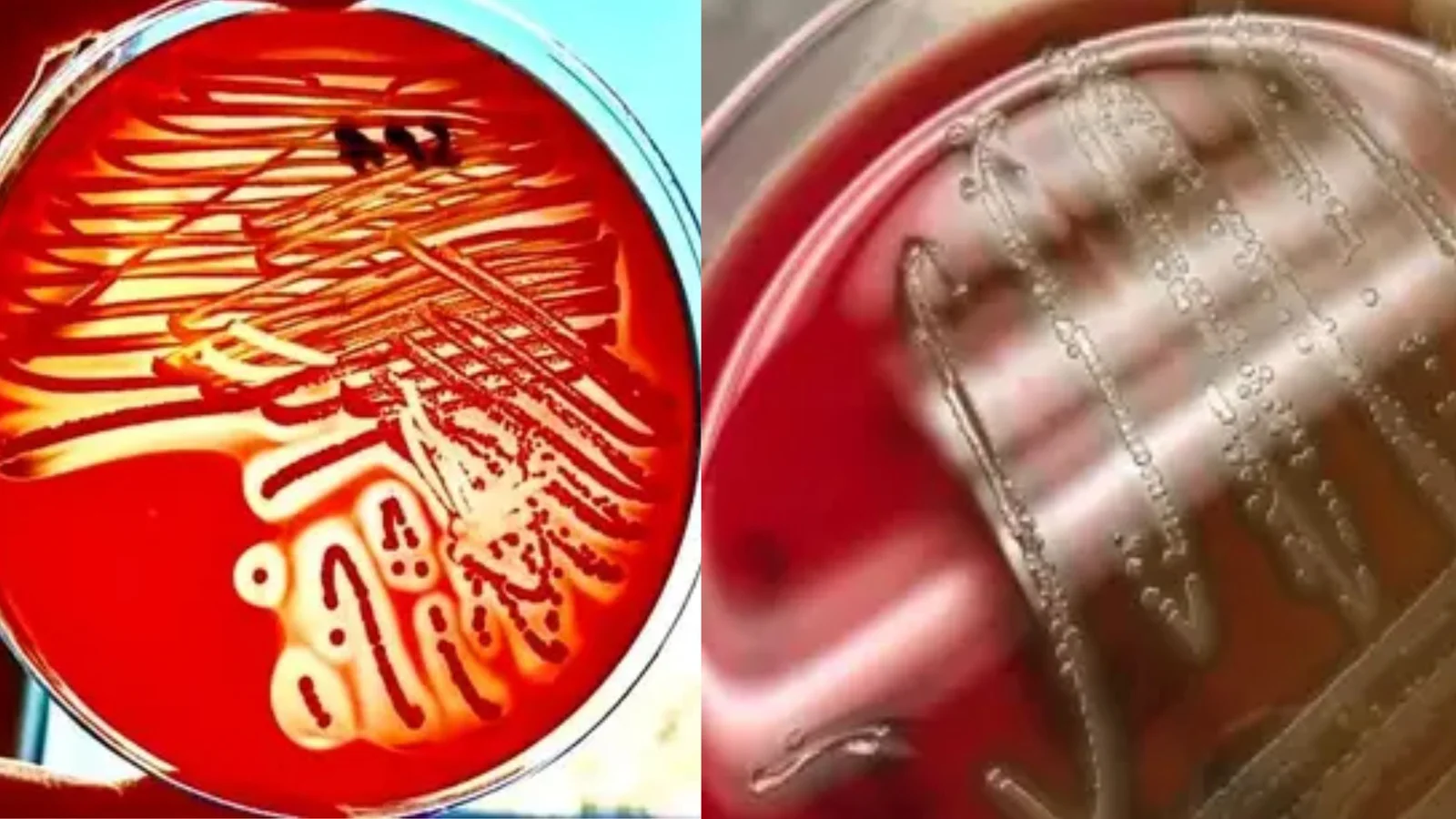
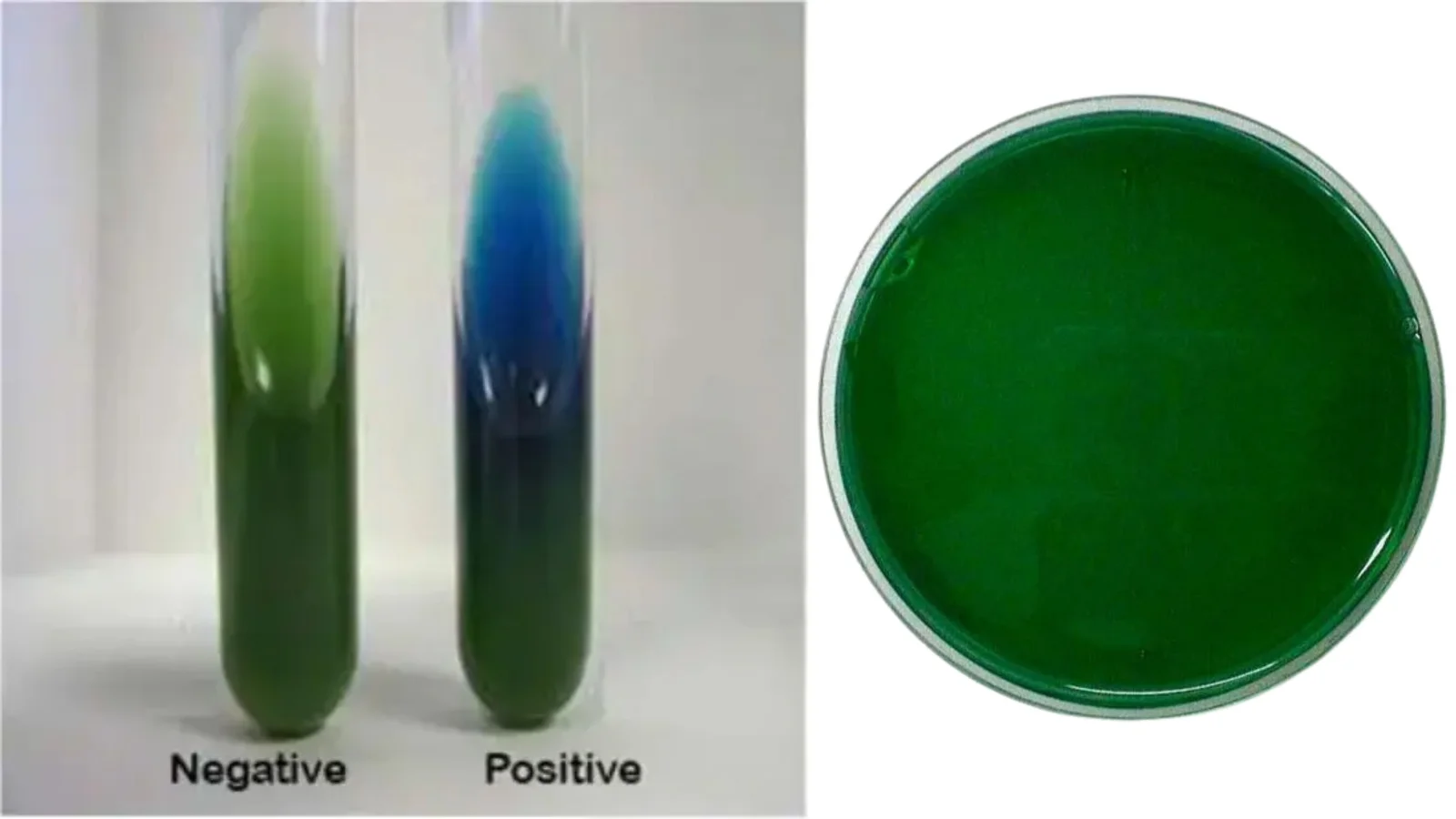
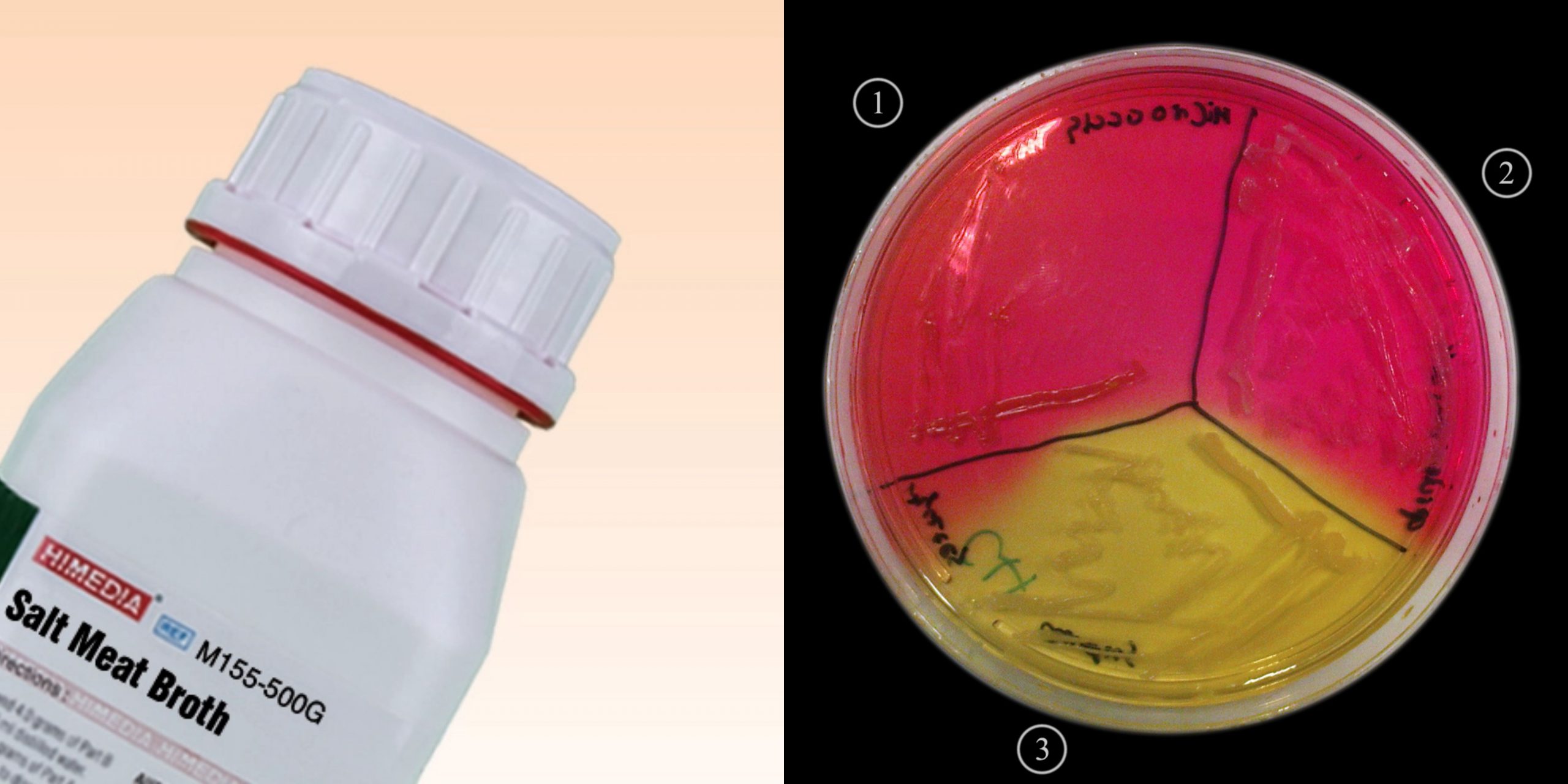
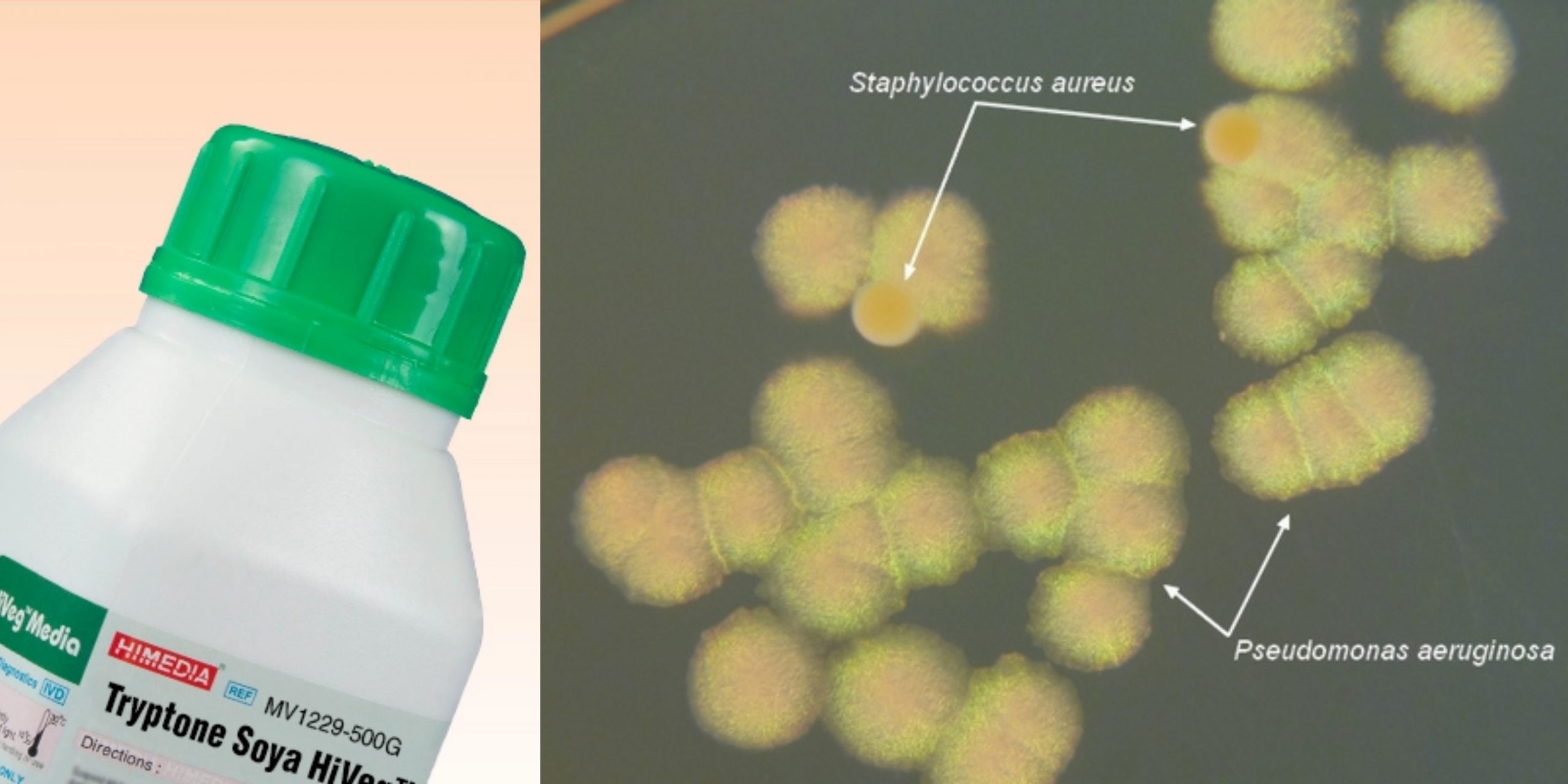
Bile Esculin Agar (BEA) – Principle, Composition, Preparation, Results, Uses
What is Bile Esculin Agar (BEA)? Bile Esculin Agar (BEA) Composition Bile Esculin Agar (BEA) contains the following ingredients per liter of the medium: The final pH of the medium, when measured at 25°C, is approximately 6.6±0.2. These specific components and their concentrations are carefully selected to create a medium that is selective and differential … Read more