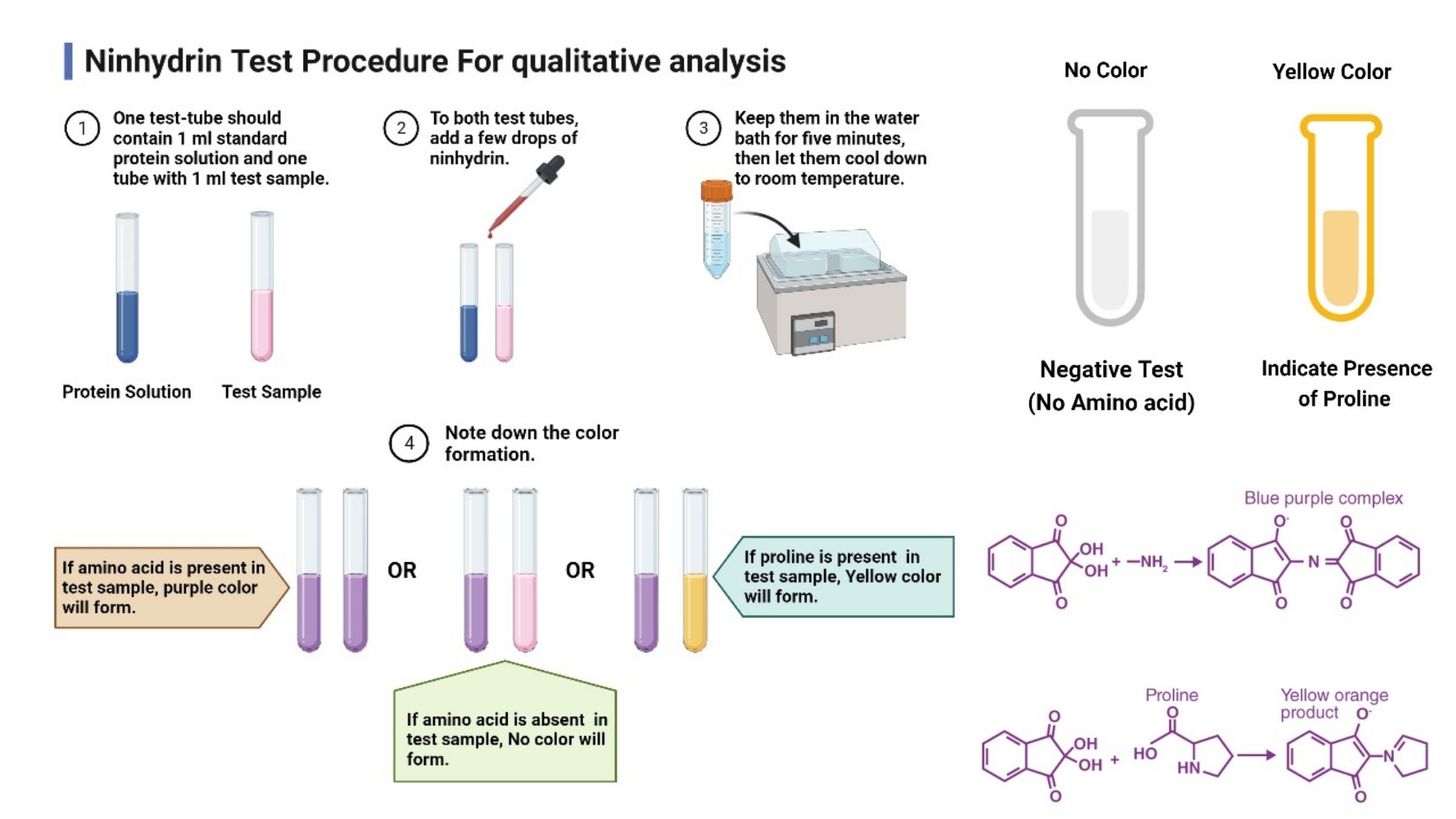
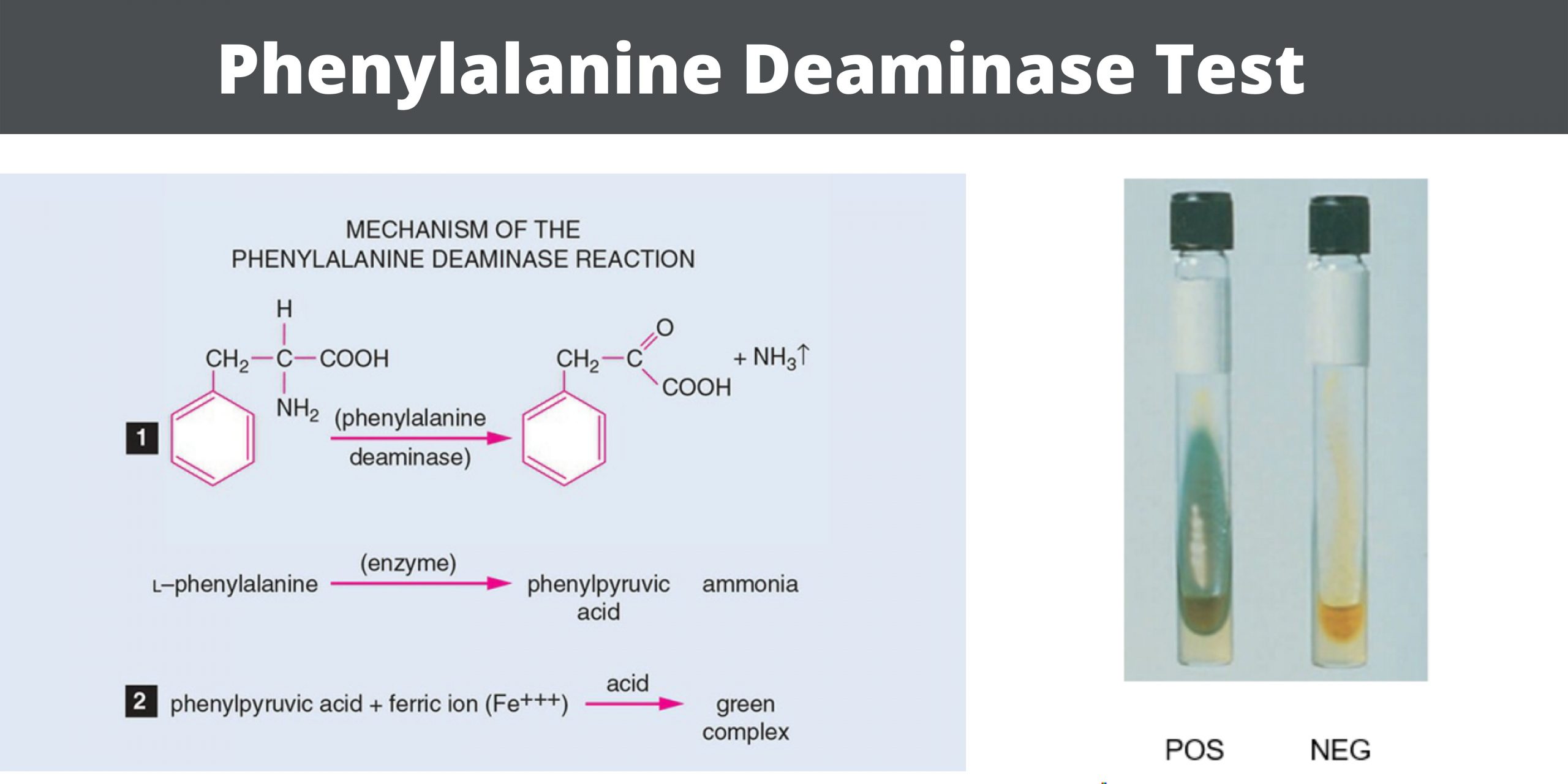
Ninhydrin Test – Principle, Procedure, Result, Uses
What is the Ninhydrin Test? It is the chemical test used for detecting amino acids and other compounds having free amino groups. It is the process in which ninhydrin (2,2-dihydroxyindane-1,3-dione) reacts with amino acids and the reaction is accompanied by oxidative deamination. In this step, the amino group is removed and there is release of … Read more