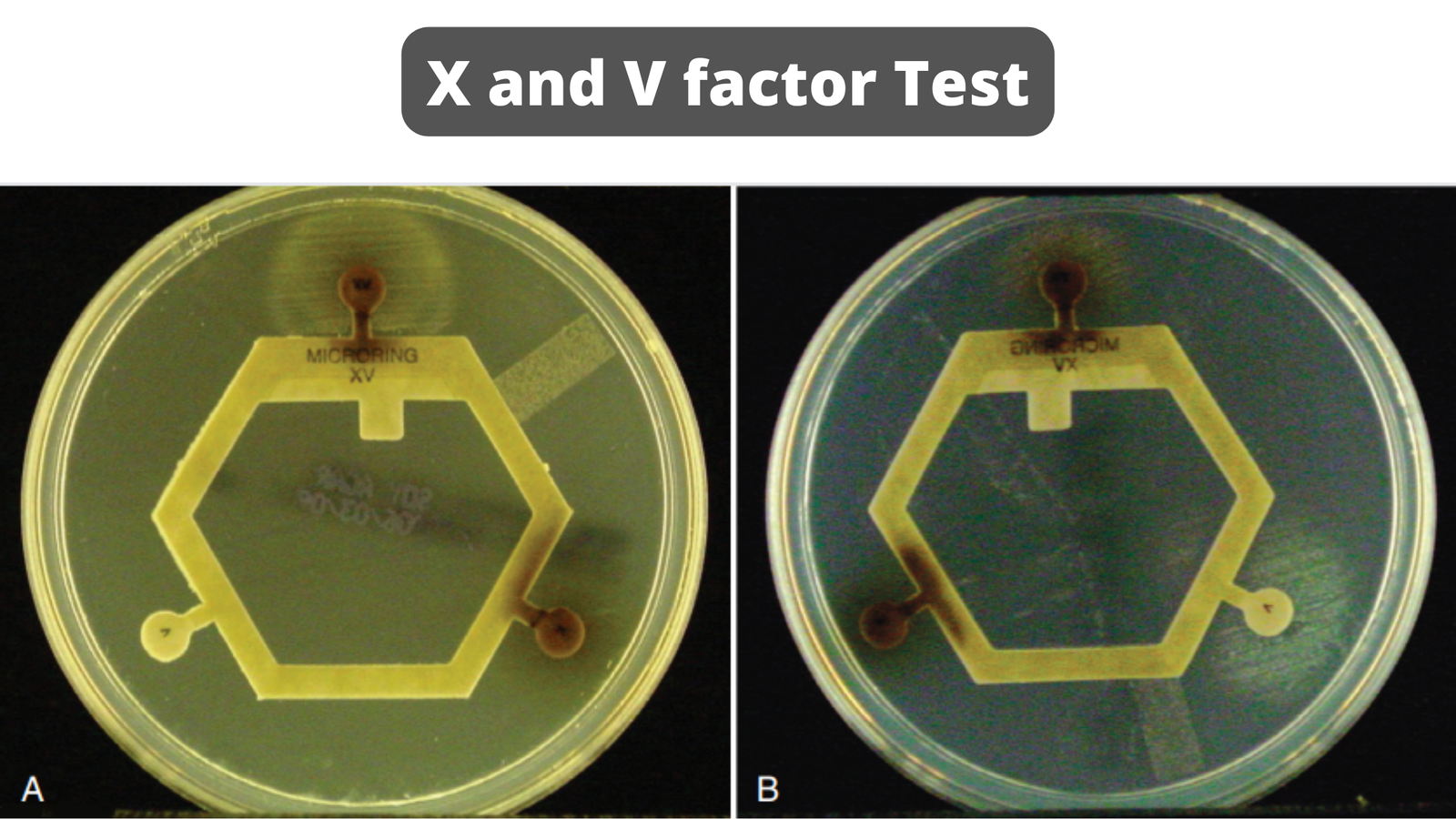
Growth at 42 Test – Principle, Procedure, Result, Uses
Growth at 42°C test is a physiological test used in microbiology for the identification and differentiation of certain non-fermentative Gram-negative bacteria. It is the process where the organism is tested for its ability to grow and survive at a higher temperature of 42°C. This test is mainly applied for the differentiation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa from … Read more