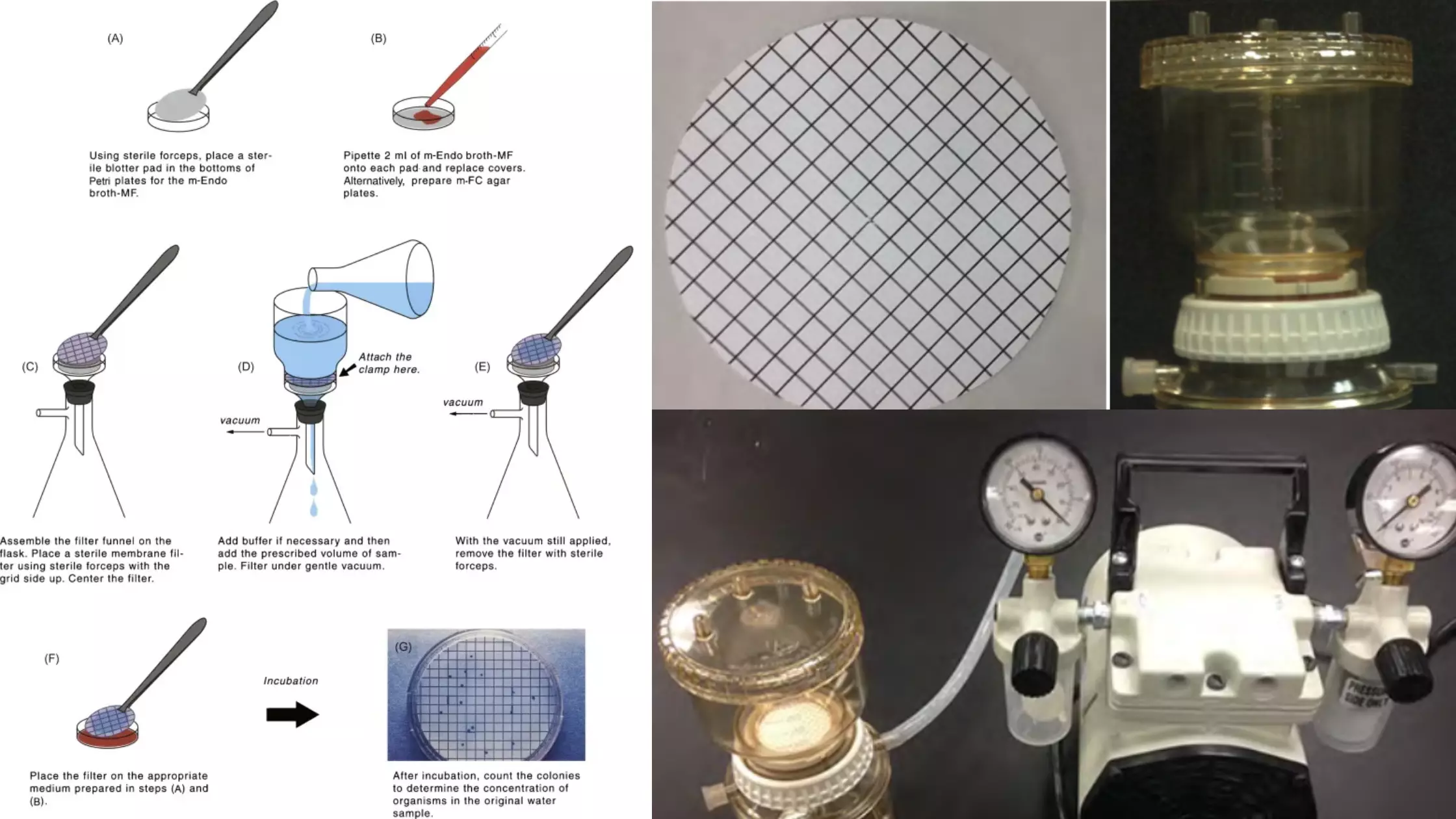
Bacteriological Examination of Waters by Using Membrane Filtration Method
Human pathogenic bacteria transmitted via the fecal-oral route, i.e., primarily intestinal pathogens, constitute one component of drinkable water quality analysis. Screening water for faecal contamination by testing for the presence of an indicator microbe is more practicable than doing thorough routine examinations for the presence of every type of disease. If you want to know … Read more